vue组件初始化过程
之前文章有写到vue构造函数的实例化过程,只是对vue实例做了个粗略的描述,并没有说明vue组件实例化的过程。本文主要对vue组件的实例化过程做一些简要的描述。
组件的实例化与vue构造函数的实例化,大部分是类似的,vue的实例可以当做一个根组件,普通组件的实例化可以当做子组件。真实的DOM是一个树形结构,虚拟DOM本质只是真实DOM的抽象,也是一个树形结构。简单来说,整个vue工程的实例化过程如下:
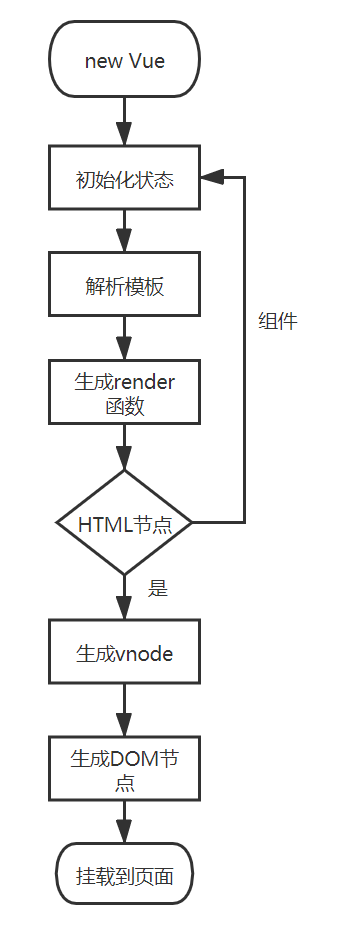
如上图所示,在调用render函数时,会依次调用createElement方法,createElement方法的代码如下,主要作用就是生成vnode。
export function _createElement (
context: Component,
tag?: string | Class<Component> | Function | Object,
data?: VNodeData,
children?: any,
normalizationType?: number
): VNode | Array<VNode> {
if (isDef(data) && isDef((data: any).__ob__)) {
process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && warn(
`Avoid using observed data object as vnode data: ${JSON.stringify(data)}\n` +
'Always create fresh vnode data objects in each render!',
context
)
return createEmptyVNode()
}
// object syntax in v-bind
if (isDef(data) && isDef(data.is)) {
tag = data.is
}
if (!tag) {
// in case of component :is set to falsy value
return createEmptyVNode()
}
// warn against non-primitive key
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' &&
isDef(data) && isDef(data.key) && !isPrimitive(data.key)
) {
if (!__WEEX__ || !('@binding' in data.key)) {
warn(
'Avoid using non-primitive value as key, ' +
'use string/number value instead.',
context
)
}
}
// support single function children as default scoped slot
if (Array.isArray(children) &&
typeof children[0] === 'function'
) {
data = data || {}
data.scopedSlots = { default: children[0] }
children.length = 0
}
// 组件格式化
if (normalizationType === ALWAYS_NORMALIZE) {
children = normalizeChildren(children)
} else if (normalizationType === SIMPLE_NORMALIZE) {
children = simpleNormalizeChildren(children)
}
let vnode, ns
if (typeof tag === 'string') {
let Ctor
ns = (context.$vnode && context.$vnode.ns) || config.getTagNamespace(tag)
// 普通的HTML标签
if (config.isReservedTag(tag)) {
// platform built-in elements
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && isDef(data) && isDef(data.nativeOn)) {
warn(
`The .native modifier for v-on is only valid on components but it was used on <${tag}>.`,
context
)
}
// 创建一个普通的DOM节点
vnode = new VNode(
config.parsePlatformTagName(tag), data, children,
undefined, undefined, context
)
} else if ((!data || !data.pre) && isDef(Ctor = resolveAsset(context.$options, 'components', tag))) {
// component
// 创建组件
vnode = createComponent(Ctor, data, context, children, tag)
} else {
// unknown or unlisted namespaced elements
// check at runtime because it may get assigned a namespace when its
// parent normalizes children
vnode = new VNode(
tag, data, children,
undefined, undefined, context
)
}
} else {
// direct component options / constructor
vnode = createComponent(tag, data, context, children)
}
if (Array.isArray(vnode)) {
return vnode
} else if (isDef(vnode)) {
if (isDef(ns)) applyNS(vnode, ns)
if (isDef(data)) registerDeepBindings(data)
return vnode
} else {
return createEmptyVNode()
}
}
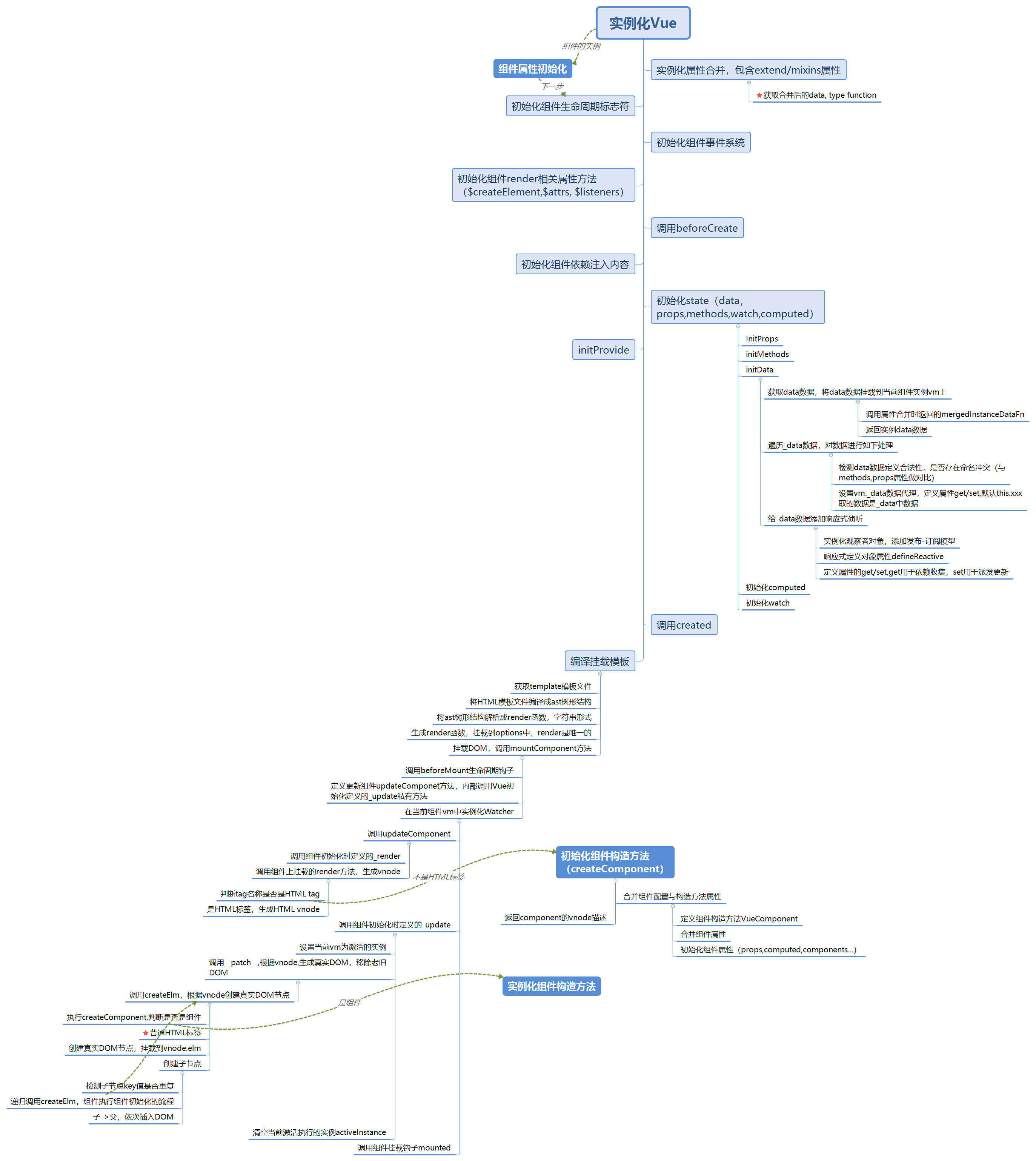
如上图所示,主流程与实例化Vue类似,只是在实例化Vue的过程中,额外走了一个创建组件的分支,其中createComponent方法实现如下:
export function createComponent (
Ctor: Class<Component> | Function | Object | void,
data: ?VNodeData,
context: Component,
children: ?Array<VNode>,
tag?: string
): VNode | Array<VNode> | void {
if (isUndef(Ctor)) {
return
}
// 获取Vue基础构造函数,在initGlobal中,将vue基础构造方法赋值给_base属性
const baseCtor = context.$options._base // plain options object: turn it into a constructor
if (isObject(Ctor)) {
// 将组件的配置,合并到构造方法中,extend是定义在Vue构造方法中的
Ctor = baseCtor.extend(Ctor)
} // if at this stage it's not a constructor or an async component factory,
// reject.
if (typeof Ctor !== 'function') {
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
warn(`Invalid Component definition: ${String(Ctor)}`, context)
}
return
} // async component
let asyncFactory
if (isUndef(Ctor.cid)) {
asyncFactory = Ctor
Ctor = resolveAsyncComponent(asyncFactory, baseCtor)
if (Ctor === undefined) {
// return a placeholder node for async component, which is rendered
// as a comment node but preserves all the raw information for the node.
// the information will be used for async server-rendering and hydration.
return createAsyncPlaceholder(
asyncFactory,
data,
context,
children,
tag
)
}
} data = data || {} // resolve constructor options in case global mixins are applied after
// component constructor creation
resolveConstructorOptions(Ctor) // transform component v-model data into props & events
if (isDef(data.model)) {
transformModel(Ctor.options, data)
} // extract props
const propsData = extractPropsFromVNodeData(data, Ctor, tag) // functional component
if (isTrue(Ctor.options.functional)) {
return createFunctionalComponent(Ctor, propsData, data, context, children)
} // extract listeners, since these needs to be treated as
// child component listeners instead of DOM listeners
const listeners = data.on
// replace with listeners with .native modifier
// so it gets processed during parent component patch.
data.on = data.nativeOn if (isTrue(Ctor.options.abstract)) {
// abstract components do not keep anything
// other than props & listeners & slot // work around flow
const slot = data.slot
data = {}
if (slot) {
data.slot = slot
}
} // install component management hooks onto the placeholder node
// 初始化组件的钩子函数
installComponentHooks(data) // return a placeholder vnode
// 体现了组件名称在这里面的作用
const name = Ctor.options.name || tag
// 创建vnode
const vnode = new VNode(
`vue-component-${Ctor.cid}${name ? `-${name}` : ''}`,
data, undefined, undefined, undefined, context,
{ Ctor, propsData, listeners, tag, children },
asyncFactory
) // Weex specific: invoke recycle-list optimized @render function for
// extracting cell-slot template.
// https://github.com/Hanks10100/weex-native-directive/tree/master/component
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (__WEEX__ && isRecyclableComponent(vnode)) {
return renderRecyclableComponentTemplate(vnode)
} return vnode
}
从上述代码中可以看出,createComponent主要作用就是返回一个vnode,中间的流程主要作用有两点,一是组装组件的构造方法,用于实例化组件,另外一点就是调用installComponentHooks,初始化组件的生命周期入口。组件的声明周期钩子虽然与vue根实例一致,但是调用的位置还是有一定的差别,具体有以下几点:
1. Vue构造方法是在src\core\instance\index.js中,而组件的构造方法是基于Vue根构造方法,在上述createComponet中调用Vue.extend方法进行组装而成,本质上都是调用Vue实例上的_init方法,但是组件的构造方法VueComponent声明了一些属于自己的自定义属性,具体实现代码如下:
Vue.extend = function (extendOptions: Object): Function {
extendOptions = extendOptions || {}
const Super = this
// 父级实例cid
const SuperId = Super.cid
const cachedCtors = extendOptions._Ctor || (extendOptions._Ctor = {})
if (cachedCtors[SuperId]) {
return cachedCtors[SuperId]
}
const name = extendOptions.name || Super.options.name
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && name) {
validateComponentName(name)
}
// 定义vue初始化方法,和实例化Vue走同一个路线
const Sub = function VueComponent (options) {
this._init(options)
}
// super -> this -> Vue 继承Vue构造方法中的属性
Sub.prototype = Object.create(Super.prototype)
// 指定子组件的构造方法为Sub -> VueComponent
Sub.prototype.constructor = Sub
Sub.cid = cid++
// 合并组件属性
Sub.options = mergeOptions(
Super.options,
extendOptions
)
// 定义父级作用域
Sub['super'] = Super
// For props and computed properties, we define the proxy getters on
// the Vue instances at extension time, on the extended prototype. This
// avoids Object.defineProperty calls for each instance created.
if (Sub.options.props) {
initProps(Sub)
}
if (Sub.options.computed) {
initComputed(Sub)
}
// allow further extension/mixin/plugin usage
// 子组件的实例,保持对vue构造方法的引用
Sub.extend = Super.extend
Sub.mixin = Super.mixin
Sub.use = Super.use
// create asset registers, so extended classes
// can have their private assets too.
ASSET_TYPES.forEach(function (type) {
Sub[type] = Super[type]
})
// enable recursive self-lookup
if (name) {
Sub.options.components[name] = Sub
}
// keep a reference to the super options at extension time.
// later at instantiation we can check if Super's options have
// been updated.
Sub.superOptions = Super.options
Sub.extendOptions = extendOptions
Sub.sealedOptions = extend({}, Sub.options)
// cache constructor
cachedCtors[SuperId] = Sub
return Sub
}
}
2. Vue根实例的模板解析与DOM挂载入口不一致,在_init方法中,提供了对根实例的模板解析与DOM挂载,而组件没有。在创建组件时,调用了installComponentHooks,componet hooks主要包含init、prepatch、insert、destory,init在实例化组件时调用,insert是插入DOM时调用,destory是在销毁组件时调用,而prepatch是在更新组件时调用,具体如下:
const componentVNodeHooks = {
// 组件初始化方法
init (vnode: VNodeWithData, hydrating: boolean): ?boolean {
if (
vnode.componentInstance &&
!vnode.componentInstance._isDestroyed &&
vnode.data.keepAlive
) {
// kept-alive components, treat as a patch
const mountedNode: any = vnode // work around flow
componentVNodeHooks.prepatch(mountedNode, mountedNode)
} else {
// 实例化组件
const child = vnode.componentInstance = createComponentInstanceForVnode(
vnode,
activeInstance
)
//挂载组件
child.$mount(hydrating ? vnode.elm : undefined, hydrating)
}
},
prepatch (oldVnode: MountedComponentVNode, vnode: MountedComponentVNode) {
const options = vnode.componentOptions
const child = vnode.componentInstance = oldVnode.componentInstance
updateChildComponent(
child,
options.propsData, // updated props
options.listeners, // updated listeners
vnode, // new parent vnode
options.children // new children
)
},
insert (vnode: MountedComponentVNode) {
const { context, componentInstance } = vnode
if (!componentInstance._isMounted) {
componentInstance._isMounted = true
callHook(componentInstance, 'mounted')
}
if (vnode.data.keepAlive) {
if (context._isMounted) {
// vue-router#1212
// During updates, a kept-alive component's child components may
// change, so directly walking the tree here may call activated hooks
// on incorrect children. Instead we push them into a queue which will
// be processed after the whole patch process ended.
queueActivatedComponent(componentInstance)
} else {
activateChildComponent(componentInstance, true /* direct */)
}
}
},
destroy (vnode: MountedComponentVNode) {
const { componentInstance } = vnode
if (!componentInstance._isDestroyed) {
if (!vnode.data.keepAlive) {
componentInstance.$destroy()
} else {
deactivateChildComponent(componentInstance, true /* direct */)
}
}
}
}
如上述代码所示,实例化组件调用的是createComponentInstanceForVnode,createComponentInstanceForVnode代码如下,调用在Vue.extend中组装的组件构造方法VueComponent,初始化调用的还是Vue原型上的_init方法,大致流程与Vue初始化类似,只是解析模板有所区别,组件解析模板调用的是child.$mount。
// 创建组件的作用域,执行组件的_init方法,同vue实例化过程
export function createComponentInstanceForVnode (
vnode: any, // we know it's MountedComponentVNode but flow doesn't
parent: any, // activeInstance in lifecycle state
): Component {
const options: InternalComponentOptions = {
_isComponent: true,
_parentVnode: vnode,
parent
}
// check inline-template render functions
const inlineTemplate = vnode.data.inlineTemplate
if (isDef(inlineTemplate)) {
options.render = inlineTemplate.render
options.staticRenderFns = inlineTemplate.staticRenderFns
}
// 实例化组件的构造方法
return new vnode.componentOptions.Ctor(options)
}
在installComponentHooks中,在vnode的data属性中初始化了hooks,后面在_patch__中,会调用patch.js中声明的createComponent -> init -> 实例化组件。组件实例化完成后,会将真实DOM元素,插入到上一级元素。patch.js中的createComponent方法如下:
// 创建组件,如果节点类型是组件,则直接走创建组件的方法
function createComponent (vnode, insertedVnodeQueue, parentElm, refElm) {
let i = vnode.data
// 判断是否存在组件的生命周期,存在,即需要走创建组件的流程
if (isDef(i)) {
const isReactivated = isDef(vnode.componentInstance) && i.keepAlive
if (isDef(i = i.hook) && isDef(i = i.init)) {
// 执行component的init方法,获取组件的实例
i(vnode, false /* hydrating */)
}
// after calling the init hook, if the vnode is a child component
// it should've created a child instance and mounted it. the child
// component also has set the placeholder vnode's elm.
// in that case we can just return the element and be done.
// 组件的vnode对象中存在当前组件的作用域
if (isDef(vnode.componentInstance)) {
initComponent(vnode, insertedVnodeQueue)
// 将子组件插入到父节点中
insert(parentElm, vnode.elm, refElm)
if (isTrue(isReactivated)) {
reactivateComponent(vnode, insertedVnodeQueue, parentElm, refElm)
}
return true
}
}
}
在实例化完成后,会将生成的真实DOM元素插入到上级元素中,vue在获取真实DOM时,是从低往上,一级级添加,最终将渲染的元素添加到DOM body中,__patch__主流程如下:
function patch (oldVnode, vnode, hydrating, removeOnly) {
if (isUndef(vnode)) {
if (isDef(oldVnode)) invokeDestroyHook(oldVnode)
return
}
let isInitialPatch = false
const insertedVnodeQueue = []
if (isUndef(oldVnode)) {
// empty mount (likely as component), create new root element
isInitialPatch = true
createElm(vnode, insertedVnodeQueue)
} else {
const isRealElement = isDef(oldVnode.nodeType)
if (!isRealElement && sameVnode(oldVnode, vnode)) {
// patch existing root node
patchVnode(oldVnode, vnode, insertedVnodeQueue, null, null, removeOnly)
} else {
if (isRealElement) {
// mounting to a real element
// check if this is server-rendered content and if we can perform
// a successful hydration.
// nodeType 1 元素 3 文字
if (oldVnode.nodeType === 1 && oldVnode.hasAttribute(SSR_ATTR)) {
oldVnode.removeAttribute(SSR_ATTR)
hydrating = true
}
if (isTrue(hydrating)) {
if (hydrate(oldVnode, vnode, insertedVnodeQueue)) {
invokeInsertHook(vnode, insertedVnodeQueue, true)
return oldVnode
} else if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
warn(
'The client-side rendered virtual DOM tree is not matching ' +
'server-rendered content. This is likely caused by incorrect ' +
'HTML markup, for example nesting block-level elements inside ' +
'<p>, or missing <tbody>. Bailing hydration and performing ' +
'full client-side render.'
)
}
}
// either not server-rendered, or hydration failed.
// create an empty node and replace it
oldVnode = emptyNodeAt(oldVnode)
}
// replacing existing element
// 获取老旧节点
const oldElm = oldVnode.elm
// 获取老旧节点的父节点
const parentElm = nodeOps.parentNode(oldElm)
// create new node
// 将虚拟DOM转换成真实DOM
// 传入父级节点,一级级添加
createElm(
vnode,
insertedVnodeQueue,
// extremely rare edge case: do not insert if old element is in a
// leaving transition. Only happens when combining transition +
// keep-alive + HOCs. (#4590)
oldElm._leaveCb ? null : parentElm,
nodeOps.nextSibling(oldElm)
)
// update parent placeholder node element, recursively
if (isDef(vnode.parent)) {
let ancestor = vnode.parent
const patchable = isPatchable(vnode)
while (ancestor) {
for (let i = 0; i < cbs.destroy.length; ++i) {
cbs.destroy[i](ancestor)
}
ancestor.elm = vnode.elm
if (patchable) {
for (let i = 0; i < cbs.create.length; ++i) {
cbs.create[i](emptyNode, ancestor)
}
// #6513
// invoke insert hooks that may have been merged by create hooks.
// e.g. for directives that uses the "inserted" hook.
const insert = ancestor.data.hook.insert
if (insert.merged) {
// start at index 1 to avoid re-invoking component mounted hook
for (let i = 1; i < insert.fns.length; i++) {
insert.fns[i]()
}
}
} else {
registerRef(ancestor)
}
ancestor = ancestor.parent
}
}
// destroy old node
// 移除老旧节点
if (isDef(parentElm)) {
removeVnodes([oldVnode], 0, 0)
} else if (isDef(oldVnode.tag)) {
invokeDestroyHook(oldVnode)
}
}
}
invokeInsertHook(vnode, insertedVnodeQueue, isInitialPatch)
return vnode.elm
}
模板的解析,是先把模板解析成HTML,然后再讲老旧节点移除。
vue组件初始化过程的更多相关文章
- 谁先执行?props还是data或是其他? vue组件初始化的执行顺序详解
初入vue的朋友可能会疑惑,组件初始化的时候,created,props,data到底谁先执行? 今天,我就带大家从源码的角度看看到底谁先执行? 我们知道,vue是个实例 那我们就从new Vue() ...
- JS vue 组件创建过程
https://www.jianshu.com/p/3504a1edba42 vue.js原生组件化开发(一)——组件开发基础 0.3472017.05.09 12:00:54字数 1120阅读 33 ...
- 封装 vue 组件的过程
首先,组件可以提升整个项目的开发效率.能够把页面抽象成多个相对独立的模块,解决了我们传统项目开发的缺点:效率低,难维护,复用性等问题: 然后,使用Vue.extend方法创建一个组件,然后使用 Vue ...
- Vue初始化过程
用vue也有一两年了,始终对vue一知半解,不怎么了解内部的执行过程,最近在看vue源码,还是不少收获的,其中不乏浏览器事件轮询机制.闭包.设计模式等,还是非常值得一读.本篇简要记录下vue的初始化过 ...
- Vue 源码解读(2)—— Vue 初始化过程
当学习成为了习惯,知识也就变成了常识. 感谢各位的 点赞.收藏和评论. 新视频和文章会第一时间在微信公众号发送,欢迎关注:李永宁lyn 文章已收录到 github 仓库 liyongning/blog ...
- Vue源码翻译之组件初始化。
废话不多说. 我们先来看看Vue的入口文件. import { initMixin } from './init' import { stateMixin } from './state' impor ...
- vue 快速入门 系列 —— Vue 实例的初始化过程
其他章节请看: vue 快速入门 系列 Vue 实例的初始化过程 书接上文,每次调用 new Vue() 都会执行 Vue.prototype._init() 方法.倘若你看过 jQuery 的源码, ...
- Spring MVC源码(一) ----- 启动过程与组件初始化
SpringMVC作为MVC框架近年来被广泛地使用,其与Mybatis和Spring的组合,也成为许多公司开发web的套装.SpringMVC继承了Spring的优点,对业务代码的非侵入性,配置的便捷 ...
- JS组件系列——又一款MVVM组件:Vue(二:构建自己的Vue组件)
前言:转眼距离上篇 JS组件系列——又一款MVVM组件:Vue(一:30分钟搞定前端增删改查) 已有好几个月了,今天打算将它捡起来,发现好久不用,Vue相关技术点都生疏不少.经过这几个月的时间,Vue ...
随机推荐
- RPM命令执行失败:bash: rpm: 未找到命令...
出现错误截图如下: 这是由于误操作导致rpm文件缺失导致 将另一台完好的服务器上RPM文件及缺失文件上传至异常服务器上即可修复 异常服务器A:192.168.1.230 完好服务器B: 任意 服务器B ...
- Xamarin.Forms学习系列之SQLite
在App中我们通常不会实时获取服务器数据,会在用户手机中保存历史数据,这个时候就需要用到数据库SQLite,由于微软的封装,在Xamarin中操作SQLite非常简单,类似EF的操作. 1.我们需要在 ...
- 复制节点(cloneNode)
DOM提供用来复制节点方法. cloneNode():将为给定节点创建一个副本,这个方法的返回值是一个指向新建克隆节点的引用指针, reference = node.cloneNode(deep) 这 ...
- java数据类型(大小等),变量定义,各进制书写方法
1. java中字符占两个字节,因为char类型占两个字节(16位),而C,C++中占1字节(8位). 2. 变量定义 第一步:声明(Declaration) 第二步:赋值(Assignment) 这 ...
- Chrome插件安装的3种方法,解决拖放不能安装的情况,并提供插件下载
本文摘录于Chrome插件网站 方法一:拖放安装 下载插件的crx文件后,打开Chrome的扩展页面(chrome://extensions/或按Chrome菜单图标>更多工具>扩展程序) ...
- mysql那些事(3)小数如何存储
创建mysql数据表的时候,经常会遇到存储小数(浮点数)的情况,如:价格,重量,身高等. 目前大的公司流行三种存储方案: 1.将数据扩大10的倍数达到使用整数类型存储目的. 比如价格,我们经常以分为单 ...
- js对象可扩展性和属性的四个特性(上)
# js对象可扩展性和属性的四个特性(上) 一.前言 再次花时间回顾一下基础,毕竟要想楼建的好,地基就要牢固,嘻嘻! 在开始之前需要具备对prototype.__proto__.constructor ...
- 全新一代云服务器S6,重新定义性价比
S6通用计算型云服务器,搭载全新一代处理器,配套华为自研高性能智能网卡,计算与网络性能全面升级.S6进一步强化高性价比定位,满足企业性能要求的同时,降低中小企业上云成本. 更多详情请访问ECS产品介绍 ...
- 转:org.apache.maven.archiver.MavenArchiver.getManifest错误
eclipse导入新的maven项目时,pom.xml第一行报错: org.apache.maven.archiver.MavenArchiver.getManifest(org.apache.mav ...
- 创建raid5(3个raid2个备份)
创建raid5(3个raid2个备份) 1.首先创建五个磁盘 2.创建RAID5并设置2块备份故障盘: 3.可查看下阵列的详细信息(Spare Devices数量为1): 4.将磁盘阵列格式化为ext ...
