基于binlog来分析mysql的行记录修改情况(python脚本分析)
1 实现内容
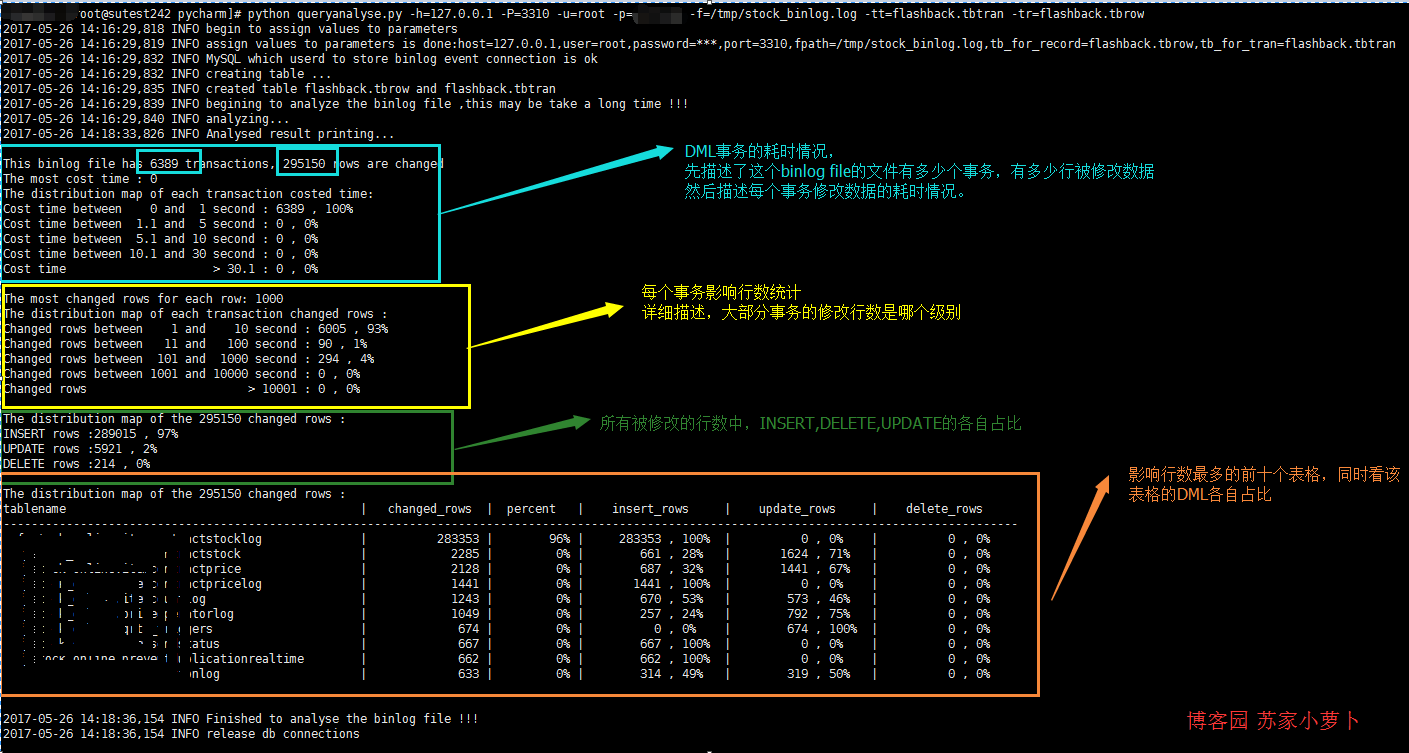
2 脚本简单描述
2.1 _get_db
2.2 create_tab
root@localhost:mysql3310.sock 14:42:29 [flashback]>show create table tbrow \G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
Table: tbrow
Create Table: CREATE TABLE `tbrow` (
`auto_id` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`sqltype` int(11) NOT NULL COMMENT '1 is insert,2 is update,3 is delete',
`tran_num` int(11) NOT NULL COMMENT 'the transaction number',
`dbname` varchar(50) NOT NULL,
`tbname` varchar(50) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`auto_id`),
KEY `sqltype` (`sqltype`),
KEY `dbname` (`dbname`),
KEY `tbname` (`tbname`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=295151 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8
1 row in set (0.00 sec) root@localhost:mysql3310.sock 14:42:31 [flashback]>SHOW CREATE TABLE TBTRAN \G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
Table: TBTRAN
Create Table: CREATE TABLE `tbtran` (
`auto_id` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`begin_time` datetime NOT NULL,
`end_time` datetime NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`auto_id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=6390 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
2.3 rowrecord
- 每个事务的结束点,是以 'Xid = ' 来查找
- 事务的开始时间,是事务内的第一个 'Table_map' 行里边的时间
- 事务的结束时间,是以 'Xid = '所在行的 里边的时间
- 每个行数据是属于哪个表格,是以 'Table_map'来查找
- DML的类型是按照 行记录开头的情况是否为:'### INSERT INTO' 、'### UPDATE' 、'### DELETE FROM'
- 注意,单个事务可以包含多个表格多种DML多行数据修改的情况。
2.4 binlogdesc
- 分析修改行数据的 事务耗时情况
- 分析修改行数据的 事务影响行数情况
- 分析DML分布情况
- 分析 最多DML操作的表格 ,取前十个分析
2.5 closeconn
3 使用说明
4 python脚本
import pymysql
from pymysql.cursors import DictCursor
import re
import os
import sys
import datetime
import time
import logging
import importlib
importlib.reload(logging)
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.DEBUG,format='%(asctime)s %(levelname)s %(message)s ') usage=''' usage: python [script's path] [option]
ALL options need to assign: -h : host, the database host,which database will store the results after analysis
-u : user, the db user
-p : password, the db user's password
-P : port, the db port
-f : file path, the binlog file
-tr : table name for record , the table name to store the row record
-tt : table name for transaction, the table name to store transactions
Example: python queryanalyse.py -h=127.0.0.1 -P=3310 -u=root -p=password -f=/tmp/stock_binlog.log -tt=flashback.tbtran -tr=flashback.tbrow ''' class queryanalyse:
def __init__(self):
#初始化
self.host=''
self.user=''
self.password=''
self.port=''
self.fpath=''
self.tbrow=''
self.tbtran='' self._get_db()
logging.info('assign values to parameters is done:host={},user={},password=***,port={},fpath={},tb_for_record={},tb_for_tran={}'.format(self.host,self.user,self.port,self.fpath,self.tbrow,self.tbtran)) self.mysqlconn = pymysql.connect(host=self.host, user=self.user, password=self.password, port=self.port,charset='utf8')
self.cur = self.mysqlconn.cursor(cursor=DictCursor)
logging.info('MySQL which userd to store binlog event connection is ok') self.begin_time=''
self.end_time=''
self.db_name=''
self.tb_name='' def _get_db(self):
#解析用户输入的选项参数值,这里对password的处理是明文输入,可以自行处理成是input格式,
#由于可以拷贝binlog文件到非线上环境分析,所以password这块,没有特殊处理
logging.info('begin to assign values to parameters')
if len(sys.argv) == 1:
print(usage)
sys.exit(1)
elif sys.argv[1] == '--help':
print(usage)
sys.exit()
elif len(sys.argv) > 2:
for i in sys.argv[1:]:
_argv = i.split('=')
if _argv[0] == '-h':
self.host = _argv[1]
elif _argv[0] == '-u':
self.user = _argv[1]
elif _argv[0] == '-P':
self.port = int(_argv[1])
elif _argv[0] == '-f':
self.fpath = _argv[1]
elif _argv[0] == '-tr':
self.tbrow = _argv[1]
elif _argv[0] == '-tt':
self.tbtran = _argv[1]
elif _argv[0] == '-p':
self.password = _argv[1]
else:
print(usage) def create_tab(self):
#创建两个表格:一个用户存储事务情况,一个用户存储每一行数据修改的情况
#注意,一个事务可以存储多行数据修改的情况
logging.info('creating table ...')
create_tb_sql ='''CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS {} (
`auto_id` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`begin_time` datetime NOT NULL,
`end_time` datetime NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`auto_id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS {} (
`auto_id` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`sqltype` int(11) NOT NULL COMMENT '1 is insert,2 is update,3 is delete',
`tran_num` int(11) NOT NULL COMMENT 'the transaction number',
`dbname` varchar(50) NOT NULL,
`tbname` varchar(50) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`auto_id`),
KEY `sqltype` (`sqltype`),
KEY `dbname` (`dbname`),
KEY `tbname` (`tbname`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
truncate table {};
truncate table {};
'''.format(self.tbtran,self.tbrow,self.tbtran,self.tbrow) self.cur.execute(create_tb_sql)
logging.info('created table {} and {}'.format(self.tbrow,self.tbtran)) def rowrecord(self):
#处理每一行binlog
#事务的结束采用 'Xid =' 来划分
#分析结果,按照一个事务为单位存储提交一次到db
try:
tran_num=1 #事务数
record_sql='' #行记录的insert sql
tran_sql='' #事务的insert sql self.create_tab() with open(self.fpath,'r') as binlog_file:
logging.info('begining to analyze the binlog file ,this may be take a long time !!!')
logging.info('analyzing...') for bline in binlog_file: if bline.find('Table_map:') != -1:
l = bline.index('server')
n = bline.index('Table_map')
begin_time = bline[:l:].rstrip(' ').replace('#', '') if record_sql=='':
self.begin_time = begin_time[0:4] + '-' + begin_time[4:6] + '-' + begin_time[6:] self.db_name = bline[n::].split(' ')[1].replace('`', '').split('.')[0]
self.tb_name = bline[n::].split(' ')[1].replace('`', '').split('.')[1]
bline='' elif bline.startswith('### INSERT INTO'):
record_sql=record_sql+"insert into {}(sqltype,tran_num,dbname,tbname) VALUES (1,{},'{}','{}');".format(self.tbrow,tran_num,self.db_name,self.tb_name) elif bline.startswith('### UPDATE'):
record_sql=record_sql+"insert into {}(sqltype,tran_num,dbname,tbname) VALUES (2,{},'{}','{}');".format(self.tbrow,tran_num,self.db_name,self.tb_name) elif bline.startswith('### DELETE FROM'):
record_sql=record_sql+"insert into {}(sqltype,tran_num,dbname,tbname) VALUES (3,{},'{}','{}');".format(self.tbrow,tran_num,self.db_name,self.tb_name) elif bline.find('Xid =') != -1: l = bline.index('server')
end_time = bline[:l:].rstrip(' ').replace('#', '')
self.end_time = end_time[0:4] + '-' + end_time[4:6] + '-' + end_time[6:]
tran_sql=record_sql+"insert into {}(begin_time,end_time) VALUES ('{}','{}')".format(self.tbtran,self.begin_time,self.end_time) self.cur.execute(tran_sql)
self.mysqlconn.commit()
record_sql = ''
tran_num += 1 except Exception:
return 'funtion rowrecord error' def binlogdesc(self):
sql=''
t_num=0
r_num=0
logging.info('Analysed result printing...\n')
#分析总的事务数跟行修改数量
sql="select 'tbtran' name,count(*) nums from {} union all select 'tbrow' name,count(*) nums from {};".format(self.tbtran,self.tbrow)
self.cur.execute(sql)
rows=self.cur.fetchall()
for row in rows:
if row['name']=='tbtran':
t_num = row['nums']
else:
r_num = row['nums']
print('This binlog file has {} transactions, {} rows are changed '.format(t_num,r_num)) # 计算 最耗时 的单个事务
# 分析每个事务的耗时情况,分为5个时间段来描述
# 这里正常应该是 以毫秒来分析的,但是binlog中,只精确时间到second
sql='''select
count(case when cost_sec between 0 and 1 then 1 end ) cos_1,
count(case when cost_sec between 1.1 and 5 then 1 end ) cos_5,
count(case when cost_sec between 5.1 and 10 then 1 end ) cos_10,
count(case when cost_sec between 10.1 and 30 then 1 end ) cos_30,
count(case when cost_sec >30.1 then 1 end ) cos_more,
max(cost_sec) cos_max
from
(
select
auto_id,timestampdiff(second,begin_time,end_time) cost_sec
from {}
) a;'''.format(self.tbtran)
self.cur.execute(sql)
rows=self.cur.fetchall() for row in rows:
print('The most cost time : {} '.format(row['cos_max']))
print('The distribution map of each transaction costed time: ')
print('Cost time between 0 and 1 second : {} , {}%'.format(row['cos_1'],int(row['cos_1']*100/t_num)))
print('Cost time between 1.1 and 5 second : {} , {}%'.format(row['cos_5'], int(row['cos_5'] * 100 / t_num)))
print('Cost time between 5.1 and 10 second : {} , {}%'.format(row['cos_10'], int(row['cos_10'] * 100 / t_num)))
print('Cost time between 10.1 and 30 second : {} , {}%'.format(row['cos_30'], int(row['cos_30'] * 100 / t_num)))
print('Cost time > 30.1 : {} , {}%\n'.format(row['cos_more'], int(row['cos_more'] * 100 / t_num))) # 计算 单个事务影响行数最多 的行数量
# 分析每个事务 影响行数 情况,分为5个梯度来描述
sql='''select
count(case when nums between 0 and 10 then 1 end ) row_1,
count(case when nums between 11 and 100 then 1 end ) row_2,
count(case when nums between 101 and 1000 then 1 end ) row_3,
count(case when nums between 1001 and 10000 then 1 end ) row_4,
count(case when nums >10001 then 1 end ) row_5,
max(nums) row_max
from
(
select
count(*) nums
from {} group by tran_num
) a;'''.format(self.tbrow)
self.cur.execute(sql)
rows=self.cur.fetchall() for row in rows:
print('The most changed rows for each row: {} '.format(row['row_max']))
print('The distribution map of each transaction changed rows : ')
print('Changed rows between 1 and 10 second : {} , {}%'.format(row['row_1'],int(row['row_1']*100/t_num)))
print('Changed rows between 11 and 100 second : {} , {}%'.format(row['row_2'], int(row['row_2'] * 100 / t_num)))
print('Changed rows between 101 and 1000 second : {} , {}%'.format(row['row_3'], int(row['row_3'] * 100 / t_num)))
print('Changed rows between 1001 and 10000 second : {} , {}%'.format(row['row_4'], int(row['row_4'] * 100 / t_num)))
print('Changed rows > 10001 : {} , {}%\n'.format(row['row_5'], int(row['row_5'] * 100 / t_num))) # 分析 各个行数 DML的类型情况
# 描述 delete,insert,update的分布情况
sql='select sqltype ,count(*) nums from {} group by sqltype ;'.format(self.tbrow)
self.cur.execute(sql)
rows=self.cur.fetchall() print('The distribution map of the {} changed rows : '.format(r_num))
for row in rows: if row['sqltype']==1:
print('INSERT rows :{} , {}% '.format(row['nums'],int(row['nums']*100/r_num)))
if row['sqltype']==2:
print('UPDATE rows :{} , {}% '.format(row['nums'],int(row['nums']*100/r_num)))
if row['sqltype']==3:
print('DELETE rows :{} , {}%\n '.format(row['nums'],int(row['nums']*100/r_num))) # 描述 影响行数 最多的表格
# 可以分析是哪些表格频繁操作,这里显示前10个table name
sql = '''select
dbname,tbname ,
count(*) ALL_rows,
count(*)*100/{} per,
count(case when sqltype=1 then 1 end) INSERT_rows,
count(case when sqltype=2 then 1 end) UPDATE_rows,
count(case when sqltype=3 then 1 end) DELETE_rows
from {}
group by dbname,tbname
order by ALL_rows desc
limit 10;'''.format(r_num,self.tbrow)
self.cur.execute(sql)
rows = self.cur.fetchall() print('The distribution map of the {} changed rows : '.format(r_num))
print('tablename'.ljust(50),
'|','changed_rows'.center(15),
'|','percent'.center(10),
'|','insert_rows'.center(18),
'|','update_rows'.center(18),
'|','delete_rows'.center(18)
)
print('-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------')
for row in rows:
print((row['dbname']+'.'+row['tbname']).ljust(50),
'|',str(row['ALL_rows']).rjust(15),
'|',(str(int(row['per']))+'%').rjust(10),
'|',str(row['INSERT_rows']).rjust(10)+' , '+(str(int(row['INSERT_rows']*100/row['ALL_rows']))+'%').ljust(5),
'|',str(row['UPDATE_rows']).rjust(10)+' , '+(str(int(row['UPDATE_rows']*100/row['ALL_rows']))+'%').ljust(5),
'|',str(row['DELETE_rows']).rjust(10)+' , '+(str(int(row['DELETE_rows']*100/row['ALL_rows']))+'%').ljust(5),
)
print('\n') logging.info('Finished to analyse the binlog file !!!') def closeconn(self):
self.cur.close()
logging.info('release db connections\n') def main():
p = queryanalyse()
p.rowrecord()
p.binlogdesc()
p.closeconn() if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
基于binlog来分析mysql的行记录修改情况(python脚本分析)的更多相关文章
- 基于binlog来分析mysql的行记录修改情况
https://www.cnblogs.com/xinysu/archive/2017/05/26/6908722.html import pymysqlfrom pymysql.cursors im ...
- 使用Anemometer分析MySQL慢查询记录
数据库管理员一般是用percona的toolkit工具来分析MySQL慢查询记录,但是不够直观. 下面介绍一款比较直观的工具来统计分析MySQL慢查询记录anemometer. 在使用之前需要安装pe ...
- 使用Python脚本分析你的网站上的SEO元素
撰稿马尼克斯德芒克 上2019年1月, Sooda internetbureau Python就是自动执行重复性任务,为您的其他搜索引擎优化(SEO)工作留出更多时间.没有多少SEO使用Python来 ...
- mysql之行(记录)的详细操作
在Mysql管理软件中, 可以通过sql语句中的dml语言来实现数据的操作, 包括 使用INSERT实现数据的插入 UPDATE实现数据的更新 使用DELETE实现数据的删除 使用SELECT查询数据 ...
- MySql之行记录的详细操作,创建用户以及库表的授权
一 介绍 MySQL数据操作: DML ======================================================== 在MySQL管理软件中,可以通过SQL语句中的 ...
- 深入浅出分析MySQL MyISAM与INNODB索引原理、优缺点分析
本文浅显的分析了MySQL索引的原理及针对主程面试的一些问题,对各种资料进行了分析总结,分享给大家,希望祝大家早上走上属于自己的"成金之路". 学习知识最好的方式是带着问题去研究所 ...
- python脚本分析nginx访问日志
日志格式如下: 223.74.135.248 [11/May/2017:11:19:47 +0800] "POST /login/getValidateCode HTTP/1.1" ...
- mysql基于binlog回滚工具_flashback(python版本)
update.delete的条件写错甚至没有写,导致数据操作错误,需要恢复被误操作的行记录.这种情形,其实时有发生,可以选择用备份文件+binlog来恢复到测试环境,然后再做数据修复,但是这样 ...
- 百万年薪python之路 -- MySQL数据库之 MySQL行(记录)的操作(一)
MySQL的行(记录)的操作(一) 1. 增(insert) insert into 表名 value((字段1,字段2...); # 只能增加一行记录 insert into 表名 values(字 ...
随机推荐
- swust oj(0088)表达式的转换
表达式的转换(0088) Time limit(ms): 5000 Memory limit(kb): 65535 Submission: 435 Accepted: 93 Accepted 16级卓 ...
- 浩哥解析MyBatis源码(九)——Type类型模块之类型处理器注册器(TypeHandlerRegistry)
原创作品,可以转载,但是请标注出处地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/V1haoge/p/6709157.html 1.回顾 上一篇研究的是类型别名注册器TypeAliasRegist ...
- 如何用unity3d实现发送带附件的邮件
以Gmail为例.点击屏幕的Capture按钮得到当前屏幕截图,点击Send按钮将之前的截图作为附件发送邮件. using UnityEngine; using System.Collections; ...
- Jenkins: 使用groovy + job-dsl 创建并触发job
Jenkins: 使用groovy + job-dsl 创建并触发job 背景: 我们的 Automation 测试脚本需要在10个不同语言的机器上跑,本地化测试产品. 我们用Jenkins启动测试执 ...
- SQL基础函数
首先咱们一起来看一下SQL的基本函数 一.聚合函数 二.数学函数 三.字符串函数 四.转换函数 五.时间函数 这样子看起来可能很多,那咱们给变得---------------------------- ...
- Python-一些实用的函数
一,返回值为bool类型的函数 1.any()函数 any(iterable)->bool 当迭代器中有一个是Ture,则返回Ture:若interable=NUll,则返回False. > ...
- Hive 的简单使用及调优参考文档
Hive 的简单使用及调优参考文档 HIVE的使用 命令行界面 使用一下命令查看hive的命令行页面, hive --help --service cli 简化命令为hive –h 会输出下面的这 ...
- Linux 练习(1)
1) 新建用户natasha,uid为1000,gid为555,备注信息为"master" useradd -u 1000 -g 555 -c 'master' natasha2) ...
- & and &&区别
&:位逻辑运算: &&:逻辑运算: &&在java中又称为短路,第一个条件是false的话后面就不执行: &是所有条件都执行: System.out.p ...
- CVSS3.0打分学习
打分计算器: Common Vulnerability Scoring System Version 3.0 Calculator: https://www.first.org/cvss/calcul ...
