Java实现Map集合二级联动
Map集合可以保存键值映射关系,这非常适合本实例所需要的数据结构,所有省份信息可以保存为Map集合的键,而每个键可以保存对应的城市信息,本实例就是利用Map集合实现了省市级联选择框,当选择省份信息时,将改变城市下拉选择框对应的内容。
思路分析:
1. 创建全国(省,直辖市,自治区)映射集合,即LinkedHashMap对象,使用Map接口的put()方法向集合中添加指定的省与城市的映射关系,其中值为String型一维数组。
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class CityMap {
/**
* 全国(省,直辖市,自治区)映射集合
*/
public static Map<String,String[]> model=new LinkedHashMap<String, String[]>();
static{
model.put("北京", new String[]{"北京"});
model.put("上海", new String[]{"上海"});
model.put("天津", new String[]{"天津"});
model.put("重庆", new String[]{"重庆"});
model.put("黑龙江", new String[]{"哈尔滨","齐齐哈尔","牡丹江","大庆","伊春","双鸭山","鹤岗","鸡西","佳木斯","七台河","黑河","绥化","大兴安岭"});
model.put("吉林", new String[]{"长春","延边","吉林","白山","白城","四平","松原","辽源","大安","通化"});
model.put("辽宁", new String[]{"沈阳","大连","葫芦岛","旅顺","本溪","抚顺","铁岭","辽阳","营口","阜新","朝阳","锦州","丹东","鞍山"});
model.put("内蒙古", new String[]{"呼和浩特","呼伦贝尔","锡林浩特","包头","赤峰","海拉尔","乌海","鄂尔多斯","通辽"});
model.put("河北", new String[]{"石家庄","唐山","张家口","廊坊","邢台","邯郸","沧州","衡水","承德","保定","秦皇岛"});
model.put("河南", new String[]{"郑州","开封","洛阳","平顶山","焦作","鹤壁","新乡","安阳","濮阳","许昌","漯河","三门峡","南阳","商丘","信阳","周口","驻马店"});
model.put("山东", new String[]{"济南","青岛","淄博","威海","曲阜","临沂","烟台","枣庄","聊城","济宁","菏泽","泰安","日照","东营","德州","滨州","莱芜","潍坊"});
model.put("山西", new String[]{"太原","阳泉","晋城","晋中","临汾","运城","长治","朔州","忻州","大同","吕梁"});
model.put("江苏", new String[]{"南京","苏州","昆山","南通","太仓","吴县","徐州","宜兴","镇江","淮安","常熟","盐城","泰州","无锡","连云港","扬州","常州","宿迁"});
model.put("安徽", new String[]{"合肥","巢湖","蚌埠","安庆","六安","滁州","马鞍山","阜阳","宣城","铜陵","淮北","芜湖","毫州","宿州","淮南","池州"});
model.put("陕西", new String[]{"西安","韩城","安康","汉中","宝鸡","咸阳","榆林","渭南","商洛","铜川","延安"});
model.put("宁夏", new String[]{"银川","固原","中卫","石嘴山","吴忠"});
model.put("甘肃", new String[]{"兰州","白银","庆阳","酒泉","天水","武威","张掖","甘南","临夏","平凉","定西","金昌"});
model.put("青海", new String[]{"西宁","海北","海西","黄南","果洛","玉树","海东","海南"});
model.put("湖北", new String[]{"武汉","宜昌","黄冈","恩施","荆州","神农架","十堰","咸宁","襄樊","孝感","随州","黄石","荆门","鄂州"});
model.put("湖南", new String[]{"长沙","邵阳","常德","郴州","吉首","株洲","娄底","湘潭","益阳","永州","岳阳","衡阳","怀化","韶山","张家界"});
model.put("浙江", new String[]{"杭州","湖州","金华","宁波","丽水","绍兴","雁荡山","衢州","嘉兴","台州","舟山","温州"});
model.put("江西", new String[]{"南昌","萍乡","九江","上饶","抚州","吉安","鹰潭","宜春","新余","景德镇","赣州"});
model.put("福建", new String[]{"福州","厦门","龙岩","南平","宁德","莆田","泉州","三明","漳州"});
model.put("贵州", new String[]{"贵阳","安顺","赤水","遵义","铜仁","六盘水","毕节","凯里","都匀"});
model.put("四川", new String[]{"成都","泸州","内江","凉山","阿坝","巴中","广元","乐山","绵阳","德阳","攀枝花","雅安","宜宾","自贡","甘孜州","达州","资阳","广安","遂宁","眉山","南充"});
model.put("广东", new String[]{"广州","深圳","潮州","韶关","湛江","惠州","清远","东莞","江门","茂名","肇庆","汕尾","河源","揭阳","梅州","中山","德庆","阳江","云浮","珠海","汕头","佛山"});
model.put("广西", new String[]{"南宁","桂林","阳朔","柳州","梧州","玉林","桂平","贺州","钦州","贵港","防城港","百色","北海","河池","来宾","崇左"});
model.put("云南", new String[]{"昆明","保山","楚雄","德宏","红河","临沧","怒江","曲靖","思茅","文山","玉溪","昭通","丽江","大理"});
model.put("海南", new String[]{"海口","三亚","儋州","琼山","通什","文昌"});
model.put("新疆", new String[]{"乌鲁木齐","阿勒泰","阿克苏","昌吉","哈密","和田","喀什","克拉玛依","石河子","塔城","库尔勒","吐鲁番","伊宁"});
}
}
2. 定义获取省份的方法,创建一个Map集合,将上一步得到的映射集合赋值给它,使用Map集合的keySet()方法获取该集合中的所有键对象组成的Set集合,即为省分集合,创建一个Object型一维数组,使用Set接口的toArray()方法将Set集合转换为数组,返回此数组作为省份选择下拉列表的参数。
3. 使用JComboBox类的setModel()方法为省份下拉列表添加省份信息,参数即为上一步中的获取省份方法。
4. 定义根据省份获取市/县的方法,创建一个Map集合,将步骤1中得到的映射集合赋值给它,使用Map集合的get()方法获取指定键的值,即为市/县集合,创建一个String[]型一维数组,将市/县集合赋值给该数组。
5. 定义省份下拉列表的选项状态更改事件,在该事件中通过JComboBox类的getSelectedItem()方法获取选中的省份,默认为省份集合中的第一个值,然后使用JComboBox类的removeAllItems()方法清空市/县列表,根据选中的省份获取市/县数组,最后使用JComboBox的setModel()方法重新添加市/县列表的值。
import java.awt.Graphics;
import java.awt.Image;
import javax.swing.JPanel;
/**
* 带背景的面板组件
*
* @author ZhongWei Lee
*/
public class BackgroundPanel extends JPanel {
/**
*
*/
private static final long serialVersionUID = 7758689434195492602L;
/**
* 背景图片
*/
private Image image;
/**
* 构造方法
*/
public BackgroundPanel() {
super();
setOpaque(false);
setLayout(null);
}
/**
* 设置图片的方法
*/
public void setImage(Image image) {
this.image = image;
}
@Override
protected void paintComponent(Graphics g) {// 重写绘制组件外观
if (image != null) {
int width = getWidth();// 获取组件大小
int height = getHeight();
g.drawImage(image, 0, 0, width, height, this);// 绘制图片与组件大小相同
}
super.paintComponent(g);// 执行超类方法
}
}
import java.awt.Image;
import java.awt.Toolkit;
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import javax.swing.ImageIcon;
/**
* Utility class for managing resources such as colors, fonts, images, etc.
*
* This class may be freely distributed as part of any application or plugin.
* <p>
* Copyright (c) 2003 - 2004, Instantiations, Inc. <br>All Rights Reserved
*
* @author scheglov_ke
*/
public class SwingResourceManager {
/**
* Maps image names to images
*/
private static HashMap<String, Image> m_ClassImageMap = new HashMap<String, Image>();
/**
* Returns an image encoded by the specified input stream
* @param is InputStream The input stream encoding the image data
* @return Image The image encoded by the specified input stream
*/
private static Image getImage(InputStream is) {
try {
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
byte buf[] = new byte[1024 * 4];
while (true) {
int n = is.read(buf);
if (n == -1)
break;
baos.write(buf, 0, n);
}
baos.close();
return Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit().createImage(baos.toByteArray());
} catch (Throwable e) {
return null;
}
}
/**
* Returns an image stored in the file at the specified path relative to the specified class
* @param clazz Class The class relative to which to find the image
* @param path String The path to the image file
* @return Image The image stored in the file at the specified path
*/
public static Image getImage(Class<?> clazz, String path) {
String key = clazz.getName() + '|' + path;
Image image = m_ClassImageMap.get(key);
if (image == null) {
if ((path.length() > 0) && (path.charAt(0) == '/')) {
String newPath = path.substring(1, path.length());
image = getImage(new BufferedInputStream(clazz.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream(newPath)));
} else {
image = getImage(clazz.getResourceAsStream(path));
}
m_ClassImageMap.put(key, image);
}
return image;
}
/**
* Returns an image stored in the file at the specified path
* @param path String The path to the image file
* @return Image The image stored in the file at the specified path
*/
public static Image getImage(String path) {
return getImage("default", path); //$NON-NLS-1$
}
/**
* Returns an image stored in the file at the specified path
* @param section String The storage section in the cache
* @param path String The path to the image file
* @return Image The image stored in the file at the specified path
*/
public static Image getImage(String section, String path) {
String key = section + '|' + SwingResourceManager.class.getName() + '|' + path;
Image image = m_ClassImageMap.get(key);
if (image == null) {
try {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(path);
image = getImage(fis);
m_ClassImageMap.put(key, image);
fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
return null;
}
}
return image;
}
/**
* Clear cached images in specified section
* @param section the section do clear
*/
public static void clearImages(String section) {
for (Iterator<String> I = m_ClassImageMap.keySet().iterator(); I.hasNext();) {
String key = I.next();
if (!key.startsWith(section + '|'))
continue;
Image image = m_ClassImageMap.get(key);
image.flush();
I.remove();
}
}
/**
* Returns an icon stored in the file at the specified path relative to the specified class
* @param clazz Class The class relative to which to find the icon
* @param path String The path to the icon file
* @return Icon The icon stored in the file at the specified path
*/
public static ImageIcon getIcon(Class<?> clazz, String path) {
return getIcon(getImage(clazz, path));
}
/**
* Returns an icon stored in the file at the specified path
* @param path String The path to the icon file
* @return Icon The icon stored in the file at the specified path
*/
public static ImageIcon getIcon(String path) {
return getIcon("default", path); //$NON-NLS-1$
}
/**
* Returns an icon stored in the file at the specified path
* @param section String The storage section in the cache
* @param path String The path to the icon file
* @return Icon The icon stored in the file at the specified path
*/
public static ImageIcon getIcon(String section, String path) {
return getIcon(getImage(section, path));
}
/**
* Returns an icon based on the specified image
* @param image Image The original image
* @return Icon The icon based on the image
*/
public static ImageIcon getIcon(Image image) {
if (image == null)
return null;
return new ImageIcon(image);
}
}
import java.awt.EventQueue;
import java.awt.event.ItemEvent;
import java.awt.event.ItemListener;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
import javax.swing.DefaultComboBoxModel;
import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.JComboBox;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JLabel;
import javax.swing.JPanel;
import javax.swing.JTextField;
import javax.swing.SwingConstants;
import javax.swing.UIManager;
import javax.swing.border.TitledBorder;
public class MainFrame extends JFrame {
/**
*
*/
private static final long serialVersionUID = -4595347311922711984L;
private JTextField textField_3;
private JTextField textField_1;
private JComboBox comboBox_1;
private JTextField textField;
private JComboBox cityComboBox;
private JComboBox comboBox;
/**
* Launch the application
*
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String args[]) {
EventQueue.invokeLater(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
try {
UIManager.setLookAndFeel("com.sun.java.swing.plaf.nimbus.NimbusLookAndFeel");
MainFrame frame = new MainFrame();
frame.setVisible(true);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}
/**
* Create the frame
*/
public MainFrame() {
getContentPane().setLayout(null);
setBounds(100, 100, 518, 379);
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
//获取默认的市/县
String province=(String)getProvince()[0];
setTitle("输入指定省/直辖市查询对应的市县");
final BackgroundPanel backgroundPanel = new BackgroundPanel();
backgroundPanel.setImage(SwingResourceManager.getImage(MainFrame.class, "/images/background.jpg"));
backgroundPanel.setBounds(0, 0, 510, 380);
getContentPane().add(backgroundPanel);
final JPanel panel = new JPanel();
panel.setOpaque(false);
panel.setBounds(36, 126, 438, 70);
backgroundPanel.add(panel);
panel.setLayout(null);
panel.setBorder(new TitledBorder(null, "居住地", TitledBorder.DEFAULT_JUSTIFICATION, TitledBorder.DEFAULT_POSITION, null, null));
cityComboBox = new JComboBox();
cityComboBox.setBounds(245, 25, 124, 27);
panel.add(cityComboBox);
cityComboBox.setModel(new DefaultComboBoxModel(getCity(province)));
comboBox = new JComboBox();
comboBox.setBounds(25, 25, 124, 27);
panel.add(comboBox);
comboBox.addItemListener(new ItemListener() {
public void itemStateChanged(final ItemEvent e) { // 选项状态更改事件
itemChange();
}
});
comboBox.setModel(new DefaultComboBoxModel(getProvince())); // 添加省份信息
final JLabel label = new JLabel();
label.setText("省/直辖市");
label.setBounds(155, 30, 66, 18);
panel.add(label);
final JLabel label_1 = new JLabel();
label_1.setText("市/县");
label_1.setBounds(375, 30, 37, 18);
panel.add(label_1);
final JLabel label_2 = new JLabel();
label_2.setBounds(36, 43, 65, 18);
backgroundPanel.add(label_2);
label_2.setHorizontalAlignment(SwingConstants.RIGHT);
label_2.setHorizontalTextPosition(SwingConstants.LEADING);
label_2.setText("姓 名:");
textField = new JTextField();
textField.setBounds(113, 38, 154, 28);
backgroundPanel.add(textField);
final JLabel label_3 = new JLabel();
label_3.setBounds(36, 84, 65, 18);
backgroundPanel.add(label_3);
label_3.setHorizontalAlignment(SwingConstants.RIGHT);
label_3.setHorizontalTextPosition(SwingConstants.LEADING);
label_3.setText("性 别:");
comboBox_1 = new JComboBox();
comboBox_1.setBounds(113, 81, 66, 25);
backgroundPanel.add(comboBox_1);
comboBox_1.setModel(new DefaultComboBoxModel(new String[] {"男", "女"}));
final JLabel label_4 = new JLabel();
label_4.setBounds(36, 212, 65, 18);
backgroundPanel.add(label_4);
label_4.setHorizontalAlignment(SwingConstants.RIGHT);
label_4.setHorizontalTextPosition(SwingConstants.LEADING);
label_4.setText("详细地址:");
textField_1 = new JTextField();
textField_1.setBounds(113, 208, 367, 28);
backgroundPanel.add(textField_1);
final JLabel label_4_1 = new JLabel();
label_4_1.setBounds(36, 252, 65, 18);
backgroundPanel.add(label_4_1);
label_4_1.setHorizontalTextPosition(SwingConstants.LEADING);
label_4_1.setHorizontalAlignment(SwingConstants.RIGHT);
label_4_1.setText("E-mail:");
textField_3 = new JTextField();
textField_3.setBounds(113, 248, 367, 27);
backgroundPanel.add(textField_3);
final JButton button = new JButton();
button.setBounds(159, 289, 75, 28);
backgroundPanel.add(button);
button.setText("保存");
final JButton button_1 = new JButton();
button_1.setBounds(265, 289, 75, 28);
backgroundPanel.add(button_1);
button_1.setText("重置");
//
}
/**
* 获取省、直辖市,自治区
*
* @return
*/
public Object[] getProvince() {
Map<String, String[]> map = CityMap.model;// 获取省份信息保存到Map中
Set<String> set = map.keySet(); // 获取Map集合中的键,并以Set集合返回
Object[] province = set.toArray(); // 转换为数组
return province; // 返回获取的省份信息
}
/**
* 获取指定省对应的市/县
*
* @param selectProvince
* @return
*/
public String[] getCity(String selectProvince) {
Map<String, String[]> map = CityMap.model; // 获取省份信息保存到Map中
String[] arrCity = map.get(selectProvince); // 获取指定键的值
return arrCity; // 返回获取的市/县
}
private void itemChange() {
String selectProvince = (String) comboBox.getSelectedItem();
cityComboBox.removeAllItems(); // 清空市/县列表
String[] arrCity = getCity(selectProvince); // 获取市/县
cityComboBox.setModel(new DefaultComboBoxModel(arrCity)); // 重新添加市/县列表的值
}
}
效果如图:
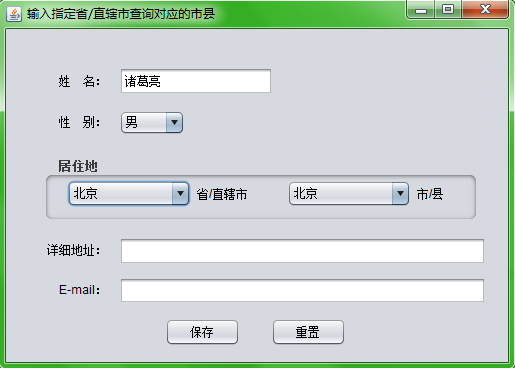
Java实现Map集合二级联动的更多相关文章
- Java基础知识:Java实现Map集合二级联动1
Java实现Map集合二级联动 Map集合可以保存键值映射关系,这非常适合本实例所需要的数据结构,所有省份信息可以保存为Map集合的键,而每个键可以保存对应的城市信息,本实例就是利用Map集合实现了省 ...
- Java基础知识:Java实现Map集合二级联动2
2. 定义获取省份的方法,创建一个Map集合,将上一步得到的映射集合赋值给它,使用Map集合的keySet()方法获取该集合中的所有键对象组成的Set 集合,即为省分集合,创建一个Object型一维数 ...
- Java基础知识:Java实现Map集合二级联动4
comboBox.setModel(new DefaultComboBoxModel(getProvince())); // 添加省份信息 final JLabel label = new JLabe ...
- Java基础知识:Java实现Map集合二级联动3
* Returns an image stored in the file at the specified path * @param path String The path to the ima ...
- java基础-Map集合
java基础-Map集合 作者:尹正杰 版权声明:原创作品,谢绝转载!否则将追究法律责任. 一.Map集合概述 我们通过查看Map接口描述,发现Map接口下的集合与Collection接口下的集合,它 ...
- java map实现二级联动查询(省市区下拉列表查询)
1.Map集合可以保存键值映射关系,这非常适合本实例所需要的数据结构,所有省份信息可以保存为Map集合的键,而每个键可以保存对应的城市信息,本实例就是利用Map集合实现了省市级联选择框,当选择省份信息 ...
- java中map集合的迭代
import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.Map; public class TestMap { pu ...
- java中Map集合的理解
Map |--Hashtable:底层是哈希表数据结构,不可以存入null键null值.该集合是线程同步的.jdk1.0.效率低. |--HashMap:底层是哈希表数据结构,允许使用 null 值和 ...
- java基础——Map集合
Map以键值对的形式存储数据,其中Map.entry,是Map的内部类,它用来描述Map中的键值对.Map是一个接口,HashMap是他的一个实现类 Map中有几个重要的方法: get(Object ...
随机推荐
- 设计模式(6)--Adapter(适配器模式)--结构型
1.模式定义: 适配器模式把一个类的接口变换成客户端所期待的另一种接口,从而使原本因接口不匹配而无法在一起工作的两个类能够在一起工作. 2.模式特点: Adapter模式使原本因接口不匹配(或者不兼 ...
- javascript定义二维数组与添加
你定义的已经就是的了啊.不是很明白你的问的什么.你是说如何向里面填充?双层循环就行了撒:for(var i = 0; i < X; i++){ for(var j = 0; j < Y; ...
- spring boot / cloud (五) 自签SSL证书以及HTTPS
spring boot / cloud (五) 自签SSL证书以及HTTPS 前言 什么是HTTPS? HTTPS(全称:Hyper Text Transfer Protocol over Secur ...
- 7_linux下PHP、Apache、Mysql服务的安装
1.首先安装之前,要确保你的虚拟机能连上外网. Mysql: 1.yum -y install mysql 连接数据库命令行模式 2.yum install mysql-server 安装mys ...
- ionic实战系列(一):ionic的开发环境配置和编译、发布
我的ionic实战系列是基于<<Ionic实战>>[美]Jeremy Wilken著-这本书的读书笔记,有诸多借鉴,不详细的地方请参考书籍本身的内容. 1.1技术栈模型 Ion ...
- python自学1——接口测试
尝试写了一个简单的接口测试,基于Python3.4,主要用到了Python读取excel以及requests库的知识,也算是对这段时间Python基础知识学习的一个巩固吧. 因为还没有学习到Pytho ...
- switch_to 家族
selenium做自动化的过程中,经常会遇到alert.frame和新的window,这是经常是switch_to家族大展拳脚的时候,先看看switch_to家族的成员: alert --返回浏览器的 ...
- python学习总结(面向对象进阶)
-------------------类属性和实例属性关系------------------- 1.类属性和实例属性关系 1.实例属性 实例对象独有的属性 2.类属性 ...
- SVG渐变
前面的话 给SVG元素应用填充和描边,除了使用纯色外,还可以使用渐变.本文将详细介绍SVG渐变 线性渐变 有两种类型的渐变:线性渐变和径向渐变.必须给渐变内容指定一个id属性,否则文档内的其他元素不能 ...
- Redis单机版和集群版的安装和部署
1.单机版的安装 本次使用redis3.0版本.3.0版本主要增加了redis集群功能. 安装的前提条件: 需要安装gcc:yum install gcc-c++ 1.1 安装redis 1.下载re ...
