spring加载Bean的解析过程(二)
1.例如:
BeanFactory bf = new XmlBeanFactory(new ClassPathResource("spring.xml"));
User user = (User) bf.getBean("user");
new ClassPathResource("spring.xml") 根据 xml通过不同参数构建Resource,
/**
* Create a new XmlBeanFactory with the given resource,
* which must be parsable using DOM.
* @param resource XML resource to load bean definitions from
* @throws BeansException in case of loading or parsing errors
*/
public XmlBeanFactory(Resource resource) throws BeansException {
this(resource, null);
} /**
* Create a new XmlBeanFactory with the given input stream,
* which must be parsable using DOM.
* @param resource XML resource to load bean definitions from
* @param parentBeanFactory parent bean factory
* @throws BeansException in case of loading or parsing errors
*/
public XmlBeanFactory(Resource resource, BeanFactory parentBeanFactory) throws BeansException {
super(parentBeanFactory);
this.reader.loadBeanDefinitions(resource); //XmlBeanDefinitionReader
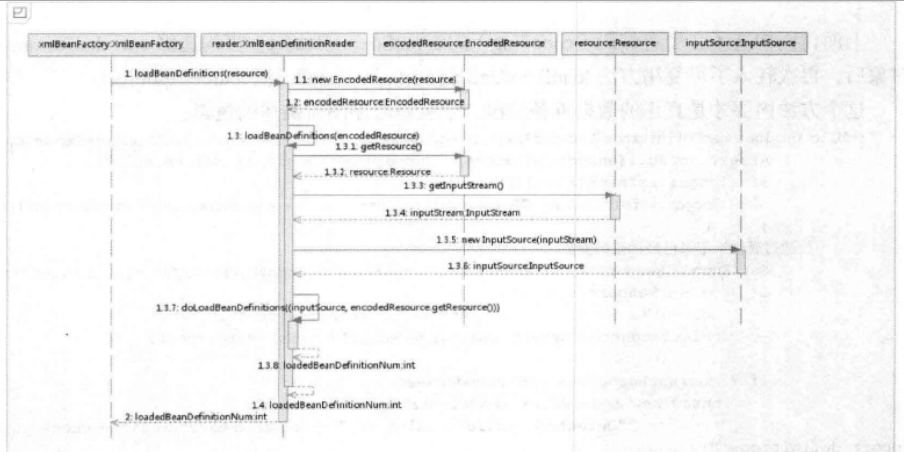
} 2. reader加载Bean public int loadBeanDefinitions(Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
return loadBeanDefinitions(new EncodedResource(resource));
} /**
* Load bean definitions from the specified XML file.
* @param encodedResource the resource descriptor for the XML file,
* allowing to specify an encoding to use for parsing the file
* @return the number of bean definitions found
* @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException in case of loading or parsing errors
*/
public int loadBeanDefinitions(EncodedResource encodedResource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
Assert.notNull(encodedResource, "EncodedResource must not be null");
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Loading XML bean definitions from " + encodedResource.getResource());
} Set<EncodedResource> currentResources = this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.get();
if (currentResources == null) {
currentResources = new HashSet<EncodedResource>(4);
this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.set(currentResources);
}
if (!currentResources.add(encodedResource)) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Detected cyclic loading of " + encodedResource + " - check your import definitions!");
}
try {
InputStream inputStream = encodedResource.getResource().getInputStream();
try {
InputSource inputSource = new InputSource(inputStream);
if (encodedResource.getEncoding() != null) {
inputSource.setEncoding(encodedResource.getEncoding());
}
return doLoadBeanDefinitions(inputSource, encodedResource.getResource()); ...... 3. 根据XML真正加载Bean /**
* Actually load bean definitions from the specified XML file.
* @param inputSource the SAX InputSource to read from
* @param resource the resource descriptor for the XML file
* @return the number of bean definitions found
* @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException in case of loading or parsing errors
*/
protected int doLoadBeanDefinitions(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
try {
int validationMode = getValidationModeForResource(resource);
Document doc = this.documentLoader.loadDocument(
inputSource, getEntityResolver(), this.errorHandler, validationMode, isNamespaceAware());
return registerBeanDefinitions(doc, resource); ..... /**
* Register the bean definitions contained in the given DOM document.
* Called by <code>loadBeanDefinitions</code>.
* <p>Creates a new instance of the parser class and invokes
* <code>registerBeanDefinitions</code> on it.
* @param doc the DOM document
* @param resource the resource descriptor (for context information)
* @return the number of bean definitions found
* @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException in case of parsing errors
* @see #loadBeanDefinitions
* @see #setDocumentReaderClass
* @see BeanDefinitionDocumentReader#registerBeanDefinitions
*/
public int registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
BeanDefinitionDocumentReader documentReader = createBeanDefinitionDocumentReader();
documentReader.setEnvironment(this.getEnvironment());
//记录加载前BeanDefinition的加载个数
int countBefore = getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount();
documentReader.registerBeanDefinitions(doc, createReaderContext(resource));
return getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount() - countBefore;
} protected XmlReaderContext createReaderContext(Resource resource) {
if (this.namespaceHandlerResolver == null) {
this.namespaceHandlerResolver = createDefaultNamespaceHandlerResolver();
}
return new XmlReaderContext(resource, this.problemReporter, this.eventListener,
this.sourceExtractor, this, this.namespaceHandlerResolver);
} /**
* {@inheritDoc}
* <p>This implementation parses bean definitions according to the "spring-beans" XSD
* (or DTD, historically).
* <p>Opens a DOM Document; then initializes the default settings
* specified at the {@code <beans/>} level; then parses the contained bean definitions.
*/
public void registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, XmlReaderContext readerContext) {
this.readerContext = readerContext; logger.debug("Loading bean definitions");
Element root = doc.getDocumentElement(); doRegisterBeanDefinitions(root);
} 4.注册Bean /**
* Register each bean definition within the given root {@code <beans/>} element.
* @throws IllegalStateException if {@code <beans profile="..."} attribute is present
* and Environment property has not been set
* @see #setEnvironment
*/
protected void doRegisterBeanDefinitions(Element root) {
String profileSpec = root.getAttribute(PROFILE_ATTRIBUTE);
if (StringUtils.hasText(profileSpec)) {
Assert.state(this.environment != null, "environment property must not be null");
String[] specifiedProfiles = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(profileSpec, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate.MULTI_VALUE_ATTRIBUTE_DELIMITERS);
if (!this.environment.acceptsProfiles(specifiedProfiles)) {
return;
}
} // any nested <beans> elements will cause recursion in this method. In
// order to propagate and preserve <beans> default-* attributes correctly,
// keep track of the current (parent) delegate, which may be null. Create
// the new (child) delegate with a reference to the parent for fallback purposes,
// then ultimately reset this.delegate back to its original (parent) reference.
// this behavior emulates a stack of delegates without actually necessitating one.
BeanDefinitionParserDelegate parent = this.delegate;
this.delegate = createHelper(readerContext, root, parent); preProcessXml(root);
parseBeanDefinitions(root, this.delegate);
postProcessXml(root); this.delegate = parent;
} /**
* Parse the elements at the root level in the document:
* "import", "alias", "bean".
* @param root the DOM root element of the document
*/
protected void parseBeanDefinitions(Element root, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) {
NodeList nl = root.getChildNodes();
for (int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); i++) {
Node node = nl.item(i);
if (node instanceof Element) {
Element ele = (Element) node;
if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(ele)) {
parseDefaultElement(ele, delegate); //默认标签解析 <bean id="test" class="">
}
else {
delegate.parseCustomElement(ele);//<tx:annotation-driven>
}
}
}
}
else {
delegate.parseCustomElement(root);
}
} /**
* Allow the XML to be extensible by processing any custom element types first,
* before we start to process the bean definitions. This method is a natural
* extension point for any other custom pre-processing of the XML.
* <p>The default implementation is empty. Subclasses can override this method to
* convert custom elements into standard Spring bean definitions, for example.
* Implementors have access to the parser's bean definition reader and the
* underlying XML resource, through the corresponding accessors.
* @see #getReaderContext()
*/
protected void preProcessXml(Element root) {
} /**
* Allow the XML to be extensible by processing any custom element types last,
* after we finished processing the bean definitions. This method is a natural
* extension point for any other custom post-processing of the XML.
* <p>The default implementation is empty. Subclasses can override this method to
* convert custom elements into standard Spring bean definitions, for example.
* Implementors have access to the parser's bean definition reader and the
* underlying XML resource, through the corresponding accessors.
* @see #getReaderContext()
*/
protected void postProcessXml(Element root) {
}
时序图:
下一篇解析默认标签
spring加载Bean的解析过程(二)的更多相关文章
- spring加载bean流程解析
spring作为目前我们开发的基础框架,每天的开发工作基本和他形影不离,作为管理bean的最经典.优秀的框架,它的复杂程度往往令人望而却步.不过作为朝夕相处的框架,我们必须得明白一个问题就是sprin ...
- Dubbo实践(六)Spring加载Bean流程
根据上一小节对于spring扩展schema的介绍,大概可以猜到dubbo中相关的内容是如何实现的. 再来回顾Dubbo实践(一)中定义的dubbo-provider.xml: <?xml ve ...
- spring 加载bean过程源码简易解剖(转载)
这一篇主要是讲用载入bean的过程.其实就是IOC.低调 低调.. 我把重要的都挑出来了.一步步往下看就明白spring载入bean.xml里面bean的原理 . 感觉像候杰的 MFC深入浅出,哈哈. ...
- spring加载bean实例化顺序
问题来源: 有一个bean为 A,一个bean为B.想要A在容器实例化的时候的一个属性name赋值为B的一个方法funB的返回值. 如果只是在A里单纯的写着: private B b;private ...
- spring加载bean报错:expected at least 1 bean which qualifies as autowire candidate. Dependency annotations: {}
看具体报错日志: 警告: Unable to proxy interface-implementing method [public final void cn.wlf.selection.proto ...
- CloudStack采用spring加载bean(cloud-framework-spring-module模块)
CloudStackContextLoaderListener /* * Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one * or ...
- IoC 之加载 Bean:总结
上文中我们将bean已经加载到了IOC容器中,接下来我们将把IOC加载Bean出来进行代码解析 备注:(有些解释是参考别个博客的相关解释 )一起探讨请加我QQ:1051980588 bean 的初始化 ...
- Spring多种加载Bean方式简析
1 定义bean的方式 常见的定义Bean的方式有: 通过xml的方式,例如: <bean id="dictionaryRelMap" class="java.ut ...
- Unity加载模块深度解析(Shader)
作者:张鑫链接:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/21949663来源:知乎著作权归作者所有.商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处. 接上一篇 加载模块深度解析(二 ...
随机推荐
- elasticsearch常见错误及解决方案
1.OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM warning: If the number of processors is expected to increase from one, th ...
- ThinkPHP3.2.3 语言包切换中英文切换
今天要用ThinkPHP3.2.3做一个小网站,其中涉及到切换中文与英文,通过查询手册和百度实现了该操作,现在将我具体的操作步骤记录下来,作为笔记和大家分享. php开发框架:ThinkPHP3.2. ...
- 你有没有乱用“leader”,担当是个好东西
PS:此文为个人认知,不足处请多多批评. 近期在一线leader(经理)身上发现了几个case,然后又回想起前几年自己做的一些傻事,可能都属于明面上leader不会说什么,但私下会有情绪的类型: Ca ...
- hash表/哈希表
https://blog.csdn.net/duan19920101/article/details/51579136 简单理解就是一个通过映射直接查找的表(散列表),用哈希函数将数据按照其存储特点进 ...
- webpack 命令行报错“webpack” 不是内部或外部命令的解决方法
1. NodeJS安装,笔者安装在D盘.安装目录中有两个文件夹node_cache,node_global如下: 2. 配置 npm安装路径,输入如下命令: npm config set prefix ...
- vulnhub-Lampiao脏牛提权
准备工作 在vulnhub官网下载lampiao靶机Lampião: 1 ~ VulnHub 导入到vmware,设置成NAT模式 打开kali准备进行渗透(ip:192.168.200.6) 信息收 ...
- Elgamal加密算法和数字签名
简述:ElGamal公钥密码体制是由 T.ElGamal于 1985年提出的,直到现在仍然是一个安全性能良好的公钥密码体制.该算法既能用于数据加密也能用于数字签名,其安全性依赖于计算有限域上离散对数这 ...
- Nmap的多进程应用与研究
Nmap的多进程应用 使用Nmap进行多目标多端口(强调端口数目较多,比如全端口)扫描时,其在执行时间上的表现并不好.本文旨在分析多目标多端口扫描时的速度瓶颈以及减少时间成本的解决方案. 实验 实验环 ...
- JavaScript学习03(函数)
函数 函数定义 JavaScript 函数是通过 function 关键词定义的. 声明定义 function functionName(parameters) { 要执行的代码 } 被声明的函数不会 ...
- C语言中的stdin,stdout,stderr[转]
我们在写C程序时经常遇到printf(),fprintf(),perror(),这些东西到底有什么作用.说到这不得不提及stdin,stdout,stderr.想想,我们在用C去写文件时的操作,Fil ...