并发编程-Future+callable+FutureTask 闭锁机制
项目中经常有些任务需要异步(提交到线程池中)去执行,而主线程往往需要知道异步执行产生的结果,这时我们要怎么做呢?用runnable是无法实现的,我们需要用callable实现。
FutureTask 也可以做闭锁,它是 Future 和 callable 的结合体。所以我们有必要来了解 FutureTask 这个类。
FutureTask 的继承关系类图
先看 FutureTask 类的继承:
public class FutureTask<V> implements RunnableFuture<V>
它继承自 RunnableFuture,可以看出他是 Runnable 和 Future 的结合体。
public interface RunnableFuture<V> extends Runnable, Future<V> { /**
* Sets this Future to the result of its computation
* unless it has been cancelled.
*/
void run();
}
我们熟悉的 Runnable 接口:
public interface Runnable {
public abstract void run();
}
不常见的Future 接口,用来获取异步计算结果:
public interface Future<V> { /**
* Attempts to cancel execution of this task. This attempt will
* fail if the task has already completed, has already been cancelled,
* or could not be cancelled for some other reason. If successful,
* and this task has not started when {@code cancel} is called,
* this task should never run. If the task has already started,
* then the {@code mayInterruptIfRunning} parameter determines
* whether the thread executing this task should be interrupted in
* an attempt to stop the task.
*/
boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning); /**
* Returns {@code true} if this task was cancelled before it completed
* normally.
*/
boolean isCancelled();//如果任务被取消,返回true /**
* Returns {@code true} if this task completed.
*/
boolean isDone();//如果任务执行结束,无论是正常结束或是中途取消还是发生异常,都返回true。 /**
* Waits if necessary for the computation to complete, and then
* retrieves its result.
*/
V get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException; //获取异步执行的结果,如果没有结果可用,此方法会阻塞直到异步计算完成。 /**
* Waits if necessary for at most the given time for the computation
* to complete, and then retrieves its result, if available.
*/
V get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException;
}
到这里,FutureTask 整个继承关系已经很清楚了。为了更直观一点,我用 starUML 画出它的类继承关系图。
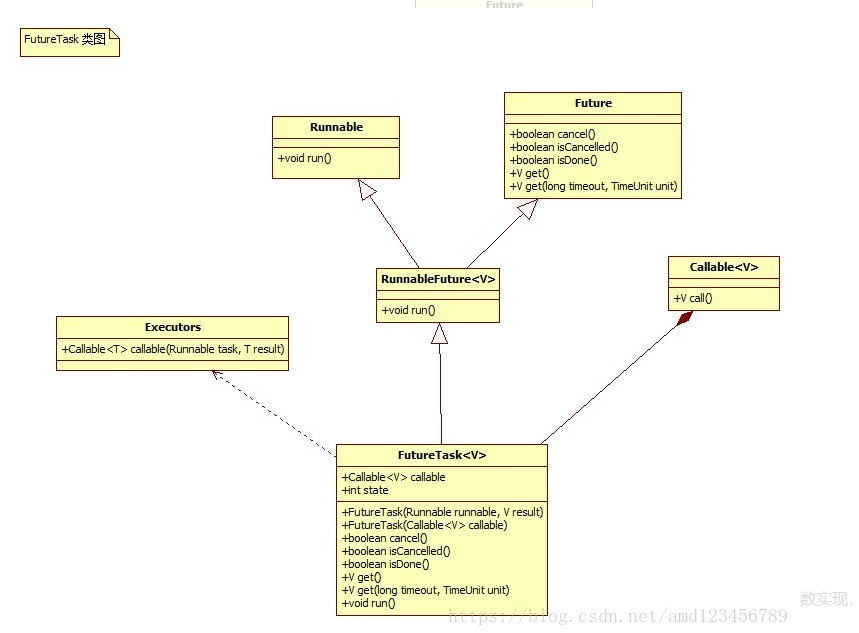
在类关系图中,我们可以看到 FutureTask 的构造函数,包含了之前没有见过的类型:Callable。我们直接看下它的两个构造函数实现,进一步了解看看:
//构造函数1
public FutureTask(Runnable runnable, V result) {
this.callable = Executors.callable(runnable, result);
this.state = NEW; // ensure visibility of callable
}
//构造函数2
public FutureTask(Callable<V> callable) {
if (callable == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
this.callable = callable;
this.state = NEW; // ensure visibility of callable
}
这里已经非常清楚了,最终都是赋值给 FutureTask 的内部变量 callable。它是一个接口,包含一个有返回值的函数 call()。
public interface Callable<V> { /**
* Computes a result, or throws an exception if unable to do so.
*
* @return computed result
* @throws Exception if unable to compute a result
*/
V call() throws Exception;
}
通过上面的讲解,我们已经知道 Future,FutureTask,Callable,Runnable的关系了。那么,说了这么多主要是想干嘛呢?
没错,主要就是为了线程执行完成后能够返回结果。我们知道,Runnable 接口执行完成后,是没法返回结果的。所以,我们如果想要能够返回执行的结果,必须使用 callable 接口。
应用场景
比如我们有个耗时的计算操作,现在创建一个子线程执行计算操作,主线程通过 FutureTask.get() 的方式获取计算结果,如果计算还没有完成,则会阻塞一直等到计算完成。
下面我们直接编写代码来实现上面的应用场景。
使用 Callable + FutureTask 获取执行结果:
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.FutureTask; public class FutureTaskTest {
// 创建一个Future对象,并把Callable的实现传给构造函数
private static final FutureTask<Integer> future = new FutureTask<Integer>(new CallableTest()); public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建一个线程
final Thread thread = new Thread(future);
// 启动线程
thread.start();
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println("Main thread is running");
// 获取计算结果,会阻塞知道计算完毕
System.out.println("get the sub thread compute result : " + future.get());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("main thread is end");
} // 实现Callable接口,耗时操作
static class CallableTest implements Callable<Integer> {
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
int ret = 0;
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println("sub thread is computing");
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
ret += i;
}
System.out.println("sub thread is finish compute");
return ret;
}
}
}
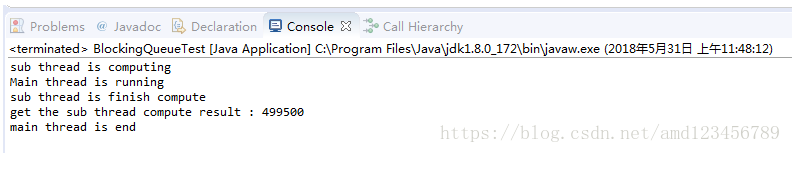
运行结果:
另外一种方式,是使用 Callable + Future + ExecutorService 的方式。ExecutorService继承自Executor,它的目的是为我们管理Thread对象,从而简化并发编程,Executor使我们无需显示的去管理线程的生命周期。
在ExecutorService接口中声明了若干个submit方法的重载版本:
<T> Future<T> submit(Callable<T> task);
<T> Future<T> submit(Runnable task, T result);
Future<?> submit(Runnable task);
第一个submit方法里面的参数类型就是Callable。
示例如下:
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
import java.util.concurrent.FutureTask; public class FutureTaskTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 返回一个线程池,通常都和这种线程宽架搭配
ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
System.out.println("Main thread is running");
// 提交给线程,返回一个Future类,并执行
Future<Integer> future = threadPool.submit(new CallableTest());
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
// 获取计算结果,会阻塞知道计算完毕
System.out.println("get the sub thread compute result : " + future.get());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("main thread is end");
} // 实现Callable接口,耗时操作
static class CallableTest implements Callable<Integer> {
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
int ret = 0;
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println("sub thread is computing");
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
ret += i;
}
System.out.println("sub thread is finish compute");
return ret;
}
}
}
执行结果:

转自:https://blog.csdn.net/amd123456789/article/details/80522855
并发编程-Future+callable+FutureTask 闭锁机制的更多相关文章
- Java并发编程:Callable、Future和FutureTask
作者:海子 出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/dolphin0520/ 本博客中未标明转载的文章归作者海子和博客园共有,欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须保留此段声明,且在文章页面明显位置 ...
- (转)Java并发编程:Callable、Future和FutureTask
Java并发编程:Callable.Future和FutureTask 在前面的文章中我们讲述了创建线程的2种方式,一种是直接继承Thread,另外一种就是实现Runnable接口. 这2种方式都有一 ...
- Java并发编程:Callable、Future和FutureTask(转)
Java并发编程:Callable.Future和FutureTask 在前面的文章中我们讲述了创建线程的2种方式,一种是直接继承Thread,另外一种就是实现Runnable接口. 这2种方式都有一 ...
- 15、Java并发编程:Callable、Future和FutureTask
Java并发编程:Callable.Future和FutureTask 在前面的文章中我们讲述了创建线程的2种方式,一种是直接继承Thread,另外一种就是实现Runnable接口. 这2种方式都有一 ...
- 007 Java并发编程:Callable、Future和FutureTask
原文https://www.cnblogs.com/dolphin0520/p/3949310.html Java并发编程:Callable.Future和FutureTask 在前面的文章中我们讲述 ...
- 并发编程 05—— Callable和Future
Java并发编程实践 目录 并发编程 01—— ThreadLocal 并发编程 02—— ConcurrentHashMap 并发编程 03—— 阻塞队列和生产者-消费者模式 并发编程 04—— 闭 ...
- Java并发编程:Callable、Future和FutureTask的实现
启动线程执行任务,如果需要在任务执行完毕之后得到任务执行结果,可以使用从Java 1.5开始提供的Callable和Future 下面就分析一下Callable.Future以及FutureTask的 ...
- [转载] Java并发编程:Callable、Future和FutureTask
转载自http://www.cnblogs.com/dolphin0520/p/3949310.html 在前面的文章中我们讲述了创建线程的2种方式,一种是直接继承Thread,另外一种就是实现Run ...
- 【Java并发编程】Callable、Future和FutureTask的实现
启动线程执行任务,如果需要在任务执行完毕之后得到任务执行结果,可以使用从Java 1.5开始提供的Callable和Future 下面就分析一下Callable.Future以及FutureTask的 ...
随机推荐
- 在 Swift 中实现单例方法
我们通常在进行开发的时候,会用到一个叫做 单例模式 的东西.相信大家也都对这种模式非常熟悉了.而且单例的使用在平时的开发中也非常频繁. 比如我们常用到的 NSUserDefaults.standard ...
- dumpbin判断windows程序是32还是64位(包括DLL)
http://blog.csdn.net/csfreebird/article/details/10105681 dumpbin /HEADERS gdal18.dll(or xxx.exe) 如果安 ...
- [转]Nodejs开发框架Express4.x开发手记
Express: ?web application framework for?Node.js? Express 是一个简洁.灵活的 node.js Web 应用开发框架, 它提供一系列强大的特性,帮 ...
- AY的Dapper研究学习-基本入门-C#开发-aaronyang技术分享
原文:AY的Dapper研究学习-基本入门-C#开发-aaronyang技术分享 ====================www.ayjs.net 杨洋 wpfui.com ...
- 关于WPF XAML 中 Trigger的反向ExitActions
触发器,顾名思义,就是当满足一定条件时,会触发一些操作,比如:改变控件的透明度,显隐,宽高等等,触发器本身做了一些操作,就是触发器触发条件不符合的时候,会自动把在触发器中更改的属性还原.但,并不是所有 ...
- Rails 最佳实践
在你业务简单的时候,让你简简单单用 ActiveRecord 模型. 复杂的时候,你可以用官方推荐的 Concerns. 更复杂的时候,可以通过 gem 和 API 来拆分. 极端复杂的时候,由于 R ...
- DELPHI美化界面(2009开始TPanel增加了ParentBackGround)
1.透明问题. 要重新调整界面确实很麻烦,以前用DELPHI开发的界面都很土,和WEB真是没办法比.(我以前用的是DELPHI7),现在回想起来,DELPHI难做的原因是:没有透明控件.所有控件都是不 ...
- 论文阅读计划1(Benchmarking Streaming Computation Engines: Storm, Flink and Spark Streaming & An Enforcement of Real Time Scheduling in Spark Streaming & StyleBank: An Explicit Representation for Neural Ima)
Benchmarking Streaming Computation Engines: Storm, Flink and Spark Streaming[1] 简介:雅虎发布的一份各种流处理引擎的基准 ...
- Linux文件系统操作与磁盘管理
简单文件操作 df---->report file system disk space usage du---->estimate file space usage 2.简单的磁盘管理 d ...
- 使用Boost的DLL库管理动态链接库
Boost 1.61新增了一个DLL库,跟Qt中的QLibrary类似,提供了跨平台的动态库链接库加载.调用等功能.http://www.boost.org/users/history/version ...
