Django框架详细介绍---请求流程
Django请求流程图
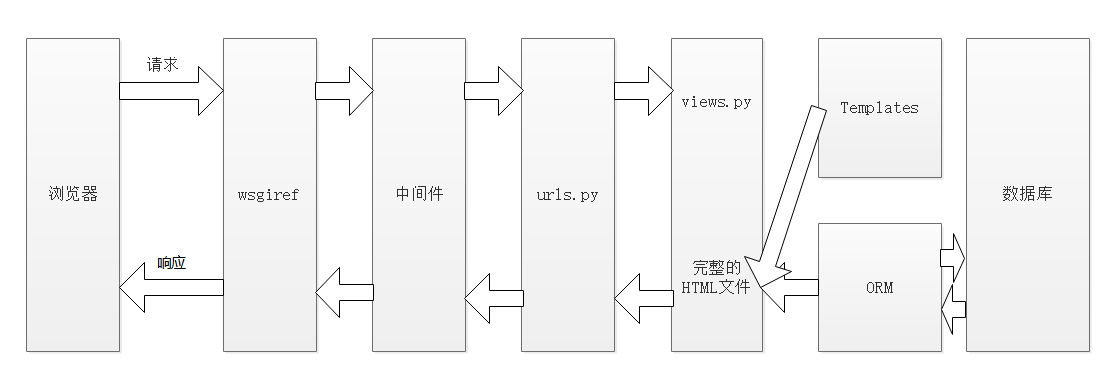
1.客户端发送请求
2.wsgiref是Django封装的套接字,它将客户端发送过来的请求(请求头、请求体封装成request)
1)解析请求数据
2)封装响应数据
3.中间件,进项身份验证等
MIDDLEWARE = [
'django.middleware.security.SecurityMiddleware',
'django.contrib.sessions.middleware.SessionMiddleware',
'django.middleware.common.CommonMiddleware',
'django.middleware.csrf.CsrfViewMiddleware',
'django.contrib.auth.middleware.AuthenticationMiddleware',
'django.contrib.messages.middleware.MessageMiddleware',
'django.middleware.clickjacking.XFrameOptionsMiddleware',
]
4.路由系统
urls映射到相应的视图
5.ORM对象关系映射,对数据库读写操作
7.templates模板,进行页面渲染
8.response响应
补充:
请求头ContentType编码类型:
1)application/x-www-form-urlencoded,form表单默认的POST提交数据的方式,wsgiref中默认只解析该方法提交过来的数据
2)multipart/form-data,form表单通过POST提交文件时需指定的方式
3)text/plain,这种方式几乎用不到
此外,在AJAX提交请求中可通过ContentType参数指定提交的方式,例如用户自定义的application/json,用来告诉服务端消息的主体是序列化后的JSON字符串,可用在要提交的数据层次比较深的场景,将数据进行序列化之后再进行提交或者将JSON字符串作为键值以application/x-www-form-urlencoded方式进行提交
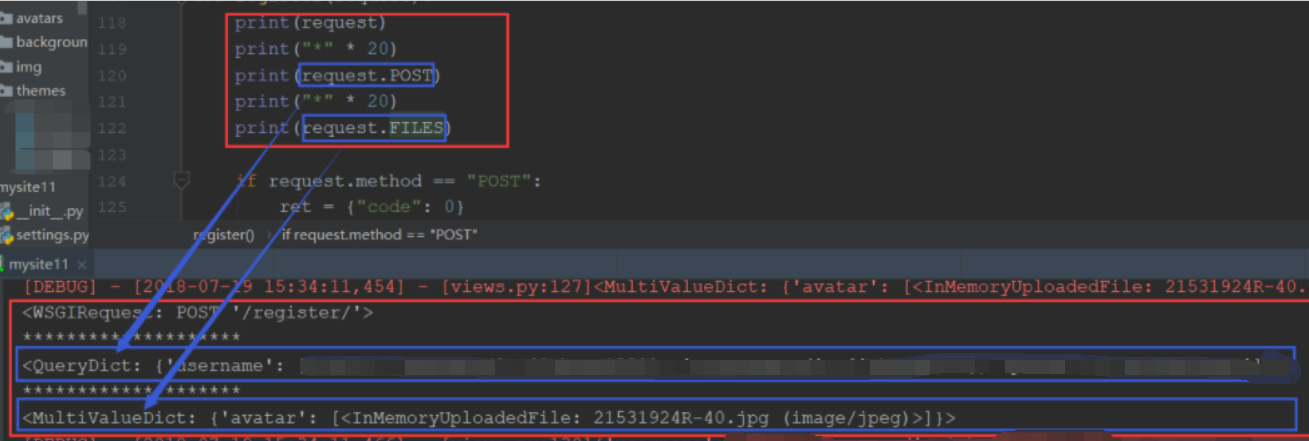
没有指定编码类型的情况下提交数据,在服务端可通过request内置的指定方法获取数据:
print(request.body) # 原始的请求体数据
print(request.GET) # GET请求数据
print(request.POST) # POST请求数据
print(request.FILES) # 上传的文件数据
Django内HttpRegiste和WSGIRequest源码:
class HttpRequest:
"""A basic HTTP request.""" # The encoding used in GET/POST dicts. None means use default setting.
_encoding = None
_upload_handlers = [] def __init__(self):
# WARNING: The `WSGIRequest` subclass doesn't call `super`.
# Any variable assignment made here should also happen in
# `WSGIRequest.__init__()`. self.GET = QueryDict(mutable=True)
self.POST = QueryDict(mutable=True)
self.COOKIES = {}
self.META = {}
self.FILES = MultiValueDict() self.path = ''
self.path_info = ''
self.method = None
self.resolver_match = None
self._post_parse_error = False
self.content_type = None
self.content_params = None def __repr__(self):
if self.method is None or not self.get_full_path():
return '<%s>' % self.__class__.__name__
return '<%s: %s %r>' % (self.__class__.__name__, self.method, self.get_full_path()) def _get_raw_host(self):
"""
Return the HTTP host using the environment or request headers. Skip
allowed hosts protection, so may return an insecure host.
"""
# We try three options, in order of decreasing preference.
if settings.USE_X_FORWARDED_HOST and (
'HTTP_X_FORWARDED_HOST' in self.META):
host = self.META['HTTP_X_FORWARDED_HOST']
elif 'HTTP_HOST' in self.META:
host = self.META['HTTP_HOST']
else:
# Reconstruct the host using the algorithm from PEP 333.
host = self.META['SERVER_NAME']
server_port = self.get_port()
if server_port != ('' if self.is_secure() else ''):
host = '%s:%s' % (host, server_port)
return host def get_host(self):
"""Return the HTTP host using the environment or request headers."""
host = self._get_raw_host() # Allow variants of localhost if ALLOWED_HOSTS is empty and DEBUG=True.
allowed_hosts = settings.ALLOWED_HOSTS
if settings.DEBUG and not allowed_hosts:
allowed_hosts = ['localhost', '127.0.0.1', '[::1]'] domain, port = split_domain_port(host)
if domain and validate_host(domain, allowed_hosts):
return host
else:
msg = "Invalid HTTP_HOST header: %r." % host
if domain:
msg += " You may need to add %r to ALLOWED_HOSTS." % domain
else:
msg += " The domain name provided is not valid according to RFC 1034/1035."
raise DisallowedHost(msg) def get_port(self):
"""Return the port number for the request as a string."""
if settings.USE_X_FORWARDED_PORT and 'HTTP_X_FORWARDED_PORT' in self.META:
port = self.META['HTTP_X_FORWARDED_PORT']
else:
port = self.META['SERVER_PORT']
return str(port) def get_full_path(self, force_append_slash=False):
# RFC 3986 requires query string arguments to be in the ASCII range.
# Rather than crash if this doesn't happen, we encode defensively.
return '%s%s%s' % (
escape_uri_path(self.path),
'/' if force_append_slash and not self.path.endswith('/') else '',
('?' + iri_to_uri(self.META.get('QUERY_STRING', ''))) if self.META.get('QUERY_STRING', '') else ''
) def get_signed_cookie(self, key, default=RAISE_ERROR, salt='', max_age=None):
"""
Attempt to return a signed cookie. If the signature fails or the
cookie has expired, raise an exception, unless the `default` argument
is provided, in which case return that value.
"""
try:
cookie_value = self.COOKIES[key]
except KeyError:
if default is not RAISE_ERROR:
return default
else:
raise
try:
value = signing.get_cookie_signer(salt=key + salt).unsign(
cookie_value, max_age=max_age)
except signing.BadSignature:
if default is not RAISE_ERROR:
return default
else:
raise
return value def get_raw_uri(self):
"""
Return an absolute URI from variables available in this request. Skip
allowed hosts protection, so may return insecure URI.
"""
return '{scheme}://{host}{path}'.format(
scheme=self.scheme,
host=self._get_raw_host(),
path=self.get_full_path(),
) def build_absolute_uri(self, location=None):
"""
Build an absolute URI from the location and the variables available in
this request. If no ``location`` is specified, bulid the absolute URI
using request.get_full_path(). If the location is absolute, convert it
to an RFC 3987 compliant URI and return it. If location is relative or
is scheme-relative (i.e., ``//example.com/``), urljoin() it to a base
URL constructed from the request variables.
"""
if location is None:
# Make it an absolute url (but schemeless and domainless) for the
# edge case that the path starts with '//'.
location = '//%s' % self.get_full_path()
bits = urlsplit(location)
if not (bits.scheme and bits.netloc):
current_uri = '{scheme}://{host}{path}'.format(scheme=self.scheme,
host=self.get_host(),
path=self.path)
# Join the constructed URL with the provided location, which will
# allow the provided ``location`` to apply query strings to the
# base path as well as override the host, if it begins with //
location = urljoin(current_uri, location)
return iri_to_uri(location) def _get_scheme(self):
"""
Hook for subclasses like WSGIRequest to implement. Return 'http' by
default.
"""
return 'http' @property
def scheme(self):
if settings.SECURE_PROXY_SSL_HEADER:
try:
header, value = settings.SECURE_PROXY_SSL_HEADER
except ValueError:
raise ImproperlyConfigured(
'The SECURE_PROXY_SSL_HEADER setting must be a tuple containing two values.'
)
if self.META.get(header) == value:
return 'https'
return self._get_scheme() def is_secure(self):
return self.scheme == 'https' def is_ajax(self):
return self.META.get('HTTP_X_REQUESTED_WITH') == 'XMLHttpRequest' @property
def encoding(self):
return self._encoding @encoding.setter
def encoding(self, val):
"""
Set the encoding used for GET/POST accesses. If the GET or POST
dictionary has already been created, remove and recreate it on the
next access (so that it is decoded correctly).
"""
self._encoding = val
if hasattr(self, 'GET'):
del self.GET
if hasattr(self, '_post'):
del self._post def _initialize_handlers(self):
self._upload_handlers = [uploadhandler.load_handler(handler, self)
for handler in settings.FILE_UPLOAD_HANDLERS] @property
def upload_handlers(self):
if not self._upload_handlers:
# If there are no upload handlers defined, initialize them from settings.
self._initialize_handlers()
return self._upload_handlers @upload_handlers.setter
def upload_handlers(self, upload_handlers):
if hasattr(self, '_files'):
raise AttributeError("You cannot set the upload handlers after the upload has been processed.")
self._upload_handlers = upload_handlers def parse_file_upload(self, META, post_data):
"""Return a tuple of (POST QueryDict, FILES MultiValueDict)."""
self.upload_handlers = ImmutableList(
self.upload_handlers,
warning="You cannot alter upload handlers after the upload has been processed."
)
parser = MultiPartParser(META, post_data, self.upload_handlers, self.encoding)
return parser.parse() @property
def body(self):
if not hasattr(self, '_body'):
if self._read_started:
raise RawPostDataException("You cannot access body after reading from request's data stream") # Limit the maximum request data size that will be handled in-memory.
if (settings.DATA_UPLOAD_MAX_MEMORY_SIZE is not None and
int(self.META.get('CONTENT_LENGTH') or 0) > settings.DATA_UPLOAD_MAX_MEMORY_SIZE):
raise RequestDataTooBig('Request body exceeded settings.DATA_UPLOAD_MAX_MEMORY_SIZE.') try:
self._body = self.read()
except IOError as e:
raise UnreadablePostError(*e.args) from e
self._stream = BytesIO(self._body)
return self._body def _mark_post_parse_error(self):
self._post = QueryDict()
self._files = MultiValueDict()
self._post_parse_error = True def _load_post_and_files(self):
"""Populate self._post and self._files if the content-type is a form type"""
if self.method != 'POST':
self._post, self._files = QueryDict(encoding=self._encoding), MultiValueDict()
return
if self._read_started and not hasattr(self, '_body'):
self._mark_post_parse_error()
return if self.content_type == 'multipart/form-data':
if hasattr(self, '_body'):
# Use already read data
data = BytesIO(self._body)
else:
data = self
try:
self._post, self._files = self.parse_file_upload(self.META, data)
except MultiPartParserError:
# An error occurred while parsing POST data. Since when
# formatting the error the request handler might access
# self.POST, set self._post and self._file to prevent
# attempts to parse POST data again.
# Mark that an error occurred. This allows self.__repr__ to
# be explicit about it instead of simply representing an
# empty POST
self._mark_post_parse_error()
raise
elif self.content_type == 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded':
self._post, self._files = QueryDict(self.body, encoding=self._encoding), MultiValueDict()
else:
self._post, self._files = QueryDict(encoding=self._encoding), MultiValueDict() def close(self):
if hasattr(self, '_files'):
for f in chain.from_iterable(l[1] for l in self._files.lists()):
f.close() # File-like and iterator interface.
#
# Expects self._stream to be set to an appropriate source of bytes by
# a corresponding request subclass (e.g. WSGIRequest).
# Also when request data has already been read by request.POST or
# request.body, self._stream points to a BytesIO instance
# containing that data. def read(self, *args, **kwargs):
self._read_started = True
try:
return self._stream.read(*args, **kwargs)
except IOError as e:
raise UnreadablePostError(*e.args) from e def readline(self, *args, **kwargs):
self._read_started = True
try:
return self._stream.readline(*args, **kwargs)
except IOError as e:
raise UnreadablePostError(*e.args) from e def __iter__(self):
while True:
buf = self.readline()
if not buf:
break
yield buf def xreadlines(self):
warnings.warn(
'HttpRequest.xreadlines() is deprecated in favor of iterating the '
'request.', RemovedInDjango30Warning, stacklevel=2,
)
yield from self def readlines(self):
return list(self)
HttpRequest源码
class WSGIRequest(HttpRequest):
def __init__(self, environ):
script_name = get_script_name(environ)
path_info = get_path_info(environ)
if not path_info:
# Sometimes PATH_INFO exists, but is empty (e.g. accessing
# the SCRIPT_NAME URL without a trailing slash). We really need to
# operate as if they'd requested '/'. Not amazingly nice to force
# the path like this, but should be harmless.
path_info = '/'
self.environ = environ
self.path_info = path_info
# be careful to only replace the first slash in the path because of
# http://test/something and http://test//something being different as
# stated in http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc2396.txt
self.path = '%s/%s' % (script_name.rstrip('/'),
path_info.replace('/', '', 1))
self.META = environ
self.META['PATH_INFO'] = path_info
self.META['SCRIPT_NAME'] = script_name
self.method = environ['REQUEST_METHOD'].upper()
self.content_type, self.content_params = cgi.parse_header(environ.get('CONTENT_TYPE', ''))
if 'charset' in self.content_params:
try:
codecs.lookup(self.content_params['charset'])
except LookupError:
pass
else:
self.encoding = self.content_params['charset']
self._post_parse_error = False
try:
content_length = int(environ.get('CONTENT_LENGTH'))
except (ValueError, TypeError):
content_length = 0
self._stream = LimitedStream(self.environ['wsgi.input'], content_length)
self._read_started = False
self.resolver_match = None def _get_scheme(self):
return self.environ.get('wsgi.url_scheme') @cached_property
def GET(self):
# The WSGI spec says 'QUERY_STRING' may be absent.
raw_query_string = get_bytes_from_wsgi(self.environ, 'QUERY_STRING', '')
return QueryDict(raw_query_string, encoding=self._encoding) def _get_post(self):
if not hasattr(self, '_post'):
self._load_post_and_files()
return self._post def _set_post(self, post):
self._post = post @cached_property
def COOKIES(self):
raw_cookie = get_str_from_wsgi(self.environ, 'HTTP_COOKIE', '')
return parse_cookie(raw_cookie) @property
def FILES(self):
if not hasattr(self, '_files'):
self._load_post_and_files()
return self._files POST = property(_get_post, _set_post)
WSGIRequest源码
Django框架详细介绍---请求流程的更多相关文章
- Django框架详细介绍---中间件(认证)
一.绪论 在cookie和session的应用中,通过在视图函数内添加装饰器判断用户是否登录,把没有登录的用户请求跳转到登录页面,通过给几个特定视图函数加装饰器实现了这个需求.但是以后添加的视图函数可 ...
- Django框架详细介绍---模型---ORM
一.概述 ORM(Object Relational Mapping),全称:对象关系映射,简单的说就是通过创建类.实例化出对象的方法,使得类.对象.对象的属性能够和数据库中的表.记录.字段意义对应. ...
- Django框架详细介绍---cookie、session、自定义分页
1.cookie 在HTTP协议介绍中提到,该协议是无状态的,也就是每次请求都是独立的,它的执行情况和结果与前面的请求和之后的请求都无直接关系,它不会受前面的请求响应情况直接影响,也不会直接影响后面的 ...
- Django框架详细介绍---Admin后台管理
1.Admin组件使用 Django内集成了web管理工具,Django在启动过程中会执行setting.py文件,初始化Django内置组件.注册APP.添加环境变量等 # Application ...
- Django框架详细介绍---request对象
几个重要的函数 1.HttpRequest.get_host() 根据从HTTP_X_FORWARDED_HOST(如果打开 USE_X_FORWARDED_HOST,默认为False和 HTTP_H ...
- Django框架详细介绍---ORM相关操作---select_related和prefetch_related函数对 QuerySet 查询的优化
Django的 select_related 和 prefetch_related 函数对 QuerySet 查询的优化 引言 在数据库存在外键的其情况下,使用select_related()和pre ...
- Django框架详细介绍---视图系统
Django视图系统 1.什么是视图 在Django中,一个视图函数/类,称为视图.实质就是一个用户自定义的简单函数,用来接收WEB请求并xing响应请求,响应的内容可以是一个HTML文件.重定向.一 ...
- Django框架详细介绍---认证系统
在web开发中通常设计网站的登录认证.注册等功能,Django恰好内置了功能完善的用户认证系统 1.auth模块 from django.contrib import auth 模块源码 import ...
- Django框架详细介绍---AJAX
一.概述 1.什么是JSON JSON 指的是 JavaScript 对象表示法(JavaScript Object Notation) JSON 是轻量级的文本数据交换格式 JSON 独立于语言 * ...
随机推荐
- Installation of CarbonData 1.1.0 with Spark 1.6.2
关键词:carbondata spark thrift 数据仓库 [Install thrift 0.9.3] 注意 要装thrift-java必须先装ant . 有人说要装boost,我在cento ...
- P2678 跳石头---(二分答案)
题目背景 一年一度的“跳石头”比赛又要开始了! 题目描述 这项比赛将在一条笔直的河道中进行,河道中分布着一些巨大岩石.组委会已经选择好了两块岩石作为比赛起点和终点.在起点和终点之间,有 NNN 块岩石 ...
- 网络流 ek
hdu3549 求最大流果题 ek算法 先bfs出一条流 然后通过不断地添加增广路 得到最大流(证明在算法书上都有) 增加了一个流 就加反向边 允许程序通过走方向边的方式进行“回滚” i^1 = i+ ...
- html中的列表
无序列表(什么前面默认一个实心的黑原点) <ul> <li>什么</li> <li>什么</li> <li>什么</li& ...
- vue发送请求---fetch-jsonp
fetch-jsonp和axios类似,都是第三方插件返送请求,而vue-resource是vue官方提供的请求插件 前两个哪个组件使用就在那里引入,vue-resource直接在vue的main.j ...
- ST表 || RMQ问题 || BZOJ 1699: [Usaco2007 Jan]Balanced Lineup排队 || Luogu P2880 [USACO07JAN]平衡的阵容Balanced Lineup
题面:P2880 [USACO07JAN]平衡的阵容Balanced Lineup 题解: ST表板子 代码: #include<cstdio> #include<cstring&g ...
- 20175320 2018-2019-2 《Java程序设计》第6周学习总结
20175320 2018-2019-2 <Java程序设计>第6周学习总结 教材学习内容总结 本周学习了教材的第七及第十章的内容.在这两章中介绍了接内部类与异常类以及输入.输出流,第七章 ...
- yum配置163源
CentOS7 配置163 yum源 1)下载repo文件 wget http://mirrors.163.com/.help/CentOS7-Base-163.repo 2)备份并替换系统的repo ...
- Integer、new Integer() 和 int 比较的面试题
基本概念的区分: 1.Integer 是 int 的包装类,int 则是 java 的一种基本数据类型2.Integer 变量必须实例化后才能使用,而int变量不需要3.Integer 实际是对象的引 ...
- Machine Learning, Homework 9, Neural Nets
Machine Learning, Homework 9, Neural NetsApril 15, 2019ContentsBoston Housing with a Single Layer an ...
