PB级数据实现秒级查询ES的安装
什么是ES?ElasticSearch是一个基于Lucene的搜索服务器。它提供了一个分布式多用户能力的全文搜索引擎,基于RESTful web接口。Elasticsearch是用Java语言开发的,并作为Apache许可条款下的开放源码发布,是一种流行的企业级搜索引擎。ElasticSearch用于云计算中,能够达到实时搜索,稳定,可靠,快速,安装使用方便。
- 本教程使用软件为6.4.3版本
下载
ElasticSearch:
Kibana:
上传至Linux服务器
略
解压并修改配置文件
# 注意:需要使用普通用户操作ES,不可使用root用户进行操作。
#使用root用户,添加用户
#添加用户命令:
[root@hadoop137 ~]# useradd shaofei
[root@hadoop137 ~]# passwd shaofei
更改用户 shaofei的密码 。
新的 密码:
无效的密码: 过于简单化/系统化
无效的密码: 过于简单
重新输入新的 密码:
passwd: 所有的身份验证令牌已经成功更新。
#切换为shaofei用户:
[root@hadoop137 ~]# su shaofei
[shaofei@hadoop137 root]$ cd
[shaofei@hadoop137 ~]$
# 解压elasticsearch
[shaofei@hadoop137 softwear]$ tar -zxvf elasticsearch-6.4.3.tar.gz -C ../module/
[shaofei@hadoop137 elasticsearch-6.4.3]$ pwd
/opt/module/elasticsearch-6.4.3
# 修改配置文件
[shaofei@hadoop137 elasticsearch-6.4.3]$ vim config/elasticsearch.yml
# 注意修改yml文件时,配置项后面要空格
elasticsearch.yml
# ======================== Elasticsearch Configuration =========================
#
# NOTE: Elasticsearch comes with reasonable defaults for most settings.
# Before you set out to tweak and tune the configuration, make sure you
# understand what are you trying to accomplish and the consequences.
#
# The primary way of configuring a node is via this file. This template lists
# the most important settings you may want to configure for a production cluster.
#
# Please consult the documentation for further information on configuration options:
# https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/index.html
#
# ---------------------------------- Cluster -----------------------------------
#
# Use a descriptive name for your cluster:
# 修改集群名称
cluster.name: myes
#
# ------------------------------------ Node ------------------------------------
#
# Use a descriptive name for the node:
# 修改当前节点名称——下一步分发到其他集群时需要修改
node.name: hadoop137
#
# Add custom attributes to the node:
#
#node.attr.rack: r1
#
# ----------------------------------- Paths ------------------------------------
#
# Path to directory where to store the data (separate multiple locations by comma):
#
#path.data: /path/to/data
#
# Path to log files:
#
#path.logs: /path/to/logs
#
# ----------------------------------- Memory -----------------------------------
#
# Lock the memory on startup:
#
#bootstrap.memory_lock: true
#
# Make sure that the heap size is set to about half the memory available
# on the system and that the owner of the process is allowed to use this
# limit.
#
# Elasticsearch performs poorly when the system is swapping the memory.
#
# ---------------------------------- Network -----------------------------------
#
# Set the bind address to a specific IP (IPv4 or IPv6):
# 当前节点的ip地址,我这里配置了hosts文件所以写了主机名称——下一步分发之后需要修改为对应主机的ip地址
network.host: hadoop137
#
# Set a custom port for HTTP:
# ES对外开放服务的端口号
http.port: 9200
#
# For more information, consult the network module documentation.
#
# --------------------------------- Discovery ----------------------------------
#
# Pass an initial list of hosts to perform discovery when new node is started:
# The default list of hosts is ["127.0.0.1", "[::1]"]
#
#discovery.zen.ping.unicast.hosts: ["host1", "host2"]
#
# Prevent the "split brain" by configuring the majority of nodes (total number of master-eligible nodes / 2 + 1):
#
#discovery.zen.minimum_master_nodes:
#
# For more information, consult the zen discovery module documentation.
#
# ---------------------------------- Gateway -----------------------------------
#
# Block initial recovery after a full cluster restart until N nodes are started:
#
#gateway.recover_after_nodes: 3
#
# For more information, consult the gateway module documentation.
#
# ---------------------------------- Various -----------------------------------
#
# Require explicit names when deleting indices:
#
#action.destructive_requires_name: true
#添加集群ip地址
discovery.zen.ping.unicast.hosts: ["192.168.23.137", "192.168.23.138", "192.168.23.139"]
分发各个集群中的其他主机
[shaofei@hadoop137 module]$ rsync -rvl elasticsearch-6.4.3 shaofei@hadoop138:`pwd`
[shaofei@hadoop137 module]$ rsync -rvl elasticsearch-6.4.3 shaofei@hadoop139:`pwd`
分别启动集群中的ES
[shaofei@hadoop137 elasticsearch-6.4.3]$ ./bin/elasticsearch
[shaofei@hadoop138 elasticsearch-6.4.3]$ ./bin/elasticsearch
[shaofei@hadoop139 elasticsearch-6.4.3]$ ./bin/elasticsearch
启动中遇到的问题:
ERROR: [4] bootstrap checks failed
[1]: max file descriptors [4096] for elasticsearch process is too low, increase to at least [65536]
[2]: max number of threads [1024] for user [shaofei] is too low, increase to at least [4096]
[3]: max virtual memory areas vm.max_map_count [65530] is too low, increase to at least [262144]
对于第【1】个问题:
[root@hadoop139 shaofei]# vi /etc/security/limits.conf
末尾添加:
# End of file
* soft nofile 65536
* hard nofile 131072
* soft nproc 2048
* hard nproc 4096
对于第【2】个问题:
[root@hadoop139 shaofei]# vim /etc/security/limits.d/90-nproc.conf
修改:
[root@hadoop139 shaofei]# cat /etc/security/limits.d/90-nproc.conf
# Default limit for number of user's processes to prevent
# accidental fork bombs.
# See rhbz #432903 for reasoning.
* soft nproc 10240
root soft nproc unlimited
# 重新登陆用户即可
对于第【3】个问题:
vi /etc/sysctl.conf
添加下面配置:
vm.max_map_count=655360
并执行命令:
sysctl -p
java.lang.UnsupportedOperationException: seccomp unavailable: CONFIG_SECCOMP not compiled into kernel, CONFIG_SECCOMP and CONFIG_SECCOMP_FILTER are needed
# 修改elasticsearch.yml 添加一下内容
bootstrap.memory_lock: false
bootstrap.system_call_filter: false
问题解决之后重新启动es即可。
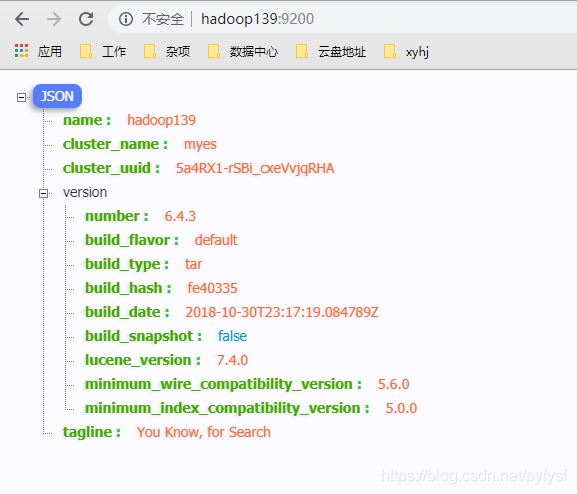
- 启动成功
安装kibana
- 下载安装包
- 解压
- 修改配置文件
kibana.yml
# Kibana is served by a back end server. This setting specifies the port to use.
# 配置端口
server.port: 5601
# Specifies the address to which the Kibana server will bind. IP addresses and host names are both valid values.
# The default is 'localhost', which usually means remote machines will not be able to connect.
# To allow connections from remote users, set this parameter to a non-loopback address.
# 配置主机ip
server.host: "hadoop137"
# Enables you to specify a path to mount Kibana at if you are running behind a proxy.
# Use the `server.rewriteBasePath` setting to tell Kibana if it should remove the basePath
# from requests it receives, and to prevent a deprecation warning at startup.
# This setting cannot end in a slash.
#server.basePath: ""
# Specifies whether Kibana should rewrite requests that are prefixed with
# `server.basePath` or require that they are rewritten by your reverse proxy.
# This setting was effectively always `false` before Kibana 6.3 and will
# default to `true` starting in Kibana 7.0.
#server.rewriteBasePath: false
# The maximum payload size in bytes for incoming server requests.
#server.maxPayloadBytes: 1048576
# The Kibana server's name. This is used for display purposes.
#server.name: "your-hostname"
# The URL of the Elasticsearch instance to use for all your queries.
#配置elasticsearch的访问
elasticsearch.url: "http://hadoop137:9200"
# When this setting's value is true Kibana uses the hostname specified in the server.host
# setting. When the value of this setting is false, Kibana uses the hostname of the host
# that connects to this Kibana instance.
#elasticsearch.preserveHost: true
# Kibana uses an index in Elasticsearch to store saved searches, visualizations and
# dashboards. Kibana creates a new index if the index doesn't already exist.
#kibana.index: ".kibana"
# The default application to load.
#kibana.defaultAppId: "home"
# If your Elasticsearch is protected with basic authentication, these settings provide
# the username and password that the Kibana server uses to perform maintenance on the Kibana
# index at startup. Your Kibana users still need to authenticate with Elasticsearch, which
# is proxied through the Kibana server.
#elasticsearch.username: "user"
#elasticsearch.password: "pass"
# Enables SSL and paths to the PEM-format SSL certificate and SSL key files, respectively.
# These settings enable SSL for outgoing requests from the Kibana server to the browser.
#server.ssl.enabled: false
#server.ssl.certificate: /path/to/your/server.crt
#server.ssl.key: /path/to/your/server.key
# Optional settings that provide the paths to the PEM-format SSL certificate and key files.
# These files validate that your Elasticsearch backend uses the same key files.
#elasticsearch.ssl.certificate: /path/to/your/client.crt
#elasticsearch.ssl.key: /path/to/your/client.key
# Optional setting that enables you to specify a path to the PEM file for the certificate
# authority for your Elasticsearch instance.
#elasticsearch.ssl.certificateAuthorities: [ "/path/to/your/CA.pem" ]
# To disregard the validity of SSL certificates, change this setting's value to 'none'.
#elasticsearch.ssl.verificationMode: full
# Time in milliseconds to wait for Elasticsearch to respond to pings. Defaults to the value of
# the elasticsearch.requestTimeout setting.
#elasticsearch.pingTimeout: 1500
# Time in milliseconds to wait for responses from the back end or Elasticsearch. This value
# must be a positive integer.
#elasticsearch.requestTimeout: 30000
# List of Kibana client-side headers to send to Elasticsearch. To send *no* client-side
# headers, set this value to [] (an empty list).
#elasticsearch.requestHeadersWhitelist: [ authorization ]
# Header names and values that are sent to Elasticsearch. Any custom headers cannot be overwritten
# by client-side headers, regardless of the elasticsearch.requestHeadersWhitelist configuration.
#elasticsearch.customHeaders: {}
# Time in milliseconds for Elasticsearch to wait for responses from shards. Set to 0 to disable.
#elasticsearch.shardTimeout: 30000
# Time in milliseconds to wait for Elasticsearch at Kibana startup before retrying.
#elasticsearch.startupTimeout: 5000
# Logs queries sent to Elasticsearch. Requires logging.verbose set to true.
#elasticsearch.logQueries: false
# Specifies the path where Kibana creates the process ID file.
#pid.file: /var/run/kibana.pid
# Enables you specify a file where Kibana stores log output.
#logging.dest: stdout
# Set the value of this setting to true to suppress all logging output.
#logging.silent: false
# Set the value of this setting to true to suppress all logging output other than error messages.
#logging.quiet: false
# Set the value of this setting to true to log all events, including system usage information
# and all requests.
#logging.verbose: false
# Set the interval in milliseconds to sample system and process performance
# metrics. Minimum is 100ms. Defaults to 5000.
#ops.interval: 5000
# The default locale. This locale can be used in certain circumstances to substitute any missing
# translations.
#i18n.defaultLocale: "en"
浏览器访问: http://hadoop137:5601/ 即可验证是否成功

PB级数据实现秒级查询ES的安装的更多相关文章
- 《深度访谈:华为开源数据格式 CarbonData 项目,实现大数据即席查询秒级响应》
深度访谈:华为开源数据格式 CarbonData 项目,实现大数据即席查询秒级响应 Tina 阅读数:146012016 年 7 月 13 日 19:00 华为宣布开源了 CarbonData ...
- PB级数据实时查询,滴滴Elasticsearch多集群架构实践
PB级数据实时查询,滴滴Elasticsearch多集群架构实践 mp.weixin.qq.com 点击上方"IT牧场",选择"设为星标"技术干货每日送达 点 ...
- 百亿级别数据量,又需要秒级响应的案例,需要什么系统支持呢?下面介绍下大数据实时分析工具Yonghong Z-Suite
Yonghong Z-Suite 除了提供优秀的前端BI工具之外,Yonghong Z-Suite让用户可以选购分布式数据集市来支持实时大数据分析. 对于这种百亿级的大数据案例,Yonghong Z- ...
- .NET Core下开源任务调度框架Hangfire的Api任务拓展(支持秒级任务)
HangFire的拓展和使用 看了很多博客,小白第一次写博客. 最近由于之前的任务调度框架总出现问题,因此想寻找一个替代品,之前使用的是Quartz.Net,这个框架方便之处就是支持cron表达式适合 ...
- 《阿里如何实现秒级百万TPS?搜索离线大数据平台大数据平台架构解读》读后感
在使用淘宝时发现搜索框很神奇,它可以将将我们想要的商品全部查询出来,但是我们并感觉不到数据库查询的过程,速度很快.通过阅读这篇文章让我知道了搜索框背后包含着很多技术,对我以后的学习可能很有借鉴. 平时 ...
- SQL Server大量数据秒级插入/新增/删除
原文:SQL Server大量数据秒级插入/新增/删除 1.快速保存,该方法有四个参数,第一个参数为数据库连接,第二个参数为需要保存的DataTable,该参数的TableName属性需要设置为数据库 ...
- 软件架构自学笔记-- 转载“虎牙在全球 DNS 秒级生效上的实践”
虎牙在全球 DNS 秒级生效上的实践 这次分享的是全球 DNS 秒级生效在虎牙的实践,以及由此产生的一些思考,整体上,分为以下 5 各部分: 背景介绍: 方案设计和对比: 高可用: 具体实践和落地: ...
- 《DNS稳定保障系列3--快如闪电,域名解析秒级生效》
在刚刚过去的双十一,又是一个全民狂欢的盛宴,天猫双十一的成交量高达2684亿.无数小伙伴在淘宝.天猫里买买买,今年你又剁手了多少?言归正传,在你疯狂秒杀的时候,有没有发现,今年的购物体验一如既往的好, ...
- 虎牙在全球 DNS 秒级生效上的实践
本文整理自虎牙中间件团队在 Nacos Meetup 的现场分享,阿里巴巴中间件受权发布. 这次分享的是全球 DNS 秒级生效在虎牙的实践,以及由此产生的一些思考,整体上,分为以下5各部分: 背景介绍 ...
随机推荐
- Vue系列:Slot 插槽的使用范例
插槽对于自定义的组件开发来说,是十分强大的功能.这篇主要做个简单梳理 插槽可以分3种: 1.简单插槽 2.具名插槽 3.作用域插槽
- LeetCode——540. Single Element in a Sorted Array
题目:Given a sorted array consisting of only integers where every element appears twice except for one ...
- HTML发展历程
HTML是超文本标记语言的缩写,不同于C或JAVA等编程语言,HTML由标签组成.通过标签可以在网页中插入文字.图片.链接.音频.视频等元素,进而描述网页.和Windows一样,随着技术的发展,HTM ...
- ABP 配置全局数据过滤器
ABP官方数据过滤的地址:https://aspnetboilerplate.com/Pages/Documents/Data-Filters 中文可以看这个:https://aspnetboiler ...
- web小知识点
写在前面: 该篇是个人平时对web前端小知识点的总结,会不定时更新...... 如有错误,敬请批评指正. 正文: 1.WWW是World Wide Web的缩写. 2.HTML(Hyper Text ...
- 学完JavaScript基础有感
紧接上一篇回来了,这几天一直学js,会不自觉的和其他的编程语言联系在一起,在没有学jQuery之前,结合我所学的c,java,数据结构,数据库以及部分html感觉到JavaScript里面又很多相似的 ...
- 交叉编译QT 5.6.2 Shell脚本
测试环境: CPU: AT91SAM9X35 Linux: Atmel提供的linux-at91-linux4sam_5.3 (Linux-4.1.0) 转载请注明: 凌云物网智科嵌入式实 ...
- 关于前端jsonp跨域和一个简单的node服务搭建
先讲下概念 同源策略:是一种约定,浏览器最核心最基本的安全功能,(同域名,同协议,同端口)为同源 跨域: 跨(跳):范围 域 (源):域名,协议,端口 域名:ip的一种昵称(为了更好记住ip地址)如: ...
- ionic App 解决android端在真机上 tab处于顶部的Bug
在app.js 页面中添加以下代码 .config(function($stateProvider, $urlRouterProvider,$ionicConfigProvider) { $ionic ...
- tf.control_dependencies
tf.control_dependencies()是用来控制计算流图的,给图中的某些节点指定计算的顺序. 原型: tf.control_dependencies(self, control_input ...