[转载]Cool, Tomcat is able to handle more than 13,000 concurrent connections
Last time I have promised you to take a look at more real life scenario regarding threads. In the last blog entry I have shown that on modern operating system and JVM it's not a problem to create 32,000 threads. Now I want to test how many threads can be handled by a Tomcat instance.
I just want to remind you the motivation. Some people believe that threads are expensive, that we should not create lot of them. They believe that it's better to use different mechanisms like asynchronous servlets, specialized libraries etc. I just want to find out if we really need such measures or if good old threads are good enough.
If you read articles about asynchronous servlets, you find out that the main motivation is AJAX. Mainly the scenario, when a HTTP connection is open for a long time and the data are sent when an event occurs.
OK, let's simulate it. We need to simulate lot of open HTTP connections waiting for an event. The easiest way to achieve it is my precious suicidal servlet.
- public class ThreadsServlet extends HttpServlet {
- private static final long serialVersionUID = 7770323867448369047L;
- @Override
- protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
- int number = Integer.valueOf(req.getParameter("number"));
- try {
- System.out.println("Servlet no. "+number+" called.");
- URL url = new URL(req.getScheme()+"://"+req.getServerName()+":"+req.getServerPort()+req.getRequestURI()+"?number="+(number+1));
- Object content = url.getContent();
- resp.setContentType("plain/text");
- resp.getWriter().write("OK: "+content);
- } catch (Throwable e) {
- String message = "Reached "+number+" of connections";
- System.out.println(message);
- System.out.println(e);
- resp.getWriter().write(message);
- }
- }
- }
The servlet is quite simple, it just opens HTTP connection to itself. So it basically tries to create infinite number of connections. Top keep track of the progress, there is a request parameter “number” that is incremented with each call. We can thus observe how many active connections we have.
Default configuration
Let's run it. Just open “http://localhost:8080/threads/something?number=1” in your browser and see what happens.
Not much, in console (or logs/catalina.out) you can see
...
Servlet no. 37 called.
Servlet no. 38 called.
Servlet no. 39 called.
Servlet no. 40 called.
What? Only 40 concurrent threads served? That's not much. Let's try better.
Connector configuration
We can reconfigure Tomcat connector to be able to serve more connections (server.xml)
- <Connector port="8080" protocol="HTTP/1.1"
- connectionTimeout="20000"
- redirectPort="8443"
- maxThreads="32000"/>
As we know from the last time, 32K is the OS limit, we can't go over that. If we execute the test, the results are slightly better:
Servlet no. 485 called.
Servlet no. 486 called.
Servlet no. 487 called.
Servlet no. 488 called.
Servlet no. 489 called.
Servlet no. 490 called.
May 1, 2010 5:55:32 PM org.apache.tomcat.util.net.JIoEndpoint$Acceptor run
SEVERE: Socket accept failed
java.net.SocketException: Too many open files
at java.net.PlainSocketImpl.socketAccept(Native Method)
at java.net.AbstractPlainSocketImpl.accept(AbstractPlainSocketImpl.java:358)
at java.net.ServerSocket.implAccept(ServerSocket.java:470)
at java.net.ServerSocket.accept(ServerSocket.java:438)
at org.apache.tomcat.util.net.DefaultServerSocketFactory.acceptSocket(DefaultServerSocketFactory.java:61)
at org.apache.tomcat.util.net.JIoEndpoint$Acceptor.run(JIoEndpoint.java:310)
at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:636)
Wow, it looks like, that there is some limit on open files. Since I am not Linux guru, the first thing I have tried was to change Tomcat connector to nonblocking.
Nonblocking Connector
To use nonblocking connector, you have to set the protocol in server.xml
- <Connector port="8080"
- connectionTimeout="20000"
- redirectPort="8443"
- protocol="org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11NioProtocol"
- maxThreads="32000"/>
Unfortunately the result is almost the same:
Servlet no. 483 called.
Servlet no. 484 called.
Servlet no. 485 called.
Servlet no. 486 called.
May 1, 2010 5:59:24 PM org.apache.tomcat.util.net.NioEndpoint$Acceptor run
SEVERE: Socket accept failed
java.io.IOException: Too many open files
at sun.nio.ch.ServerSocketChannelImpl.accept0(Native Method)
at sun.nio.ch.ServerSocketChannelImpl.accept(ServerSocketChannelImpl.java:163)
at org.apache.tomcat.util.net.NioEndpoint$Acceptor.run(NioEndpoint.java:1198)
at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:636)
Increase Open File Limit
Apparently, the blocking connector was not the issue. After some time spent with Google I have found the answer. Linux is limiting number of open connections. You can execute “ulimit -n” to see what's your limit. Luckily, it's possible to change the limit. You can either set it by “ulimit -n 32768” if you have permissions or by adding following lines to /etc/security/limits.conf (lukas is my username)
lukas hard nofile 32768
lukas soft nofile 32768
To apply this change you have to logout and login. After that, you will see this:
Servlet no. 5856 called.
Servlet no. 5857 called.
Servlet no. 5858 called.
Servlet no. 5859 called.
May 1, 2010 6:07:58 PM org.apache.tomcat.util.net.NioEndpoint$SocketProcessor run
SEVERE:
java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: GC overhead limit exceeded
at java.util.Arrays.copyOf(Arrays.java:2894)
at java.lang.AbstractStringBuilder.expandCapacity(AbstractStringBuilder.java:117)
at java.lang.AbstractStringBuilder.append(AbstractStringBuilder.java:407)
at java.lang.StringBuilder.append(StringBuilder.java:136)
at java.lang.StringBuilder.append(StringBuilder.java:132)
at java.lang.Throwable.printStackTrace(Throwable.java:529)
at java.util.logging.SimpleFormatter.format(SimpleFormatter.java:94)
at java.util.logging.StreamHandler.publish(StreamHandler.java:196)
at java.util.logging.ConsoleHandler.publish(ConsoleHandler.java:105)
at java.util.logging.Logger.log(Logger.java:476)
at java.util.logging.Logger.doLog(Logger.java:498)
at java.util.logging.Logger.logp(Logger.java:698)
at org.apache.juli.logging.DirectJDKLog.log(DirectJDKLog.java:167)
at org.apache.juli.logging.DirectJDKLog.error(DirectJDKLog.java:135)
at org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11NioProtocol$Http11ConnectionHandler.process(Http11NioProtocol.java:755)
at org.apache.tomcat.util.net.NioEndpoint$SocketProcessor.run(NioEndpoint.java:2080)
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.runWorker(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:1110)
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor$Worker.run(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:603)
at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:636)
We have reached 5856 threads before we run out of memory. Cool.
Increase Heap Size
Let's try to increase the heap size. Just add “-Xmx2048m” to JAVA_OPTS. Before I have started running out of heap, I got to cca 11000 threads! Is it enough? I do not know, but I think it's pretty good.
Moreover, if you do a heap dump, you will see, that most of the memory is consumed by char and byte arrays. (This heap dump has been taken with approximately 5000 connections, screenshot from VisualVM)
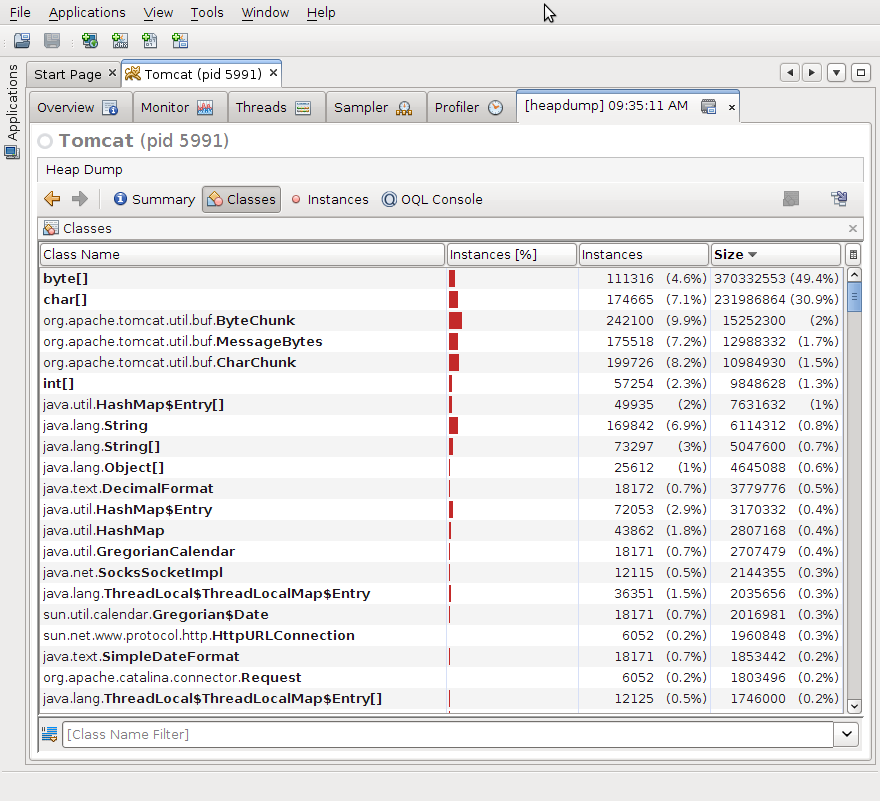
It's understandable, we have lot of open buffers on both sides. I assume that we have at least four buffers per servlet. One for sevlet request, one for servlet response, one for URL request and one for URL response. But maybe there will be other buffers as well. To be honest, I have to admit that memory consumed by stacks would not appear here, it's probably handled by OS. But we have run out of the heap, so that's why I am talking about it.
Smaller buffers
We can try to make some of the buffers smaller. I was able to find only one setting that had some effect. Again it is connector setting in server.xml config file.
- <Connector port="8080"
- connectionTimeout="200000"
- redirectPort="8443"
- protocol="org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11NioProtocol"
- maxThreads="32000"
- socket.appReadBufSize="1024"
- socket.appWriteBufSize="1024"
- bufferSize="1024"/>
With this setting, I was able to get near to 13000 open connections.
...
Servlet no. 13327 called.
Servlet no. 13328 called.
Servlet no. 13329 called.
Servlet no. 13330 called.
Servlet no. 13331 called.
Servlet no. 13332 called.
After that the machine started to run out of physical memory, GC took ages so I had to stop the server. (Just to remind you, my test machine is two year old laptop with Intel Core 2 Duo T8100 2.1GHz with 4GB of RAM. There is 64bit Linux 2.6.32 and OpenJDK (IcedTea6 1.8) running on top of it.)
As we have seen, threads are not the major issue on modern machines. There is probably significant amout of memory consumed by the stack traces too, but I think the biggest problem are the buffers. And the important point is, that we would need the buffers even if we used asynchronous servlets! Of course, there is still some overhead connected with threads, so asynchronous libraries have their place. In fact, it would be nice to try similar experiment with asynchronous servlets. I am afraid, that I will not be able to do it, but I will be glad to help if there is some volunteer.
Please also note that your numbers may vary. After all this has been quite artificial test. I think it's simulates lot of real-life use cases, but you know, the reality is always different.
On the other hand, with more physical memory and better Tomcat configuration, we might got to higher numbers. I have heard legends about 16K threads.
I think that I will finish with my favorite message. Do not use complicated constructs unless you are sure you need them. Please remember golden rules of optimization:
The First Rule of Program Optimization: Don't do it.
The Second Rule of Program Optimization (for experts only!): Don't do it yet.
If you want to verify my results, the source code is here. If you have some comments, different results or advices, do not hesitate to add a comment.
Resources:
Tomcat connector config
Why we need asynchronous servlets
Note: If you wonder why the hell I have started to write in
something that looks almost like English when apparently I do even more
mistakes than in Czech, the answer is simple. I just need to practice my
English (apart from that I want to be world famous, not just known in
Czech Republic)
[转载]Cool, Tomcat is able to handle more than 13,000 concurrent connections的更多相关文章
- Using the FutureRequestExecutionService Based on classic (blocking) I/O handle a great number of concurrent connections is more important than performance in terms of a raw data throughput
Chapter 7. Advanced topics http://hc.apache.org/httpcomponents-client-ga/tutorial/html/advanced.html ...
- handle exceptions, opening and closing database connections
https://www.tutorialspoint.com/spring/spring_jdbc_framework.htm Spring - JDBC Framework Overview Whi ...
- Could not create cudnn handle: CUDNN_STATUS_INTERNAL_ERROR tensorflow-1.13.1和1.14windows版本目前不支持CUDA10.0
报错出现 Could not create cudnn handle: CUDNN_STATUS_INTERNAL_ERROR tensorflow-1.13.1和1.14windows版本目前不支持 ...
- 【转载】Tomcat崩溃事件
转载地址:http://www.blogjava.net/tedeyang/archive/2008/06/04/205740.html Tomcat崩溃事件 今天一大早产品一部项目经理就来找我,他们 ...
- 转载:Tomcat多数据源配置方法
转载网址:http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_53803b7b010144u5.html 关于在TOMCAT下配置多数据源,网上有很多方式,但是感觉也很混乱,俺只说俺们使用的 ...
- [转载]启动tomcat时,一直卡在Deploying web application directory这块的解决方案
转载:https://www.cnblogs.com/mycifeng/p/6972446.html 本来今天正常往服务器上扔一个tomcat 部署一个项目的, 最后再启动tomcat 的时候 发现项 ...
- 【转载】tomcat部署web项目的3中方法
转载自:http://blog.csdn.net/wjx85840948/article/details/6749964/ 1.直接把项目复制到Tomcat安装目录的webapps目录中,这是最简单的 ...
- (转载)Tomcat 7集群浅析
本文转载自:http://blog.csdn.net/wangyangzhizhou. 如有侵权,请联系处理! 简介 每个节点都要维护一份集群节点信息列表,集群组通知的默认实现是在使用 UDP 数 ...
- 【转载】tomcat+nginx+redis实现均衡负载、session共享(一)
http://www.cnblogs.com/zhrxidian/p/5432886.html 在项目运营时,我们都会遇到一个问题,项目需要更新时,我们可能需先暂时关闭下服务器来更新.但这可能会出现一 ...
随机推荐
- Android的相关事件
Android的相关事件 1.Toast信息提醒 import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity; import android.os.Bundle; ...
- Vue使用过渡类名实现动画和自定义前缀
Vue使用过渡类名实现动画和自定义前缀 1.效果演示 2.相关代码 <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> ...
- python中使用eval() 和 ast.literal_eval()的区别 分类: Python 2015-05-11 15:21 1216人阅读 评论(0) 收藏
eval函数在python中做数据类型的转换还是很有用的.它的作用就是把数据还原成它本身或者是能够转化成的数据类型. 那么eval和ast.literal_val()的区别是什么呢? eval在做计算 ...
- IntelliJ IDEA使用心得之非Maven项目篇
今天和大家分享下非Maven项目在IDEA中的配置方法,由于非Maven项目的配置方法基本相同,所以此篇只对不同点进行说明. 1.声明依赖库 我们可以使用库的方式来添加项目依赖,这是一个非常好的实践. ...
- jenkins 踩坑路 之 jenkins ssh 脚本
背景: 由于公司业务调整,整个业务要从阿里云迁移到aws,自然 jenkins 也是要进行迁移的.jenkins 迁移过程中遇到的问题在此记录下,希望能给遇到类似问题的朋友些许帮助.也便于我后期遇到此 ...
- Go RabbitMQ (一)
RabbitMQ 简介 RabbitMQ是一个消息代理,用来负责接收和转发消息. 术语 生产者:生产者是负责发送消息的 队列:队列是RabbitMQ用来存储消息的,受主机内存和磁盘大小的限制,本质上是 ...
- linux 查找删除找定文件
find . -name "*.lastUpdated" -exec rm -rf {} \; 这个命令是find的基本用法,可以分两部分,find ~/ -name " ...
- Django请求响应对象
请求与响应对象 HttpRequest HttpRequest存储了客户请求的相关参数和一些查询方法. path 请求页面的全路径,不包括域名-例如, "/hello/". met ...
- Xshell基础入门
启动 双击快捷方式,启动 新建回话 建立连接 在这里需要填写的是: 1. 连接名称 2. 服务器IP 3. 服务器端口(默认22) 填写完毕后,点击确定,保存配置,回到连接页面,可以看到多了一个测试服 ...
- Xshell 6 免费版本安装过程
下载 官网下载:https://www.netsarang.com/ 点击download 注册 填写下方红色方框标注的注册信息,注册类型填写“home or school use”,名字,邮箱.最后 ...
