表(list)
表
表(list)是常见的数据结构。从数学上来说,表是一个有序的元素集合。在C语言的内存中,表储存为分散的节点(node)。每个节点包含有一个元素,以及一个指向下一个(或者上一个)元素的指针。如下图所示:

表: 橙色储存数据,蓝色储存指针
图中的表中有四个节点。第一个节点是头节点(head node),这个节点不用于储存元素,只用于标明表的起始。头节点可以让我们方便的插入或者删除表的第一个元素。整个表中包含有三个元素(5, 2, 15)。每个节点都有一个指针,指向下一个节点。最后一个节点的指针为NULL,我们用“接地”来图示该指针。
表的功能与数组(array)很类似,数组也是有序的元素集合,但数组在内存中为一段连续内存,而表的每个节点占据的内存可以是离散的。在数组中,我们通过跳过固定的内存长度来寻找某个编号的元素。但在表中,我们必须沿着指针联系起的长链,遍历查询元素。此外,数组有固定的大小,表可以根据运行情况插入或者删除节点,动态的更改大小。表插入节点时需要从进程空间的堆中开辟内存空间,用以储存节点。删除节点可以将节点占据的内存归还给进程空间。

删除节点, free释放内存

插入节点,malloc开辟内存
表有多种变种。上面的表中,指针指向是从前向后的,称为单向链表(linked list)。还有双向链表(double-linked list),即每个节点增加一个指向前面一个元素的指针。以及循环链表(tabular list),最后一个元素的指针并不为NULL,而是指向头节点。不同类型的链表有不同的应用场景。
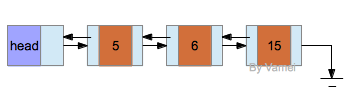
双向链表
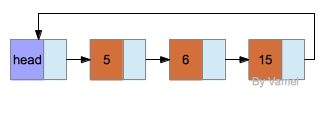
循环链表

双向循环链表
单向链表的C实现
一个数据结构的实现有两方面: 1. 数据结构的内存表达方式; 2. 定义在该数据结构上的操作。我们这里实现最简单的单向链表。表所支持的操作很灵活多样,我们这里定义一些最常见的操作。每个操作都写成一个函数。

/* By Vamei */
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct node *LIST;
typedef struct node *position; /* node,节点 */
struct node {
int element;
position next;
}; /*
* operations (stereotype)
* 操作
*/
LIST init_list(void);
void delete_list(LIST);
int is_null(LIST);
void insert_node(position, int);
void delete_node(LIST, position);
position find_last(LIST);
position find_value(LIST, int);
position find_previous(LIST, position);
void print_list(LIST);
/* for testing purpose */
void main()
{
LIST L;
position np; int i;
/* elements to be put into the list */
int a[] = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9}; /* initiate a list */
L = init_list();
print_list(L); /* insert nodes. Insert just after head node */
for (i=4; i>=0; i--) {
insert_node(L, a[i]);
}
print_list(L); /* delete first node with value 5 */
np = find_value(L, 5);
delete_node(L, np);
print_list(L); /* delete list */
delete_list(L); /* initiate a list */
L = init_list();
print_list(L); /* insert nodes. Insert just after head node */
for (i=4; i>=0; i--) {
insert_node(L, a[i]);
}
print_list(L); /* delete list */
delete_list(L);
} /*
* Traverse the list and print each element
* 打印表
*/
void print_list(LIST L)
{
position np;
if(is_null(L)) {
printf("Empty List\n\n");
return;
} np = L;
while(np->next != NULL) {
np = np->next;
printf("%p: %d \n", np, np->element);
}
printf("\n"); } /*
* Initialize a linked list. This list has a head node
* head node doesn't store valid element value
* 创建表
*/
LIST init_list(void)
{
LIST L;
L = (position) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
L->next = NULL;
return L;
} /*
* Delete all nodes in a list
* 删除表
*/
void delete_list(LIST L)
{
position np, next; np = L;
do {
next = np->next;
free(np);
np = next;
} while(next != NULL);
} /*
* if a list only has head node, then the list is null.
* 判断表是否为空
*/
int is_null(LIST L)
{
return ((L->next)==NULL);
} /*
* insert a node after position np
* 在np节点之后,插入节点
*/
void insert_node(position np, int value)
{
position nodeAddr; nodeAddr = (position) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
nodeAddr->element = value;
nodeAddr->next = np->next;
np->next = nodeAddr;
} /*
* delete node at position np
* 删除np节点
*/
void delete_node(LIST L, position np)
{
position previous, next;
next = np->next;
previous = find_previous(L, np);
if(previous != NULL) {
previous->next = next;
free(np);
}
else {
printf("Error: np not in the list");
}
} /*
* find the last node of the list
* 寻找表的最后一个节点
*/
position find_last(LIST L)
{
position np;
np = L;
while(np->next != NULL) {
np = np->next;
}
return np;
} /*
* This function serves for 2 purposes:
* 1. find previous node
* 2. return NULL if the position isn't in the list
* 寻找npTarget节点前面的节点
*/
position find_previous(LIST L, position npTarget)
{
position np;
np = L;
while (np->next != NULL) {
if (np->next == npTarget) return np;
np = np->next;
}
return NULL;
} /*
* find the first node with specific value
* 查询
*/
position find_value(LIST L, int value)
{
position np;
np = L;
while (np->next != NULL) {
np = np->next;
if (np->element == value) return np;
}
return NULL;
}

在main()函数中,我们初始化表,然后插入(1, 3, 5, 7, 9)。又删除元素5。可以看到,节点零散的分布在内存中。删除节点操作不会影响其他节点的存储位置。
我们随后删除表,又重新创建表。可以看到,这次表占据内存的位置与第一次不同。
下面是main()函数的运行结果。
Empty List
0x154d0b0: 1
0x154d090: 3
0x154d070: 5
0x154d050: 7
0x154d030: 9
0x154d0b0: 1
0x154d090: 3
0x154d050: 7
0x154d030: 9
Empty List
0x154d070: 1
0x154d010: 3
0x154d0b0: 5
0x154d090: 7
0x154d050: 9
总结
表: 内存中离散分布的有序节点
插入,删除节点
表(list)的更多相关文章
- In-Memory:在内存中创建临时表和表变量
在Disk-Base数据库中,由于临时表和表变量的数据存储在tempdb中,如果系统频繁地创建和更新临时表和表变量,大量的IO操作集中在tempdb中,tempdb很可能成为系统性能的瓶颈.在SQL ...
- In-Memory:内存优化表的事务处理
内存优化表(Memory-Optimized Table,简称MOT)使用乐观策略(optimistic approach)实现事务的并发控制,在读取MOT时,使用多行版本化(Multi-Row ve ...
- 试试SQLSERVER2014的内存优化表
试试SQLSERVER2014的内存优化表 SQL Server 2014中的内存引擎(代号为Hekaton)将OLTP提升到了新的高度. 现在,存储引擎已整合进当前的数据库管理系统,而使用先进内存技 ...
- SQL Server表分区
什么是表分区 一般情况下,我们建立数据库表时,表数据都存放在一个文件里. 但是如果是分区表的话,表数据就会按照你指定的规则分放到不同的文件里,把一个大的数据文件拆分为多个小文件,还可以把这些小文件放在 ...
- 一起学微软Power BI系列-使用技巧(5)自定义PowerBI时间日期表
1.日期函数表作用 经常使用Excel或者PowerBI,Power Pivot做报表,时间日期是一个重要的纬度,加上做一些钻取,时间日期函数表不可避免.所以今天就给大家分享一个自定义的做日期表的方法 ...
- 分享一个SQLSERVER脚本(计算数据库中各个表的数据量和每行记录所占用空间)
分享一个SQLSERVER脚本(计算数据库中各个表的数据量和每行记录所占用空间) 很多时候我们都需要计算数据库中各个表的数据量和每行记录所占用空间 这里共享一个脚本 CREATE TABLE #tab ...
- ASP.NET Aries 入门开发教程9:业务表单的开发
前言: 经过前面那么多篇的列表的介绍,终于到了大伙期待的表单开发了. 也是本系列的最后一篇文章了! 1:表单页面的权限设置与继承 对于表单页面,权限的设置有两种: 1:你可以选择添加菜单(设置为不显示 ...
- [PHP内核探索]PHP中的哈希表
在PHP内核中,其中一个很重要的数据结构就是HashTable.我们常用的数组,在内核中就是用HashTable来实现.那么,PHP的HashTable是怎么实现的呢?最近在看HashTable的数据 ...
- C语言 · 乘法表
问题描述 输出九九乘法表. 输出格式 输出格式见下面的样例.乘号用"*"表示. 样例输出 下面给出输出的前几行:1*1=12*1=2 2*2=43*1=3 3*2=6 3*3=94 ...
- In-Memory:内存优化表 DMV
在内存优化表的DMV中,有两个对象ID(Object ID): xtp_object_id 是内部的内存优化表(Internal Memory-Optimized Table)的ID,在对象的整个生命 ...
随机推荐
- Linq To Sql 语法 子查询 & In & Join
子查询 描述:查询订单数超过5的顾客信息 查询句法: var 子查询 =from cin ctx.Customers where ...
- 转!!Java 基础面试题的剖析: short s1=1;s1 = s1 +1 报错? s1+=1 呢
short s1=1;s1 = s1 +1会报错吗? package common; public class ShortTypeTest { /* * @param args */ publi ...
- angular-file-upload 中文API
github地址: https://github.com/nervgh/angular-file-upload Directives(指令) nv-file-drop <!-- 最少配置 --& ...
- visual studio 自带单元测试demo
0) 创建类,编写方法类1) 在方法点击鼠标右键,在运行测试(T)和调试测试(D)之间会有一个 <创建单元测试>选项.有则进入2,没有则看1.01.0) 菜单栏 工具-->自定义-- ...
- Ramdisk文件系统无法启动
当kernel是使用ramdisk时,bootm命令有两种使用方式: 1.bootm ${kernel_addr} 此种方式要求bootargs变量包含ramdisk的地址和大小,ramdisk的格式 ...
- java 导入包
导入包 问题:类名冲突时,要如何解决. 解决:sun提供导入包语句让我们解决该问题. 导入包语句的作用:简化书写. 导入包语句的格式:import 包名.类名;(导入xxx包的XX类) 导入包语句的细 ...
- java final
final:(最终的)看不懂时有必要分析内存画图,不同方法的局部变量是相互独立的额不要被所起的名所困扰. 1)每个方法运行时jvm,都会为其开辟一片内存空间.内存空间是属于这个方法的, 同时,方法中的 ...
- 能源项目xml文件 -- app-init.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.sp ...
- [Eclipse] 详细设置护眼背景色和字体颜色并导出
http://jingyan.baidu.com/article/d5a880eb6c4f7813f147ccef.html Eclipse是一款码农们喜闻乐见的集成开发平台,但是其默认的主题和惨白的 ...
- MyBatis实体类映射文件模板
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC " ...
