二十四种设计模式:迭代器模式(Iterator Pattern)
迭代器模式(Iterator Pattern)
介绍
提供一种方法顺序访问一个聚合对象中各个元素,而又不需暴露该对象的内部表示。
示例
有一个Message实体类,某聚合对象内的各个元素均为该实体对象,现在要提供一种方法顺序地访问这个聚合对象中的各个元素。
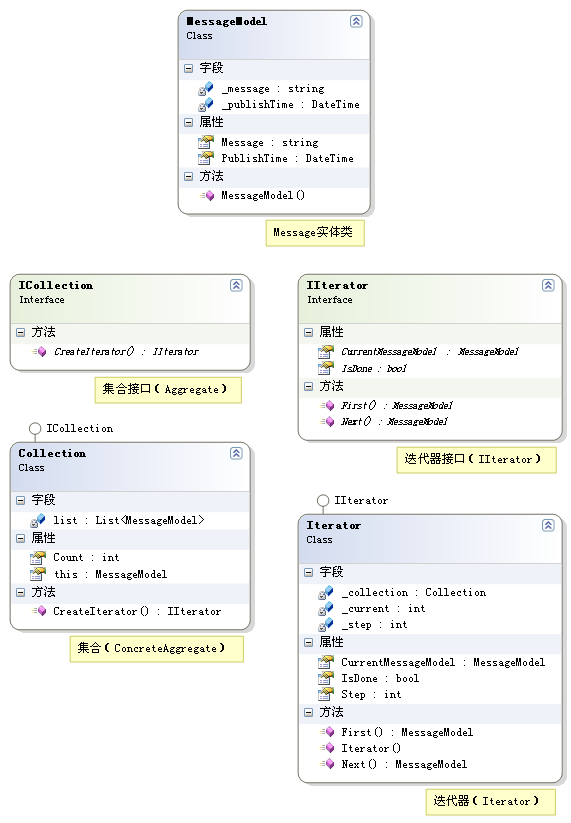
MessageModel
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text; namespace Pattern.Iterator
{
/// <summary>
/// Message实体类
/// </summary>
public class MessageModel
{
/// <summary>
/// 构造函数
/// </summary>
/// <param name="msg">Message内容</param>
/// <param name="pt">Message发布时间</param>
public MessageModel(string msg, DateTime pt)
{
this._message = msg;
this._publishTime = pt;
} private string _message;
/// <summary>
/// Message内容
/// </summary>
public string Message
{
get { return _message; }
set { _message = value; }
} private DateTime _publishTime;
/// <summary>
/// Message发布时间
/// </summary>
public DateTime PublishTime
{
get { return _publishTime; }
set { _publishTime = value; }
}
}
}
ICollection
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text; namespace Pattern.Iterator
{
/// <summary>
/// 集合接口(Aggregate)
/// </summary>
public interface ICollection
{
/// <summary>
/// 创建迭代器对象
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
IIterator CreateIterator();
}
}
Collection
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text; namespace Pattern.Iterator
{
/// <summary>
/// 集合(ConcreteAggregate)
/// </summary>
public class Collection : ICollection
{
private List<MessageModel> list = new List<MessageModel>(); /// <summary>
/// 创建迭代器对象
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public IIterator CreateIterator()
{
return new Iterator(this);
} /// <summary>
/// 集合内的对象总数
/// </summary>
public int Count
{
get { return list.Count; }
} /// <summary>
/// 索引器
/// </summary>
/// <param name="index">index</param>
/// <returns></returns>
public MessageModel this[int index]
{
get { return list[index]; }
set { list.Add(value); }
} }
}
IIterator
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text; namespace Pattern.Iterator
{
/// <summary>
/// 迭代器接口(IIterator)
/// </summary>
public interface IIterator
{
/// <summary>
/// 第一个对象
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
MessageModel First(); /// <summary>
/// 下一个对象
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
MessageModel Next(); /// <summary>
/// 当前对象
/// </summary>
MessageModel CurrentMessageModel { get; } /// <summary>
/// 是否迭代完毕
/// </summary>
bool IsDone { get; }
}
}
Iterator
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text; namespace Pattern.Iterator
{
/// <summary>
/// 迭代器(Iterator)
/// </summary>
public class Iterator : IIterator
{
private Collection _collection;
private int _current = 0;
private int _step = 1; /// <summary>
/// 构造函数
/// </summary>
/// <param name="collection"></param>
public Iterator(Collection collection)
{
this._collection = collection;
} /// <summary>
/// 第一个对象
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public MessageModel First()
{
_current = 0;
return _collection[_current];
} /// <summary>
/// 下一个对象
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public MessageModel Next()
{
_current += _step; if (!IsDone)
{
return _collection[_current];
}
else
{
return null;
}
} /// <summary>
/// 当前对象
/// </summary>
public MessageModel CurrentMessageModel
{
get { return _collection[_current]; }
} /// <summary>
/// 是否迭代完毕
/// </summary>
public bool IsDone
{
get { return _current >= _collection.Count ? true : false; }
} /// <summary>
/// 步长
/// </summary>
public int Step
{
get { return _step; }
set { _step = value; }
}
}
}
Test
using System;
using System.Data;
using System.Configuration;
using System.Collections;
using System.Web;
using System.Web.Security;
using System.Web.UI;
using System.Web.UI.WebControls;
using System.Web.UI.WebControls.WebParts;
using System.Web.UI.HtmlControls; using I = Pattern.Iterator; public partial class Iterator : System.Web.UI.Page
{
protected void Page_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
I::Collection collection = new I::Collection(); collection[0] = new I::MessageModel("第1条信息", DateTime.Now);
collection[1] = new I::MessageModel("第2条信息", DateTime.Now);
collection[2] = new I::MessageModel("第3条信息", DateTime.Now);
collection[3] = new I::MessageModel("第4条信息", DateTime.Now);
collection[4] = new I::MessageModel("第5条信息", DateTime.Now);
collection[5] = new I::MessageModel("第6条信息", DateTime.Now);
collection[6] = new I::MessageModel("第7条信息", DateTime.Now);
collection[7] = new I::MessageModel("第8条信息", DateTime.Now);
collection[8] = new I::MessageModel("第9条信息", DateTime.Now); I::Iterator iterator = new I::Iterator(collection); iterator.Step = 2; for (I::MessageModel mm = iterator.First(); !iterator.IsDone; mm = iterator.Next())
{
Response.Write(mm.Message);
Response.Write("<br />");
}
}
}
运行结果
第1条信息
第3条信息
第5条信息
第7条信息
第9条信息
二十四种设计模式:迭代器模式(Iterator Pattern)的更多相关文章
- 二十四种设计模式:适配器模式(Adapter Pattern)
适配器模式(Adapter Pattern) 介绍将一个类的接口转换成客户希望的另外一个接口.Adapter模式使得原本由于接口不兼容而不能一起工作的那些类可以一起工作.示例有一个Message实体类 ...
- 二十四种设计模式:观察者模式(Observer Pattern)
观察者模式(Observer Pattern) 介绍定义对象间的一种一对多的依赖关系,以便当一个对象的状态发生改变时,所有依赖于它的对象都得到通知并自动刷新. 示例有一个Message实体类,某些对象 ...
- 二十四种设计模式:装饰模式(Decorator Pattern)
装饰模式(Decorator Pattern) 介绍动态地给一个对象添加一些额外的职责.就扩展功能而言,它比生成子类方式更为灵活.示例有一个Message实体类,某个对象对它的操作有Insert()和 ...
- 二十四种设计模式:单例模式(Singleton Pattern)
单例模式(Singleton Pattern) 介绍保证一个类仅有一个实例,并提供一个访问它的全局访问点. 示例保证一个类仅有一个实例. Singleton using System; using S ...
- 设计模式 - 迭代器模式(iterator pattern) 具体解释
迭代器模式(iterator pattern) 详细解释 本文地址: http://blog.csdn.net/caroline_wendy 迭代器模式(iterator pattern) : 提供一 ...
- 二十四种设计模式:命令模式(Command Pattern)
命令模式(Command Pattern) 介绍将一个请求封装为一个对象,从而使你可用不同的请求对客户进行参数化:对请求排队或记录请求日志,以及支持可取消的操作. 示例有一个Message实体类,某个 ...
- 二十四种设计模式:解释器模式(Interpreter Pattern)
解释器模式(Interpreter Pattern) 介绍给定一个语言, 定义它的文法的一种表示,并定义一个解释器,该解释器使用该表示来解释语言中的句子. 示例有一个Message实体类,某个类对它的 ...
- 二十四种设计模式:策略模式(Strategy Pattern)
策略模式(Strategy Pattern) 介绍定义一系列的算法,把它们一个个封装起来,并且使它们可相互替换.本模式使得算法的变化可独立于使用它的客户. 示例有一个Message实体类,对它的操作有 ...
- 二十四种设计模式:组合模式(Composite Pattern)
组合模式(Composite Pattern) 介绍将对象组合成树形结构以表示"部分-整体"的层次结构.它使得客户对单个对象和复合对象的使用具有一致性.示例有一个Message实体 ...
随机推荐
- [ python ] 类的组合
首先,使用面向对象是一个人狗大战的实例: class Person: def __init__(self, name, hp, aggr, sex): self.name = name self.hp ...
- java生成缩略图,旋转,水印,截图
转自:http://rensanning.iteye.com/blog/1545708 感谢,方便自己查看
- HDU-5335
Walk Out Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/65536 K (Java/Others)Total Su ...
- LockSupport学习
LockSupport工具类定义了一组的公共静态方法,这些方法提供了最基本的线程阻塞和唤醒功能.Java锁和同步器框架的核心工具类AQS:AbstractQueueSynchronizer,就是通过调 ...
- 【hdoj_2391】FilthyRich
题目:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=2391 题目大意:给定一个矩阵,从左上角第一个元素开始到右下最后一个元素,寻找一条路线,使得路线经过的矩阵元 ...
- ThinkPHP 多数据库自动连接设计
配置文件 database.php <?php return array( 'dbname1'=>'mysql://root:root@localhost/dbname1#utf8', ' ...
- 转:智能模糊测试工具 Winafl 的使用与分析
本文为 椒图科技 授权嘶吼发布,如若转载,请注明来源于嘶吼: http://www.4hou.com/technology/2800.html 注意: 函数的偏移地址计算方式是以IDA中出现的Imag ...
- Python函数式编程——map()、reduce()
文章来源:http://www.pythoner.com/46.html 提起map和reduce想必大家并不陌生,Google公司2003年提出了一个名为MapReduce的编程模型[1],用于处理 ...
- 如何使用weinre来进行远程调试phonegap应用
使用phonegap开发的应用在真机上和PC上的显示效果以及浏览器渲染方式还是有些区别的.在PC端很好调试,各种浏览器都自带了调试工具,使用起来很方便,但是在一旦安装到了手机上,这个时候要进行调试就需 ...
- SQLSEVER 中的那些键和约束
SQL Server中有五种约束类型,分别是 PRIMARY KEY约束.FOREIGN KEY约束.UNIQUE约束.DEFAULT约束.和CHECK约束.查看或者创建约束都要使用到 Microso ...
