Kubernetes 1.15部署日记-使用kubeadm--<1-2-3-4>
2019年9月17日
由于此次日记篇幅较长blog限制直接使用word发布所以分成几篇来发。
1.环境准备
|
10.110.149.172|192.168.111.51 |
K8s-1 |
Centos7.5 |
|
10.110.149.173|192.168.111.5 |
K8s-2 |
Centos7.5 |
1.1添加记录到hosts文件
[root@k8s-1 ~]# cat /etc/hosts 10.110.149.172 k8s-1 10.110.149.173 k8s-2
两台都添加。
1.2关闭防火墙,不关闭则需要添加k8s以及docker相关通信端口
systemctl stop firewalld systemctl disable firewalld
1.3禁用selinux
setenforce 0 vi /etc/selinux/config SELINUX=disabled
1.4关闭swap
swapoff -a
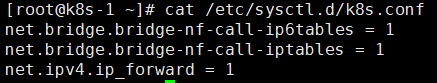
1.5创建/etc/sysctl.d/k8s.conf文件,添加如下内容:
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables = 1 net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables = 1 net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1
执行命令使其生效 [root@k8s-2 ~]# modprobe br_netfilter [root@k8s-2 ~]# sysctl -p /etc/sysctl.d/k8s.conf
1.6为kube-proxy开启ipvs 需要加载以下模块
ip_vs ip_vs_rr ip_vs_wrr ip_vs_sh nf_conntrack_ipv4
[root@k8s-1 ~]# cat > /etc/sysconfig/modules/ipvs.modules <<EOF > #!/bin/bash > modprobe -- ip_vs > modprobe -- ip_vs_rr > modprobe -- ip_vs_wrr > modprobe -- ip_vs_sh > modprobe -- nf_conntrack_ipv4 > EOF [root@k8s-1 ~]# [root@k8s-1 ~]# [root@k8s-1 ~]# chmod 755 /etc/sysconfig/modules/ipvs.modules [root@k8s-1 ~]# [root@k8s-1 ~]# [root@k8s-1 ~]# bash /etc/sysconfig/modules/ipvs.modules [root@k8s-1 ~]# [root@k8s-1 ~]# [root@k8s-1 ~]# lsmod | grep -e ip_vs -e nf_conntrack_ipv4 nf_conntrack_ipv4 15053 0 nf_defrag_ipv4 12729 1 nf_conntrack_ipv4 ip_vs_sh 12688 0 ip_vs_wrr 12697 0 ip_vs_rr 12600 0 ip_vs 141432 6 ip_vs_rr,ip_vs_sh,ip_vs_wrr nf_conntrack 133053 2 ip_vs,nf_conntrack_ipv4 libcrc32c 12644 3 xfs,ip_vs,nf_conntrack [root@k8s-1 ~]#
上面执行的脚本以及相关命令是为了保证节点重启后ipvs的功能能正常加载。查看ipvs的相关代理规则推荐安装ipvsadm管理工具。直接yum install ipvsadm 即可。
2.安装docker
2.1配置docker yum源
yum install -y yum-utils device-mapper-persistent-data lvm2 ipvsadm yum-config-manager \ --add-repo \ https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo
查看docker版本 yum安装docker yum list docker-ce.x86_64 --showduplicates |sort -r 本地缓存 yum makecache fast yum install -y --setopt=obsoletes=0 \ docker-ce-18.09.7-3.el7
启动服务
systemctl start docker
systemctl enable docker
2.2修改docker的cgroup driver 为systemd
[root@k8s-2 ~]# systemctl restart docker
[root@k8s-2 ~]#
[root@k8s-2 ~]#
[root@k8s-2 ~]# docker info | grep Cgroup
Cgroup Driver: systemd
[root@k8s-2 ~]# cat /etc/docker/daemon.json
{
"exec-opts": ["native.cgroupdriver=systemd"]
}
[root@k8s-2 ~]#
3.使用kubeadm 部署kubernetes
3.1配置安装kubeadm kubelet kubectl
配置yum 源 国外的的kubernetes 源无法使用 ,这里使用阿里云的kubernetes yum源。 cat <<EOF > /etc/yum.repos.d/kubernetes.repo [kubernetes] name=Kubernetes baseurl=https://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/repos/kubernetes-el7-x86_64/ enabled=1 gpgcheck=1 repo_gpgcheck=1 gpgkey=https://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/doc/yum-key.gpg https://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/doc/rpm-package-key.gpg EOF yum makecache fast yum install kubeadm kubelet kubectl
4.使用kubeadm初始化集群
4.1配置kubeadm.yaml
[root@k8s-1 libj]# cat kubeadm.yaml apiVersion: kubeadm.k8s.io/v1beta2 kind: InitConfiguration localAPIEndpoint: advertiseAddress: 192.168.111.51 bindPort: 6443 --- apiVersion: kubeadm.k8s.io/v1beta2 kind: ClusterConfiguration kubernetesVersion: v1.15.0 networking: serviceSubnet: 10.1.0.0/16 podSubnet: 10.2.0.0/16 imageRepository: "registry.aliyuncs.com/google_containers"
4.2执行初始化
[root@k8s-1 libj]# kubeadm init --config kubeadm.yaml [init] Using Kubernetes version: v1.15.0 [preflight] Running pre-flight checks [WARNING IsDockerSystemdCheck]: detected "cgroupfs" as the Docker cgroup driver. The recommended driver is "systemd". Please follow the guide at https://kubernetes.io/docs/setup/cri/ [preflight] Pulling images required for setting up a Kubernetes cluster [preflight] This might take a minute or two, depending on the speed of your internet connection [preflight] You can also perform this action in beforehand using 'kubeadm config images pull' [kubelet-start] Writing kubelet environment file with flags to file "/var/lib/kubelet/kubeadm-flags.env" [kubelet-start] Writing kubelet configuration to file "/var/lib/kubelet/config.yaml" [kubelet-start] Activating the kubelet service [certs] Using certificateDir folder "/etc/kubernetes/pki" [certs] Generating "ca" certificate and key [certs] Generating "apiserver-kubelet-client" certificate and key [certs] Generating "apiserver" certificate and key [certs] apiserver serving cert is signed for DNS names [k8s-1 kubernetes kubernetes.default kubernetes.default.svc kubernetes.default.svc.cluster.local] and IPs [10.1.0.1 192.168.111.51] [certs] Generating "front-proxy-ca" certificate and key [certs] Generating "front-proxy-client" certificate and key [certs] Generating "etcd/ca" certificate and key [certs] Generating "apiserver-etcd-client" certificate and key [certs] Generating "etcd/server" certificate and key [certs] etcd/server serving cert is signed for DNS names [k8s-1 localhost] and IPs [192.168.111.51 127.0.0.1 ::1] [certs] Generating "etcd/healthcheck-client" certificate and key [certs] Generating "etcd/peer" certificate and key [certs] etcd/peer serving cert is signed for DNS names [k8s-1 localhost] and IPs [192.168.111.51 127.0.0.1 ::1] [certs] Generating "sa" key and public key [kubeconfig] Using kubeconfig folder "/etc/kubernetes" [kubeconfig] Writing "admin.conf" kubeconfig file [kubeconfig] Writing "kubelet.conf" kubeconfig file [kubeconfig] Writing "controller-manager.conf" kubeconfig file [kubeconfig] Writing "scheduler.conf" kubeconfig file [control-plane] Using manifest folder "/etc/kubernetes/manifests" [control-plane] Creating static Pod manifest for "kube-apiserver" [control-plane] Creating static Pod manifest for "kube-controller-manager" [control-plane] Creating static Pod manifest for "kube-scheduler" [etcd] Creating static Pod manifest for local etcd in "/etc/kubernetes/manifests" [wait-control-plane] Waiting for the kubelet to boot up the control plane as static Pods from directory "/etc/kubernetes/manifests". This can take up to 4m0s [apiclient] All control plane components are healthy after 17.503969 seconds [upload-config] Storing the configuration used in ConfigMap "kubeadm-config" in the "kube-system" Namespace [kubelet] Creating a ConfigMap "kubelet-config-1.15" in namespace kube-system with the configuration for the kubelets in the cluster [upload-certs] Skipping phase. Please see --upload-certs [mark-control-plane] Marking the node k8s-1 as control-plane by adding the label "node-role.kubernetes.io/master=''" [mark-control-plane] Marking the node k8s-1 as control-plane by adding the taints [node-role.kubernetes.io/master:NoSchedule] [bootstrap-token] Using token: u5455t.tnp9bx2lkm0wgzhl [bootstrap-token] Configuring bootstrap tokens, cluster-info ConfigMap, RBAC Roles [bootstrap-token] configured RBAC rules to allow Node Bootstrap tokens to post CSRs in order for nodes to get long term certificate credentials [bootstrap-token] configured RBAC rules to allow the csrapprover controller automatically approve CSRs from a Node Bootstrap Token [bootstrap-token] configured RBAC rules to allow certificate rotation for all node client certificates in the cluster [bootstrap-token] Creating the "cluster-info" ConfigMap in the "kube-public" namespace [addons] Applied essential addon: CoreDNS [addons] Applied essential addon: kube-proxy Your Kubernetes control-plane has initialized successfully! To start using your cluster, you need to run the following as a regular user: mkdir -p $HOME/.kube sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config You should now deploy a pod network to the cluster. Run "kubectl apply -f [podnetwork].yaml" with one of the options listed at: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/cluster-administration/addons/ Then you can join any number of worker nodes by running the following on each as root: kubeadm join 192.168.111.51:6443 --token u5455t.tnp9bx2lkm0wgzhl \ --discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:7811481be449b5464c80532986be38a670553ce3de102ef375b7cc1fceabcac9 执行初始化完成。
4.3配置kubectl 命令
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
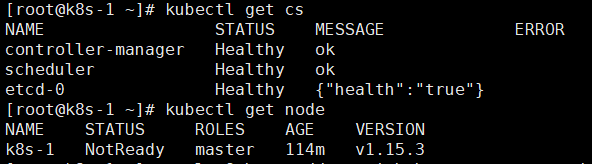
使用kubectl 检查k8s集群
4.4配置kubectl自动补全
yum install -y bash-completion [root@k8s-1 ~]# source /usr/share/bash-completion/bash_completion [root@k8s-1 ~]# source <(kubectl completion bash) [root@k8s-1 ~]# [root@k8s-1 ~]# echo "source <(kubectl completion bash)" >> ~/.bashrc [root@k8s-1 ~]# [root@k8s-1 ~]#
1-2-3-4前期准备、安装docker、安装kubectl kubelet kubeadm 、部署集群配置kubectl命令已完成。
吐槽下 不知都是那里出了问题word无法直接发布博客了 发布上来格式还大篇幅的错误格式费解。。。之前还好好的。一定是那里出了问题。
友情推荐:一键安装Kubernetes HA。
Kubernetes 1.15部署日记-使用kubeadm--<1-2-3-4>的更多相关文章
- Kubernetes 1.15部署日记-使用kubeadm--<7-8>
7. 在k8s集群中run一个应用 nginx已经跑起来了到此kubernetes集群部署结束了. 8. 总结 此次部署kubernetes的起因是AI团队中的kubernetes项目跑在其他IP段网 ...
- Kubernetes 1.15部署日记-使用kubeadm--<5-6>
5.配置pod网络 5.1下载calico 网络配置文件 [root@k8s-1 libj]# curl -O https://docs.projectcalico.org/v3.6/getting- ...
- Centos 使用kubeadm安装Kubernetes 1.15.3
本来没打算搞这个文章的,第一里面有瑕疵(没搞定的地方),第二在我的Ubuntu 18 Kubernetes集群的安装和部署 以及Helm的安装 也有安装,第三 和社区的问文章比较雷同 https:// ...
- kubernetes 1.15.1 高可用部署 -- 从零开始
这是一本书!!! 一本写我在容器生态圈的所学!!! 重点先知: 1. centos 7.6安装优化 2. k8s 1.15.1 高可用部署 3. 网络插件calico 4. dashboard 插件 ...
- 使用kubeadm安装Kubernetes 1.15.3 并开启 ipvs
一.安装前准备 机器列表 主机名 IP node-1(master) 1.1.1.101 node-2(node) 1.1.1.102 node-3(node) 1.1.1.103 设置时区 cp / ...
- 使用kubeadm进行单master(single master)和高可用(HA)kubernetes集群部署
kubeadm部署k8s 使用kubeadm进行k8s的部署主要分为以下几个步骤: 环境预装: 主要安装docker.kubeadm等相关工具. 集群部署: 集群部署分为single master(单 ...
- Kubeadm安装Kubernetes 1.15.1
一.实验环境准备 服务器虚拟机准备 IP CPU 内存 hostname 192.168.198.200 >=2c >=2G master 192.168.198.201 >=2c ...
- kubeadm安装Kubernetes 1.15 实践
原地址参考github 一.环境准备(在全部设备上进行) 3 台 centos7.5 服务器,网络使用 Calico. IP地址 节点角色 CPU 内存 Hostname 10.0.1.45 mast ...
- 在CentOS 7.6 以 kubeadm 安装 Kubernetes 1.15 最佳实践
前言 Kubernetes作为容器编排工具,简化容器管理,提升工作效率而颇受青睐.很多新手部署Kubernetes由于"scientifically上网"问题举步维艰,本文以实战经 ...
随机推荐
- 027_MacOs上如何将多页word打印到一个页面上
工作中需要把word的多页面内容打印到同一张A4纸,所以就想了办法,首先word导出到pdf. 然后使用MacOs默认的PDF阅读器进行多页打印. 操作如下: 文件-打印布局选择每张纸需要打印的页数左 ...
- python笔记之按文件名搜索指定路径下的文件
1.搜索文件名中以指定的字符串开头(如搜索dll,结果中含有dll a,dll abc等) 我的目录下有dll a.txt和dll.txt文件 其中a文件夹下还有这两个文件 我希望通过python选择 ...
- Linux 服务器CPU占用率100%,使用率高解决方案
机器高负载告警一般是CPU负载在99-100%,同时伴有大量的网络出包和入包量,常见的原因是机器在某个时段进行LOG,数据等备份操作,或者服务器被黑导致 输入top命令查看CPU使用情况 top 通过 ...
- (转)自动微分(Automatic Differentiation)简介——tensorflow核心原理
现代深度学习系统中(比如MXNet, TensorFlow等)都用到了一种技术——自动微分.在此之前,机器学习社区中很少发挥这个利器,一般都是用Backpropagation进行梯度求解,然后进行SG ...
- 【tensorflow基础】Tensorpack-API
安装 pip install tensorpack 使用 参考 1. Tensorpack: 2. Tensorpack,一个基于TensorFlow的神经网络训练界面,源码包含很多示例: 完
- [LeetCode] 636. Exclusive Time of Functions 函数的独家时间
Given the running logs of n functions that are executed in a nonpreemptive single threaded CPU, find ...
- C1128节数超过对象文件格式限制: 请使用 /bigobj 进行编译
今天debug C++项目是遇到 解决方案: 右键项目—>属性 输入 /bigobj 再次编译问题解决
- 用ArcMap在PostgreSQL中创建要素类需要执行”create enterprise geodatabase”吗
问:用Acmap在PostgreSQL中创建要素类需要执行"create enterprise geodatabase"吗? 关于这个问题,是在为新员工做postgresql培训后 ...
- kube-proxy运行机制分析【转载】
转自:http://blog.itpub.net/28624388/viewspace-2155433/ 1.Service在很多情况下只是一个概念,而真正将Service的作用实现的是kube-pr ...
- 如何在运行时更改JMeter的负载
在某些情况下,能够在不停止测试的情况下更改性能测试产生的负载是有用的或必要的.这可以通过使用Apache JMeter™的恒定吞吐量计时器和Beanshell服务器来完成.在这篇文章中,我们将介绍如何 ...
