MATLAB 图像打开保存
一、图片读取保存
(1)读取
clear all
[filename,pathname]=uigetfile({'*.jpg';'*.bmp';'*.gif'},'选择图片');
if isequal(filename,0)
disp('Users Selected Canceled');
else
str=[pathname filename];
im = imread(str);
imshow(im);
end
(2)保存
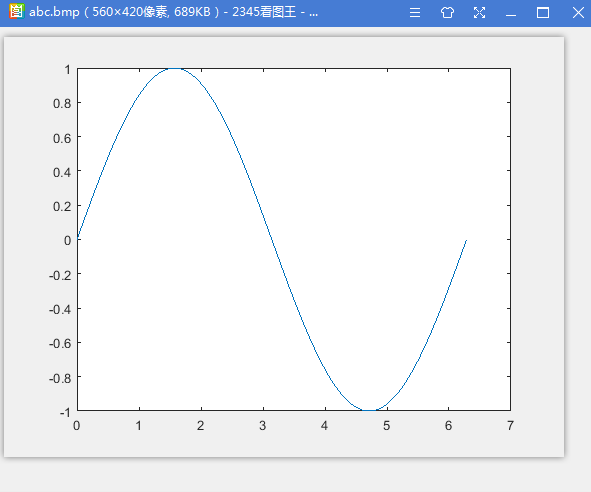
clear all
x=0:0.01:2*pi;
plot(x,sin(x)); [filename,pathname]=uiputfile({'*.bmp';},'保存图片');%路径和图片名
if ~isequal(filename,0)
str = [pathname filename];%路径名
data= getframe(gcf);%图片内容数据
imwrite(data.cdata,str,'bmp');
% saveas(gcf,str,'bmp');%两种方式都可以保存图片
close(gcf);
else
disp('保存失败');
end
二、灰度图和彩色图
(1)
图像中的单个点称为像素(pixel),每个像素都有一个值,称为像素值,它表示特定颜色的强度。
对于黑白图,是指每个像素的颜色用二进制的1位来表示,那末颜色只有“1”和“0”这两个值。这也就是说,要么是黑,要么是白。
对于灰度图,如果不用合成的方式来表达,可以表示为(0),(123),(255)。
如果用颜色合成的方式来表达,即它的一个像素值往往用R,G,B三个分量表示,注意,是RGB合成来表示一个像素的颜色。但要注意的 是RGB 分量必须都相等,否则就成彩色了。比如为(0,0,0)为黑,(123,123,123)为某种灰色,(255,255,255)为白。
clear all;
[filename,pathname]=uigetfile('*.*','select an image');
sample=imread([pathname filename]);%原始图
gray=rgb2gray(sample);%灰白图
bw=im2bw(sample);%黑白图
subplot(311),imshow(sample);
title('原图')
subplot(312),imshow(gray);
title('灰度图')
subplot(313),imshow(bw);
title('黑白图')

(2)rgb三分量分别表示
r=sample(:,:,1);
g=sample(:,:,2);
b=sample(:,:,3);
subplot(131),imshow(r);
subplot(132),imshow(g);
subplot(133),imshow(b);

三、filter2、conv2和imfilter 平滑处理
(1)
clear all;
clear all
[filename,pathname]=uigetfile('*.*','select an image');
sample=imread([pathname filename]); mean3Sample = filter2(fspecial('average',3),sample)/255;
mean5Sample = filter2(fspecial('average',5),sample)/255;
mean7Sample = filter2(fspecial('average',7),sample)/255;
gaussianSample = filter2(fspecial('gaussian'),sample)/255; subplot(2,2,1);
imshow(sample); %原始图像
title('原始图像') subplot(2,2,2);
imshow(mean3Sample); %采用均值进行平滑处理
title('平均滤波器(3)平滑处理') subplot(2,2,3);
imshow(mean7Sample); %原始图像
title('平均滤波器(7)平滑处理') subplot(2,2,4);
imshow(gaussianSample); %高斯滤波器进行平滑处理
title('高斯滤波器平滑处理') conv3Sample = conv2(fspecial('average',3),sample)/255;
conv7Sample = conv2(fspecial('average',7),sample)/255;
convSample = conv2(fspecial('gaussian'),sample)/255; figure
subplot(321),imshow(mean3Sample)
title('filter2滤波')
subplot(322),imshow(conv3Sample)
title('conv2法') subplot(323),imshow(mean7Sample)
subplot(324),imshow(conv7Sample) subplot(325),imshow(gaussianSample)
subplot(326),imshow(convSample)


这两个函数只能针对二维图像。滤波器本质就是加权。
(2)分别采用’prewitt’和’sobel’边缘算子对图像做边缘增强处理,并显示边缘处理后的图像
figure
%采用’prewitt’算子:
prewittSample = uint8(filter2(fspecial('prewitt'),sample));
subplot(211),imshow(prewittSample);
%采用’ sobel’算子:
sobelSample = uint8(filter2(fspecial('sobel'),sample));
subplot(212),imshow(sobelSample);
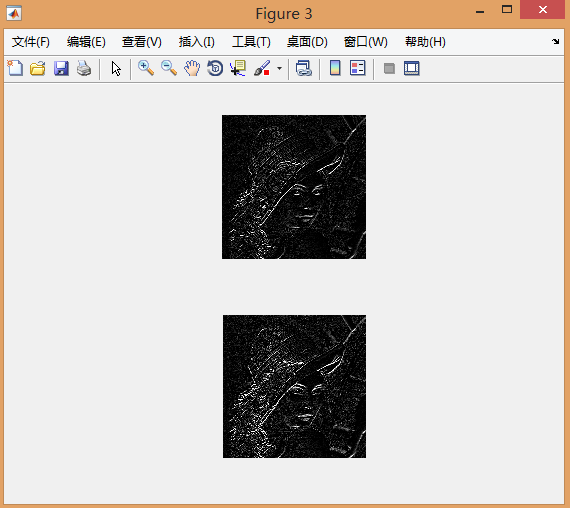
(3)采用“原图*2-平滑图像”,以及“原图+边缘处理图像”的方法锐化图像
figure
%采用“原图*2-平滑图像”方法:
subSample = sample.*2 - uint8(mean7Sample);
subplot(211),imshow(subSample);
%采用“原图+边缘处理图像”方法
addSample = sample + uint8(prewittSample);
subplot(212),imshow(addSample);
(4)imfilter 彩色图像的平滑
clear all;
I = imread('lena.jpg'); %读取一张噪声图像
%提取图像的三个(R、G、B)分量图像
R = I(:,:,1);
G = I(:,:,2);
B = I(:,:,3);
%生成一个8x8的均值滤波器
w = fspecial('average',8);
fR = imfilter(R,w,'replicate');
fG = imfilter(G,w,'replicate');
fB = imfilter(B,w,'replicate');
fc_filtered = cat(3,fR,fG,fB); %三分量平滑后合为一个整体
figure
subplot(121); imshow(I);title('彩色噪声图像');
subplot(122); imshow(fc_filtered);title('彩色图像平滑处理');

clear all;
I = imread('lena.jpg'); %读取一张噪声图像
%提取图像的三个(R、G、B)分量图像
R = I(:,:,1);
G = I(:,:,2);
B = I(:,:,3);
%生成一个8x8的均值滤波器
w = fspecial('average',8);
fc_filtered = imfilter(I, w, 'replicate'); %不用rgb分量单独平滑,彩色图像的平滑函数
figure
subplot(121); imshow(I);title('彩色噪声图像');2
subplot(122); imshow(fc_filtered);title('彩色图像平滑处理');

四、锐化处理
锐化本质是边缘增强,可以采用原图加边缘增强得到
(1)
clear all
A=imread('123.png');
figure(1);
subplot(2,2,1);
imshow(A);
title('原图'); I=double(A);
h=[-1 -1 -1;-1 9 -1;-1 -1 -1];
J=conv2(I,h,'same');
K=uint8(J);
subplot(2,2,2);
imshow(J);
title('使用拉普拉斯算子锐化处理后的图(double格式)');
subplot(2,2,3);
imshow(K);
title('使用拉普拉斯算子锐化处理后的图(uint8格式)');
L=(K+A)/2;
subplot(2,2,4);
imshow(L);
title('原图+锐化');

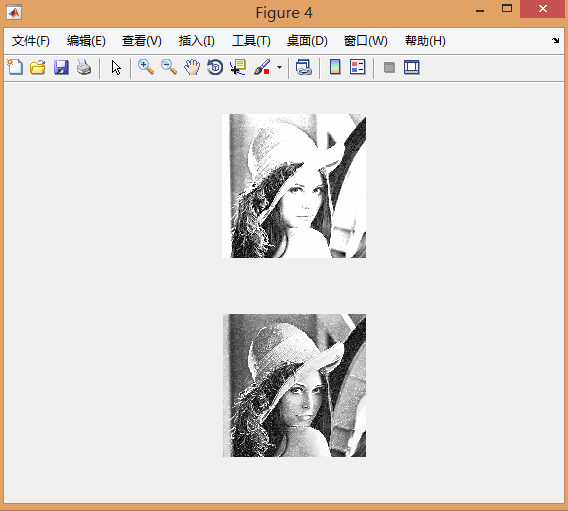
(2)
clear all
A=imread('123.png');
figure(1);
subplot(3,2,1);
imshow(A);
title('原图'); BW=edge(A,'canny');%黑白图
subplot(3,2,2);
imshow(BW);
title('candy算子边缘检测'); K=uint8(BW);%转换格式,1白色
M=uint8(~K);%反转数值,1黑色
L_1=A-50*M;%黑色区域增强
subplot(3,2,3);
imshow(L_1);
title('黑色区域增强');
L_2=(A+K*50);%白色区域增强
subplot(3,2,4);
imshow(L_2);
title('白色区域增强'); L_3=A-50*M+50*K;
subplot(3,2,5);
imshow(L_3);
title('黑白都增强');


(3)
clear all;
I=imread('lena.jpg');
subplot(3,2,1),imshow(I);
xlabel('a)原始图像'); H=fspecial('sobel');%sobel滤波器
J=imfilter(I, H, 'replicate');%灰度值
subplot(3,2,3),imshow(J);
xlabel('Sobel锐化滤波处理');
K=I+0.32*J;%比例相加
subplot(324),imshow(K)
xlabel('Sobel锐化滤波处理+原图'); H=fspecial('laplacian');%laplacian滤波器
J=imfilter(I, H, 'replicate');%灰度值
subplot(3,2,5),imshow(J);
xlabel('laplacian锐化滤波处理');
K=I+J;%比例相加
subplot(326),imshow(K)
xlabel('laplacian锐化滤波处理+原图');

滤波器决定了是锐化或者平滑
五、RGB和HSI
(1)直方图均衡
clear all
sourcePic=imread('lena.jpg');
[m,n,o]=size(sourcePic);
grayPic=rgb2gray(sourcePic);%灰度图
subplot(321),imshow(sourcePic); title('原图')
subplot(323),imshow(grayPic); title('灰度图') gp=zeros(1,256); %计算各灰度出现的概率 (0,255)出现的概率
for i=1:256
gp(i)=length(find(grayPic==(i-1)))/(m*n); %i灰度的概率
end
subplot(324),,bar(0:255,gp);
title('原图像直方图');
xlabel('灰度值');
ylabel('概率');
axis([0 256 0 0.02]) newGp=zeros(1,256); %计算新的各灰度出现的概率
S1=zeros(1,256);
S2=zeros(1,256);
tmp=0;
for i=1:256
tmp=tmp+gp(i);
S1(i)=tmp; %累计概率(映射到0~1)
S2(i)=round(S1(i)*256); %映射到0~255
end
%映射
for i=1:256
newGp(i)=sum(gp(find(S2==(i-1)))); %灰度值为联系
end
subplot(325),bar(0:255,newGp);
title('均衡化后的直方图');
xlabel('灰度值');
ylabel('概率');
axis([0 256 0 0.02]) newGrayPic=grayPic; %填充各像素点新的灰度值
for i=1:256
newGrayPic(find(grayPic==(i-1)))=S2(i);
end
subplot(326),imshow(newGrayPic);
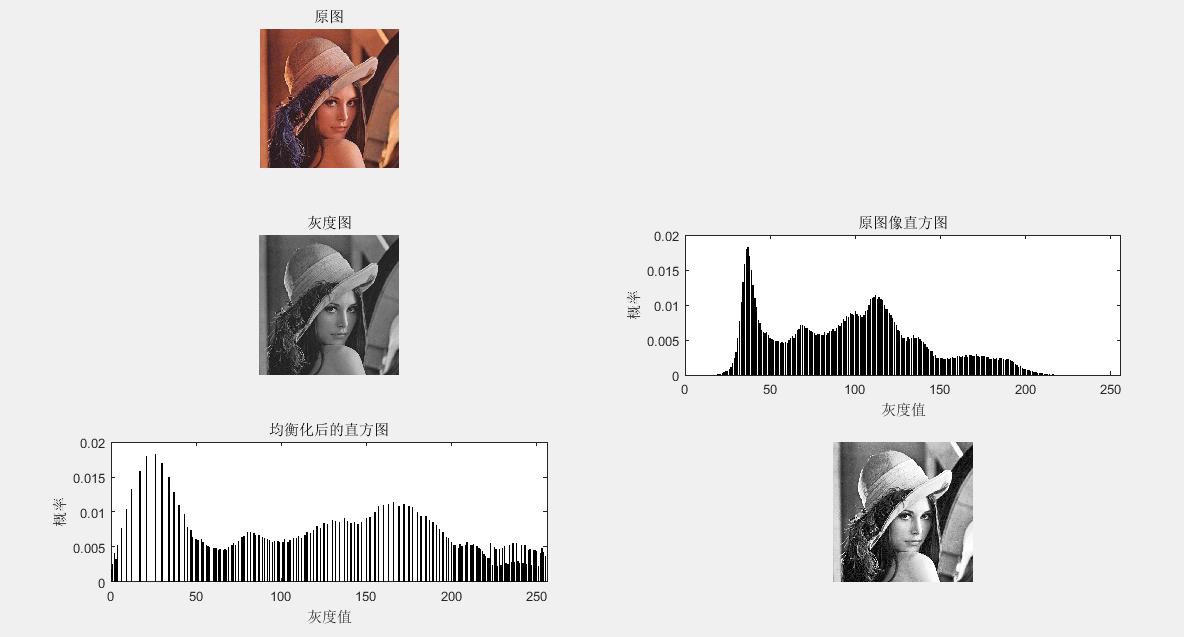
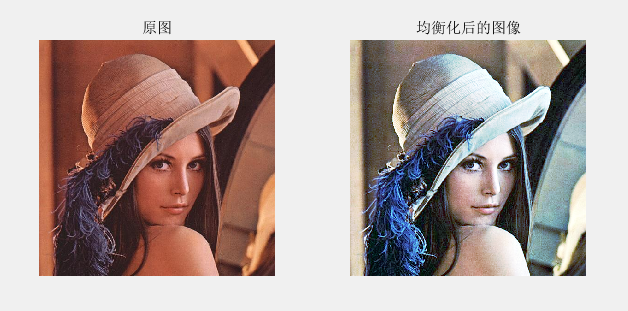
clear all
sourcePic=imread('lena.jpg');
[m,n,o]=size(sourcePic);
subplot(121),imshow(sourcePic);
title('原图')
%%
grayPic=sourcePic(:,:,1);
gp=zeros(1,256); %计算各灰度出现的概率
for i=1:256
gp(i)=length(find(grayPic==(i-1)))/(m*n);
end newGp=zeros(1,256); %计算新的各灰度出现的概率
S1=zeros(1,256);
S2=zeros(1,256);
tmp=0;
for i=1:256
tmp=tmp+gp(i);
S1(i)=tmp;
S2(i)=round(S1(i)*256);
end
for i=1:256
newGp(i)=sum(gp(find(S2==i)));
end newGrayPic=grayPic; %填充各像素点新的灰度值
for i=1:256
newGrayPic(find(grayPic==(i-1)))=S2(i);
end
nr=newGrayPic;
%%
grayPic=sourcePic(:,:,2); gp=zeros(1,256); %计算各灰度出现的概率
for i=1:256
gp(i)=length(find(grayPic==(i-1)))/(m*n);
end newGp=zeros(1,256); %计算新的各灰度出现的概率
S1=zeros(1,256);
S2=zeros(1,256);
tmp=0;
for i=1:256
tmp=tmp+gp(i);
S1(i)=tmp;
S2(i)=round(S1(i)*256);
end
for i=1:256
newGp(i)=sum(gp(find(S2==i)));
end newGrayPic=grayPic; %填充各像素点新的灰度值
for i=1:256
newGrayPic(find(grayPic==(i-1)))=S2(i);
end
ng=newGrayPic;
%%
grayPic=sourcePic(:,:,3); gp=zeros(1,256); %计算各灰度出现的概率
for i=1:256
gp(i)=length(find(grayPic==(i-1)))/(m*n);
end newGp=zeros(1,256); %计算新的各灰度出现的概率
S1=zeros(1,256);
S2=zeros(1,256);
tmp=0;
for i=1:256
tmp=tmp+gp(i);
S1(i)=tmp;
S2(i)=round(S1(i)*256);
end
for i=1:256
newGp(i)=sum(gp(find(S2==i)));
end newGrayPic=grayPic; %填充各像素点新的灰度值
for i=1:256
newGrayPic(find(grayPic==(i-1)))=S2(i);
end
nb=newGrayPic;
%%
res=cat(3,nr,ng,nb);
subplot(122),imshow(res);
title('均衡化后的图像')
(2)hsi(色调、饱和度、亮度)和hsv(色调(H),饱和度(S),明度(V))。
clear all
% hsi = rgb2hsi(rgb)把一幅RGB图像转换为HSI图像,
% 输入图像是一个彩色像素的M×N×3的数组,
% 其中每一个彩色像素都在特定空间位置的彩色图像中对应红、绿、蓝三个分量。
% 假如所有的RGB分量是均衡的,那么HSI转换就是未定义的。
% 输入图像可能是double(取值范围是[0, 1]),uint8或 uint16。
%
% 输出HSI图像是double,
% 其中hsi(:, :, 1)是色度分量,它的范围是除以2*pi后的[0, 1];
% hsi(:, :, 2)是饱和度分量,范围是[0, 1];
% hsi(:, :, 3)是亮度分量,范围是[0, 1]。 % 抽取图像分量
rgb=imread('lena.jpg');
rgb = im2double(rgb);
r = rgb(:, :, 1);
g = rgb(:, :, 2);
b = rgb(:, :, 3); % 执行转换方程
num = 0.5*((r - g) + (r - b));
den = sqrt((r - g).^2 + (r - b).*(g - b));
theta = acos(num./(den + eps)); %防止除数为0 H = theta;
H(b > g) = 2*pi - H(b > g);
H = H/(2*pi); num = min(min(r, g), b);
den = r + g + b;
den(den == 0) = eps; %防止除数为0 S = 1 - 3.* num./den;
H(S == 0) = 0;
I = (r + g + b)/3; % 将3个分量联合成为一个HSI图像
hsi = cat(3, H, S, I);
subplot(121),imshow(hsi)
title('hsi图像')
subplot(122),imshow(rgb2hsv(rgb))%自带函数
title('hsv图形')

MATLAB 图像打开保存的更多相关文章
- matlab 图像的保存
gcf:获取当前显示图像的句柄: 默认 plot 的 position 是 [232 246 560 420] 0. save >> A = randn(3, 4); >> B ...
- MFC多文档中opencv处理图像打开、保存
需要在C**Doc和C**View中进行相应修改 图像打开: Doc.cpp中: BOOL CCVMFCDoc::Load(IplImage** pp, LPCTSTR csFilename) { I ...
- Win8 Metro(C#) 数字图像处理--1 图像打开,保存
原文:Win8 Metro(C#) 数字图像处理--1 图像打开,保存 作为本专栏的第一篇,必不可少的需要介绍一下图像的打开与保存,一便大家后面DEMO的制作. Win8Metro编程中,图像相关 ...
- Matlab中图片保存的5种方法
matlab的绘图和可视化能力是不用多说的,可以说在业内是家喻户晓的. Matlab提供了丰富的绘图函数,比如ez**系类的简易绘图函数,surf.mesh系类的数值绘图函数等几十个.另外其他专业工具 ...
- matlab的绘图保存
matlab的绘图和可视化能力是不用多说的,可以说在业内是家喻户晓的.Matlab提供了丰富的绘图函数,比如ez**系类的简易绘图函数,surf.mesh系类的数值绘图函数等几十个.另外其他专业工 ...
- Matlab中图片保存的四种方法
matlab的绘图和可视化能力是不用多说的,可以说在业内是家喻户晓的.Matlab提供了丰富的绘图函数,比如ez**系类的简易绘图函数,surf.mesh系类的数值绘图函数等几十个.另外其他专业工具箱 ...
- matlab图像类型转换以及uint8、double、im2double、im2uint8和mat2gray等说明
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/fx677588/article/details/53301740 1. matlab图像保存说明 matlab中读取图片后保存的数据是uint8类型( ...
- opencv::将两幅图像合并后,在同一个窗口显示;并将合并的图像流保存成视频文件
/** * @file main-opencv.cpp * @date July 2014 * @brief An exemplative main file for the use of ViBe ...
- C#项目打开/保存文件夹/指定类型文件,获取路径
C#项目打开/保存文件夹/指定类型文件,获取路径 转:http://q1q2q363.xiaoxiang.blog.163.com/blog/static/1106963682011722424325 ...
随机推荐
- Typescript 01 安装与使用
---恢复内容开始--- 一. 介绍 1. TypeScript 是由微软开发的一款开源的编程语言. 2. TypeScript 是 Javascript 的超级,遵循最新的 ES6.Es5 规范.T ...
- 原生js实现在表格用鼠标框选并有反选功能
今天应同学要求,需要写一个像Excel那样框选高亮,并且实现框选区域实现反选功能.要我用原生js写,由于没什么经验翻阅了很多资料,第一次写文章希望各位指出不足!! 上来先建表 <div clas ...
- 原生js写一个无缝轮播图插件(支持vue)
轮播图插件(Broadcast.js) 前言:写这个插件的原因 前段时间准备用vue加上网易云的nodejs接口,模拟网易云音乐移动端.因为想自己写一遍所有的代码以及加固自己的flex布局,所以没有使 ...
- psql的时间类型,通过时间查询
psql的时间类型,通过时间查询 psql有date/timestamp类型,date只显示年月日1999-01-08,而timestamp显示年月日时分秒 1999-01-08 09:54:03.2 ...
- 复习笔记——1. C语言基础知识回顾
1. 数据类型 1.1 基本数据类型 整型:int, long,unsigned int,unsigned long,long long-- 字符型:char 浮点型:float, double-- ...
- R|生存分析 - KM曲线 ,值得拥有姓名和颜值
本文首发于“生信补给站”:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/lpkWwrLNtkLH8QA75X5STw 生存分析作为分析疾病/癌症预后的出镜频率超高的分析手段,而其结果展示的KM ...
- DataFrame简介(一)
1. DataFrame 本片将介绍Spark RDD的限制以及DataFrame(DF)如何克服这些限制,从如何创建DataFrame,到DF的各种特性,以及如何优化执行计划.最后还会介绍DF有哪些 ...
- python网络协议
一 互联网的本质 咱们先不说互联网是如何通信的(发送数据,文件等),先用一个经典的例子,给大家说明什么是互联网通信. 现在追溯到八九十年代,当时电话刚刚兴起,还没有手机的概念,只是有线电话,那么此时你 ...
- go源码分析(五) 获取函数名和调用者的函数名
参考资料 实现代码保存在我的github // input flag 1:FunName 2:CallerFunName func GetFuncName(flag int) string { ...
- 动态表单数据验证 vue
idCard: [{ validator: (rule, value, callback) => { if (this.idCardVif === 'idCard') { this.valida ...
