Zabbix数据库表分区
zabbix的监控主机数量将近300,且运行了一年时间了,最近zabbix server服务监控历史数据等服务不断自身告警、查询性能也变得很低
关于历史数据的两个参数,在zabbix server的配置文件中
可以选择关闭housekeeper禁止自动定期清除历史记录数据,因为对于大数据的删除会直接影响zabbix的性能、或者调整相应参数
HousekeepingFrequency
取值范围:0-24
默认值:1
说明:housekeep执行频率,默认每小时回去删除一些过期数据。如果server重启,那么30分钟之后才执行一次,接下来,每隔一小时在执行一次。
MaxHousekeeperDelete
取值范围: 0-1000000
默认值:5000
housekeeping一次删除的数据不能大于MaxHousekeeperDelete
数据库优化
一、设置独立表空间(innodb_file_per_table=1) # 5.6版本以上自动开启 以上版本跳过这一段
1、清空history数据
[root@Zabbix-Server ~]# mysql -u zabbix -p MariaDB [(none)]> use zabbix;
Reading table information for completion of table and column names
You can turn off this feature to get a quicker startup with -A Database changed
MariaDB [zabbix]>
MariaDB [zabbix]> truncate table history;
Query OK, rows affected (0.19 sec) MariaDB [zabbix]> optimize table history;
+----------------+----------+----------+-------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Table | Op | Msg_type | Msg_text |
+----------------+----------+----------+-------------------------------------------------------------------+
| zabbix.history | optimize | note | Table does not support optimize, doing recreate + analyze instead |
| zabbix.history | optimize | status | OK |
+----------------+----------+----------+-------------------------------------------------------------------+
rows in set (0.81 sec) MariaDB [zabbix]> truncate table history_str;
Query OK, rows affected (0.05 sec) MariaDB [zabbix]> truncate table history_uint;
Query OK, rows affected (6.32 sec)
2、修改表结构
MariaDB [(none)]> use zabbix;
Reading table information for completion of table and column names
You can turn off this feature to get a quicker startup with -A Database changed
MariaDB [zabbix]> Alter table history_text drop primary key, add index (id), drop index history_text_2, add index history_text_2 (itemid, id);
Query OK, rows affected (1.11 sec)
Records: Duplicates: Warnings: MariaDB [zabbix]> Alter table history_log drop primary key, add index (id), drop index history_log_2, add index history_log_2 (itemid, id);
Query OK, rows affected (0.14 sec)
Records: Duplicates: Warnings:
修改完之后再按照官网上的过程创建四个存储过程:
3、将官方的四个分散代码拷贝至一个文件保存为sql,导入数据库;
cat /root/zabbix-partition.sql
DELIMITER $$
CREATE PROCEDURE `partition_create`(SCHEMANAME varchar(), TABLENAME varchar(), PARTITIONNAME varchar(), CLOCK int)
BEGIN
/*
SCHEMANAME = The DB schema in which to make changes
TABLENAME = The table with partitions to potentially delete
PARTITIONNAME = The name of the partition to create
*/
/*
Verify that the partition does not already exist
*/ DECLARE RETROWS INT;
SELECT COUNT() INTO RETROWS
FROM information_schema.partitions
WHERE table_schema = SCHEMANAME AND table_name = TABLENAME AND partition_description >= CLOCK; IF RETROWS = THEN
/*
1. Print a message indicating that a partition was created.
2. Create the SQL to create the partition.
3. Execute the SQL from #2.
*/
SELECT CONCAT( "partition_create(", SCHEMANAME, ",", TABLENAME, ",", PARTITIONNAME, ",", CLOCK, ")" ) AS msg;
SET @sql = CONCAT( 'ALTER TABLE ', SCHEMANAME, '.', TABLENAME, ' ADD PARTITION (PARTITION ', PARTITIONNAME, ' VALUES LESS THAN (', CLOCK, '));' );
PREPARE STMT FROM @sql;
EXECUTE STMT;
DEALLOCATE PREPARE STMT;
END IF;
END$$
DELIMITER ; DELIMITER $$
CREATE PROCEDURE `partition_drop`(SCHEMANAME VARCHAR(), TABLENAME VARCHAR(), DELETE_BELOW_PARTITION_DATE BIGINT)
BEGIN
/*
SCHEMANAME = The DB schema in which to make changes
TABLENAME = The table with partitions to potentially delete
DELETE_BELOW_PARTITION_DATE = Delete any partitions with names that are dates older than this one (yyyy-mm-dd)
*/
DECLARE done INT DEFAULT FALSE;
DECLARE drop_part_name VARCHAR(); /*
Get a list of all the partitions that are older than the date
in DELETE_BELOW_PARTITION_DATE. All partitions are prefixed with
a "p", so use SUBSTRING TO get rid of that character.
*/
DECLARE myCursor CURSOR FOR
SELECT partition_name
FROM information_schema.partitions
WHERE table_schema = SCHEMANAME AND table_name = TABLENAME AND CAST(SUBSTRING(partition_name FROM ) AS UNSIGNED) < DELETE_BELOW_PARTITION_DATE;
DECLARE CONTINUE HANDLER FOR NOT FOUND SET done = TRUE; /*
Create the basics for when we need to drop the partition. Also, create
@drop_partitions to hold a comma-delimited list of all partitions that
should be deleted.
*/
SET @alter_header = CONCAT("ALTER TABLE ", SCHEMANAME, ".", TABLENAME, " DROP PARTITION ");
SET @drop_partitions = ""; /*
Start looping through all the partitions that are too old.
*/
OPEN myCursor;
read_loop: LOOP
FETCH myCursor INTO drop_part_name;
IF done THEN
LEAVE read_loop;
END IF;
SET @drop_partitions = IF(@drop_partitions = "", drop_part_name, CONCAT(@drop_partitions, ",", drop_part_name));
END LOOP;
IF @drop_partitions != "" THEN
/*
1. Build the SQL to drop all the necessary partitions.
2. Run the SQL to drop the partitions.
3. Print out the table partitions that were deleted.
*/
SET @full_sql = CONCAT(@alter_header, @drop_partitions, ";");
PREPARE STMT FROM @full_sql;
EXECUTE STMT;
DEALLOCATE PREPARE STMT; SELECT CONCAT(SCHEMANAME, ".", TABLENAME) AS `table`, @drop_partitions AS `partitions_deleted`;
ELSE
/*
No partitions are being deleted, so print out "N/A" (Not applicable) to indicate
that no changes were made.
*/
SELECT CONCAT(SCHEMANAME, ".", TABLENAME) AS `table`, "N/A" AS `partitions_deleted`;
END IF;
END$$
DELIMITER ; DELIMITER $$
CREATE PROCEDURE `partition_maintenance`(SCHEMA_NAME VARCHAR(), TABLE_NAME VARCHAR(), KEEP_DATA_DAYS INT, HOURLY_INTERVAL INT, CREATE_NEXT_INTERVALS INT)
BEGIN
DECLARE OLDER_THAN_PARTITION_DATE VARCHAR();
DECLARE PARTITION_NAME VARCHAR();
DECLARE OLD_PARTITION_NAME VARCHAR();
DECLARE LESS_THAN_TIMESTAMP INT;
DECLARE CUR_TIME INT; CALL partition_verify(SCHEMA_NAME, TABLE_NAME, HOURLY_INTERVAL);
SET CUR_TIME = UNIX_TIMESTAMP(DATE_FORMAT(NOW(), '%Y-%m-%d 00:00:00')); SET @__interval = ;
create_loop: LOOP
IF @__interval > CREATE_NEXT_INTERVALS THEN
LEAVE create_loop;
END IF; SET LESS_THAN_TIMESTAMP = CUR_TIME + (HOURLY_INTERVAL * @__interval * );
SET PARTITION_NAME = FROM_UNIXTIME(CUR_TIME + HOURLY_INTERVAL * (@__interval - ) * , 'p%Y%m%d%H00');
IF(PARTITION_NAME != OLD_PARTITION_NAME) THEN
CALL partition_create(SCHEMA_NAME, TABLE_NAME, PARTITION_NAME, LESS_THAN_TIMESTAMP);
END IF;
SET @__interval=@__interval+;
SET OLD_PARTITION_NAME = PARTITION_NAME;
END LOOP; SET OLDER_THAN_PARTITION_DATE=DATE_FORMAT(DATE_SUB(NOW(), INTERVAL KEEP_DATA_DAYS DAY), '%Y%m%d0000');
CALL partition_drop(SCHEMA_NAME, TABLE_NAME, OLDER_THAN_PARTITION_DATE); END$$
DELIMITER ; DELIMITER $$
CREATE PROCEDURE `partition_verify`(SCHEMANAME VARCHAR(), TABLENAME VARCHAR(), HOURLYINTERVAL INT())
BEGIN
DECLARE PARTITION_NAME VARCHAR();
DECLARE RETROWS INT();
DECLARE FUTURE_TIMESTAMP TIMESTAMP; /*
* Check if any partitions exist for the given SCHEMANAME.TABLENAME.
*/
SELECT COUNT() INTO RETROWS
FROM information_schema.partitions
WHERE table_schema = SCHEMANAME AND table_name = TABLENAME AND partition_name IS NULL; /*
* If partitions do not exist, go ahead and partition the table
*/
IF RETROWS = THEN
/*
* Take the current date at 00:00:00 and add HOURLYINTERVAL to it. This is the timestamp below which we will store values.
* We begin partitioning based on the beginning of a day. This is because we don't want to generate a random partition
* that won't necessarily fall in line with the desired partition naming (ie: if the hour interval is 24 hours, we could
* end up creating a partition now named "p201403270600" when all other partitions will be like "p201403280000").
*/
SET FUTURE_TIMESTAMP = TIMESTAMPADD(HOUR, HOURLYINTERVAL, CONCAT(CURDATE(), " ", '00:00:00'));
SET PARTITION_NAME = DATE_FORMAT(CURDATE(), 'p%Y%m%d%H00'); -- Create the partitioning query
SET @__PARTITION_SQL = CONCAT("ALTER TABLE ", SCHEMANAME, ".", TABLENAME, " PARTITION BY RANGE(`clock`)");
SET @__PARTITION_SQL = CONCAT(@__PARTITION_SQL, "(PARTITION ", PARTITION_NAME, " VALUES LESS THAN (", UNIX_TIMESTAMP(FUTURE_TIMESTAMP), "));"); -- Run the partitioning query
PREPARE STMT FROM @__PARTITION_SQL;
EXECUTE STMT;
DEALLOCATE PREPARE STMT;
END IF;
END$$
DELIMITER ;
[root@Zabbix-Server ~]# mysql -u zabbix -p zabbix
Enter password:
Reading table information for completion of table and column names
You can turn off this feature to get a quicker startup with -A Welcome to the MariaDB monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MariaDB connection id is
Server version: 5.5.-MariaDB MariaDB Server Copyright (c) , , Oracle, MariaDB Corporation Ab and others. Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement. MariaDB [zabbix]> use zabbix;
Database changed
MariaDB [zabbix]> source /root/zabbix-partition.sql;
Query OK, rows affected (0.04 sec) Query OK, rows affected (0.00 sec) Query OK, rows affected (0.00 sec) Query OK, rows affected (0.00 sec) MariaDB [zabbix]> CALL partition_maintenance('zabbix', 'history_log', , , );
+---------------------------------------------------------------+
| msg |
+---------------------------------------------------------------+
| partition_create(zabbix,history_log,p201801100000,) |
+---------------------------------------------------------------+
row in set (0.18 sec) +---------------------------------------------------------------+
| msg |
+---------------------------------------------------------------+
| partition_create(zabbix,history_log,p201801110000,) |
+---------------------------------------------------------------+
row in set (0.48 sec) +---------------------------------------------------------------+
| msg |
+---------------------------------------------------------------+
| partition_create(zabbix,history_log,p201801120000,) |
+---------------------------------------------------------------+
row in set (0.67 sec) +---------------------------------------------------------------+
| msg |
+---------------------------------------------------------------+
| partition_create(zabbix,history_log,p201801130000,) |
+---------------------------------------------------------------+
row in set (1.02 sec) +---------------------------------------------------------------+
| msg |
+---------------------------------------------------------------+
| partition_create(zabbix,history_log,p201801140000,) |
+---------------------------------------------------------------+
row in set (1.22 sec) +---------------------------------------------------------------+
| msg |
+---------------------------------------------------------------+
| partition_create(zabbix,history_log,p201801150000,) |
+---------------------------------------------------------------+
row in set (1.44 sec) +---------------------------------------------------------------+
| msg |
+---------------------------------------------------------------+
| partition_create(zabbix,history_log,p201801160000,) |
+---------------------------------------------------------------+
row in set (1.64 sec) +---------------------------------------------------------------+
| msg |
+---------------------------------------------------------------+
| partition_create(zabbix,history_log,p201801170000,) |
+---------------------------------------------------------------+
row in set (1.85 sec) +---------------------------------------------------------------+
| msg |
+---------------------------------------------------------------+
| partition_create(zabbix,history_log,p201801180000,) |
+---------------------------------------------------------------+
row in set (2.04 sec) +---------------------------------------------------------------+
| msg |
+---------------------------------------------------------------+
| partition_create(zabbix,history_log,p201801190000,) |
+---------------------------------------------------------------+
row in set (2.23 sec) +---------------------------------------------------------------+
| msg |
+---------------------------------------------------------------+
| partition_create(zabbix,history_log,p201801200000,) |
+---------------------------------------------------------------+
row in set (2.42 sec) +---------------------------------------------------------------+
| msg |
+---------------------------------------------------------------+
| partition_create(zabbix,history_log,p201801210000,) |
+---------------------------------------------------------------+
row in set (2.62 sec) +---------------------------------------------------------------+
| msg |
+---------------------------------------------------------------+
| partition_create(zabbix,history_log,p201801220000,) |
+---------------------------------------------------------------+
row in set (2.85 sec) +--------------------+--------------------+
| table | partitions_deleted |
+--------------------+--------------------+
| zabbix.history_log | N/A |
+--------------------+--------------------+
row in set (3.10 sec) Query OK, rows affected, warning (3.10 sec)
4、对想要分区的表进行表分区
DELIMITER $$
CREATE PROCEDURE `partition_maintenance_all`(SCHEMA_NAME VARCHAR())
BEGIN
CALL partition_maintenance(SCHEMA_NAME, 'history', , , );
CALL partition_maintenance(SCHEMA_NAME, 'history_log', , , );
CALL partition_maintenance(SCHEMA_NAME, 'history_str', , , );
CALL partition_maintenance(SCHEMA_NAME, 'history_text', , , );
CALL partition_maintenance(SCHEMA_NAME, 'history_uint', , , );
CALL partition_maintenance(SCHEMA_NAME, 'trends', , , );
CALL partition_maintenance(SCHEMA_NAME, 'trends_uint', , , );
END$$
DELIMITER ;
以上代码部分的含义为(库名,表名,保存多少天的数据,每隔多久生成一个分区,本次生成多少分区)
mysql> source /root/partition_maintenance_all.sql;
Query OK, rows affected (0.00 sec) mysql> CALL partition_maintenance_all('zabbix');
5、Housekeeper 设置
Zabbix用户界面中的 "Administration" -> "部分提供了所有选项。确保在右上角的下拉列表中选择"Housekeeping" 您应该看到类似于以下的屏幕:
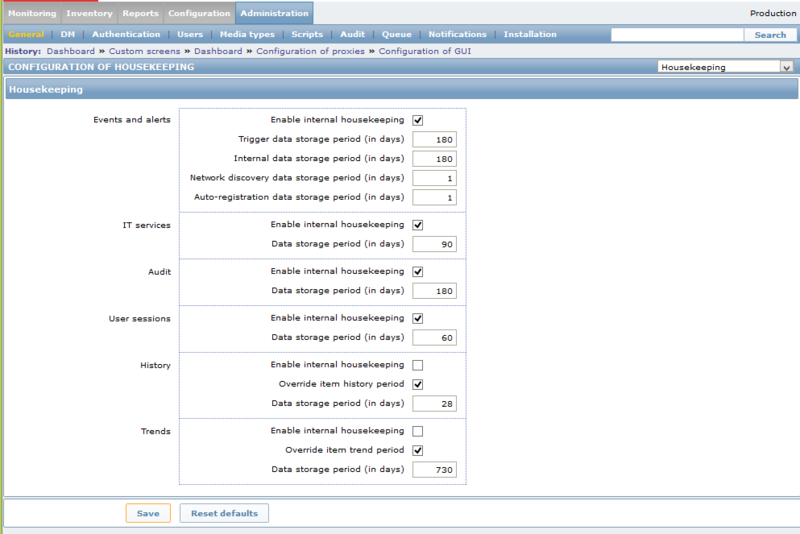
- 确保“历史”和“趋势”两个选项的“启用内部管理”复选框未被选中。
- 确保历史和趋势的检查标题为“覆盖项目<趋势/历史>期间”复选框。
- 将历史和趋势的“数据存储期限(天数)”框设置为您保留两者的时间。在上面给出的表分区中,正确的值是7和365。
6、加入计划任务
不要让数据库用完你的分区,上面示例是如何创建14天额外分区的,在第15天,数据库将无法粘贴历史/趋势数据,因此会发生数据丢失。
所以每隔一段时间(通过cron或其他方法)重新运行这些存储过程。通过这样做,分区将始终存在,可以插入数据。
#Q-2018-1/9
30 4 * * 1 /usr/bin/mysql -uzabbix -pzabbix -e "use zabbix;" -e "CALL partition_maintenance_all('zabbix');"
实际在生产环境中上述操作运行一段时间后,Zabbix server的log文件会报如下错误,events表主键重复、主键不能自动增长、导致zabbix不能告警
::213930.461 [Z3005] query failed: [] Duplicate entry '' for key 'PRIMARY' [insert into events (eventid,source,object,objectid,clock,ns,value) values (,,,,,,);
可以使用如下命令删除events记录
[root@Zabbix-Server zabbix]# mysql -u zabbix -pzabbix -e "use zabbix;" -e 'delete from events';
如果想要删除表的所有数据,truncate语句要比 delete 语句快。
因为 truncate 删除了表,然后根据表结构重新建立它,而 delete 删除的是记录,并没有尝试去修改表。
不过truncate命令虽然快,却不像delete命令那样对事务处理是安全的。
另外注意的是mysql数据库清空表默认是不回收空间的(对应步骤1)
回收表空间的命令
optimize table history
optimize table history_uint
针对MySQL的不同数据库存储引擎,在optimize使用清除碎片,回收闲置的数据库空间,把分散存储(fragmented)的数据和索引重新挪到一起(defragmentation),对I/O速度有好处。
当然optimize在对表进行操作的时候,会加锁,所以不宜经常在程序中调用。可以参考http://www.cnblogs.com/w787815/p/8433548.html
zabbix社区文档参考
https://www.zabbix.org/wiki/Docs/howto/mysql_partition
Zabbix数据库表分区的更多相关文章
- zabbix(4)数据库表分区优化
一.zabbix 数据库存储 zabbix-server将采集到的数据存储在数据库(mysql.oracle等),而数据存储的大小与每秒处理的数量量有关,因此数据存储取决于以下两个因数: (1)Req ...
- 千万级SQL Server数据库表分区的实现
千万级SQL Server数据库表分区的实现 2010-09-10 13:37 佚名 数据库 字号:T | T 一般在千万级的数据压力下,分区是一种比较好的提升性能方法.本文将介绍SQL Server ...
- 15.5 自学Zabbix之路15.5 Zabbix数据库表结构简单解析-其他 表
点击返回:自学Zabbix之路 自学Zabbix之路15.5 Zabbix数据库表结构简单解析-其他 表 1. Actions表 actions表记录了当触发器触发时,需要采用的动作. 2.Aler ...
- Oracle数据库表分区
一.Oracle数据库表分区概念和理解 1.1.已经存在的表没有方法可以直接转化为分区表. 1.2.不在分区字段上建立分区索引,在别的字段上建立索引相当于全局索引.效率 ...
- 自学Zabbix之路15.1 Zabbix数据库表结构简单解析-Hosts表、Hosts_groups表、Interface表
点击返回:自学Zabbix之路 点击返回:自学Zabbix4.0之路 点击返回:自学zabbix集锦 自学Zabbix之路15.1 Zabbix数据库表结构简单解析-Hosts表.Hosts_grou ...
- 自学Zabbix之路15.2 Zabbix数据库表结构简单解析-Items表
点击返回:自学Zabbix之路 点击返回:自学Zabbix4.0之路 点击返回:自学zabbix集锦 自学Zabbix之路15.2 Zabbix数据库表结构简单解析-Items表 Items表记录了i ...
- 自学Zabbix之路15.3 Zabbix数据库表结构简单解析-Triggers表、Applications表、 Mapplings表
点击返回:自学Zabbix之路 点击返回:自学Zabbix4.0之路 点击返回:自学zabbix集锦 自学Zabbix之路15.3 Zabbix数据库表结构简单解析-Triggers表.Applica ...
- 自学Zabbix之路15.4 Zabbix数据库表结构简单解析-Expressions表、Media表、 Events表
点击返回:自学Zabbix之路 点击返回:自学Zabbix4.0之路 点击返回:自学zabbix集锦 自学Zabbix之路15.4 Zabbix数据库表结构简单解析-Expressions表.Medi ...
- 自学Zabbix之路15.5 Zabbix数据库表结构简单解析-其他 表
点击返回:自学Zabbix之路 点击返回:自学Zabbix4.0之路 点击返回:自学zabbix集锦 自学Zabbix之路15.5 Zabbix数据库表结构简单解析-其他 表 1. Actions表 ...
随机推荐
- 「SpringBoot」如何优雅地管理SpringBoot项目
本文主要讲述一下如何优雅地管理SpringBoot项目. 背景 课堂上,当小明形如流水地回答完沐芳老师提出来的问题时,却被至今没有对象的胖虎无情嘲讽了? 沐芳老师:小明,你平时是如何启动.停止你的Sp ...
- TCP漫谈之keepalive和time_wait
TCP是一个有状态通讯协议,所谓的有状态是指通信过程中通信的双方各自维护连接的状态. 一.TCP keepalive 先简单回顾一下TCP连接建立和断开的整个过程.(这里主要考虑主流程,关于丢包.拥塞 ...
- 利用Python批量重命名文件夹下文件
#!/usr/bin/python # -*- coding: UTF-8 -*- # -*- coding:utf8 -*- import os from string import digits ...
- MetaQNN : 与Google同场竞技,MIT提出基于Q-Learning的神经网络搜索 | ICLR 2017
论文提出MetaQNN,基于Q-Learning的神经网络架构搜索,将优化视觉缩小到单层上,相对于Google Brain的NAS方法着眼与整个网络进行优化,虽然准确率差了2-3%,但搜索过程要简单地 ...
- 10年阿里自动化测试架构师帮您收集的:git常用命令大全以及git原理图【泣血推荐,建议收藏】
一.Git分布式版本控制简介 Git 是一个很强大的分布式版本控制系统.它不但适用于管理大型开源软件的源代码,管理私人的文档和源代码也有很多优势.本来想着只把最有用.最常用的 Git 命令记下来, ...
- .gitattributes
.gitattributes文件是一个文本文件,文件中的一行定义一个路径的若干属性.以行为单位设置一个路径下所有文件的属性,格式如下: 要匹配的文件模式 属性1 属性2 GRLF和LF CRLF,LF ...
- qW3xT.2,解决挖矿病毒
在阿里云使用redis,开启了6379端口,但是当时并没有对redis的密码进行设置. 在晚上一点左右.阿里云给我发短信,告诉我服务器出现紧急安全事件.建议登录云盾-态势感知控制台查看详情和处理. 于 ...
- docker 容器容器之间网络通信 docker-compose.yaml 配置固定ip
1.创建自己的桥接网络 $ docker network create --subnet=172.18.0.0/16 mynetwork 2.docker-compose.yaml 文件格式demo ...
- Shell脚本的编写及测试
Shell脚本的编写及测试 1.1问题 本例要求两个简单的Shell脚本程序,任务目标如下: 编写一 ...
- Windows 手动安装 Apache24 web服务器
文章更新于:2020-02-18 按照惯例,需要的文件附上链接放在文首 文件名:httpd-2.4.41-o111c-x64-vc15-r2.7z 文件大小:6.1MB 下载链接:https://ww ...
