理解 LinkedList
java -version :jdk 1.8.0_191
构造
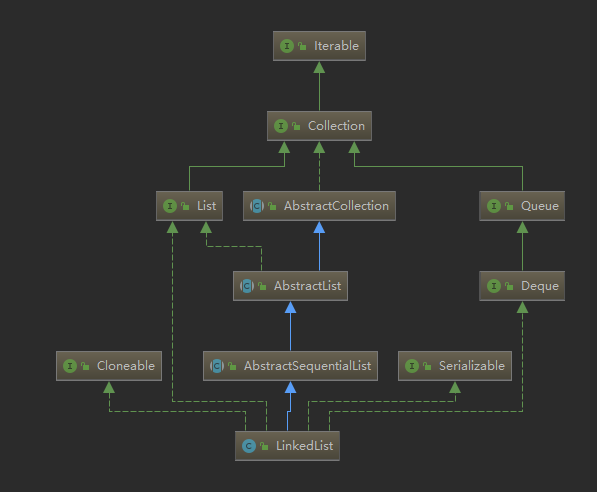
类内参数,方法
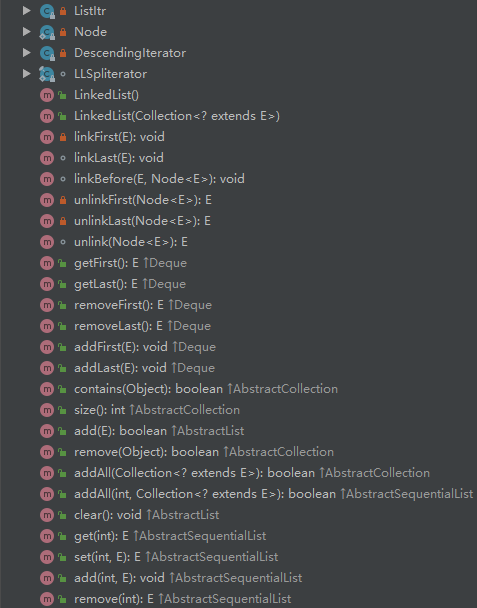
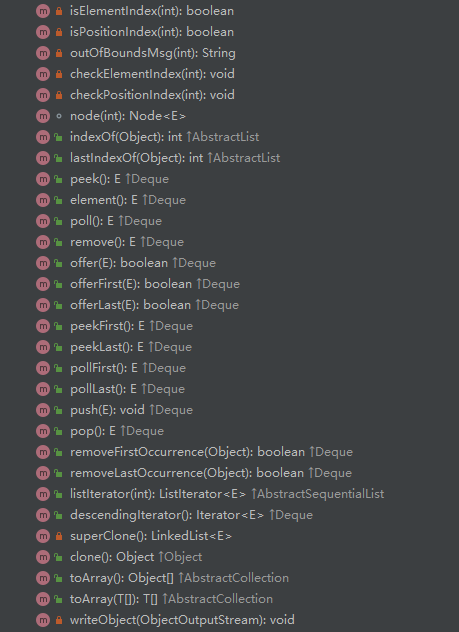
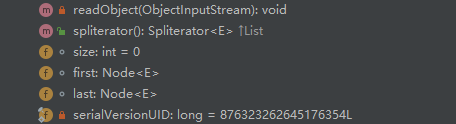
实现
基于双向链表实现。
插入时间复杂度 O(1)
查找时间复杂度 O(n)
删除时间复杂度 O(1)
修改时间复杂度 O(n)
链表不存在扩容的问题。
静态参数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
/**
* Pointer to first node.
* Invariant: (first == null && last == null) ||
* (first.prev == null && first.item != null)
*/
transient Node<E> first;
链表的第一个,不能被序列化
/**
* Pointer to last node.
* Invariant: (first == null && last == null) ||
* (last.next == null && last.item != null)
*/
transient Node<E> last;
链表的最后一个,不能被序列化
节点参数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
private static class Node<E> {
//数据
E item;
//下一个节点
Node<E> next;
//上一个节点
Node<E> prev;
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}
add方法
public boolean add(E e)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
/**
* Appends the specified element to the end of this list.
*
* <p>This method is equivalent to {@link #addLast}.
*
* @param e element to be appended to this list
* @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
//插入到链表的尾端
linkLast(e);
return true;
}
/**
* Links e as last element.
*/
void linkLast(E e) {
final Node<E> l = last;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
last = newNode;
if (l == null)
first = newNode;
else
l.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
public void add(int index, E element)
将 e 添加到指定位置
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the specified position in this list.
* Shifts the element currently at that position (if any) and any
* subsequent elements to the right (adds one to their indices).
*
* @param index index at which the specified element is to be inserted
* @param element element to be inserted
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public void add(int index, E element) {
//先判断是否会越界
checkPositionIndex(index);
//刚好是最后一个
if (index == size)
linkLast(element);
else
linkBefore(element, node(index));
}
get方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
/**
* Returns the element at the specified position in this list.
*
* @param index index of the element to return
* @return the element at the specified position in this list
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E get(int index) {
checkElementIndex(index);
return node(index).item;
}
for 循环遍历下标,找到对应的节点,根据下标的大小判断是从头遍历还是从尾部遍历
/**
* Returns the (non-null) Node at the specified element index.
*/
Node<E> node(int index) {
// assert isEle 大专栏 理解 LinkedListmentIndex(index);
从头遍历
if (index < (size >> 1)) {
Node<E> x = first;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++)
x = x.next;
return x;
} else {
从尾部遍历
Node<E> x = last;
for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--)
x = x.prev;
return x;
}
}
remove方法
循环遍历找到对应的节点,然后将上一个节点的next指向该节点的下一个节点。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
/**
* Removes the first occurrence of the specified element from this list,
* if it is present. If this list does not contain the element, it is
* unchanged. More formally, removes the element with the lowest index
* {@code i} such that
* <tt>(o==null ? get(i)==null : o.equals(get(i)))</tt>
* (if such an element exists). Returns {@code true} if this list
* contained the specified element (or equivalently, if this list
* changed as a result of the call).
*
* @param o element to be removed from this list, if present
* @return {@code true} if this list contained the specified element
*/
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (x.item == null) {
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
} else {
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (o.equals(x.item)) {
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
序列化
LinkedList 和 ArrayList 一样,不能通过一般方式的序列化
序列化writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
/**
* Saves the state of this {@code LinkedList} instance to a stream
* (that is, serializes it).
*
* @serialData The size of the list (the number of elements it
* contains) is emitted (int), followed by all of its
* elements (each an Object) in the proper order.
*/
private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException {
// Write out any hidden serialization magic
s.defaultWriteObject();
// Write out size
s.writeInt(size);
// Write out all elements in the proper order.
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next)
s.writeObject(x.item);
}
反序列化readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
/**
* Reconstitutes this {@code LinkedList} instance from a stream
* (that is, deserializes it).
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
// Read in any hidden serialization magic
s.defaultReadObject();
// Read in size
int size = s.readInt();
// Read in all elements in the proper order.
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
linkLast((E)s.readObject());
}
其他
LinkedList 和 ArrayList 一样,都不是线程安全的数据结构。
理解 LinkedList的更多相关文章
- 理解ArrayList与LinkedList的区别
一.先来看看ArrayList与LinkedList 在JDK中所在的位置 从图中可以看出,ArrayList与LinkedList都是List接口的实现类,因此都实现了List的所有未实现的方法,只 ...
- 深入理解ArrayList与LinkedList的区别
一.先来看看ArrayList与LinkedList 在JDK中所在的位置 从图中可以看出,ArrayList与LinkedList都是List接口的实现类,因此都实现了List的所有未实现的方法,只 ...
- 理解java容器底层原理--手动实现LinkedList
Node java 中的 LIinkedList 的数据结构是链表,而链表中每一个元素是节点. 我们先定义一下节点: package com.xzlf.collection; public class ...
- 容器--LinkedList
一.前言 上一篇我们介绍了List的重要实现之一ArrayList, 在大多数情况下,我们写代码时会直接使用到ArrayList,因为其在随机访问的优势是其它List无法比拟的.除了ArrayLis ...
- LinkedList源码分析
LinkedList也和ArrayList一样实现了List接口,但是它执行插入和删除操作时比ArrayList更加高效,因为它是基于链表的.基于链表也决定了它在随机访问方面要比ArrayList逊色 ...
- Java 集合深入理解(8):AbstractSequentialList
点击查看 Java 集合框架深入理解 系列, - ( ゜- ゜)つロ 乾杯~ 今天有点无聊,来学学 AbstractSequentialList 解解闷 吧! AbstractSequentialLi ...
- LinkedList源码浅析(jdk1.8)
LinkedList由双向链表实现的集合,因此可以从头或尾部双向循环遍历. LinkedList的操作都是对双向链表的操作,理解双向链表的数据结构就很容易理解LinkedList的实现. 双向链表由带 ...
- LinkedList 源码分析(JDK 1.8)
1.概述 LinkedList 是 Java 集合框架中一个重要的实现,其底层采用的双向链表结构.和 ArrayList 一样,LinkedList 也支持空值和重复值.由于 LinkedList 基 ...
- Java集合框架之二:LinkedList源码解析
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,转载请注明出处,欢迎交流学习! LinkedList底层是通过双向循环链表来实现的,其结构如下图所示: 链表的组成元素我们称之为节点,节点由三部分组成:前一个节点的引用地 ...
随机推荐
- typescript 使用的几种情况
接口的创建 可以使用 type 和 interface 来创建类型 type 特有的优点: 声明基本类型别名,联合类型,元组等类型 type S = string; type IFoo = IBar ...
- redhat7.0安装postgresql
安装命令 sudo yum install postgresql-server 查看安装的包 sudo yum list postgres* postgresql.x86_64 postgresql- ...
- shell脚本中的条件测试if中的-z到-d的意思
文件表达式 if [ -f file ] 如果文件存在if [ -d ... ] 如果目录存在if [ -s file ] 如果文件存在且非空 if [ -r file ] ...
- tesseract系列(4) -- tesseract训练问题总结
1. 每次训练模型删除目录下,上述重复的名字 2. 生成inttemp.pffmtable文件的时候,如果下述命令(1)不行的话,或者报错,使用命令(2) (1)mftraining -F font_ ...
- 从 0 到 1 到完美,写一个 js 库、node 库、前端组件库
之前讲了很多关于项目工程化.前端架构.前端构建等方面的技术,这次说说怎么写一个完美的第三方库. 1. 选择合适的规范来写代码 js 模块化的发展大致有这样一个过程 iife => commonj ...
- redis维护节点常用操作
维护节点 添加主节点 hash槽重新分配 添加从节点 删除结点 1 添加主节点 集群创建成功后可以向集群中添加节点,下面是添加一个master主节点 添加7007结点作为新节点 执行命令:./redi ...
- Sequence Diagram时序图 - 应该是最简洁有力的业务了
直接看UML吧,一目了然,不用解释.自信男人,无须多言. 这是用ListView显示Post的流程. 这是Uppdate User Profile的流程.自信男人,无须多言.
- A. Coffee Break(思维题,类似于邻接表的head数组用法)
题:https://codeforces.com/gym/101911/problem/A 题意:每天工作m分钟,每次喝coffee得间隔d分钟,然后给出n个数,每个数表示想在一天中的a[i]的时刻喝 ...
- day15-接口类
# 一.接口类的作用是规范它的子类,跟后面学习的接口没关系. from abc import abstractmethod,ABCMeta class Pay(metaclass=ABCMeta): ...
- 3dmax2017卸载/安装失败/如何彻底卸载清除干净3dmax2017注册表和文件的方法
3dmax2017提示安装未完成,某些产品无法安装该怎样解决呢?一些朋友在win7或者win10系统下安装3dmax2017失败提示3dmax2017安装未完成,某些产品无法安装,也有时候想重新安装3 ...
