HDU 4587 TWO NODES 枚举+割点
原题链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=4587
TWO NODES
Time Limit: 24000/12000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65535/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 1448 Accepted Submission(s): 441
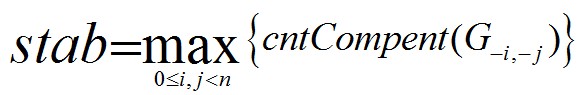
Among the expression,G-i, -j is the remainder after removing node i, node j and all edges that are directly relevant to the previous two nodes. cntCompent is the number of connected components of X independently.
Thus, given a certain undirected graph G, you are supposed to calculating the value of stab.
Please note that the endpoints of edge is marked in the range of [0,N-1], and input cases ends with EOF.
0 1
1 2
2 3
3 0
0 2
题意
给你个图,问你去掉两个点之后能有最多多少连通块。
题解
先枚举其中一个点,然后在剩下的点中求割点,Tarjan的时候统计一下每个割点分割几个连通块,取个最大的割点,然后再dfs一次求连通块个数。
代码
#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#define MAX_N 5555
using namespace std; vector<int> G[MAX_N];
bool vis[MAX_N];
int dfn[MAX_N],low[MAX_N],ind=; int cut[MAX_N]; int node; void Tarjan(int u,int p){
int child=;
dfn[u]=low[u]=++ind;
vis[u]=;
for(int i=;i<G[u].size();i++){
int v=G[u][i];
if(v==p||v==node)continue;
if(!vis[v]){
Tarjan(v,u);
low[u]=min(low[v],low[u]);
child++;
if((p==-&&child>)||(p!=-&&low[v]>=dfn[u]))
cut[u]++;
}
else
low[u]=min(dfn[v],low[u]);
}
} int n,m; void init(){
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)G[i].clear();
ind=;
memset(vis,,sizeof(vis));
memset(cut,,sizeof(cut));
} bool used[MAX_N];
int cu;
void dfs(int u,int p){
if(u==p||used[u]||u==node||u==cu)return;
used[u]=;
for(int i=;i<G[u].size();i++)dfs(G[u][i],u);
} int main(){
while(scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)==){
int stab=;
init();
int u,v;
for(int i=;i<m;i++) {
scanf("%d%d", &u, &v);
G[u].push_back(v);
G[v].push_back(u);
}
for(int i=;i<n;i++){
node=i;
memset(vis,,sizeof(vis));
ind=;
memset(cut,,sizeof(cut));
for(int j=;j<n;j++)
if((!vis[j])&&j!=node)
Tarjan(j,-);
int maxC=;
for(int j=;j<n;j++)
if(j!=node&&cut[j]>=maxC){
cu=j;
maxC=cut[j];
}
int ans=;
memset(used,,sizeof(used));
for(int j=;j<n;j++)
if((!used[j])&&j!=node&&j!=cu){
dfs(j,-);
ans++;
}
stab=max(stab,ans);
}
printf("%d\n",stab);
} return ;
}
HDU 4587 TWO NODES 枚举+割点的更多相关文章
- HDU 4587 TWO NODES(割点)(2013 ACM-ICPC南京赛区全国邀请赛)
Description Suppose that G is an undirected graph, and the value of stab is defined as follows: Amon ...
- HDU 4587 TWO NODES 割点
题目链接: http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=4587 题意: 删除两个点,使连通块的数目最大化 题解: 枚举删除第一个点,然后对删除了第一个点的图跑 ...
- HDU - 4587 TWO NODES (图的割点)
Suppose that G is an undirected graph, and the value of stab is defined as follows: Among the expres ...
- HDU 4587 TWO NODES(割两个点的最大连通分支数)
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=4587 题意: 给一图,求割去两个点后所能形成的最大连通分支数. 思路: 对于这种情况,第一个只能枚举,然后在删除 ...
- hdu 4587 推断孤立点+割点+ 删除点之后,剩下多少连通分量
做了非常久...... 题目链接: http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=4587 先枚举删除的第一个点,第二个点就是找割点.没有割点当然也有答案 学到 ...
- hdu 4587(割点的应用)
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=4587 思路:题目的意思很简单,就是删除任意2个节点以及关联的边,求图的最大连通分量数.我们知道删除割点 ...
- HDU 4587 B - TWO NODES tarjan
B - TWO NODESTime Limit: 20 Sec Memory Limit: 256 MB 题目连接 http://acm.hust.edu.cn/vjudge/contest/view ...
- hdu 4587 2013南京邀请赛B题/ / 求割点后连通分量数变形。
题意:求一个无向图的,去掉两个不同的点后最多有几个连通分量. 思路:枚举每个点,假设去掉该点,然后对图求割点后连通分量数,更新最大的即可.算法相对简单,但是注意几个细节: 1:原图可能不连通. 2:有 ...
- hdu 4587(枚举+割顶)
TWO NODES Time Limit: 24000/12000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65535/32768 K (Java/Others)Total ...
随机推荐
- Python中的列表(1)
1.什么是列表? 列表是由一组按特定顺序排列的元素组成. 2.如何表示? 在Python中用方括号([ ])来表示列表.栗子如下: contries = ['China','England','Fra ...
- python数据类型之元组(tuple)
元组是python的基础类型之一,是有序的. 元组是不可变的,一旦创建便不能再修改,所以叫只读列表. name = ('alex', 'jack') name[0] = 'mark' # TypeEr ...
- Linux学习-账号管理
新增与移除使用者: useradd, 相关配置文件, passwd, usermod, userdel 我们登入系统时会输入 (1)账号与 (2)密码,所以建立一个可用的账号同样的也需要这两个数据.那 ...
- Python动态属性和特性(二)
内置的property经常用作装饰器,但它其实是一个类.在Python中,函数和类通常可以互换,因为二者都是可调用对象,而且没有实例化的new运算符,所以调用构造方法和调用工厂函数没有区别,只要能返回 ...
- jenkins 之 iOS 打包及上传至蒲公英
准备条件 iMAC(要 Mac OS 系统,安卓 和 苹果 可以在同一台电脑上打包) xcode 最新版,要已安装对应的开发证书(生成一个 Ad-Hoc 类型的包就有了) brew(当前管理员账户安装 ...
- 老男孩全栈python学习进程表
老男孩Python高级全栈开发工程师-1 0001.开学典礼_ALEX简介 00:55:53 ☆ 0002.职业生涯_来培训的目的 01:12:29 ☆ 0003.课程目标 00:29: ...
- 使用sami生成文档
从composer安装sami $ composer require sami/sami composer自动配置完以后,可以先测试一下是否安装成功.只要不带参数的运行一下sami,就会知道结果. $ ...
- poj3255 Roadblocks 次短路
Roadblocks Time Limit: 2000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total Submissions: 10098 Accepted: 3620 Descr ...
- ACM程序设计选修课——1036: Hungar的菜鸟赛季(YY)
1036: Hungar的菜鸟赛季 Time Limit: 1 Sec Memory Limit: 64 MB Submit: 20 Solved: 14 [Submit][Status][Web ...
- spring分布式事务控制
应用场景问题描述解决方法多数据源配置单元测试第一种方法:最大努力一次提交模式第二种方法:最大努力一次提交模式 但使用ChainedTransactionManagerChainedTransactio ...
