6.Android-五大布局
Android 五大布局如下所示:
|
LinearLayout |
线性布局 |
只能指定一个方向(垂直/水平)来布局 |
|
RelativeLayout |
相对布局 |
通过某个控件为参照物,来定位其它控件的位置的布局方式(解决屏幕适配) |
|
TableLayout |
表格布局 |
如果子元素为<TableRow>,则可在一行中放各种控件 |
|
FrameLayout |
帧布局 |
子元素任意 |
|
AbsoluteLayout |
绝对布局 |
通过android:layout_x和android:layout_y来指定元素绝对位置,由于不支持适配,已过时 |
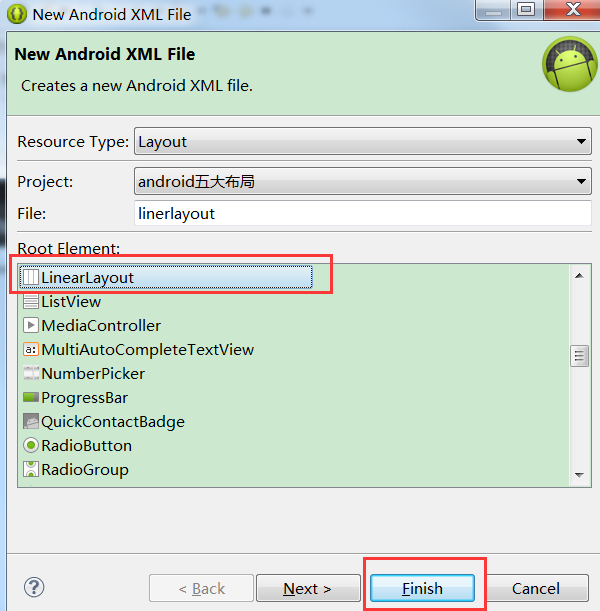
1.如何创建布局
在layout下选择New Android XML File:

然后输入名称,即可完成:
2.LinearLayout线性布局
LinearLayout特有的属性如下所示:
android:orientation= //设置布局方向,填写“horizontal”或者“vertaical”
vertaical方向
xml如下所示:

对应的布局则是垂直向下的,一排只能拥有一个控件:

horizontal方向
xml如下所示:
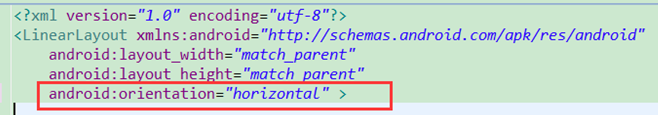
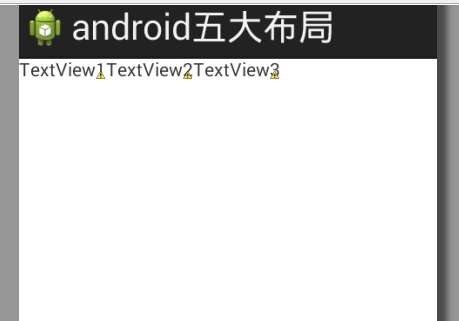
对应的布局则是水平向右的,一列只能拥有一个控件:
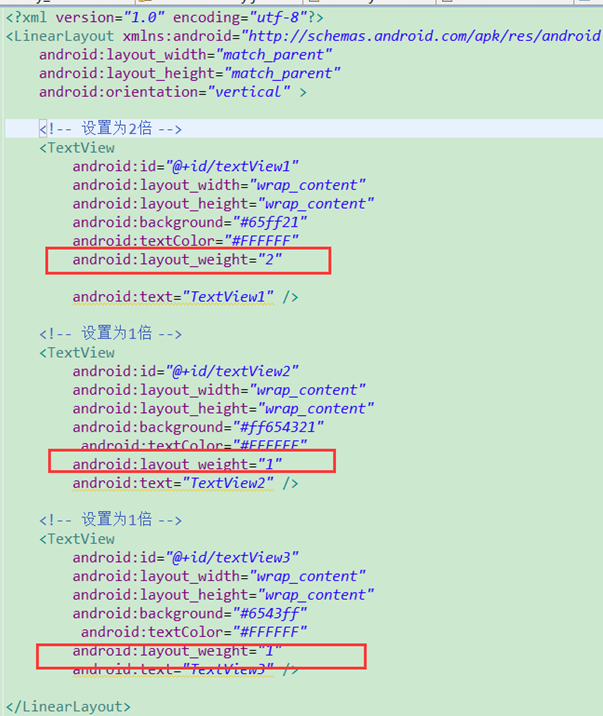
设置控件不同比例
如果要想设置两个控件的比例大小,则设置android:layout_weight(不是android:layout_width),值越大则比例越大(垂直布局则设置高度大小比例,水平布局则设置宽度大小比例)
以垂直线性布局为例,我们设置TextView1占据高度为2倍,其余为1倍
xml设置如下:
界面如下所示:

PS:在布局中也可以再次添加一个布局.
比如LinearLayout垂直布局中添加一个LinearLayout水平布局,实现登录案例
xml如下:
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context=".MainActivity" > <EditText
android:id="@+id/et_username"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:hint="请输入用户名" />
<EditText
android:id="@+id/et_password"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:inputType="textPassword"
android:hint="请输入密码" /> <!-- 再添加一个水平布局.添加保存信息和登陆button -->
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<CheckBox
android:id="@+id/cb_isSave"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="勾选保存信息"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn_login"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="登陆"
/> </LinearLayout> </LinearLayout>
效果如下:
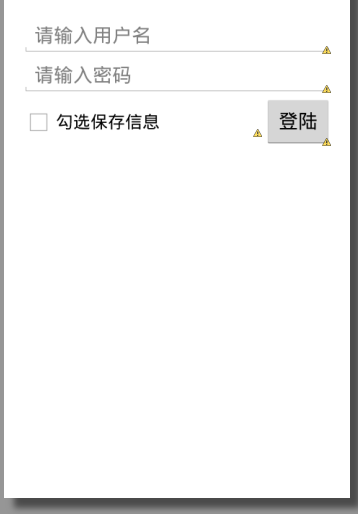
如果只有一个控件设置了android:layout_weight="1",则需要将自身的android:layout_width="0dp",并表示该控件占据剩余的所有空间,如上图的"保存信息"
3.RelativeLayout相对布局
为某一个组件为参照物,来定位下一个组件的位置的布局方式。一般为了解决屏幕分辨率不同的自适应问题(适配神器)
LinearLayout特有的属性如下所示:
|
android:layout_alignParentLeft android:layout_alignParentRight android:layout_alignParentTop android:layout_alignParentBottom |
“true” “false” |
控件在LinearLayout布局中的相对位置 |
|
android:orientation |
“horizontal” “vertaical” |
布局中子控件排布方向 |
|
android:layout_toRightOf android:layout_toLeftOf android:layout_below android:layout_above |
“@+id/***” |
控件和某个控件的位置关系(居右、左、下、上) |
|
android:layout_alignTop android:layout_alignBottom android:layout_alignLeft android:layout_alignRight android:layout_alignBaseline |
“@+id/***” |
控件与其他控件对齐(顶部对齐、底部、左、右对齐、基线(文本内容)对齐) |
|
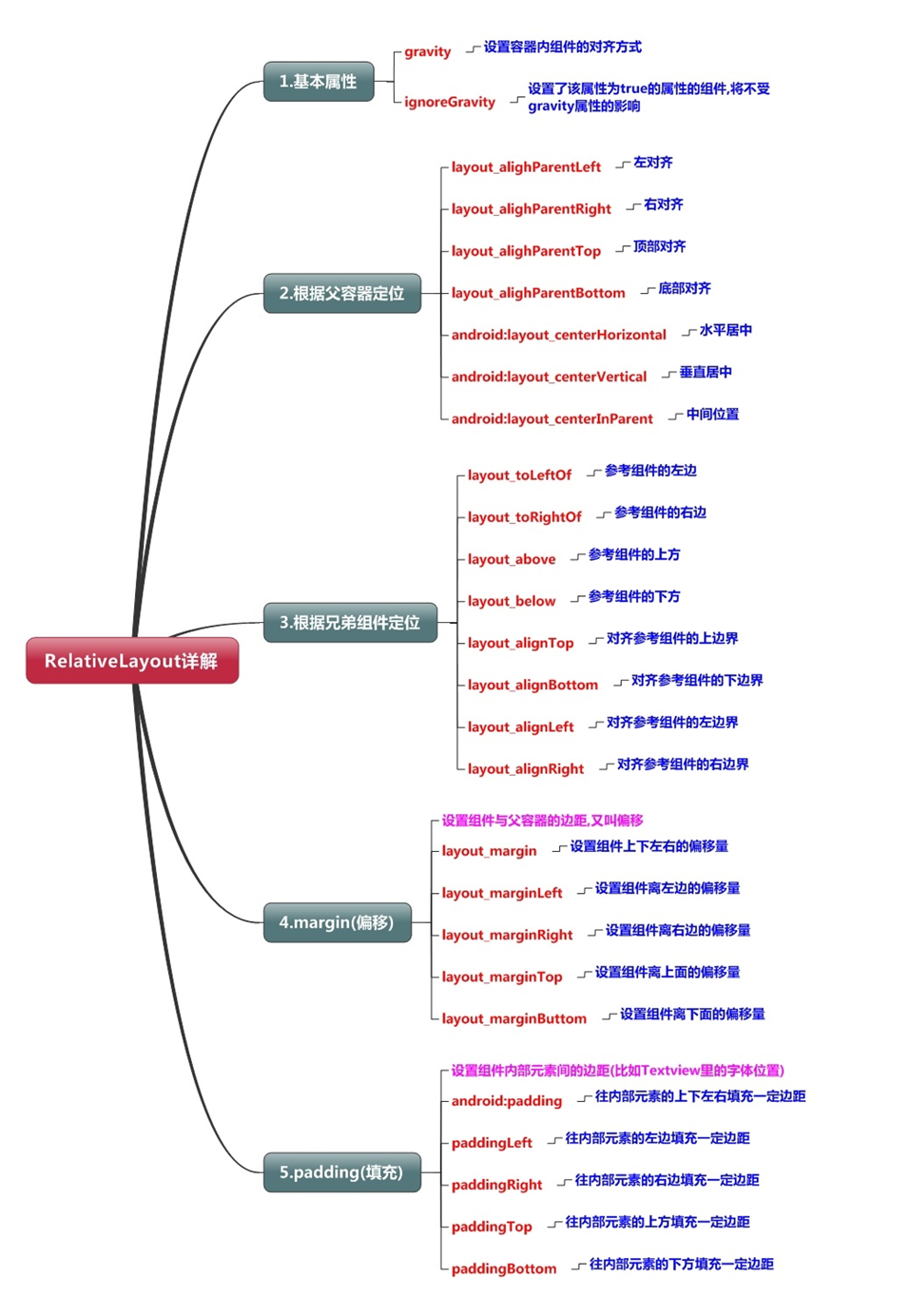
android:layout_centerHorizontal android:layout_centerVirtical android:layout_centerInParent |
“true” “false” |
指定控件位于水平/垂直/父控件的中间位置 |
如下图所示:
注意:在指定位置关系时,引用的ID必须在引用之前,先被定义,否则将出现异常。
示例-通过RelativeLayout实现固定九宫格(如果要动态实现增删格子,最好还是用GridLayout)
xml如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" > <Button
android:id="@+id/button5"
android:layout_width="50dp"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:text="5" /> <Button
android:id="@+id/button2"
android:layout_width="50dp"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:layout_above="@id/button5"
android:text="2" /> <Button
android:id="@+id/button8"
android:layout_width="50dp"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:layout_below="@id/button5"
android:text="8" /> <Button
android:id="@+id/button1"
android:layout_width="50dp"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:layout_alignTop="@id/button2"
android:layout_toLeftOf="@id/button2"
android:text="1" /> <Button
android:id="@+id/button3"
android:layout_width="50dp"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:layout_alignTop="@id/button2"
android:layout_toRightOf="@id/button2"
android:text="3" /> <Button
android:id="@+id/button4"
android:layout_width="50dp"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:layout_alignTop="@id/button5"
android:layout_toLeftOf="@id/button5"
android:text="4" /> <Button
android:id="@+id/button6"
android:layout_width="50dp"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:layout_alignTop="@id/button5"
android:layout_toRightOf="@id/button5"
android:text="6" /> <Button
android:id="@+id/button7"
android:layout_width="50dp"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:layout_alignTop="@+id/button8"
android:layout_toLeftOf="@+id/button8"
android:text="7" /> <Button
android:id="@+id/button9"
android:layout_width="50dp"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:layout_alignTop="@+id/button8"
android:layout_toRightOf="@+id/button8"
android:text="9" />
</RelativeLayout>
布局如下:

4.FrameLayout帧布局
默认所有的控件都是左上对齐(每个控件对应每个界面)。控件可以通过android:layout_gravity属性控制自己在父控件中的位置。
而android:gravity表示:设置文本位置,如设置成”center”,文本将居中显示。
比如下面xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" > <TextView
android:id="@+id/textView1"
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:textColor="#000000"
android:background="#ffFF00"
android:text="TextView1" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView2"
android:layout_width="200dp"
android:layout_height="30dp"
android:textColor="#000000"
android:background="#00FFf0"
android:text="TextView2" />
</FrameLayout>
布局如下:
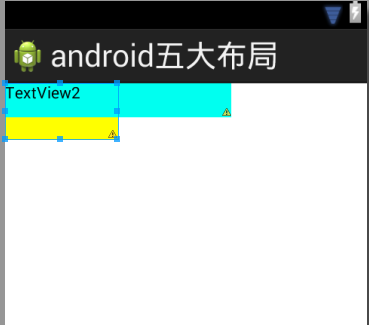
可以看到TextView1已经被覆盖了.
修改textview1,设置为居中:
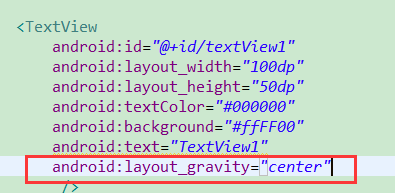
布局效果如下所示:

5.TableLayout表格布局
TableLayout特有元素TableRow
通过TableRow可以在一行中放各种控件.
示例如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<TableLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" > <TableRow>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="TextView1"
android:background="#FF0000"/> <TextView
android:id="@+id/textView2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="TextView2"
android:background="#FFF000" />
</TableRow> <TextView
android:id="@+id/textView3"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="TextView3" /> </TableLayout>
布局效果如下:
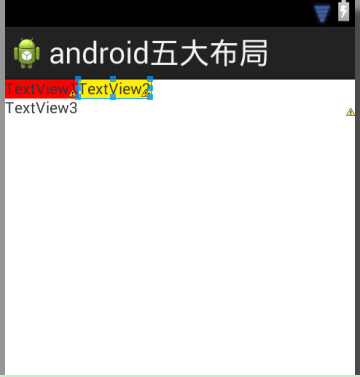
如上图所示,可以看到只有通过TableRow元素包含的控件才能占据为1行.
TableLayout特有属性如下所示:
- android:collapseColumns: 设置需要被隐藏的列的序号
- android:shrinkColumns: 设置允许被收缩的列的列序号
- android:stretchColumns: 设置运行被拉伸的列的列序号
collapseColumns和android:stretchColumns属性示例
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<TableLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:collapseColumns="1,2"
android:stretchColumns="3"
> <TableRow>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="TextView0"
android:background="#FF0000"/> <TextView
android:id="@+id/textView2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="TextView1"
android:background="#FFF000" /> <Button
android:id="@+id/button1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="2" /> <Button
android:id="@+id/button2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="3" /> <Button
android:id="@+id/button3"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="4" />
</TableRow>
</TableLayout>
布局效果如下:
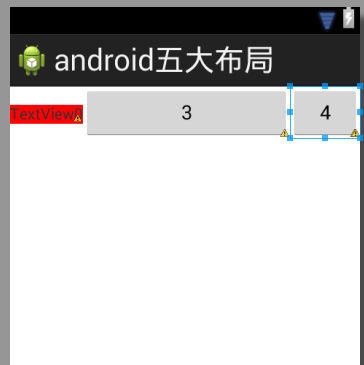
由于设置android:collapseColumns="1,2",所以TextView1和TextView2所在的列被隐藏了.
然后android:stretchColumns="3",由于第一个button位于第3列,所以被拉伸了(列数是从0开始的)
android:shrinkColumns属性示例
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<TableLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:shrinkColumns="1"
>
<TableRow>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="TextView0"
android:background="#FF0000"/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="TextView1"
android:background="#FFF000" /> <Button
android:id="@+id/button1"
android:layout_width="80dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="2" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button2"
android:layout_width="80dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="3" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button3"
android:layout_width="80dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="4" />
</TableRow>
</TableLayout>
布局如下所示:
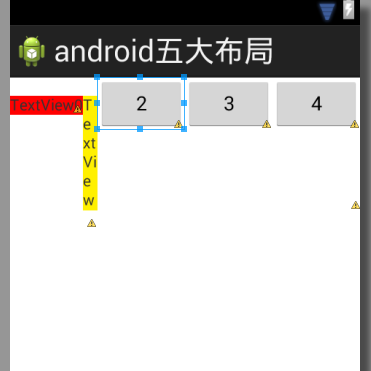
由于android:shrinkColumns="1",所以第二个列支持收缩.
6.AbsoluteLayout绝对布局
已过时, 通过android:layout_x和android:layout_y来指定元素绝对位置,所以不能适配各个不同屏幕大小.
示例如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<AbsoluteLayoutxmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" > <TextView
android:id="@+id/textView1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_x="91dp"
android:layout_y="108dp"
android:text="TextView" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_x="130dp"
android:layout_y="202dp"
android:text="Button" />
</AbsoluteLayout>
布局如下:

6.Android-五大布局的更多相关文章
- Android 五大布局
Android 五大布局: FrameLayout(框架布局),LinearLayout (线性布局),AbsoluteLayout(绝对布局),RelativeLayout(相对布局),Table ...
- Android 五大布局(LinearLayout、FrameLayout、AbsoulteLayout、RelativeLayout、TableLayout )
前言 欢迎大家我分享和推荐好用的代码段~~ 声明 欢迎转载,但请保留文章原始出处: CSDN:http://www.csdn.net ...
- 浅谈Android五大布局
Android的界面是有布局和组件协同完成的,布局好比是建筑里的框架,而组件则相当于建筑里的砖瓦.组件按照布局的要求依次排列,就组成了用户所看见的界面.Android的五大布局分别是LinearLay ...
- [转]浅谈Android五大布局(二)——RelativeLayout和TableLayout
在浅谈Android五大布局(一)中已经描述了LinearLayout(线性布局).FrameLayout(单帧布局)和AbsoulteLayout(绝对布局)三种布局结构,剩下的两种布局Relati ...
- [转]浅谈Android五大布局(一)——LinearLayout、FrameLayout和AbsoulteLayout
Android的界面是有布局和组件协同完成的,布局好比是建筑里的框架,而组件则相当于建筑里的砖瓦.组件按照布局的要求依次排列,就组成了用户所看见的界面.Android的五大布局分别是LinearLay ...
- Android五大布局介绍&属性设置大全
前言 在进行Android开发中,常常需要用到各种布局来进行UI的绘制,今天我们就来讲下Android开发中最常用的五大布局介绍和相关属性的设置. 目录 Android五大布局介绍&属性设置. ...
- Android五大布局详解——LinearLayout(线性布局)
Android五大布局 本篇开始介绍Android的五大布局的知识,一个丰富的界面显示总是要有众多的控件来组成的,那么怎样才能让这些控件能够按你的想法进行摆放,从而自定义你所想要的用户界面呢?这就牵涉 ...
- Android笔记——Android五大布局
一.五大布局 Android的界面是有布局和组件协同完成的,布局好比是建筑里的框架,而组件则相当于建筑里的砖瓦.组件按照布局的要求依次排列,就组成了用户所看见的界面.Android的五大布局分别是Li ...
- Android——五大布局
Android的五大布局分为: 线性布局 相对布局 帧布局 绝对布局 表格布局 一.线性布局 线性布局在开发中使用最多,具有垂直方向与水平方向的布局方式 通过设置属性"android:ori ...
- 浅谈Android五大布局(一)——LinearLayout、FrameLayout和AbsoulteLayout
Android的界面是有布局和组件协同完成的,布局好比是建筑里的框架,而组件则相当于建筑里的砖瓦.组件按照布局的要求依次排列,就组成了用户所看见的界面.Android的五大布局分别是LinearLay ...
随机推荐
- 跟着兄弟连系统学习Linux-【day08】
day08-20200605 p27.软件包管理简 windows 和 linux 软件是不同的版本. Linux源码包,开源的.绝大部分都是C语言写的.源码包安装速度比较慢.需要先编译后再安装.脚本 ...
- BasicInterpreter1.00 运行简单Basic脚本 打印变量及字符串
源码下载:https://files.cnblogs.com/files/heyang78/basicInterpreter-20200529-1.rar 脚本: count= print(count ...
- Native Comments
local variables referenced from a Lambda expression must be final or effectively final. Lambda表达式中引用 ...
- 10 张图聊聊线程的生命周期和常用 APIs
上一篇文章我们聊了多线程的基础内容,比如为什么要使用多线程,线程和进程之间的不同,以及创建线程的 4 种方式.本文已收录至我的 Github: https://github.com/xiaoqi666 ...
- 为什么ping不通google.com
前言 为什么在ping不通Google的时候,我们却可以web直接访问Google (已开启SSR 翻 墙) SSR访问Google 因为GFW的限制导致国内无法直接访问谷歌,那么SSR为什么能绕过限 ...
- c++基础 写二进制文件
问题描述 有许多数据待拟合,需要从 root 中提取出来,写成文本文件数据量过大,想转成二进制文件. 解决 #include "TString.h" #include " ...
- adb命令—monkey篇
monkey 目录 monkey 1.Monkey介绍 2.Monkey是用来做什么的 3.Monkey程序介绍 下面就是一些Monkey命令了 1.Monkey介绍 顾名思义,Monkey就是猴子, ...
- Linux实战(19):Shell交互式read 用法
read 用法有好几种,我在实战过程中用到了 -p,记一笔以防不用忘记了. 实例 #!/bin/bash echo "检测IP是否被占用" while read -p " ...
- Mysql实战(1):创建用户
此文为个人实操汇总. 创建用户设置权限 create user 'user'@'%' identified by 'password'; #创建用户设置密码 grant all privileges ...
- k8s架构分析(二)
master节点 k8s的集群由master和node组成,节点上运行着若干k8s服务. master节点之上运行着的后台服务有kube-apiserver .kube-scheduler.kube- ...
