android HAL 教程(含实例)
http://www.cnblogs.com/armlinux/archive/2012/01/14/2396768.html
Android Hal 分析
-------rockchip Andy
本文是基于android4.0.3.对应其他低版本的代码,可能有所差异,但基本大同小异。
1.产生HAL的原因
Android的HAL是为了保护一些硬件提供商的知识产权而提出的,是为了避开linux的GPL束缚。思路是把控制硬件的动作都放到了Android HAL中,而linux driver仅仅完成一些简单的数据交互作用,甚至把硬件寄存器空间直接映射到user space。而Android是基于Apache的license,因此硬件厂商可以只提供二进制代码,所以说Android只是一个开放的平台,并不是一个开源的平台。也许也正是因为Android不遵从GPL,所以Greg Kroah-Hartman才在2.6.33内核将Andorid驱动从linux中删除。GPL和硬件厂商目前还是有着无法弥合的裂痕。Android想要把这个问题处理好也是不容易的。
总结下来,Android HAL存在的原因主要有:
- 并不是所有的硬件设备都有标准的linux kernel的接口
- KERNEL DRIVER涉及到GPL的版权。某些设备制造商并不原因公开硬件驱动,所以才去用HAL方 式绕过GPL。
- 针对某些硬件,An有一些特殊的需求
现有HAL架构由Patrick Brady (Google) 在2008 Google I/O演讲中提出的,如下图:
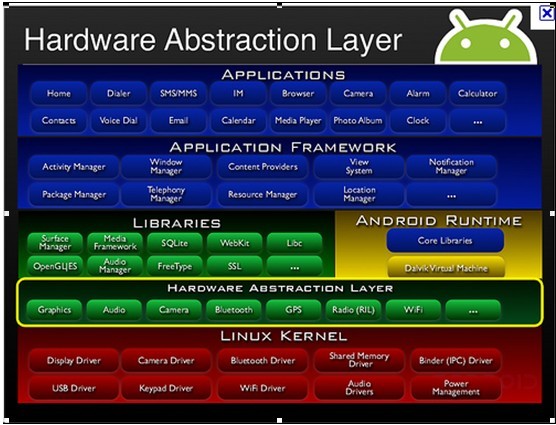
2.源码目录介绍
- /hardware/libhardware_legacy/ 旧的架构、采取链接库模块的方式
- /hardware/libhardware 新架构、调整为 HAL stub。
- /hardware/ril 无线电抽象层
- 一般除了它们3个都是硬件厂商相关的hal目录。
2.1 libhardware目录的结构如下
/hardware/libhardware/hardware.c 编译成libhardware.s置于/system/lib
/hardware/libhardware/include/hardware目录下包含如下头文件:
hardware.h 通用硬件模块头文件
copybit.h copybit模块头文件
gralloc.h gralloc模块头文件
lights.h 背光模块头文件
overlay.h overlay模块头文件
qemud.h qemud模块头文件
sensors.h 传感器模块头文件
/hardware/libhardware/modules 目录下定义了很多硬件模块
2.2 下面几个是各个厂商平台相关的hal
/hardware/msm7k
/hardware/qcom
/hardware/ti
/device/Samsung
/device/moto
这些硬件模块都编译成xxx.xxx.so,目标位置为/system/lib/hw目录
3.HAL层的两种架构与两种访问方式
3.1 两种架构
位于libhardware_legacy目录下的“旧HAL架构”和位于libhardware目录下的“新HAL架构”。两种框架如下图所示:

- libhardware_legacy 是将 *.so 文件当作shared library来使用,在runtime(JNI 部份)以 direct function call 使用 HAL module。通过直接函数调用的方式,来操作驱动程序。当然,应用程序也可以不需要通过 JNI 的方式进行,直接加载 *.so (dlopen)的做法调用*.so 里的符号(symbol)也是一种方式。总而言之是没有经过封装,上层可以直接操作硬件。
- 现在的libhardware 架构,就有stub的味道了。HAL stub 是一种代理人(proxy)的概念,stub 虽然仍是以 *.so的形式存在,但HAL已经将 *.so 隐藏起来了。Stub 向 HAL提供操作函数(operations),而 runtime 则是向 HAL 取得特定模块(stub)的 operations,再 callback 这些操作函数。这种以 indirect function call 的架构,让HAL stub 变成是一种包含关系,即 HAL 里包含了许许多多的 stub(代理人)。Runtime 只要说明类型,即 module ID,就可以取得操作函数。对于目前的HAL,可以认为Android定义了HAL层结构框架,通过几个接口访问硬件从而统一了调用方式。
Android的HAL的实现需要通过JNI(Java Native Interface),JNI简单来说就是java程序可以调用C/C++写的动态链接库,这样的话,HAL可以使用C/C++语言编写,效率更高。
3.2 调用过程如下
JNI->通用硬件模块->硬件模块->内核驱动接口.
具体一点:JNI->libhardware.so->xxx.xxx.so->kernel.
再具体来说:android frameworks中JNI调用hardware.c中定义的hw_get_module函数来获取硬件模块,然后调用硬件模块中的方法,硬件模块中的方法直接调用内核接口完成相关功能
3.3 两种访问方式
(1)Android的app可以直接通过service调用.so格式的jni
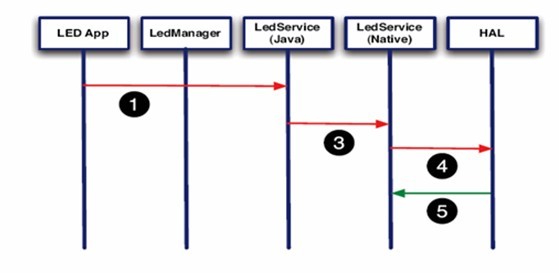
(2)经过Manager调用service
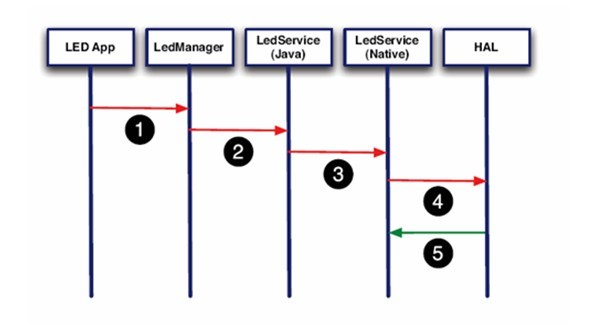
上面两种方法应该说是各有优缺点:
- 第一种方法简单高效,但不正规。
- 第二种方法实现起来比较复杂,但更符合目前的Android框架。第二种方法中,LegManager和LedService(java)在两个进程中,需要进程通讯。
在现在的android框架中,这两种方式都存在,比如对于lights,是直接透过LightsService调用JNI,而对于sensor,中间则是通过SensorsManager来调用JNI的。
4.通用硬件模块(libhardware.so)
一般来说HAL moudle需要涉及的是三个关键结构体:
- struct hw_module_t;
- struct hw_module_methods_t;
- struct hw_device_t;
这三个结构体定义在hardware.h中。
路径为:/hardware/libhardware/include/hardware/hardware.h
头文件中主要定义了通用硬件模块结构体hw_module_t,声明了JNI调用的接口函数hw_get_module。hw_module_t定义如下:
/** * Every hardware module must have a data structure named HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM * and the fields of this data structure must begin with hw_module_t * followed by module specific information. */
typedef struct hw_module_t { /** tag must be initialized to HARDWARE_MODULE_TAG */
uint32_t tag; /** major version number for the module */
uint16_t version_major; /** minor version number of the module */
uint16_t version_minor; /** Identifier of module */
const char *id; /** Name of this module */
const char *name; /** Author/owner/implementor of the module */
const char *author; /** Modules methods */
struct hw_module_methods_t* methods; //硬件模块的方法 /** module's dso */
void* dso; /** padding to 128 bytes, reserved for future use */
uint32_t reserved[-]; } hw_module_t;
如注释所说,所有的hal模块都要有一个以HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM命名的结构,而且这个结构要以hw_module_t为第一个成员,即要继承hw_module_t这个结构,比如lights,sensor:
struct sensors_module_t {
struct hw_module_t common;
int (*get_sensors_list)(struct sensors_module_t* module,
struct sensor_t const** list);
};
/*
* The lights Module
*/
struct light_module_t HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM = {
.common: {
tag: HARDWARE_MODULE_TAG,
version_major: ,
version_minor: ,
id: LIGHTS_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID,
name: "Lights module",
author: "Rockchip",
methods: &light_module_methods,
}
};
const struct sensors_module_t HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM = {
.common = {
.tag = HARDWARE_MODULE_TAG,
.version_major = ,
.version_minor = ,
.id = SENSORS_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID,
.name = "Stingray SENSORS Module",
.author = "Motorola",
.methods = &sensors_module_methods,
},
.get_sensors_list = sensors__get_sensors_list
};
hw_module_t中比较重要的是硬件模块方法结构体hw_module_methods_t定义如下:
typedef struct hw_module_methods_t {
/** Open a specific device */
int (*open)(const struct hw_module_t* module, const char* id,
struct hw_device_t** device);
} hw_module_methods_t;
该方法在定义HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM的时候被初始化。目前该结构中只定义了一个open方法,其中调用的设备结构体参数hw_device_t定义如下:
/**
* Every device data structure must begin with hw_device_t
* followed by module specific public methods and attributes.
*/
typedef struct hw_device_t { /** tag must be initialized to HARDWARE_DEVICE_TAG */
uint32_t tag; /** version number for hw_device_t */
uint32_t version; /** reference to the module this device belongs to */
struct hw_module_t* module; /** padding reserved for future use */
uint32_t reserved[]; /** Close this device */
int (*close)(struct hw_device_t* device); } hw_device_t; struct light_device_t {
struct hw_device_t common;
int (*set_light)(struct light_device_t* dev,
struct light_state_t const* state);
}; /** * Every device data structure must begin with hw_device_t
* followed by module specific public methods and attributes.
*/
struct sensors_poll_device_t {
struct hw_device_t common;
int (*activate)(struct sensors_poll_device_t *dev,
int handle, int enabled); int (*setDelay)(struct sensors_poll_device_t *dev,
int handle, int64_t ns); int (*poll)(struct sensors_poll_device_t *dev,
sensors_event_t* data, int count); };
亦如注释所说,每一个设备的数据结构都必须也以hw_device_t为第一个成员。
5.以lights模块为例进行分析
5.1 源文件位置:(android5.1源码)
- /frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/lights/
- /frameworks/base/services/core/jni/com_android_server_lights_LightsService.cpp
- /hardware/libhardware/include/hardware/lights.h
5.2 访问设备大概流程
app--->frameworks--->hardware--->kernel驱动
frameworks通过jni调用hw_get_module()获得HAL对应的模块,它的声明如下:
int hw_get_module(const char *id, const struct hw_module_t **module);
- 参数id为模块标识,定义在/hardware/libhardware/include/hardware录下的硬件模块头文件中
- 参数module是硬件模块地址,定义在/hardware/libhardware/include/hardware/hardware.h中
在lights.h中定义有lights模块的ID.
#define LIGHTS_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID "lights"
在5.1源码frameworks/base/services/core/jni/com_android_server_LightsService.cpp的init_native方法中调用hw_ge_module(),代码如下:
static jint init_native(JNIEnv *env, jobject clazz)
{
int err;
hw_module_t* module;
Devices* devices;
devices = (Devices*)malloc(sizeof(Devices));
err = hw_get_module(LIGHTS_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID, (hw_module_t const**)&module);
if (err == ) {
devices->lights[LIGHT_INDEX_BACKLIGHT]
= get_device(module, LIGHT_ID_BACKLIGHT);
//………………………………………….
}
hw_get_module函数在hardware.c中实现:
int hw_get_module(const char *id, const struct hw_module_t **module)
{
return hw_get_module_by_class(id, NULL, module);
}
再看hw_get_module_by_class时如何实现的:
首先在hardware.c的开始有如下定义和注释:
/** Base path of the hal modules */
#define HAL_LIBRARY_PATH1 "/system/lib/hw"
#define HAL_LIBRARY_PATH2 "/vendor/lib/hw" /**
* There are a set of variant filename for modules. The form of the filename
* is "<MODULE_ID>.variant.so" so for the led module the Dream variants
* of base "ro.product.board", "ro.board.platform" and "ro.arch" would be:
*
* led.trout.so
* led.msm7k.so
* led.ARMV6.so
* led.default.so
*/ static const char *variant_keys[] = {
"ro.hardware", /* This goes first so that it can pick up a different
file on the emulator. */
"ro.product.board",
"ro.board.platform",
"ro.arch"
}; static const int HAL_VARIANT_KEYS_COUNT =
(sizeof(variant_keys)/sizeof(variant_keys[])); int hw_get_module_by_class(const char *class_id, const char *inst,
const struct hw_module_t **module) {
int status;
int i;
const struct hw_module_t *hmi = NULL;
char prop[PATH_MAX];
char path[PATH_MAX];
char name[PATH_MAX]; if (inst)
snprintf(name, PATH_MAX, "%s.%s", class_id, inst);
else
strlcpy(name, class_id, PATH_MAX); /*
* Here we rely on the fact that calling dlopen multiple times on
* the same .so will simply increment a refcount (and not load
* a new copy of the library).
* We also assume that dlopen() is thread-safe.
*/ /* Loop through the configuration variants looking for a module */
for (i = ; i < HAL_VARIANT_KEYS_COUNT + 1 ; i++) {
if (i < HAL_VARIANT_KEYS_COUNT) {
if (property_get(variant_keys[i], prop, NULL) == ) {
continue;
}
snprintf(path, sizeof(path), "%s/%s.%s.so",
HAL_LIBRARY_PATH2, name, prop);
if (access(path, R_OK) == ) break; snprintf(path, sizeof(path), "%s/%s.%s.so",
HAL_LIBRARY_PATH1, name, prop);
if (access(path, R_OK) == ) break;
} else {
snprintf(path, sizeof(path), "%s/%s.default.so",
HAL_LIBRARY_PATH1, name);
if (access(path, R_OK) == ) break;
}
}
status = -ENOENT;
if (i < HAL_VARIANT_KEYS_COUNT + ) {
/* load the module, if this fails, we're doomed, and we should not try
* to load a different variant. */
status = load(class_id, path, module);
}
return status; }
可以看到,在hw_get_module_by_class函数中:
- 先通过property_get获得varient_key中定义的系统属性,
- 如果系统中有定义该属性,就会获得一个模块名.属性名组成的一个so的名称,
- 然后去/system/lib/hw、/vendor/lib/hw下查看,该so是否存在,如果存在,调用load函数,打开.so.
例如在rockchip的rk29平台上,有定义ro.product.board = rk29sdk,在这里会得到lights.rk29sdk.so。
再看load函数的实现:
/**
* Load the file defined by the variant and if successful
* return the dlopen handle and the hmi.
* @return 0 = success, !0 = failure.
*/
static int load(const char *id,
const char *path,
const struct hw_module_t **pHmi)
{
int status;
void *handle;
struct hw_module_t *hmi; /*
* load the symbols resolving undefined symbols before
* dlopen returns. Since RTLD_GLOBAL is not or'd in with
* RTLD_NOW the external symbols will not be global
*/
handle = dlopen(path, RTLD_NOW);
if (handle == NULL) {
char const *err_str = dlerror();
ALOGE("load: module=%s\n%s", path, err_str?err_str:"unknown");
status = -EINVAL;
goto done;
}
/* Get the address of the struct hal_module_info. */
const char *sym = HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM_AS_STR;
hmi = (struct hw_module_t *)dlsym(handle, sym);
if (hmi == NULL) {
ALOGE("load: couldn't find symbol %s", sym);
status = -EINVAL;
goto done;
} /* Check that the id matches */
if (strcmp(id, hmi->id) != ) {
ALOGE("load: id=%s != hmi->id=%s", id, hmi->id);
status = -EINVAL;
goto done;
}
hmi->dso = handle;
/* success */
status = ;
done:
if (status != ) {
hmi = NULL;
if (handle != NULL) {
dlclose(handle);
handle = NULL;
}
} else {
ALOGV("loaded HAL id=%s path=%s hmi=%p handle=%p",
id, path, *pHmi, handle);
}
*pHmi = hmi;
return status;
}
在这里会打开对应了so,比如lights.rk29sdk.so,然后获得这个模块中定义的hw_module_t的地址。后面JNI就能通过这个接口和hal层进行沟通了。
6.HAL与frameworks关联代码如下
public class LightsService extends SystemService {
//...
private void setLightLocked(int color, int mode, int onMS, int offMS, int brightnessMode) {
if (color != mColor || mode != mMode || onMS != mOnMS || offMS != mOffMS) {
if (DEBUG) Slog.v(TAG, "setLight #" + mId + ": color=#"
+ Integer.toHexString(color));
mColor = color;
mMode = mode;
mOnMS = onMS;
mOffMS = offMS;
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_POWER, "setLight(" + mId + ", " + color + ")");
try {
setLight_native(mNativePointer, mId, color, mode, onMS, offMS, brightnessMode);
} finally {
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_POWER);
}
}
}
public LightsService(Context context) {
super(context);
mNativePointer = init_native();
//...
}
private static native long init_native();//这里调用HAL层的hw_get_module
private static native void finalize_native(long ptr);
static native void setLight_native(long ptr, int light, int color, int mode,
int onMS, int offMS, int brightnessMode);//访问硬件
private long mNativePointer;//保存hal返回的句柄
}
android HAL 教程(含实例)的更多相关文章
- 【转】Android HAL实例解析
原文网址:http://www.embedu.org/Column/Column339.htm 作者:刘老师,华清远见嵌入式学院讲师. 一.概述 本文希望通过分析台湾的Jollen的mokoid 工程 ...
- Android HAL实例解析
一.概述 本文希望通过分析台湾的Jollen的mokoid 工程代码,和在s5pc100平台上实现过程种遇到的问题,解析Andorid HAL的开发方法. 二.HAL介绍 现有HAL架构由Patric ...
- mybaits入门(含实例教程和源码) http://blog.csdn.net/u013142781/article/details/50388204
前言:mybatis是一个非常优秀的存储过程和高级映射的优秀持久层框架.大大简化了,数据库操作中的常用操作.下面将介绍mybatis的一些概念和在eclipse上的实际项目搭建使用. 一.mybati ...
- .NET开发邮件发送功能的全面教程(含邮件组件源码)
今天,给大家分享的是如何在.NET平台中开发“邮件发送”功能.在网上搜的到的各种资料一般都介绍的比较简单,那今天我想比较细的整理介绍下: 1) 邮件基础理论知识 2) ...
- ArcGIS Runtime for Android开发教程V2.0(1)基本概念
原文地址: ArcGIS Runtime for Android开发教程V2.0(1)基本概念 - ArcGIS_Mobile的专栏 - 博客频道 - CSDN.NET http://blog.csd ...
- Spring中@Transactional事务回滚(含实例详细讲解,附源码)
一.使用场景举例 在了解@Transactional怎么用之前我们必须要先知道@Transactional有什么用.下面举个栗子:比如一个部门里面有很多成员,这两者分别保存在部门表和成员表里面,在删除 ...
- [读后感]spring Mvc 教程框架实例以及系统演示下载
[读后感]spring Mvc 教程框架实例以及系统演示下载 太阳火神的漂亮人生 (http://blog.csdn.net/opengl_es) 本文遵循"署名-非商业用途-保持一致&qu ...
- Spring中@Transactional事务回滚(含实例具体解说,附源代码)
一.使用场景举例 在了解@Transactional怎么用之前我们必须要先知道@Transactional有什么用. 以下举个栗子:比方一个部门里面有非常多成员,这两者分别保存在部门表和成员表里面,在 ...
- linux.linuxidc.com - /2011年资料/Android入门教程/
本文转自 http://itindex.net/detail/15843-linux.linuxidc.com-%E8%B5%84%E6%96%99-android Shared by Yuan 用户 ...
随机推荐
- 关于phpmyadmin的小笔记
默认情况下,phpmyadmin联系的是localhost. 如果此时hostname不是localhost而是其它什么的话,在phpmyadmin是不能连接上的,虽然在命令行mysql -h loc ...
- 异常:java.io.IOException: Too many open files:
原因: 操作系统的中打开文件的最大句柄数受限所致,常常发生在很多个并发用户访问服务器的时候.因为为了执行每个用户的应用服务器都要加载很多文件(new一个socket就需要一个文件句柄),这就会导致打开 ...
- xshell的快捷命令
xshell的快捷命令 reconnect Type `help' to learn how to use Xshell prompt.[c:\~]$ ?Internal Commands:new: ...
- SQL性能优化
引言: 以前在面试的过程中,总有面试官问道:你做过sql性能优化吗?对此,我的答复是没有.一次没有不是自己的错误,两次也不是,但如果是多次呢?今天痛下决心,把有关sql性能优化的相关知识总结一下,以便 ...
- 搭建git for windows服务器(100%可以成功)
既然Git在Linux下面非常好用,为什么还要搭建git windows的服务器,因为不是所有的用户都需要在linux下面做开发,对吧,还有很多用户选择使用windows做开发. 看到很多网友尝试部分 ...
- centos7最小安装后常常需要添加的命令
本人下载的最小镜像文件下载地址:http://pan.baidu.com/s/1kUD2jbT 原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/nmgrd/article/details/5176 ...
- >>> 主页推荐链接
Apple专区 App Store 排行榜 App Store 排行榜 - 中国区 PC6苹果网 威锋网 第三方 环信 - 即时通讯云领导者 腾讯Bugly - Android Crash | iOS ...
- Leetcode: Word Squares && Summary: Another Important Implementation of Trie(Retrieve all the words with a given Prefix)
Given a set of words (without duplicates), find all word squares you can build from them. A sequence ...
- iis配置js支持读取json文件配置
默认情况下,iis不支持解析.json文件,这就需要我们自己在iis下配置方法一:iis配置1.点击开始菜单选择控制面板: 2.控制面板内点击管理工具,选择Internet信息服务(IIS)管理器. ...
- mui小总结
下拉刷新 第一: mui.init({ pullRefresh: { container: '#pullrefresh', up: { contentrefresh: '正在加载...', callb ...
