Python学习笔记:装饰器
Python 装饰器的基本概念和应用
- 代码编写要遵循开放封闭原则,虽然在这个原则是用的面向对象开发,但是也适用于函数式编程,简单来说,它规定已经实现的功能代码不允许被修改,但可以被扩展,即:
- 封闭:已实现的功能代码块
- 开放:对扩展开发
装饰器是 Python 高阶函数的语法糖,可以为已经存在的对象添加额外的功能,比如:
- 引入日志
- 函数执行时间统计
- 执行函数前预备处理
- 执行函数后清理功能
- 权限校验等场景
- 缓存
Python 装饰器的基本实现
装饰器的例程:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
#-*- coding:utf-8 -*-
#File Name:04_decorator_simple.py
#Created Time:2019-01-09 15:24:38 import time def timefun(func):
# wrapped_fun 即为闭包, func 为要装饰的函数
def wrapped_fun():
start_time = time.time()
func()
end_time = time.time()
print("%s\t运行用时 %f s" % (func.__name__, end_time - start_time))
return wrapped_fun # 返回内部函数的引用 def foo1():
for i in range(10000):
pass @timefun # 相当于 foo = timefun(foo)
def foo():
for i in range(100000):
pass if __name__ == "__main__":
foo1 = timefun(foo1)
foo1()
foo()
装饰器例程
foo1 运行用时 0.000491 s
foo 运行用时 0.002976 s
装饰器例程的运行结果
运行过程分析见下图:

Python 装饰器实现的基础为闭包,其会在闭包中调用目标函数,关于闭馆的详细内容,请参考 Python 学习笔记:闭包
Python 装饰器的使用
多个装饰器
#!/usr/bin/env python3
#-*- coding:utf-8 -*-
#File Name:05_decorator_multi.py
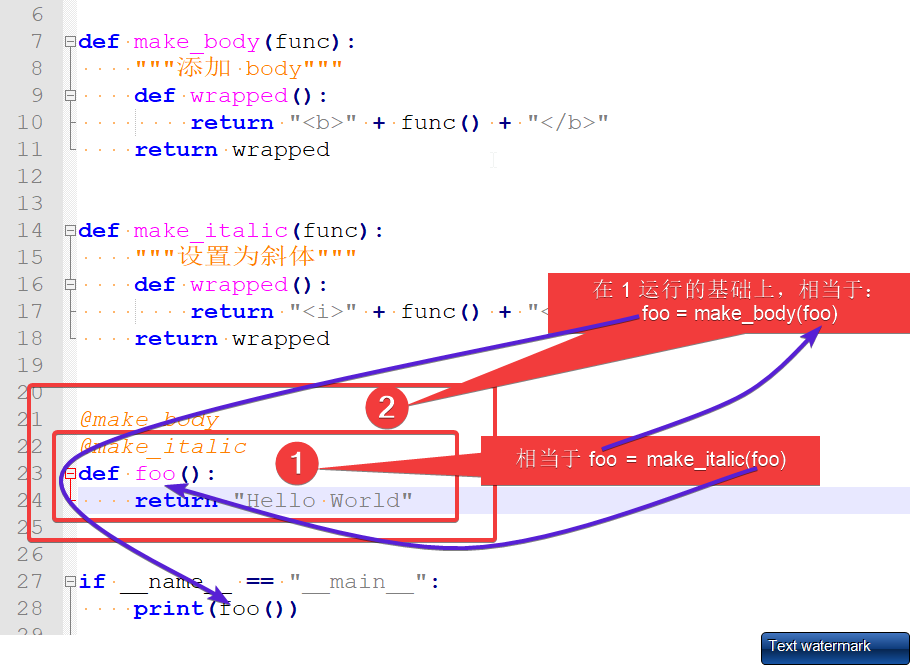
#Created Time:2019-01-09 15:55:31 def make_body(func):
"""添加 body"""
def wrapped():
return "<b>" + func() + "</b>"
return wrapped def make_italic(func):
"""设置为斜体"""
def wrapped():
return "<i>" + func() + "</i>"
return wrapped # 相当于 make_body(make_italic(foo))
@make_body
@make_italic
def foo():
return "Hello World" def foo1():
return "Hello Python" if __name__ == "__main__":
print(foo())
foo1 = make_body(make_italic(foo1))
print(foo1())
01 多个装饰器
<b><i>Hello World</i></b>
<b><i>Hello Python</i></b>
01 多个装饰器——运行结果
多个装饰器的运行过程分析:
含有不定长参数
#!/usr/bin/env python3
#-*- coding:utf-8 -*-
#File Name:06_decorator_multi_var.py
#Created Time:2019-01-09 16:20:30 from time import ctime def timefun(func):
def wrapped_func(*args, **kwargs):
print("%s called at %s" % (func.__name__, ctime()))
print("wrapped_func: ", end="")
print(args, kwargs)
func(*args, **kwargs) # 拆包
return wrapped_func @timefun
def foo(a,b,*args, **kwargs):
print("foo: %s, %s, %s, %s" %(a, b, args, kwargs)) if __name__ == "__main__":
foo(1,2,3,4,5, tmp=2)
02 含有不定长参数
foo called at Wed Jan 9 16:32:48 2019
wrapped_func: (1, 2, 3, 4, 5) {'tmp': 2}
foo: 1, 2, (3, 4, 5), {'tmp': 2}
02 含有不定长参数——运行结果
带有返回值
#!/usr/bin/env python3
#-*- coding:utf-8 -*-
#File Name: 07_decorator_multi_retrun.py
#Created Time:2019-01-09 16:20:30 from time import ctime def timefun(func):
def wrapped_func(*args, **kwargs):
print("%s called at %s" % (func.__name__, ctime()))
print("wrapped_func: ", end="")
print(args, kwargs)
return func(*args, **kwargs) # 此处如何没有 return,则26行会输出 None
return wrapped_func @timefun
def foo(a,b,*args, **kwargs):
print("foo: %s, %s, %s, %s" %(a, b, args, kwargs))
return "Hello world!" if __name__ == "__main__":
print(foo(1,2,3,4,5, tmp=2))
03带有返回值
foo called at Wed Jan 9 16:38:05 2019
wrapped_func: (1, 2, 3, 4, 5) {'tmp': 2}
foo: 1, 2, (3, 4, 5), {'tmp': 2}
Hello world!
03带有返回值——运行结果
装饰器中设置外部变量
#!/usr/bin/env python3
#-*- coding:utf-8 -*-
#File Name: 08_decorator_outside_var.py
#Created Time:2019-01-09 16:20:30 def timefun_arg(outside_var="Hello"):
def timefun(func):
def wrapped_func(*args, **kwargs):
print("wrapped_func: %s" % outside_var)
return func(*args, **kwargs)
return wrapped_func
return timefun @timefun_arg()
def foo(a,b,*args, **kwargs):
return "foo: Hello world!" @timefun_arg("Python") # 相当于 foo1 = timefun_arg("Python")(foo1)
def foo1(a,b,*args, **kwargs):
return "foo1: Hello world!" if __name__ == "__main__":
print(foo(1,2,3,4,5, tmp=2))
print(foo1(1,2,3,4,5, tmp=2))
04 装饰器中设置外部变量
定义多层函数,相当于双层的装饰器。
wrapped_func: Hello
foo: Hello world!
wrapped_func: Python
foo1: Hello world!
04装饰器中设置外部变量——运行结果
类装饰器
#!/usr/bin/env python3
#-*- coding:utf-8 -*-
#File Name:09_decorator_class.py
#Created Time:2019-01-09 16:53:33 class Test(object):
def __init__(self, func):
print("******初始化******")
print("Called by %s." % func.__name__)
self.func = func def __call__(self):
return self.func() @Test # 相当于 foo = Test(foo)
def foo():
return "Hello world!" def foo1():
return "Hello python!" if __name__ == "__main__":
print(foo())
foo1 = Test(foo1)
print(foo1())
05 类装饰器
类对象借助 __call__() 魔术方法,即可实现相应的类装饰器
******初始化******
Called by foo.
Hello world!
******初始化******
Called by foo1.
Hello python!
05 类装饰器运行结果
Python学习笔记:装饰器的更多相关文章
- python学习笔记--装饰器
1.首先是一个很无聊的函数,实现了两个数的加法运算: def f(x,y): print x+y f(2,3) 输出结果也ok 5 2.可是这时候我们感觉输出结果太单一了点,想让代码的输出多一点看起来 ...
- Python学习笔记--装饰器的实验
装饰器既然可以增加原来函数的功能,那能不能改变传给原函数的参数呢? 我们实验一下,先上代码: #!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # @Date ...
- Python学习笔记: 装饰器Decorator
介绍 装饰器是对功能函数的加强. 在原来的功能函数之外,另外定义一个装饰器函数,对原来的功能函数进行封装(wrapper)并在wrapper的过程中增加一些辅助功能. 应用场景 如下场景: 业务函数f ...
- python 学习分享-装饰器篇
本篇内容为偷窃的~哈哈,借用一下,我就是放在自己这里好看. 引用地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/rhcad/archive/2011/12/21/2295507.html 第一步: ...
- python学习之装饰器-
python的装饰器 2018-02-26 在了解python的装饰器之前我们得了解python的高阶函数 python的高阶函数我们能返回一个函数名并且能将函数名作为参数传递 def outer() ...
- python学习day14 装饰器(二)&模块
装饰器(二)&模块 #普通装饰器基本格式 def wrapper(func): def inner(): pass return func() return inner def func(): ...
- Python学习 :装饰器
装饰器(函数) 装饰器作为一个函数,可以为其他函数在不修改原函数代码的前提下添加新的功能 装饰器的返回值是一个函数对象.它经常用于有切面需求的场景,比如:插入日志.性能测试.事务处理.缓存.权限校验等 ...
- python学习之-- 装饰器
高阶函数+嵌套函数 == 装饰器 什么是装饰器: 其实也是一个函数. 功能:为其他的函数添加附加功能 原则:不能修改被装饰的函数的源代码和调用方式 学习装饰器前首先要明白以下3条事项: 1:函数 即 ...
- 6月4日 python学习总结 装饰器复习
1. 装饰器的原理以及为什么要使用装饰器 在代码运行期间动态增加功能的方式,称之为"装饰器"(Decorator). 在不影响原代码结构的情况下为其添加功能 2. 装饰器的基本 ...
- 学习笔记——装饰器模式Decorator
装饰器模式,最典型的例子. 工厂新开了流水线,生产了手机外壳,蓝天白云花色.刚准备出厂,客户说还要印奶牛在上面,WTF…… 时间上来不及,成本也不允许销毁了重来,怎么办?弄来一机器A,专门在蓝天白云的 ...
随机推荐
- Java中的Enum(枚举)用法介绍
1. 关于Java Enum:学过C/C++等语言的人,应该都对Enum类型略知一二.Enum一般用来表示一组相同类型的常量.如性别.日期.月份.颜色等.对这些属性用常量的好处是显而易见的,不仅可以保 ...
- android 开发-ListView与ScrollView事件冲突处理(事件分发机制处理)
ListView和ScrollView都存在滚动的效果,所以一般不建议listView和scrollView进行嵌套使用,但有些需求则需要用到两者嵌套.在android的学习中学了一种事件分发处理机制 ...
- Centos6.8 Mysql5.6 安装配置教程
MySQL是一个关系型数据库管理系统,由瑞典MySQL AB 公司开发,目前属于 Oracle 旗下产品.MySQL 最流行的关系型数据库管理系统,在 WEB 应用方面MySQL是最好的 RDBMS ...
- jquery进阶(1)
今天我们接着来学习jQuery中的内容,包括css的操作.尺寸的操作.文档的操作.动画(有待补充),事件处理操作. 一.CSS 在css中可以设置css的基本属性 - .css("color ...
- UPDATE SQL 不同环境执行结果不一样
背景:1.前台:JQUERY 提交数据 2.后台:OWIN C# 处理接收数据 3.数据库: postgresql ========================================= ...
- $(formName).data(“bootstrapValidator”).getFieldElements('fieldName'); 校验单个字段
问题也出自于业务系统后台,应该来说也比较常见吧 房产类型分为一抵和二抵,二抵的时候用户必须填写一抵债权金额,一抵的时候则不显示一抵债权金额也不校验,因为我所有的校验都是写在标签上,哪些必填直接写在标签 ...
- 页面中引入百度地图,实例化后影响html5的表单元素date的上下箭头
复现步骤: 使用百度地图的JavaScript的API,引入文件地址"http://api.map.baidu.com/api?key=&v=1.1&services=tru ...
- 【MFC】MFCMenuButton 的用法
背景:因为对话框界面上的空间有限,为了节省空间,我决定采用一个MFCMenuButton用来实现同一类按钮事件.本来我打算设置两个按钮:“单个删除文件”和“清空所有文件”两个按钮,但是空间太小,而且这 ...
- centOS7虚拟机和本机ping通
1.配置centOS虚拟机网卡 先设置桥接模式 此处的address要和本机的vmware在同一个网段 2.重启centOS网卡 3.关闭本机和虚拟机防火墙,防止ping不通 centOS命令: fi ...
- sk-learning(1)
sk-learning学习笔记(1) 简介 scikit learning 是一个python的机器学习库,内置许多机器学习的算法诸如svm.随机森林.逻辑回归.贝叶斯网络等算法.覆盖了分类.聚类.回 ...
