Deformable Templates For Eye Detection
1 Abstract
This approach was published On "Deformable Templates for Face Recognition" by Alan L. Yuille. I found that the method for eye recognition is useful for my current research, so just make notes.
The original paper mainly described three aspects:
1) Global templates which introduce a model that connect a set of basic features of the face by springs, the features include eyes, hair, mouth, nose, and left and right edges of the face, the method was proposed by Fischler and Elschlager. Now I am not going to focus on it.
2) A detailed descriptions of using deformable templates to extract facial features. I am just interested in eye templates.
3) A more robust method for deformable templates, which promises to obtain more reliable recognition. it is important for Real Application.
2 Feature Template For Eye Extraction
Suppose we want to detect eyes using traditional method. we know how to extract edges in the image, but it is hard to organize the low level edge features into a sensible global percept. The difficulty reminds me of the generalized hough transform, but it can not describe such a sophisticated shape which has iris and white of eye. however, the deformable template can deal with it. In the deformable template approach the templates are specified by a set of parameters that enables a priori knowledge about the expected shape of the features to guide the detection process. The templates are flexible to be able to change their parameter values so as to match themselves to the data. The final values of these parameters then can be used to describe the features.
The key idea to the deformable templates is the energy function, which gives a measure of fit of the template to the image. that is, Minimizing the energy attracts the template to salient features, such as peaks, valleys, and edges in the image. The minimum of the energy function means best(local) fit with the image. The template is first given some initial parameters which decide an initial position of the feature, then the parameter of the template is updated by steepest descent method, this correspond to following a path in parameter space(Recalling hough transform method, we sample the parameter space and then increase the space at every possible points, it is a computational cost method).

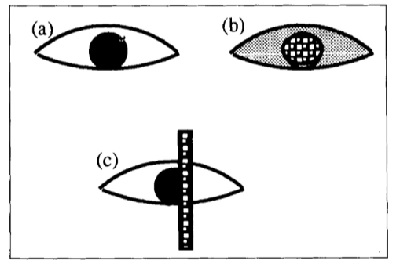
By observing the above image, The template consists of the following features:
1) A circle of radius r, centered on a point  . This corresponds to the boundary between the iris and the whites of the eye and is attracted to edges in the image intensity. The interior of the circle is attracted to valleys.
. This corresponds to the boundary between the iris and the whites of the eye and is attracted to edges in the image intensity. The interior of the circle is attracted to valleys.
2) A bounding contour of the eye attracted to edges, which can be modeled by two parabolic sections representing the upper and lower parts of the boundary. It has a center 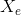 , width 2b, maximum height a of the boundary above the center, maximum height c of the boundary below the center, and an angle of orientation
, width 2b, maximum height a of the boundary above the center, maximum height c of the boundary below the center, and an angle of orientation 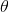 .
.
3) Two points corresponds to the centers of the whites of the eyes, which are attracted to peaks in the image intensity. These points are labeled by 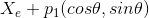 and
and  , where
, where 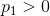 and
and  .
.
4) The regions between the bounding contour and the iris correspond to the white of the eye. They will be attracted to large value in the image intensity.
5) 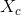 and
and 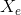 meant to be close together most of the time, but not always true.
meant to be close together most of the time, but not always true.
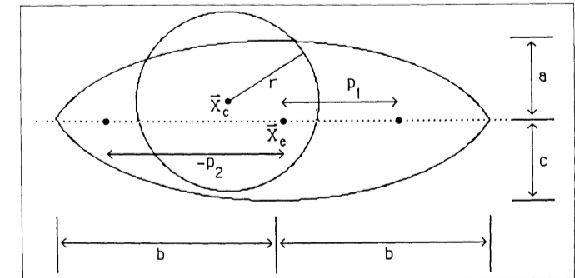
The template is illustrated in above figure. It has a total of 9 parameters:  ,
, 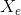 ,
,  ,
, 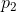 , r, a, b, c and
, r, a, b, c and 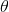 . All of these are allowed to vary during the matching.
. All of these are allowed to vary during the matching.
The parameter 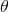 rotates the template, then the parabola functions get more complicated. For simplicity, we should first reconstruct coordinate using rotation parameter, then things become simpler. We define two unit vectors as follows:
rotates the template, then the parabola functions get more complicated. For simplicity, we should first reconstruct coordinate using rotation parameter, then things become simpler. We define two unit vectors as follows:
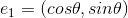 ,
, 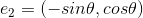 , Any points x in space can be represented by
, Any points x in space can be represented by  where
where 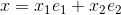 .
.
The circle function is then defined as 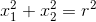 , which centered at
, which centered at 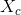 .
.
The top half of the parabola is defined as 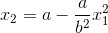 , the lower half is defined as
, the lower half is defined as 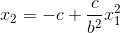 , they both centered at
, they both centered at 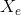 .
.
Up to now, All we need is constructing an energy function of the deformable templates. Before this, we should define some representations of the images.
1) 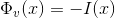 , the valley of the image,
, the valley of the image, 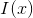 represents the image itself.
represents the image itself.
2) 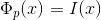 , the peak of the image.
, the peak of the image.
3)  , the edge of the image, the original paper use first equation, but I prefer the second one.
, the edge of the image, the original paper use first equation, but I prefer the second one.
These representations are chosen to extract properties of the image, such as valleys, peaks and edges. Once we have prepared these representations of the image, we can construct an energy function of the deformable templates.
1)  , the energy takes the minimum value over the interior of the circle.
, the energy takes the minimum value over the interior of the circle.
2) 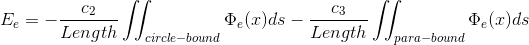 , the energy takes the minimum value over the edge.
, the energy takes the minimum value over the edge.
3) 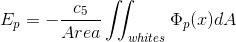 , the energy takes the minimum value between the circle and the parabolas.
, the energy takes the minimum value between the circle and the parabolas.
4) 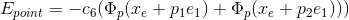 , the energy takes the minimum value at two peak points in the white of eyes.
, the energy takes the minimum value at two peak points in the white of eyes.
5) 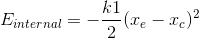 , the energy takes the minimum value when two points get close together, but we should use it with caution.
, the energy takes the minimum value when two points get close together, but we should use it with caution.
Add all of the energy function above, we get a complete energy function 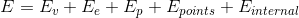 .
.
Using the energy function, we can define an algorithm to detect the eye.
1) Set 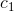 to be large enough, set other coefficients to be 0. During this epoch the valley forces pull the template to the eye(Iris).
to be large enough, set other coefficients to be 0. During this epoch the valley forces pull the template to the eye(Iris).
2) Increase the coefficient of the boundary of the circle 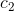 . This fine tunes the size of the circle as it locks onto the iris.
. This fine tunes the size of the circle as it locks onto the iris.
3) Increase the coefficient of the peak 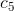 . This rotates the template and get the correct orientation.
. This rotates the template and get the correct orientation.
4) Increase the coefficient of the edges of the boundary 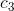 . This fine tunes the position of the boundaries.
. This fine tunes the position of the boundaries.
Right now, we have only one problem not solved yet. That is, how to decide the initial values of the template parameters. Here is the strategy:
Since the eye template might start at places where the valley representation was strong, we search in the whole image to find some local minimum in intensity. These local minimum positions may be the Initial  s. Then we should start several deformable templates off in parallel and see which gives the best results. At last we use some criteria such as the final energy function to decide which one is the best. However, the criteria may fail sometime, so we should check the template parameters meanwhile to avoid making mistake. Generally, if we come across a group of template parameters that are extremely unlikely, we should discard them even if the energy function is minimum.
s. Then we should start several deformable templates off in parallel and see which gives the best results. At last we use some criteria such as the final energy function to decide which one is the best. However, the criteria may fail sometime, so we should check the template parameters meanwhile to avoid making mistake. Generally, if we come across a group of template parameters that are extremely unlikely, we should discard them even if the energy function is minimum.
3 Robust Feature Templates
The method described in the previous section may fail in several situations, such as partial occlusion or noise.
Consider the problem of estimating the mean from a set of samples 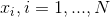 .
.
The sample mean is 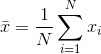 , and the least square error is
, and the least square error is  .
.
The sample mean is extremely sensitive to outliers. A robust technique for estimating the mean should be relatively independent of such outliers and should also enable us to identify the outliers themselves. We can use least trimmed squares to achieve the goal. For each value of x we order the residuals 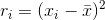 so that
so that 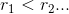 , we choose M(M < N) points that has less residuals, then use these points to calculate the mean and least square error.
, we choose M(M < N) points that has less residuals, then use these points to calculate the mean and least square error.
We can use the above idea to reformulate the deformable templates algorithm. The geometry model keep same as before. The measures of fit aim to find the parameters of the template that minimize the mean in the iris region, maximize the mean for the whites of the eyes, and maximize the mean edge strength at the boundaries. We order each variables by residuals, and then just use portion of them for the energy function. This give us better effect when partial occlusion or noise.
4 References
Alan L. Yuille. Deformable Templates for Face Recognition.
Deformable Templates For Eye Detection的更多相关文章
- 行人检测(Pedestrian Detection)资源整合
一.纸 评论文章分类: [1] D. Geronimo, and A. M.Lopez. Vision-based Pedestrian Protection Systems for Intellig ...
- CV界的明星人物们
CV界的明星人物们 来自:http://blog.csdn.net/necrazy/article/details/9380151,另外根据自己关注的地方,加了点东西. 今天在cvchina论坛上看到 ...
- paper 99:CV界的明星人物经典介绍
CV人物1:Jianbo Shi史建波毕业于UC Berkeley,导师是Jitendra Malik.其最有影响力的研究成果:图像分割.其于2000年在PAMI上多人合作发表”Nor ...
- CV牛人牛事简介之一
CV牛人牛事简介之一 [论坛按] 发帖人转载自:http://doctorimage.cn/2013/01/01/cv-intro-niubility/#6481970-qzone-1-83120-8 ...
- ECCV 2014 Results (16 Jun, 2014) 结果已出
Accepted Papers Title Primary Subject Area ID 3D computer vision 93 UPnP: An optimal O(n) soluti ...
- 基于Emgu CV的人脸检测代码
这个提供的代码例子是Emgu CV提供的源码里面自带的例子,很好用,基本不需要改,代码做的是人脸检测不是人脸识别,这个要分清楚.再就是新版本的Emgu CV可能会遇到系统32位和64位处理方式有区别的 ...
- Dynamices CRM Permission Issue (Security role UI to privilege mapping)'s solution
select * from privilege where privilegeid = 'a4736385-9763-4a64-a44b-cd5933edc631' Security role UI ...
- CV code references
转:http://www.sigvc.org/bbs/thread-72-1-1.html 一.特征提取Feature Extraction: SIFT [1] [Demo program][SI ...
- CV codes代码分类整理合集 《转》
from:http://www.sigvc.org/bbs/thread-72-1-1.html 一.特征提取Feature Extraction: SIFT [1] [Demo program] ...
随机推荐
- 怎样查看Jenkins的版本
where to check jenkins version To identify your current version of Jenkins, you can do one of two th ...
- kubernetes (k8s) CKA认证之第二课:亲和性与 Pod 的调度
手动调度一个 pod // cat manual-schedule.yaml apiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: labels: run: pod-manual-sc ...
- Linux上天之路(九)之文件和文件夹的权限
主要内容 linux 基本权限 linux特殊权限 linux隐藏权限 linux file ACL 权限 1. Linux的基本权限 使用ls -l filename 命令查看文件或文件夹详细权限 ...
- jQuery里的mouseover与mouseenter事件类型区别
JQ里面有mouseover和mouseenter 2个事件类型干着差不多的活,用不好经常出现些小问题. 今天我解释一下原理: 事件类型翻译: mouseover 鼠标移上 mouseenter 鼠 ...
- 【Java】Eclipse常用快捷键
Eclipse常用快捷键 * 1.补全代码的声明:alt + / * 2.快速修复: ctrl + 1 * 3.批量导包:ctrl + shift + o * 4.使用单行注释:ctrl + / * ...
- host解析
首先了解一下什么是hosts文件: hosts是一个没有扩展名的系统文件,可以用记事本等文本编辑工具打开,起作用就是将一些常用的"网址域名"与其对应的"IP地址" ...
- C# 实现Parallel.For
static class MyParallel { //4.0及以上用Task, Task的背后的实现也是使用了线程池线程 //static List<Task> tasks = new ...
- 【记录一个问题】opencv官网的opencv android sdk使用opencl并未用到GPU
UMat u_mat;mat.copyTo(u_mat);cv::cvtColor(u_mat, cv::BGR2GARY);这样的代码反复执行,并未发现GPU占用提升.执行时间与不使用UMat相当. ...
- Cesium中级教程8 - Introduction to Particle Systems 粒子系统入门
Cesium中文网:http://cesiumcn.org/ | 国内快速访问:http://cesium.coinidea.com/ What is a particle system? 什么是粒子 ...
- CSS快速入门(三)
目录 字体相关调整 背景相关调整 控制背景平铺 调整背景图像的大小 边框属性 圆与圆角 盒模型 块级盒子(Block box) 和 内联盒子(Inline box) display属性 盒子模型 盒模 ...
