JUnit4 笔记
1. JUnit4基础
JUnit4 与 JUnit3不同的是,不需要继承测试类,而是通过JDK5提供的注解去标识测试方法。
常用的注解如下:
@Before:初始化方法 对于每一个测试方法都要执行一次(注意与BeforeClass区别,后者是对于所有方法执行一次)
@After:释放资源 对于每一个测试方法都要执行一次(注意与AfterClass区别,后者是对于所有方法执行一次)
@Test:测试方法,在这里可以测试期望异常和超时时间
--@Test(expected=ArithmeticException.class)检查被测方法是否抛出ArithmeticException异常
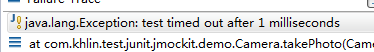
--@Test(timeout=100)检查测试方法运行耗费的时间,如果超时,则抛出异常:test timed out after xxx milliseconds
@Ignore:忽略的测试方法
@BeforeClass:针对所有测试,只执行一次,且必须为static void
@AfterClass:针对所有测试,只执行一次,且必须为static void
一个JUnit4的单元测试用例执行顺序为:
@BeforeClass -> @Before -> @Test -> @After -> @AfterClass;
一个Junit4的单元测试方法执行顺序为:
@Before -> @Test -> @After
示例代码:
package com.khlin.test.junit.jmockit.demo; import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.AfterClass;
import org.junit.Assert;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.BeforeClass;
import org.junit.Test; public class CameraTest { private static Camera camera; //针对所有测试,只运行一次。且只能是static方法
@BeforeClass
public static void init() {
camera = new Camera();
System.out.println("annotation BeforeClass:");
} //每个测试方法调用前都会调用此方法
@Before
public void initClass() {
System.out.println("annotation Before:");
} @Test(timeout=1)
public void testTakePhoto() {
Assert.assertEquals(48, camera.takePhoto("abc"));
System.out.println("test method");
} @After
public void teardownClass() {
System.out.println("annotation After:");
} @AfterClass
public static void teardown() {
System.out.println("annotation AfterClass:");
}
}
2.JUnit4高级特性
此外,JUnit4为单元测试提供了默认的测试运行器,它的测试方法都是由它负责执行的。
开发者也可以通过继承org.junit.runner.Runner来定制自己的运行器,然后通过RunWith注解指定对应的测试运行器。
作为非专业测试人员,一般的默认运行器就可以满足需要了。当要使用一些高级特性时,就必须显式指定测试运行器。
高级特性常用的有参数化和套件测试。
1)参数化测试
构建无限组数据,对一个方法进行测试,优点是多次测试时测试方法只需要写一个,缺点是这样只能对一个方法进行测试,除非有必要大量测试,否则意义不是很大。
步骤如下:
1.在测试类上添加注解@RunWith(Parameterized.class),指定测试运行器
2.创建用于存储期望值和参数的变量
3.声明构造方法,为上述变量赋值
4.声明数据供给方法,static,返回值为Collection类型(二维数组),用@Parameters注解
示例代码:
package com.khlin.test.junit.jmockit.demo; import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collection; import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.Assert;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.junit.runners.Parameterized;
import org.junit.runners.Parameterized.Parameters; //0.注解,表示是参数化测试
@RunWith(Parameterized.class)
public class CalculatorTest { private Calculator calculator; //1.创建用于存储期望值和参数 private int expected; private int i; private int j; //2. 构造方法赋值
public CalculatorTest(int expected, int i, int j) {
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
this.expected = expected;
this.i = i;
this.j = j;
} //3. 数据供给方法,static,返回值为Collection类型,用@Parameters注解
@Parameters
public static Collection initParameter() {
return Arrays.asList(new Object[][] { { 2, 1, 1 }, { 3, 2, 1 },
{ 88, 22, 66 }});
} // 每次方法前都会调用
@Before
public void init() {
calculator = new Calculator();
} @Test
public void testAdd() {
Assert.assertEquals(expected, calculator.add(i, j));
} @After
public void teardown() {
this.calculator = null;
}
}
2)套件测试
实际上就是将所有的测试类,集合到一个总的测试类当中,运行时将会依次去调用所有测试类的测试方法,意义。。。。好像也不是很大的样子。
步骤如下:
1.创建一个空的测试类
2.在该测试类上使用注解,@RunWith(Suite.class)指定运行器,@SuiteClasses({xxx.class, xxx.class})指定集合进来的测试类
3.保证这个空类使用public 修饰,而且存在公开的不带有任何参数的构造函数
以上面两段代码为例,套件测试类的代码如下:
package com.khlin.test.junit.jmockit.demo; import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.junit.runners.Suite;
import org.junit.runners.Suite.SuiteClasses; @RunWith(Suite.class)
@SuiteClasses({CalculatorTest.class, CameraTest.class})
public class SuitTest { }
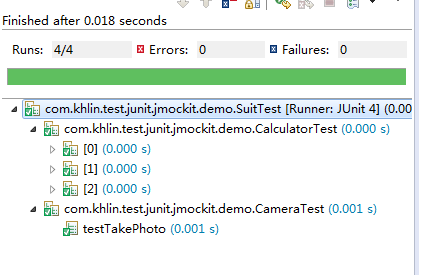
运行结果,依次调用了测试方法:
JUnit4 笔记的更多相关文章
- junit4笔记
这两天在复习hibernate,看的小峰的视频,觉得很不错. 现在把里面的junit4的一些使用方法记下来.方便以后的差用.代码如下. package com.java1234.service; im ...
- Junit4学习笔记
一.初始化标注 在老Junit4提供了setUp()和tearDown(),在每个测试函数调用之前/后都会调用. @Before: Method annotated with @Before exec ...
- Java 学习笔记 Junit4单元测试使用
Junit使用 1.导入Junit包 到官网下载个Junit4.12.jar文件,放在lib目录 或者在类的空白处打@Test,之后按下alt+enter,选择添加Junit4依赖 之后就会弹出一个窗 ...
- JUnit4 学习笔记
一.环境搭建: 1.需要用的包: JUnit4.7:http://files.cnblogs.com/files/ShawnYang/junit4.7.zip hamcrest-1.2:http:// ...
- Junit4学习笔记--方法的执行顺序
package com.lt.Demo.TestDemo; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.Collection; import org.junit ...
- JUnit4源码学习笔记
先上一个在Spring-test下运行的调用栈 自底向上: JUnitStarter IDEA对JUnit的支持,调用JUnitCore.run(Runner),将注解@RunWith指定的Runne ...
- JUnit4 入门笔记
Test注解的两个可选参数 expected timeout The Test annotation supports two optional parameters. The first, expe ...
- ActiveMQ学习笔记(5)——使用Spring JMS收发消息
摘要 ActiveMQ学习笔记(四)http://my.oschina.net/xiaoxishan/blog/380446 中记录了如何使用原生的方式从ActiveMQ中收发消息.可以看出,每次 ...
- Robotium编写测试用例如何模拟Junit4的BeforeClass和AfterClass方法2 - SingleLaunchActivityTestCase
本文来源于:http://blog.csdn.net/zhubaitian/article/details/39296753 在上一遍笔记博客中本以为只能在Setup和TearDown中做条件判断来实 ...
随机推荐
- Asp.net性能优化技巧
[摘 要] 我只是提供我几个我认为有助于提高写高性能的asp.net应用程序的技巧,本文提到的提高asp.net性能的技巧只是一个起步,更多的信息请参考<Improving ASP.NET Pe ...
- AHOI2009最小割
1797: [Ahoi2009]Mincut 最小割 Time Limit: 10 Sec Memory Limit: 162 MBSubmit: 1072 Solved: 446[Submit] ...
- zz-rtl8188eu的linux-usb-wifi调试及驱动编译150210
//zz//####################################################################### zz-rtl8188eu的linux-usb ...
- PS CS5如何在一张图片里插入另一张图片?
帮你介绍两种比较简便的方法:1.ctrl+A全选,ctrl+C复制,在另一个图中ctrl+V粘贴即可:2.PS中的窗口可以拖动的,拉动一个窗口,选择移动工具,直接移到另一张图上即可!
- 尝试加载 Oracle 客户端库时引发 BadImageFormatException。如果在安装 32 位 Oracle 客户端组件的情况下以 64 位模式运行,将出现此问题。
从10G开始,Oracle提供了一个较为轻量级的客户包,叫做Instant Client. 将它安装好后,就不用再安装庞大的Oracle Client了. 这样一来,只要客户端下载Instant Cl ...
- 用java api读取HDFS文件
import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.security.PrivilegedExceptionActi ...
- oracle之spool详细使用总结
今天实际项目中用到了spool,发现网上好多内容不是很全,自己摸索了好半天,现在总结一下. 一.通过spool 命令,可以将select 数据库的内容写到文件中,通过在sqlplus设置一些参数,使得 ...
- 如何禁止掉SharePoint页面个性化(网站操作-编辑页面)
使用SharePoint Designer打开,或者创建一个新的Master Page,找到SPWebPartManager控件,如下所示,修改它的属性“Personalization-Enabled ...
- keystone 手动建立租户,用户,角色,服务,端口
建立租户: root@cloud:~# keystone tenant-create --name=admin WARNING: Bypassing authentication using a to ...
- 【Java基础】final关键字总结
Java中的final关键字非常重要,它可以应用于类.方法以及变量.这篇文章中我将带你看看什么是final关键字?将变量,方法和类声明为final代表了什么?使用final的好处是什么?最后也有一些使 ...
