(转)pathlib路径库使用详解
原文:https://xin053.github.io/2016/07/03/pathlib%E8%B7%AF%E5%BE%84%E5%BA%93%E4%BD%BF%E7%94%A8%E8%AF%A6%E8%A7%A3/
pathlib简介
pathlib库在python 3.4以后已经成为标准库,基本上可以代替os.path来处理路径。它采用完全面对对象的编程方式。
总共有6个类用来处理路径,大体可以分为两类:
- pure paths 单纯的路径计算操作而没有IO功能
- concrete paths 路经计算操作和IO功能
这6个类的继承关系如下:
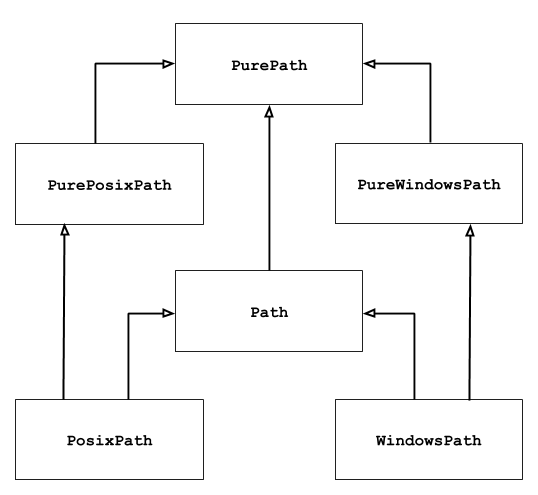
可以看到PurePath是所有类的基类,我们重点要掌握PurePath和Path这两个类,在Windows平台下路径对象会有Windows前缀,Unix平台上路径对象会有Posix前缀。
基本使用
列出所有子目录
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
>>> import pathlib
>>> p = pathlib.Path('.')
>>> [x for x in p.iterdir() if x.is_dir()]
[WindowsPath('.git'), WindowsPath('.idea'), WindowsPath('.vscode'),
WindowsPath('1_函数参数'), WindowsPath('2_生成器'), WindowsPath('3_常用函数'),
WindowsPath('4_装饰器), WindowsPath('5_常用模块')]
# 在linux环境下,上述的WindowsPath都会变为PosixPath
|
列出指定类型的文件
|
1
|
list(p.glob('**/*.py'))
|
路径拼接
可以使用/符号来拼接路径
|
1
2
3
4
|
>>> p = pathlib.Path(r'F:\cookies\python')
>>> q = p / 'learnPython'
>>> print(q)
F:\cookies\python\learnPython
|
查询属性
|
1
2
3
4
|
>>> q.exists()
True
>>> q.is_dir()
True
|
打开文件
|
1
2
3
4
|
>>> q = q / "hello_world.py"
>>> with q.open() as f:
>>> print(f.readline())
#!/usr/bin/env python
|
Pure paths
产生Pure paths的三种方式
class pathlib.PurePath(*pathsegments)
|
1
2
3
|
>>> PurePath('setup.py')
PurePosixPath('setup.py') # Running on a Unix machine
PureWindowsPath('setup.py') # Running on a Windows machine
|
|
1
2
3
4
|
>>> PurePath('foo', 'some/path', 'bar')
PureWindowsPath('foo/some/path/bar')
>>> PurePath(Path('foo'), Path('bar'))
PureWindowsPath('foo/bar')
|
如果参数为空,则默认指定当前文件夹
|
1
2
|
>>> PurePath()
PureWindowsPath('.')
|
当同时指定多个绝对路径,则使用最后一个
|
1
2
|
>>> PureWindowsPath('c:/Windows', 'd:bar')
PureWindowsPath('d:bar')
|
在Windows平台上,参数路径上如果有\或者/,则使用之前设置的盘符
|
1
2
|
>>> PureWindowsPath('F:\cookies\python\learnPython','\game')
PureWindowsPath('F:/game')
|
class pathlib.PurePosixPath(*pathsegments)
|
1
2
|
>>> PurePosixPath('/etc')
PurePosixPath('/etc')
|
class pathlib.PureWindowsPath(*pathsegments)
|
1
2
|
>>> PureWindowsPath('c:/Program Files/')
PureWindowsPath('c:/Program Files')
|
Path计算
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
>>> PurePosixPath('foo') == PurePosixPath('FOO')
False
>>> PureWindowsPath('foo') == PureWindowsPath('FOO')
True
>>> PureWindowsPath('FOO') in { PureWindowsPath('foo') }
True
>>> PureWindowsPath('C:') < PureWindowsPath('d:')
True
>>> PureWindowsPath('foo') == PurePosixPath('foo')
False
>>> PureWindowsPath('foo') < PurePosixPath('foo')
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
TypeError: unorderable types: PureWindowsPath() < PurePosixPath()
|
str() 和 bytes()
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
>>> p = PurePath('/etc')
>>> str(p)
'/etc'
>>> p = PureWindowsPath('c:/Program Files')
>>> str(p)
'c:\\Program Files'
>>> bytes(p)
b'/etc'
|
常用属性和方法
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
|
>>> PureWindowsPath('c:/Program Files/').drive
'c:'
>>> PurePosixPath('/etc').root
'/'
>>> p = PureWindowsPath('c:/foo/bar/setup.py')
>>> p.parents[0]
PureWindowsPath('c:/foo/bar')
>>> p.parents[1]
PureWindowsPath('c:/foo')
>>> p.parents[2]
PureWindowsPath('c:/')
>>> PureWindowsPath('//some/share/setup.py').name
'setup.py'
>>> PureWindowsPath('//some/share').name
''
>>> PurePosixPath('my/library/setup.py').suffix
'.py'
>>> PurePosixPath('my/library.tar.gz').suffix
'.gz'
>>> PurePosixPath('my/library').suffix
''
>>> PurePosixPath('my/library.tar.gar').suffixes
['.tar', '.gar']
>>> PurePosixPath('my/library.tar.gz').suffixes
['.tar', '.gz']
>>> PurePosixPath('my/library').suffixes
[]
>>> PurePosixPath('my/library.tar.gz').stem
'library.tar'
>>> PurePosixPath('my/library.tar').stem
'library'
>>> PurePosixPath('my/library').stem
'library'
>>> p = PureWindowsPath('c:\\windows')
>>> str(p)
'c:\\windows'
>>> p.as_posix()
'c:/windows'
>>> p = PurePosixPath('/etc/passwd')
>>> p.as_uri()
'file:///etc/passwd'
>>> p = PureWindowsPath('c:/Windows')
>>> p.as_uri()
'file:///c:/Windows'
>>> PurePath('a/b.py').match('*.py')
True
>>> PurePath('/a/b/c.py').match('b/*.py')
True
>>> PurePath('/a/b/c.py').match('a/*.py')
False
>>> p = PurePosixPath('/etc/passwd')
>>> p.relative_to('/')
PurePosixPath('etc/passwd')
>>> p.relative_to('/etc')
PurePosixPath('passwd')
>>> p.relative_to('/usr')
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
File "pathlib.py", line 694, in relative_to
.format(str(self), str(formatted)))
ValueError: '/etc/passwd' does not start with '/usr'
>>> p = PureWindowsPath('c:/Downloads/pathlib.tar.gz')
>>> p.with_name('setup.py')
PureWindowsPath('c:/Downloads/setup.py')
>>> p = PureWindowsPath('c:/')
>>> p.with_name('setup.py')
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
File "/home/antoine/cpython/default/Lib/pathlib.py", line 751, in with_name
raise ValueError("%r has an empty name" % (self,))
ValueError: PureWindowsPath('c:/') has an empty name
>>> p = PureWindowsPath('c:/Downloads/pathlib.tar.gz')
>>> p.with_suffix('.bz2')
PureWindowsPath('c:/Downloads/pathlib.tar.bz2')
>>> p = PureWindowsPath('README')
>>> p.with_suffix('.txt')
PureWindowsPath('README.txt')
|
Concrete paths
产生Concrete paths的三种方式
class pathlib.Path(*pathsegments)
|
1
2
3
|
>>> Path('setup.py')
PosixPath('setup.py') # Running on a Unix machine
WindowsPath('setup.py') # Running on a Windows machine
|
class pathlib.PosixPath(*pathsegments)
|
1
2
|
>>> PosixPath('/etc')
PosixPath('/etc')
|
class pathlib.WindowsPath(*pathsegments)
|
1
2
|
>>> WindowsPath('c:/Program Files/')
WindowsPath('c:/Program Files')
|
常用方法
cwd()设置path对象为当前路径
|
1
2
|
>>> Path.cwd()
WindowsPath('D:/Python 3.5')
|
stat()获取文件或目录属性
|
1
2
3
|
>>> p = Path('setup.py')
>>> p.stat().st_size
956
|
chmod()Unix系统修改文件或目录权限
exists()判断文件或目录是否存在
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
>>> from pathlib import *
>>> Path('.').exists()
True
>>> Path('setup.py').exists()
True
>>> Path('/etc').exists()
True
>>> Path('nonexistentfile').exists()
False
|
glob()列举文件
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
>>> sorted(Path('.').glob('*.py'))
[PosixPath('pathlib.py'), PosixPath('setup.py'), PosixPath('test_pathlib.py')]
>>> sorted(Path('.').glob('*/*.py'))
[PosixPath('docs/conf.py')]
>>> sorted(Path('.').glob('**/*.py'))
[PosixPath('build/lib/pathlib.py'),
PosixPath('docs/conf.py'),
PosixPath('pathlib.py'),
PosixPath('setup.py'),
PosixPath('test_pathlib.py')]
# The "**" pattern means "this directory and all subdirectories, recursively"
|
is_dir()判断是否是目录
is_file()判断是否是文件
is_symlink()判断是否是链接文件
iterdir()如果path指向一个目录,则返回该目录下所有内容的生成器
mkdir(mode=0o777, parents=False)创建目录
open(mode='r', buffering=-1, encoding=None, errors=None, newline=None)打开文件
owner()获取文件所有者
rename(target)修改名称
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
>>> p = Path('foo')
>>> p.open('w').write('some text')
9
>>> target = Path('bar')
>>> p.rename(target)
>>> target.open().read()
'some text'
|
resolve()Make the path absolute, resolving any symlinks. A new path object is returned
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
>>> p = Path()
>>> p
PosixPath('.')
>>> p.resolve()
PosixPath('/home/antoine/pathlib')
|
rmdir()删除目录,目录必须为空
touch(mode=0o777, exist_ok=True)创建空文件
(转)pathlib路径库使用详解的更多相关文章
- STC8H开发(二): 在Linux VSCode中配置和使用FwLib_STC8封装库(图文详解)
目录 STC8H开发(一): 在Keil5中配置和使用FwLib_STC8封装库(图文详解) STC8H开发(二): 在Linux VSCode中配置和使用FwLib_STC8封装库(图文详解) 前面 ...
- Python爬虫之selenium库使用详解
Python爬虫之selenium库使用详解 本章内容如下: 什么是Selenium selenium基本使用 声明浏览器对象 访问页面 查找元素 多个元素查找 元素交互操作 交互动作 执行JavaS ...
- STC8H开发(一): 在Keil5中配置和使用FwLib_STC8封装库(图文详解)
介绍 FwLib_STC8 是一个针对STC8G, STC8H系列MCU的C语言封装库, 适用于基于这些MCU的快速原型验证. 项目地址: Gitee FwLib_STC8 镜像地址: GitHub ...
- JNI_Android项目中调用.so动态库实现详解
转自:http://www.yxkfw.com/?p=7223 1. 在Eclipse中创建项目:TestJNI 2. 新创建一个class:TestJNI.java package com.wwj. ...
- JNI_Android项目中调用.so动态库实现详解【转】
转自 http://www.cnblogs.com/sevenyuan/p/4202759.html 1. 在Eclipse中创建项目:TestJNI 2. 新创建一个class:TestJNI.ja ...
- CREATE DATABASE建库语句详解
原创地址:http://blog.csdn.net/guguda2008/article/details/5716939 一个完整的建库语句是类似这样的: IF DB_ID('TEST') IS NO ...
- Linux 库文件详解
转自: http://www.cppblog.com/deane/articles/165216.html http://blog.sciencenet.cn/blog-1225851-904348. ...
- (笔记)Linux下的静态库和动态库使用详解
库从本质上来说是一种可执行代码的二进制格式,可以被载入内存中执行.库分静态库和动态库两种. 一.静态库和动态库的区别 1. 静态函数库 这类库的名字一般是libxxx.a:利用静态函数库编译成的文件比 ...
- 深入探讨Linux静态库与动态库的详解(转)
2.生成动态库并使用 linux下编译时通过 -shared 参数可以生成动态库(.so)文件,如下 库从本质上来说是一种可执行代码的二进制格式,可以被载入内存中执行.库分静态库和动态库两种. 一.静 ...
随机推荐
- 很实用的linux 上的svn安装和svnserver 的重启
虽然在windows上搭建SVN很简单,但是效能却不高,这当然是和linux相比了.然而在linux上搭建SVN却非常繁琐,所以今天这篇文章就来一步一步教您如何在Centos上搭建SVN 安装 #yu ...
- C++的重载流输出运算符
// 下列代码输出什么?#include <iostream>#include <string>// typedef basic_ostream<char> ost ...
- 位图bitbucket
问题:假设有500w条数据,数据是在2^32-1的范围内,数据重复,如何减少内存对数字进行统计呢? 如果用字典来标记数字是否已经统计过来,数字做为key, value仅为0 or1,那么这样需要消耗 ...
- ScheduledExecutorService的使用
http://407827531.iteye.com/blog/1329597 ScheduledExecutorService接口 在ExecutorService的基础上,ScheduledExe ...
- python处理excel之读:xlrd模块
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- import xlrd path = r'D:/工作簿1(已自动还原).xlsx' # 打开excel文件读取数据 data = xlrd.open_wo ...
- debian7(wheezy)升级安装mercurial hg最新版2.8-RC,解决tortoisehg2.9.2不能使用。
debian&(wheezy)之前的仓库版本是2.2.2. 注: 本文以 # 为开始的行是工作在root下的模式,在终端显示为root的提示符# ,用户目录的($:)需要切换到root(使用 ...
- shell 命令 ls -a
接手其他人的shell脚本时,遇到了一个"."开头的文件目录, ll 始终找不到. 咨询了一下,才知道,"."开头的是隐藏文件. 这时候用 ll -a 或 ls ...
- Mysql 分区(range,list,hash)转载
MySQL支持RANGE,LIST,HASH和KEY四种分区.其中,每个分区又都有一种特殊的类型.对于RANGE分区,有RANGE COLUMNS分区.对于LIST分区,有LIST COLUMNS分区 ...
- Java 学习的几个基础实验(Learn by doing)
0 引子 不少情况下,学生连开发环境都搭建不好,有了实验楼,这个问题基本就解决了. 实验楼是国内首家IT在线实训平台,拥有最丰富的计算机在线实验课,而且全部免费.创业团队对师生的服务非常贴心细致. 1 ...
- ELK冷热数据分离
通常情况下,我们使用ELK日志分析平台最常用的数据时间为1周或一个月(因业务场景不同,可能存在差别),时间比较长的数据没有特殊情况可能我们就没有必要再进行查询了,但是因业务需求或者作为凭证,这些日 ...
