python实现单向循环链表
单向循环链表
单链表的一个变形是单向循环链表,链表中最后一个节点的next域不再为None,而是指向链表的头节点。
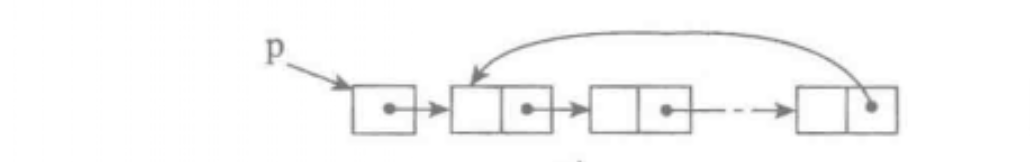
实现
class Node(object):
"""节点"""
def __init__(self, item):
self.item = item
self.next = None
节点实现
class SinCycLinkList(object):
"""单向循环链表"""
def __init__(self):
self.head = None def is_empty(self):
"""判断链表是否为空"""
return self.head is None def length(self):
"""返回链表的长度"""
if self.is_empty():
return 0
count = 1
cur = self.head
# 遍历,直到某个节点指向头节点
while cur.next != self.head:
count += 1
cur = cur.next
return count def travel(self):
"""遍历链表"""
if self.is_empty():
return
cur = self.head
print(cur.item)
while cur.next != self.head:
cur = cur.next
print(cur.item)
print("结束了") def add(self, item):
"""头部添加节点"""
node = Node(item)
# 如果链表为空
if self.is_empty():
# 把插入节点置为首节点
self.head = node
# node的下一个节点置为自身
node.next = self.head
else:
# node指向以前的首节点
node.next = self.head
# 遍历,找到尾节点
cur = self.head
while cur.next != self.head:
cur = cur.next
# 尾节点指向插入的节点
cur.next = node
# 把插入的节点置为当前的头节点
self.head = node def append(self, item):
"""尾部添加节点"""
node = Node(item)
if self.is_empty():
self.head = node
node.next = self.head
else:
# 找到尾节点
cur = self.head
while cur.next != self.head:
cur = cur.next
# 让尾节点指向插入的节点
cur.next = node
# 让插入的节点指向首节点
node.next = self.head def insert(self, pos, item):
"""在指定的位置添加节点"""
# 如果插入的索引小于0
if pos <= 0:
self.add(item)
elif pos > self.length()-1:
self.append(item)
else:
node = Node(item)
num = 0
cur = self.head
# 找到插入位置的前一个节点
while num < pos-1:
num += 1
cur = cur.next
# 注意这里的更改顺序!!!
node.next = cur.next
cur.next = node def remove(self, item):
"""删除节点"""
# 链表为空,则直接返回
if self.is_empty():
return
cur = self.head
pre = None
# 如果头节点的元素就是要查找的元素item
if cur.item == item:
# 如果链表不止一个节点
if cur.next != self.head:
while cur.next != self.head:
cur = cur.next
cur.next = self.head.next
self.head = self.head.next
else:
# 链表只有一个节点
self.head = None
else:
pre = self.head
# 第一个节点不是要删除的
while cur.next != self.head:
# 找到要删除的节点
if cur.item == item:
# 删除
pre.next = cur.next
return
else:
pre = cur
cur = cur.next
# 循环结束之后cur为尾节点
if cur.item == item:
pre.next = cur.next def search(self, item):
"""查找节点是否存在"""
if self.is_empty():
return False
cur = self.head
if cur.item == item:
return True
while cur.next != self.head:
# 放在判断的前面
cur = cur.next
if cur.item == item:
return True
# 遍历一圈后都找不到,返回False
return False
链表实现
if __name__ == '__main__':
lst1 = SinCycLinkList() # self.head=None
lst1.add(1)
lst1.add(2)
lst1.append(3)
lst1.append(4)
lst1.travel()
lst1.insert(1, 5)
lst1.travel()
lst1.insert(-2, 6)
lst1.travel()
lst1.insert(10, 7)
lst1.travel()
lst1.remove(1)
lst1.travel()
lst1.remove(10)
lst1.travel()
print('head:', lst1.head.item)
print('length:', lst1.length())
测试
python实现单向循环链表的更多相关文章
- 数据结构与算法-python描述-单向循环链表
# coding:utf-8 # 单向循环链表的相关操作: # is_empty() 判断链表是否为空 # length() 返回链表的长度 # travel() 遍历 # add(item) 在头部 ...
- Python 单向循环链表
操作 is_empty() 判断链表是否为空 length() 返回链表的长度 travel() 遍历 add(item) 在头部添加一个节点 append(item) 在尾部添加一个节点 inser ...
- python中的单向循环链表实现
引子 所谓单向循环链表,不过是在单向链表的基础上,如响尾蛇般将其首尾相连,也因此有诸多类似之处与务必留心之点.尤其是可能涉及到头尾节点的操作,不可疏忽. 对于诸多操所必须的遍历,这时的条件是什么?又应 ...
- 基于visual Studio2013解决算法导论之021单向循环链表
题目 单向循环链表的操作 解决代码及点评 #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <time.h> ...
- python实现 双向循环链表
最近身边的朋友在研究用python来实现数据结构.遇到一个问题就是双向循环链表的实现,改指向的时候总是发蒙. 我自己尝实现了一个python的双向循环链表.附上代码,希望对大家有帮助. 如果不懂什么是 ...
- 单向循环链表C语言实现
我们都知道,单向链表最后指向为NULL,也就是为空,那单向循环链表就是不指向为NULL了,指向头节点,所以下面这个程序运行结果就是,你将会看到遍历链表的时候就是一个死循环,因为它不指向为NULL,也是 ...
- c/c++ 线性表之单向循环链表
c/c++ 线性表之单向循环链表 线性表之单向循环链表 不是存放在连续的内存空间,链表中的每个节点的next都指向下一个节点,最后一个节点的下一个节点不是NULL,而是头节点.因为头尾相连,所以叫单向 ...
- 复习下C 链表操作(单向循环链表、查找循环节点)
循环链表 稍复杂点. 肯能会有0 或 6 字型的单向循环链表. 接下来创建 单向循环链表 并 查找单向循环链表中的循环节点. 这里已6字型单向循环链表为例. //创建 循环链表 Student * ...
- (java实现)单向循环链表
什么是单向循环链表 单向循环链表基本与单向链表相同,唯一的区别就是单向循环链表的尾节点指向的不是null,而是头节点(注意:不是头指针). 因此,单向循环链表的任何节点的下一部分都不存在NULL值. ...
随机推荐
- dns配置文件
/etc/resolv.conf 该文件是DNS域名解析的配置文件,它的格式很简单,每行以一个关键字开头,后接配置参数. resolv.conf的关键字主要有四个,分别是: nameserver ...
- docker-compose.yml(2)
实例2:version: '3'services: user-service: image: "$DOCKER_SERVICE_IMAGE_TAG" network_mode: & ...
- sublime text3 replace和反向引用
实用小技巧,主要用于替换爬虫请求头,节省时间. chrome原信息显示: UserID: sds UserPass: sdsd codeKey: 350753 code: 277 B1: 提 subl ...
- 关于windows下NODE_ENV=test无效的情况解决办法
redux的单元测试命令为 NODE_ENV=test mocha --recursive --compilers js:babel-core/register --require ./test/se ...
- Git中撤销提交
Git的几种状态 未修改 原始内容 已修改 ↓ 工 作 区 已暂存 ↓ git add 暂 存 区 已提交 ↓ git commit 本地仓库 已推送 ↓ git push 远程仓库 注意:下面所有命 ...
- COGS 2392 2393 2395 有标号的二分图计数
有黑白关系: 枚举左部点(黑色点),然后$2^{i*(n-i)}$处理方法同:COGS 2353 2355 2356 2358 有标号的DAG计数 无关系: 发现,假设$f(i)$是一个连通块,对于一 ...
- 微信小程序框架——wepy使后感
更新:2018年1月10日15:32:22 在ios8及部分机型下会有样式混乱的问题,经查找,原因是缺少浏览器前缀,需要加prefix. 解决方案见链接:wepy-less-autoprefix 另外 ...
- 【CH6801】棋盘覆盖
题目大意:给定一个 N*N 的棋盘,棋盘上有些位置不能防止任何东西,现用 1*2 的骨牌填充棋盘,问最多能铺多少块骨牌. 题解:由于骨牌只能覆盖相邻的两个格子,那么按照对角线进行划分的格子可以保证一定 ...
- JavaScript深入系列(一)--原型和原型链详解
构造函数创建对象 首先我们先使用构造函数创建一个对象: function Person(){} var person = new Person(); person.name = 'tom'; cons ...
- 面试集——redis
背景:该贴主要用来记面试过程中redis相关的问题,方便后期回顾. 为什么说Redis是单线程的以及Redis为什么这么快! https://blog.csdn.net/xlgen157387/art ...
