Hystrix工作流
Hystrix工作流程图:
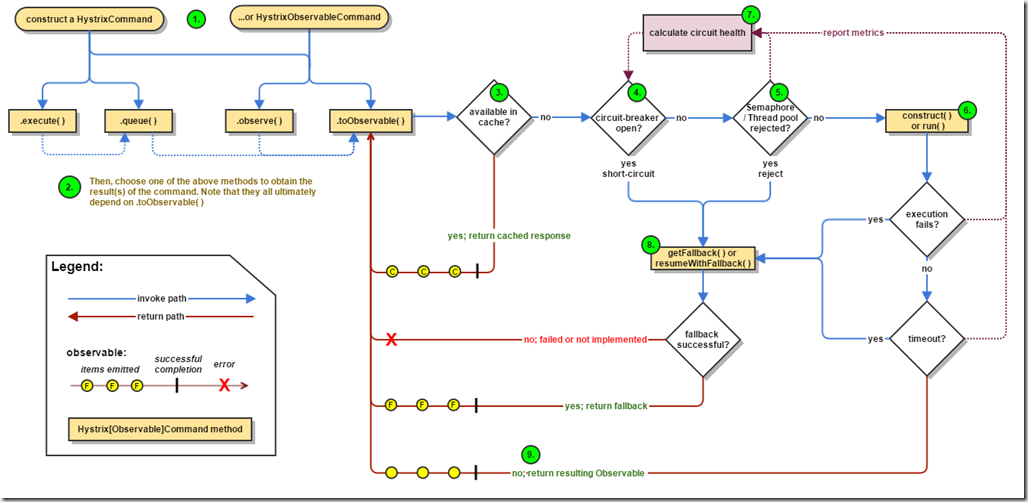
流程图详解
1. 构造HystrixCommand对象或者HystrixObservableCommand对象
构造HystrixCommand 或HystrixObservableCommand对象表示当前流程的依赖,当然,请求中所有需要的参数必须在构造函数中提现,以方便后续使用。
如果希望依赖返回一个结果,那么就构造HystrixCommand对象
HystrixCommand command = new HystrixCommand(arg1, arg2);
如果希望返回依赖的一个观察对象,那么久构造HystrixObservableCommand对象
HystrixObservableCommand command = new HystrixObservableCommand(arg1, arg2);
2. 执行命令
我们可以通过四种方式调起依赖
1) execute()方法,会返回响应结果,如果出现异常,则抛出ERROR。只可以执行HystrixCommand对象
2) queue()方法,会返回Future对象,你可以从中获取响应信息。只可以执行HystrixCommand对象。当我们查看execute源码的时候,不难发现它实际就是调用queue().get()方法
//@see com.netflix.hystrix.HystrixCommand.execute()
public R execute() {
try {
return queue().get();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw Exceptions.sneakyThrow(decomposeException(e));
}
}
当然,在某些业务场景下我们还是需要执行queue方法的,它提供有更丰富的方法供我们调用,而不只是返回处理结果:
//取消命令执行
boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning);
//检查命令是否被取消
boolean isCancelled();
//检查依赖是否完成
boolean isDone();
//获取依赖执行结果
V get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException;
//获取依赖执行结果,如果超过获取时间限制,则抛出TimeoutException异常
V get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException;
而queue()方法中实际调用的是toObservable().toBlocking().toFuture()方法
//@see com.netflix.hystrix.HystrixCommand.queue()
public Future<R> queue() {
/*
* The Future returned by Observable.toBlocking().toFuture() does not implement the
* interruption of the execution thread when the "mayInterrupt" flag of Future.cancel(boolean) is set to true;
* thus, to comply with the contract of Future, we must wrap around it.
*/
final Future<R> delegate = toObservable().toBlocking().toFuture();
………
return f;
}
3) observe()订阅依赖的执行结果,当然我们也可以通过此方式执行依赖
Observable<String> fWorld = new CommandHelloWorld("World").observe();
Observable<String> fBob = new CommandHelloWorld("Bob").observe();
// blocking
assertEquals("Hello World!", fWorld.toBlocking().single());
assertEquals("Hello Bob!", fBob.toBlocking().single());
而在observe()内部又调用的是toObservable()方法
//@see com.netflix.hystrix.AbstractCommand.observe()
public Observable<R> observe() {
// us a ReplaySubject to buffer the eagerly subscribed-to Observable
ReplaySubject<R> subject = ReplaySubject.create();
// eagerly kick off subscription
final Subscription sourceSubscription = toObservable().subscribe(subject);
// return the subject that can be subscribed to later while the execution has already started
return subject.doOnUnsubscribe(new Action0() {
@Override
public void call() {
sourceSubscription.unsubscribe();
}
});
}
4) toObservable() 返回你订阅依赖的Observable对象
用法:
K value = command.execute();
Future<K> fValue = command.queue();
Observable<K> ohValue = command.observe(); //hot observable
Observable<K> ocValue = command.toObservable(); //cold observable
说明:
同步调用execute()方法,实际是调用queue().get(),而queue()方法中实际调用的是toObservable().toBlocking().toFuture()。也就是说所有的HystrixCommand都绑定了Observable对象,即使这个命令只是获取一个简单值。
3. 执行结果是否缓存
接下来会检查当前命令是否支持缓存,如果支持缓存,就会检查当前请求是否之前已经执行过,执行了,就直接从换从中获取结果。不支持缓存,则继续后续流程处理。
具体流程如下:
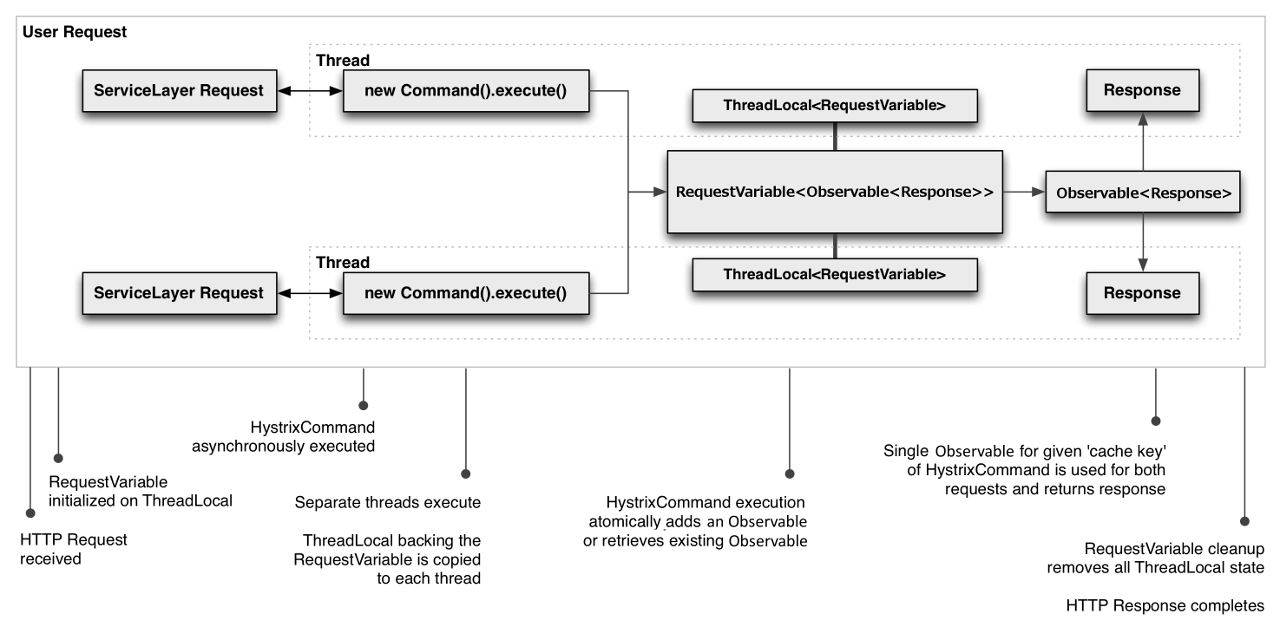
4. 熔断检查
当你执行依赖的时候,Hystrix会检查熔断器,判定当前流程是否通畅。
如果达到熔断条件,则不执行依赖,直接跳到第八步,执行FallBack方法。
如果未达到熔断条件,则继续向后执行。
5. 检查线程池、队列、阈值是否达到上限
如果线程池或者队列已经满了,那么就直接跳到第八步。
6. 执行HystrixObservableCommand的构造函数或者执行HystrixCommand的run方法
通过执行HystrixCommand.run()和HystrixObservableCommand.constract()执行依赖的方法。
如果run方法执行时间超时,那么当前线程就会抛出TimeoutException(如果要执行的依赖进程未启动或被占用,就会启动一个单独的Timer线程)。然后Hystrix就直接路由到第八步,执行Fallback,并且丢弃依赖的run()和constract()方法(如果依赖进程未被取消、中断),我使用1.5.13版本进行测试时,发现如果依赖进程未未执行超时,那么Timer进程就会将依赖进程杀死,然后执行Fallback方法。
注意:没有什么途径终止依赖进程的run方法,只有Hystrix抛出InterruptedException来终止。如果容器不理会Hystrix抛出的异常,那么依赖进程会继续执行,尽管客户端收到了TimeoutException。这种情况有可能导致Hystrix线程池沾满。大多数HTTP Client包不支持InterruptedException,所以,要确保HTTPclient中的read/write超时时间设定正确。
7. 检查回路是否正常
Hystrix reports successes, failures, rejections, and timeouts to the circuit breaker, which maintains a rolling set of counters that calculate statistics.
It uses these stats to determine when the circuit should “trip,” at which point it short-circuits any subsequent requests until a recovery period elapses, upon which it closes the circuit again after first checking certain health checks.
8. 获取Fallback数据
Hystrix tried to revert to your fallback whenever a command execution fails: when an exception is thrown by construct() or run() (6.), when the command is short-circuited because the circuit is open (4.), when the command’s thread pool and queue or semaphore are at capacity (5.), or when the command has exceeded its timeout length.
Write your fallback to provide a generic response, without any network dependency, from an in-memory cache or by means of other static logic. If you must use a network call in the fallback, you should do so by means of another HystrixCommand or HystrixObservableCommand.
In the case of a HystrixCommand, to provide fallback logic you implement HystrixCommand.getFallback() which returns a single fallback value.
In the case of a HystrixObservableCommand, to provide fallback logic you implement HystrixObservableCommand.resumeWithFallback() which returns an Observable that may emit a fallback value or values.
If the fallback method returns a response then Hystrix will return this response to the caller. In the case of a HystrixCommand.getFallback(), it will return an Observable that emits the value returned from the method. In the case of HystrixObservableCommand.resumeWithFallback() it will return the same Observable returned from the method.
If you have not implemented a fallback method for your Hystrix command, or if the fallback itself throws an exception, Hystrix still returns an Observable, but one that emits nothing and immediately terminates with an onError notification. It is through this onError notification that the exception that caused the command to fail is transmitted back to the caller. (It is a poor practice to implement a fallback implementation that can fail. You should implement your fallback such that it is not performing any logic that could fail.)
The result of a failed or nonexistent fallback will differ depending on how you invoked the Hystrix command:
execute()— throws an exceptionqueue()— successfully returns aFuture, but thisFuturewill throw an exception if itsget()method is calledobserve()— returns anObservablethat, when you subscribe to it, will immediately terminate by calling the subscriber’sonErrormethodtoObservable()— returns anObservablethat, when you subscribe to it, will terminate by calling the subscriber’sonErrormethod
9. 返回处理成功的响应信息
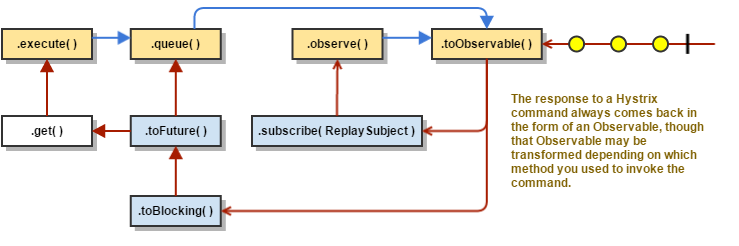
Hystrix工作流的更多相关文章
- Hystrix原理与实战
Hystrix原理与实战 背景 分布式系统环境下,服务间类似依赖非常常见,一个业务调用通常依赖多个基础服务. 比如:订单服务调用商品服务,商品服务调用库存服务. 对于同步调用,当库存服务不可用时,商品 ...
- SpringCloud(四)之Netflix开源组件断路器Hystrix介绍
一.前言? 1.Netflix Hystrix断路器是什么? Netflix Hystrix是SOA/微服务架构中提供服务隔离.熔断.降级机制的工具/框架.Netflix Hystrix是断路器的一种 ...
- 一文带大家彻底搞懂Hystrix!
前言? Netflix Hystrix断路器是什么? Netflix Hystrix是SOA/微服务架构中提供服务隔离.熔断.降级机制的工具/框架.Netflix Hystrix是断路器的一种实现,用 ...
- 一文彻底搞定Hystrix!
前言 Netflix Hystrix断路器是什么? Netflix Hystrix是SOA/微服务架构中提供服务隔离.熔断.降级机制的工具/框架.Netflix Hystrix是断路器的一种实现,用于 ...
- springcloud 微服务分布式 框架源码 activiti工作流 前后分离
1.代码生成器: [正反双向](单表.主表.明细表.树形表,快速开发利器)freemaker模版技术 ,0个代码不用写,生成完整的一个模块,带页面.建表sql脚本.处理类.service等完整模块2. ...
- 微服务分布式 spring cloud springboot 框架源码 activiti工作流 前后分离
1.代码生成器: [正反双向](单表.主表.明细表.树形表,快速开发利器)freemaker模版技术 ,0个代码不用写,生成完整的一个模块,带页面.建表sql脚本.处理类.service等完整模块2. ...
- springcloud vue.js 微服务分布式 前后分离 集成代码生成器 shiro权限 activiti工作流
1.代码生成器: [正反双向](单表.主表.明细表.树形表,快速开发利器)freemaker模版技术 ,0个代码不用写,生成完整的一个模块,带页面.建表sql脚本.处理类.service等完整模块2. ...
- springcloud Springboot vue.js Activiti6 前后分离 跨域 工作流 集成代码生成器 shiro权限
1.代码生成器: [正反双向](单表.主表.明细表.树形表,快速开发利器)freemaker模版技术 ,0个代码不用写,生成完整的一个模块,带页面.建表sql脚本.处理类.service等完整模块2. ...
- springcloud 微服务 分布式 Activiti6 工作流 vue.js html 跨域 前后分离
1.代码生成器: [正反双向](单表.主表.明细表.树形表,快速开发利器)freemaker模版技术 ,0个代码不用写,生成完整的一个模块,带页面.建表sql脚本.处理类.service等完整模块2. ...
随机推荐
- GO基础之函数的高级用法
一.可变参数 支持可变长参数列表的函数可以支持任意个传入参数,比如fmt.Println函数就是一个支持可变长参数列表的函数. package main import "fmt" ...
- PHP fnmatch 文件系统函数
定义和用法 fnmatch - 用模式匹配文件名 目前该函数无法在 Windows 或其它非 POSIX 兼容的系统上使用. 版本支持 PHP4 PHP5 PHP7 4.3.0(含)+支持 支持 支持 ...
- RabbitMQ的第一次亲密接触
企业应用系统,如果系统之间的通信.集成与整合,尤其当面临异构系统时,那么需要分布式的调用与通信.系统中一般会有很多对实时性要求不高但零零碎碎且耗时的地方,比如发送短信,邮件提醒,记录用户操作日志等,在 ...
- 个人项目开源之c++基于epoll实现高并发游戏盒子(服务端+客户端)源代码
正在陆续开源自己的一些项目 此为c++实现高并发的游戏盒子,平台问题需要迁移重构,所以有一些遗留问题,客户端异常断开没有处理,会导致服务器崩溃,还有基于快写代码编程平台实现的小程序切换,线程读写缓存没 ...
- SQL Server关于AlwaysOn的理解
(一)SQL Server-AlwaysOn 技术:SQL Server AlwaysOn 即“全面的高可用性和灾难恢复解决方案” 1.数据库级可用性-只读副本:SQL Server 2012-4个, ...
- java8-06-四大函数式接口
在使用lamdba表达式需要函数式接口的支持 java8已经提供了很多函数式接口 在java.util.function包下
- 8. Vue - Router
一.Vue Router 的使用 JavaScript: 1.创建组件:创建单页面应用需要渲染的组件 2.创建路由:创建VueRouter实例 3.映射路由:调用VueRouter实例的map方法 4 ...
- 数据库访问接口(ODBC,OLEDB,ADO)
数据库访问接口发展历史 ODBC历史 ODBC(Open Database Connectivity,开放数据库互连).要了解ODBC是什么,先了解一下数据库连接的相关知识.在最开始连接数据库时,由于 ...
- Codeforces Round #603 (Div. 2) E. Editor 线段树
E. Editor The development of a text editor is a hard problem. You need to implement an extra module ...
- Unity BehaviorDesigner行为树基础总结
BehaviorDesigner——行为树,用于控制和实现AI逻辑,类似于这样: 上面这个行为树实现了这样的逻辑: 当Player有Input时按照Input值来移动,无Input时查找最近的可攻击目 ...
