spark通过JDBC读取外部数据库,过滤数据
官网链接:
http://spark.apache.org/docs/latest/sql-programming-guide.html#jdbc-to-other-databases
http://spark.apache.org/docs/latest/sql-data-sources-jdbc.html
1. 过滤数据
情景:使用spark通过JDBC的方式读取postgresql数据库中的表然后存储到hive表中供后面数据处理使用,但是只读取postgresql表中的某些字段,并且做一下数据上的过滤
根据平常的方式,基本都是读取整张表,感觉不应该这么不友好的,于是去官网翻了翻,如下:
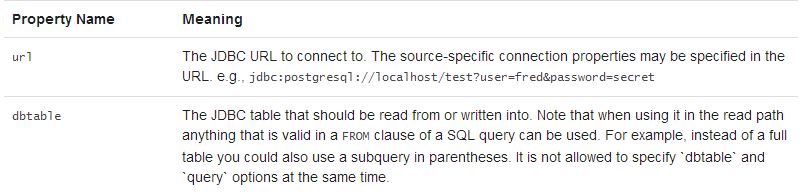
指定dbtable参数时候可以使用子查询的方式,不单纯是指定表名
测试代码如下:
package com.kong.test.test;
import java.util.Properties;
import org.apache.spark.sql.SaveMode;
import org.apache.spark.sql.SparkSession;
import org.apache.spark.sql.types.DataTypes;
public class SparkHiveTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SparkSession spark = SparkSession
.builder()
.appName("SparkCalibration")
.master("local")
.enableHiveSupport()
.getOrCreate();
spark.sparkContext().setLogLevel("ERROR");
spark.sparkContext().setLocalProperty("spark.scheduler.pool", "production");
String t2 = "(select id, name from test1) tmp";//这里需要有个别名
String createSql = "create table if not exists default.test1 (\r\n" +
"id string,\r\n" +
"name string\r\n" +
")ROW FORMAT DELIMITED FIELDS TERMINATED BY ',' stored as TEXTFILE";
spark.sql(createSql);
spark.read().format("jdbc")
.option("url", "jdbc:postgresql://ip address/database")
.option("dbtable", t2).option("user", "login user").option("password", "login passwd")
.option("fetchsize", "1000")
.load()
.createOrReplaceTempView("test1_tmp");
spark.sql("insert overwrite table default.test1 select * from test1_tmp").show();
}
}
另外:如果对于hive表的存储格式没有要求,可以更简洁,如下:
spark.read().format("jdbc")
.option("url", "jdbc:postgresql://ip address/database")
.option("dbtable", t2).option("user", "login user").option("password", "login passwd")
.option("fetchsize", "1000")
.load().write().mode(SaveMode.Overwrite).saveAsTable("default.test");
至于基于哪种保存模式(SaveMode.Overwrite)可以结合实际场景;另外spark saveAsTable()默认是以parquet+snappy的形式写数据(生成的文件名.snappy.parquet),当然,也可以通过format()传入参数,使用orc等格式,并且可以指定其他压缩方式。
2. spark通过JDBC读取外部数据库的源码实现
2.1 最简洁的api,单分区
源码如下:
/**
* Construct a `DataFrame` representing the database table accessible via JDBC URL
* url named table and connection properties.
*
* @since 1.4.0
*/
def jdbc(url: String, table: String, properties: Properties): DataFrame = {
assertNoSpecifiedSchema("jdbc")
// properties should override settings in extraOptions.
this.extraOptions ++= properties.asScala
// explicit url and dbtable should override all
this.extraOptions += (JDBCOptions.JDBC_URL -> url, JDBCOptions.JDBC_TABLE_NAME -> table)
format("jdbc").load()
}
2.2 指定表某个字段的上下限值(数值类型),生成相对应的where条件并行读取,源码如下:
/**
* Construct a `DataFrame` representing the database table accessible via JDBC URL
* url named table. Partitions of the table will be retrieved in parallel based on the parameters
* passed to this function.
*
* Don't create too many partitions in parallel on a large cluster; otherwise Spark might crash
* your external database systems.
*
* @param url JDBC database url of the form `jdbc:subprotocol:subname`.
* @param table Name of the table in the external database.
* @param columnName the name of a column of integral type that will be used for partitioning.
* @param lowerBound the minimum value of `columnName` used to decide partition stride.
* @param upperBound the maximum value of `columnName` used to decide partition stride.
* @param numPartitions the number of partitions. This, along with `lowerBound` (inclusive),
* `upperBound` (exclusive), form partition strides for generated WHERE
* clause expressions used to split the column `columnName` evenly. When
* the input is less than 1, the number is set to 1.
* @param connectionProperties JDBC database connection arguments, a list of arbitrary string
* tag/value. Normally at least a "user" and "password" property
* should be included. "fetchsize" can be used to control the
* number of rows per fetch.
* @since 1.4.0
*/
def jdbc(
url: String,
table: String,
columnName: String,
lowerBound: Long,
upperBound: Long,
numPartitions: Int,
connectionProperties: Properties): DataFrame = {
// columnName, lowerBound, upperBound and numPartitions override settings in extraOptions.
this.extraOptions ++= Map(
JDBCOptions.JDBC_PARTITION_COLUMN -> columnName,
JDBCOptions.JDBC_LOWER_BOUND -> lowerBound.toString,
JDBCOptions.JDBC_UPPER_BOUND -> upperBound.toString,
JDBCOptions.JDBC_NUM_PARTITIONS -> numPartitions.toString)
jdbc(url, table, connectionProperties)
}
2.3 通过predicates: Array[String],传入每个分区的where子句中的谓词条件,并行读取,比如 :
String[] predicates = new String[] {"date <= '20180501'","date > '20180501' and date <= '20181001'","date > '20181001'"};
/**
* Construct a `DataFrame` representing the database table accessible via JDBC URL
* url named table using connection properties. The `predicates` parameter gives a list
* expressions suitable for inclusion in WHERE clauses; each one defines one partition
* of the `DataFrame`.
*
* Don't create too many partitions in parallel on a large cluster; otherwise Spark might crash
* your external database systems.
*
* @param url JDBC database url of the form `jdbc:subprotocol:subname`
* @param table Name of the table in the external database.
* @param predicates Condition in the where clause for each partition.
* @param connectionProperties JDBC database connection arguments, a list of arbitrary string
* tag/value. Normally at least a "user" and "password" property
* should be included. "fetchsize" can be used to control the
* number of rows per fetch.
* @since 1.4.0
*/
def jdbc(
url: String,
table: String,
predicates: Array[String],
connectionProperties: Properties): DataFrame = {
assertNoSpecifiedSchema("jdbc")
// connectionProperties should override settings in extraOptions.
val params = extraOptions.toMap ++ connectionProperties.asScala.toMap
val options = new JDBCOptions(url, table, params)
val parts: Array[Partition] = predicates.zipWithIndex.map { case (part, i) =>
JDBCPartition(part, i) : Partition
}
val relation = JDBCRelation(parts, options)(sparkSession)
sparkSession.baseRelationToDataFrame(relation)
}
spark通过JDBC读取外部数据库,过滤数据的更多相关文章
- 读取mysql数据库的数据,转为json格式
# coding=utf-8 ''' Created on 2016-10-26 @author: Jennifer Project:读取mysql数据库的数据,转为json格式 ''' import ...
- spring(读取外部数据库配置信息、基于注解管理bean、DI)
###解析外部配置文件在resources文件夹下,新建db.properties(和数据库连接相关的信息) driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driverurl=jdbc ...
- 读取mysq数据库l数据,并使用dataview显示
来自<sencha touch权威指南>,约198页开始 通过php脚本,可以将mysql数据库的数据作为json数据格式进行读取. (1)php代码(bookinfo.php): < ...
- AndroidStudio 中查看获取MD5和SHA1值以及如何查看手机应用信息以及读取*.db数据库里面数据
查看获取MD5和SHA1值具体操作方式链接 查看获取MD5和SHA1值实际操作命令CMD语句: C:\Users\Administrator>cd .android C:\Users\Admin ...
- C# 读取Oracle数据库视图数据异常问题处理
会出现类似现在这种提示的错误 System.Data.OracleClient 需要 Oracle 客户端软件 version 8.1.7 或更高版本 情况1.开发过程中遇到这种问题解决 由于.net ...
- 在jsp页面直接读取mysql数据库显示数据
闲来无事,学学java,虽说编程语言相通,但是接触一门新知识还是有些疑惑,边学边记录,方便以后温故. 直接给出代码: <%@page import="java.sql.ResultSe ...
- Excel2003读取sqlserver数据库表数据(图)
- 使用JDBC在MySQL数据库中快速批量插入数据
使用JDBC连接MySQL数据库进行数据插入的时候,特别是大批量数据连续插入(10W+),如何提高效率呢? 在JDBC编程接口中Statement 有两个方法特别值得注意: void addBatch ...
- [原创]java使用JDBC向MySQL数据库批次插入10W条数据测试效率
使用JDBC连接MySQL数据库进行数据插入的时候,特别是大批量数据连续插入(100000),如何提高效率呢?在JDBC编程接口中Statement 有两个方法特别值得注意:通过使用addBatch( ...
随机推荐
- .net持续集成cake篇之cake任务依赖、自定义配置荐及环境变量读取
系列目录 新建一个构建任务及任务依赖关系设置 上节我们通过新建一个HelloWorld示例讲解了如何编写build.cake以及如何下载build.ps1启动文件以及如何运行.实际项目中,我们使用最多 ...
- 【题解】【A % B Problem(P1865)】-C++
题目背景 题目名称是吸引你点进来的 实际上该题还是很水的 题目描述 区间质数个数 输入输出格式 输入格式: 一行两个整数 询问次数n,范围m 接下来n行,每行两个整数 l,r 表示区间 输出格式: 对 ...
- 我这边测了一下,发现#后面参数变化浏览器不会刷新,但是#一旦去掉就会刷新了,你那边的url拼的时候能不能在没参数的时候#也拼在里面,这样应该就OK了
我这边测了一下,发现#后面参数变化浏览器不会刷新,但是#一旦去掉就会刷新了,你那边的url拼的时候能不能在没参数的时候#也拼在里面,这样应该就OK了
- 洛谷 P1970 花匠
题目描述 花匠栋栋种了一排花,每株花都有自己的高度.花儿越长越大,也越来越挤.栋栋决定把这排中的一部分花移走,将剩下的留在原地,使得剩下的花能有空间长大,同时,栋栋希望剩下的花排列得比较别致. 具体而 ...
- 个人永久性免费-Excel催化剂功能第71波-定义名称管理器维护增强
Excel使用得好坏一个分水岭之一乃是对定义名称的使用程度如何,大量合理地使用定义名称功能,对整个Excel的高级应用带来极大的便利性和日常公式函数嵌套的可读性得到很大的提升.Excel催化剂再次以插 ...
- 个人永久性免费-Excel催化剂功能第60波-数据有效性验证增强版,补足Excel天生不足
Excel在数据处理.数据分析上已经是公认的最好用的软件之一,其易用性和强大性也吸引无数的初中高级用户每天都在使用Excel.但这些优点的同时,也带出了一些问题,正因为其不同于一般的专业软件,需要专业 ...
- [PTA] 数据结构与算法题目集 6-4 链式表的按序号查找 & 6-5 链式表操作集 & 6-6 带头结点的链式表操作集
带不带头结点的差别就是,在插入和删除操作中,不带头结点的链表需要考虑两种情况:1.插入(删除)在头结点.2.在其他位置. 6.4 //L是给定单链表,函数FindKth要返回链式表的第K个元素.如果该 ...
- 快速掌握mongoDB(五)——读写分离的副本集实现和Sharing介绍
1 mongoDB副本集 1 副本集简介 前边我们介绍都是单机MongoDB的使用,在实际开发中很少会用单机MongoDB,因为使用单机会有数据丢失的风险,同时单台服务器无法做到高可用性(即当服务器宕 ...
- Jenkins持续部署-创建差量更新包
目录 Jenkins持续部署-创建差量更新包 目录 前言 目的 详细流程 生成版本号 获取版本号 创建文件更新清单 压缩 获取上个版本的包 创建差量更新包 读取服务器Json配置 远程创建文件夹目录 ...
- Python解释器安装教程和环境变量配置
Python解释器安装教程和环境变量配置 Python解释器安装 登录Python的官方网站 https://www.python.org/ 进行相应版本的下载. 第一步:根据电脑系统选择软件适 ...
