RR算法 调度
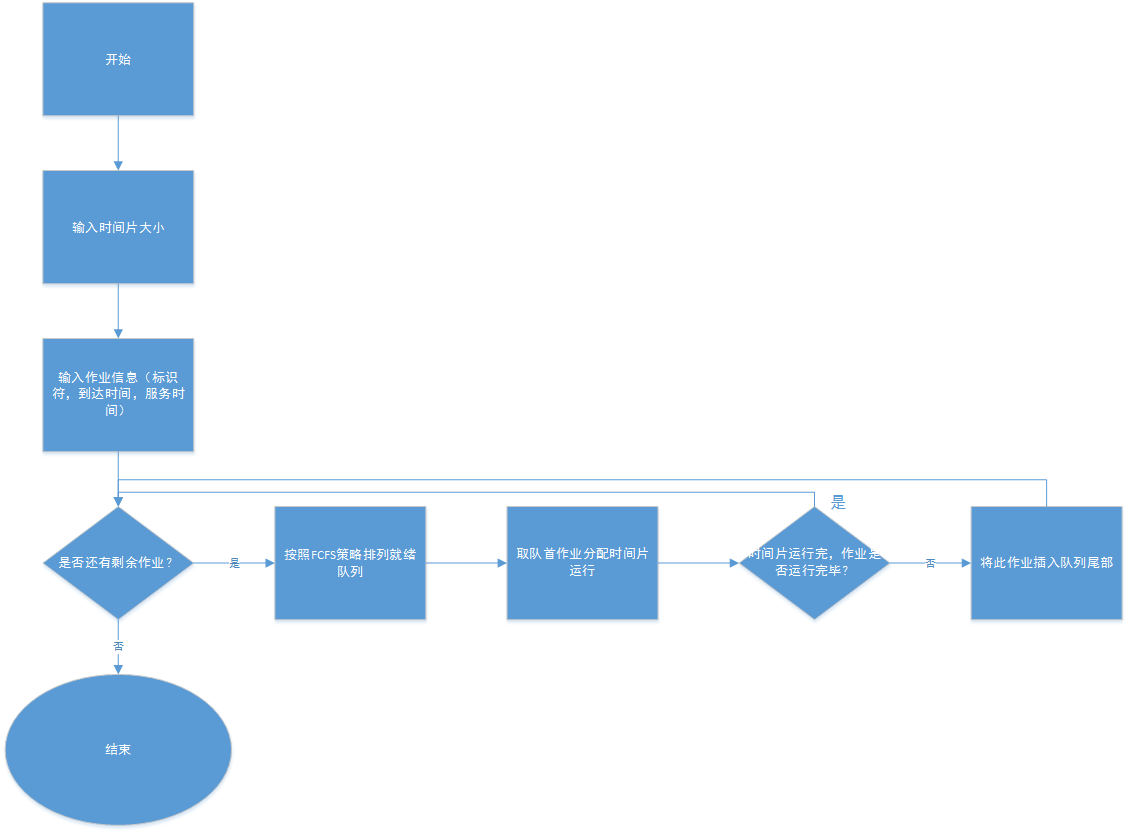
RR算法是使用非常广泛的一种调度算法。
首先将所有就绪的队列按FCFS策略排成一个就绪队列,然后系统设置一定的时间片,每次给队首作业分配时间片。如果此作业运行结束,即使时间片没用完,立刻从队列中去除此作业,并给下一个作业分配新的时间片;如果作业时间片用完没有运行结束,则将此作业重新加入就绪队列尾部等待调度。
- //main.cpp
- #include "RR.h"
- int main()
- {
- std::vector<PCB> PCBList;
- int timeslice;
- //输入时间片大小,作业信息
- InputPCB(PCBList, timeslice);
- //RR算法
- RR(PCBList, timeslice);
- //显示结果
- show(PCBList);
- return 0;
- }
- //RR.h
- #ifndef RR_H_
- #define RR_H_
- #include <iostream>
- #include <algorithm>
- #include <iomanip>
- #include <vector>
- #include <queue>
- //作业结构体
- typedef struct PCB
- {
- int ID; //标识符
- int ComeTime; //到达时间
- int ServerTime; //服务时间
- int FinishTime; //完成时间
- int TurnoverTime; //周转时间
- double WeightedTurnoverTime; //带权周转时间
- }PCB;
- /*
- 函数功能:输入作业信息
- 参数说明:
- PCBList std::vector<PCB>& PCB链
- timeslice int 时间片
- */
- void InputPCB(std::vector<PCB> &PCBList, int ×lice);
- /*
- 函数功能:RR算法
- 参数说明:
- PCBList std::vector<PCB>& PCB链
- */
- void RR(std::vector<PCB> &PCBList, int timeslice);
- /*
- 函数功能:显示结果
- 参数说明:
- PCBList std::vector<PCB>& PCB链
- */
- void show(std::vector<PCB> &PCBList);
- /*
- 函数功能:比较函数,用于sort(),按ComeTime升序排列
- 参数说明:
- p1 const PCB& PCB
- p2 const PCB& PCB
- */
- bool CmpByComeTime(const PCB &p1, const PCB &p2);
- #endif
- //RR.cpp
- #include "RR.h"
- //输入作业信息
- void InputPCB(std::vector<PCB> &PCBList,int ×lice)
- {
- std::cout << "输入时间片大小: ";
- std::cin >> timeslice;
- do {
- PCB temp;
- std::cout << "输入标识符: ";
- std::cin >> temp.ID;
- std::cout << "输入到达时间: ";
- std::cin >> temp.ComeTime;
- std::cout << "输入服务时间: ";
- std::cin >> temp.ServerTime;
- temp.FinishTime = 0; //暂时存放运行了多少时间,来判断此作业是否运行结束
- PCBList.push_back(temp);
- std::cout << "继续输入?Y/N: ";
- char ans;
- std::cin >> ans;
- if ('Y' == ans || 'y' == ans)
- continue;
- else
- break;
- } while (true);
- }
- //RR算法
- void RR(std::vector<PCB> &PCBList, int timeslice)
- {
- std::sort(PCBList.begin(), PCBList.end(), CmpByComeTime); //按到达时间排序
- std::vector<PCB> result; //保存结果
- std::queue<PCB> Ready; //就绪队列
- int BeginTime = (*PCBList.begin()).ComeTime; //第一个作业开始时间
- Ready.push(*PCBList.begin());
- PCBList.erase(PCBList.begin());
- while (!PCBList.empty() || !Ready.empty())
- {
- if (!PCBList.empty() && BeginTime >= (*PCBList.begin()).ComeTime) //有新作业到达,加入就绪队列
- {
- Ready.push(*PCBList.begin());
- PCBList.erase(PCBList.begin());
- }
- if (Ready.front().FinishTime + timeslice < Ready.front().ServerTime) //时间片用完没运行完,加入队尾
- {
- Ready.front().FinishTime += timeslice;
- Ready.push(Ready.front());
- Ready.pop();
- BeginTime += timeslice;
- }
- else //此作业运行完
- {
- BeginTime += Ready.front().ServerTime - Ready.front().FinishTime;
- Ready.front().FinishTime = BeginTime;
- Ready.front().TurnoverTime = Ready.front().FinishTime - Ready.front().ComeTime;
- Ready.front().WeightedTurnoverTime = (double)Ready.front().TurnoverTime / Ready.front().ServerTime;
- //从就绪队列中移除作业
- result.push_back(Ready.front());
- Ready.pop();
- }
- }
- //按ComeTime升序排序,便于显示结果
- PCBList = result;
- std::sort(PCBList.begin(), PCBList.end(), CmpByComeTime);
- }
- //显示结果
- void show(std::vector<PCB> &PCBList)
- {
- int SumTurnoverTime = 0;
- double SumWeightedTurnoverTime = 0;
- std::cout.setf(std::ios::left);
- std::cout << std::setw(20) << "标识符";
- for (std::vector<PCB>::iterator it = PCBList.begin(); it < PCBList.end(); ++it)
- std::cout << std::setw(5) << (*it).ID;
- std::cout << std::endl;
- std::cout << std::setw(20) << "到达时间";
- for (std::vector<PCB>::iterator it = PCBList.begin(); it < PCBList.end(); ++it)
- std::cout << std::setw(5) << (*it).ComeTime;
- std::cout << std::endl;
- std::cout << std::setw(20) << "服务时间";
- for (std::vector<PCB>::iterator it = PCBList.begin(); it < PCBList.end(); ++it)
- std::cout << std::setw(5) << (*it).ServerTime;
- std::cout << std::endl;
- std::cout << std::setw(20) << "完成时间";
- for (std::vector<PCB>::iterator it = PCBList.begin(); it < PCBList.end(); ++it)
- std::cout << std::setw(5) << (*it).FinishTime;
- std::cout << std::endl;
- std::cout << std::setw(20) << "周转时间";
- for (std::vector<PCB>::iterator it = PCBList.begin(); it < PCBList.end(); ++it)
- {
- std::cout << std::setw(5) << (*it).TurnoverTime;
- SumTurnoverTime += (*it).TurnoverTime;;
- }
- std::cout << std::endl;
- std::cout << std::setw(20) << "带权周转时间";
- for (std::vector<PCB>::iterator it = PCBList.begin(); it < PCBList.end(); ++it)
- {
- std::cout << std::setw(5) << (*it).WeightedTurnoverTime;
- SumWeightedTurnoverTime += (*it).WeightedTurnoverTime;;
- }
- std::cout << std::endl;
- std::cout << "平均周转时间: " << (double)SumTurnoverTime / PCBList.size() << std::endl;
- std::cout << "平均带权周转时间: " << SumWeightedTurnoverTime / PCBList.size() << std::endl;
- }
- //比较函数,按ComeTime升序排列
- bool CmpByComeTime(const PCB &p1, const PCB &p2)
- {
- return p1.ComeTime < p2.ComeTime;
- }
RR算法 调度的更多相关文章
- 操作系统概念学习笔记 10 CPU调度
操作系统概念学习笔记 10 CPU调度 多道程序操作系统的基础.通过在进程之间切换CPU.操作系统能够提高计算机的吞吐率. 对于单处理器系统.每次仅仅同意一个进程执行:不论什么其它进程必须等待,直到C ...
- [Linux]Linux系统调用列表
本文列出了大部分常见的Linux系统调用,并附有简要中文说明. 以下是Linux系统调用的一个列表,包含了大部分常用系统调用和由系统调用派生出的的函数.这可能是你在互联网上所能看到的唯一一篇中文注释的 ...
- LVS负载均衡集群服务搭建详解(二)
lvs-nat模型构建 1.lvs-nat模型示意图 本次构建的lvs-nat模型的示意图如下,其中所有的服务器和测试客户端均使用VMware虚拟机模拟,所使用的CentOS 7 VS内核都支持ipv ...
- 常用的Linux系统调用命令
常用的Linux系统调用命令 下面一些函数已经过时,被新的更好的函数所代替了(gcc在链接这些函数时会发出警告),但因为兼容的原因还保留着,这些函数将在前面标上“*”号以示区别. 一.进程控制 ...
- Linux系统调用(转载)
目录: 1. Linux系统调用原理 2. 系统调用的实现 3. Linux系统调用分类及列表 4.系统调用.用户编程接口(API).系统命令和内核函数的关系 5. Linux系统调用实例 6. Li ...
- Linux系统调用列表
转自Linux系统调用列表 一.进程控制: fork 创建一个新进程 clone 按指定条件创建子进程 execve 运行可执行文件 exit 中止进程 _exit 立即中止当前进程 getdtabl ...
- Linux常用系统调用
转载 http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/linux/kernel/syscall/part1/appendix.html#icomments 按照惯例,这个列表 ...
- 【转】Linux系统调用列表
一.进程控制: fork 创建一个新进程 clone 按指定条件创建子进程 execve 运行可执行文件 exit 中止进程 _exit 立即中止当前进程 getdtablesize 进程所能打开的最 ...
- Linux系统常见调用及其分类
Linux系统调用主要可以分为以下几类: 进程控制 fork 创建一个新进程 clone 按指定条件创建子进程 execve 运行可执行文件 exit 中止进程 _exit 立即中止当前进程 get ...
随机推荐
- BZOJ.1927.[SDOI2010]星际竞速(无源汇上下界费用流SPFA /最小路径覆盖)
题目链接 上下界费用流: /* 每个点i恰好(最少+最多)经过一次->拆点(最多)+限制流量下界(i,i',[1,1],0)(最少) 然后无源汇可行流 不需要源汇. 注: SS只会连i',求SS ...
- ClassLoader加载资源时的搜索路径
先来个例子: /** * 测试classloader加载路径在哪里<p> * main3 */ public static void main3(String[] args) { Prop ...
- 通过html页面打开Android本地的app
http://www.cnblogs.com/yejiurui/p/3413796.html 一.通过html页面打开Android本地的app 1.首先在编写一个简单的html页面 <html ...
- Android防止进程被第三方软件杀死
http://blog.csdn.net/wangliang198901/article/details/12342845 http://stackoverflow.com/questions/385 ...
- 请远离include_once和require_once
尽量使用include, 而不是include_once, 理由是 include_once需要查询一遍已加载的文件列表, 确认是否存在, 然后再加载. 诚然, 这个理由是对的, 不过, 我今天要说的 ...
- 奇怪吸引子---Hadley
奇怪吸引子是混沌学的重要组成理论,用于演化过程的终极状态,具有如下特征:终极性.稳定性.吸引性.吸引子是一个数学概念,描写运动的收敛类型.它是指这样的一个集合,当时间趋于无穷大时,在任何一个有界集上出 ...
- c++数组的引用
引用就是某一变量(目标)的一个别名,对引用的操作与对变量直接操作完全一样.引用的声明方法:类型标识符 &引用名=目标变量名: 引用最大的好处就是提高函数效率以及节省空间; 关键问题一.传递引用 ...
- eclipse:报错信息The superclass "javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet" was not found on the Java Build Path
JavaWeb: 报错信息The superclass "javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet" was not found on the Java Bui ...
- WCF中记录SOAP消息日志
Windows Communication Foundation (WCF) 默认启用消息日志,WCF使用了在System.Diagnostics名称空间中定义的跟踪机制.在这个跟踪机制中,通过在配置 ...
- 【Linux】ps命令
Linux中的ps命令是Process Status的缩写.ps命令用来列出系统中当前运行的那些进程.ps命令列出的是当前那些进程的快照,就是执行ps命令的那个时刻的那些进程,如果想要动态的显示进程信 ...