第3章—高级装配—配置profile bean
配置profile bean
3.1.@profile注解是spring提供的一个用来标明当前运行环境的注解。
我们正常开发的过程中经常遇到的问题是,开发环境是一套环境,qa测试是一套环境,线上部署又是一套环境。这样从开发到测试再到部署,会对程序中的配置修改多次,尤其是从qa到上线这个环节,让qa的也不敢保证改了哪个配置之后能不能在线上运行。
为了解决上面的问题,我们一般会使用一种方法,就是配置文件,然后通过不同的环境读取不同的配置文件,从而在不同的场景中跑我们的程序。
那么,spring中的@profile注解的作用就体现在这里。在spring使用DI来依赖注入的时候,能够根据当前制定的运行环境来注入相应的bean。最常见的就是使用不同的DataSource了。
下面详细的介绍一下,如何通过spring的@profile注解实现上面的功能。
创建一个Maven项目,其中的配置如下:
pom.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.home</groupId>
<artifactId>ProfileTest</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<name>ProfileTest Maven Webapp</name>
<!-- FIXME change it to the project's website -->
<url>http://www.example.com</url>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<maven.compiler.source>1.7</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>1.7</maven.compiler.target>
<springframework.version>4.3.7.RELEASE</springframework.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework/spring-context -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>${springframework.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework/spring-test -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>
<version>${springframework.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.11</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-jupiter-api</artifactId>
<version>RELEASE</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<finalName>ProfileTest</finalName>
<pluginManagement><!-- lock down plugins versions to avoid using Maven defaults (may be moved to parent pom) -->
<plugins>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-clean-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.0.0</version>
</plugin>
<!-- see http://maven.apache.org/ref/current/maven-core/default-bindings.html#Plugin_bindings_for_war_packaging -->
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-resources-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.0.2</version>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.7.0</version>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-surefire-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.20.1</version>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-war-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.2.0</version>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-install-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.5.2</version>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-deploy-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.8.2</version>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</pluginManagement>
</build>
</project>
App:
package com.hom.demo;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
/**
* Hello world!
// */
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages = {"com.hom.demo"})
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(com.hom.demo.App.class);
Person p = context.getBean(Person.class);
p.speak();
}
}
接口MoveFactor:
package com.hom.demo;
public interface MoveFactor {
void speak();
}
Chines:
package com.hom.demo;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Profile;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Configuration
@Profile(value = "dev")
@Component
public class Chinese implements MoveFactor {
@Override
public void speak() {
System.out.println("我是中国人");
}
}
English:
package com.hom.demo;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Profile;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@Profile("qa")
public class English implements MoveFactor{
@Override
public void speak() {
System.out.println("i am an English");
}
}
German:
package com.hom.demo;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Profile;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@Profile("prod")
public class German implements MoveFactor{
@Override
public void speak() {
System.out.println("i am a German");
}
}
Person:
package com.hom.demo;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class Person {
@Autowired
private MoveFactor moveFactor;
public void speak(){
moveFactor.speak();
}
}
SpringTest:
package com.hom.demo;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.test.context.ActiveProfiles;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(classes = App.class)
@ActiveProfiles("dev")
public class SpringTest {
@Autowired
Person p;
@Test
public void testProfile(){
p.speak();
}
}
运行后的结果如下:
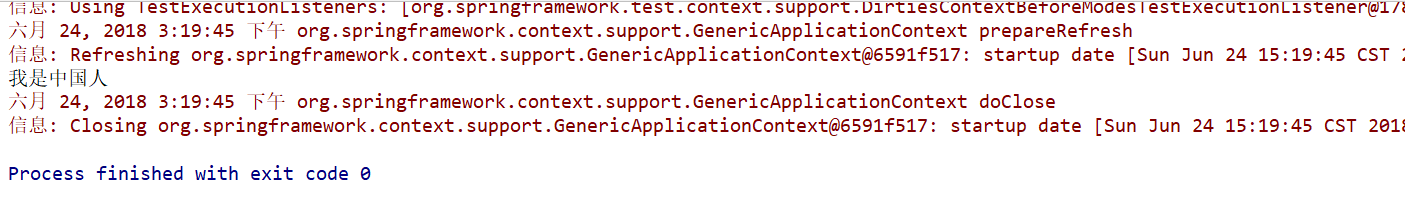
当修改@ActiveProfile中的值时,输出的内容也会随之改变。
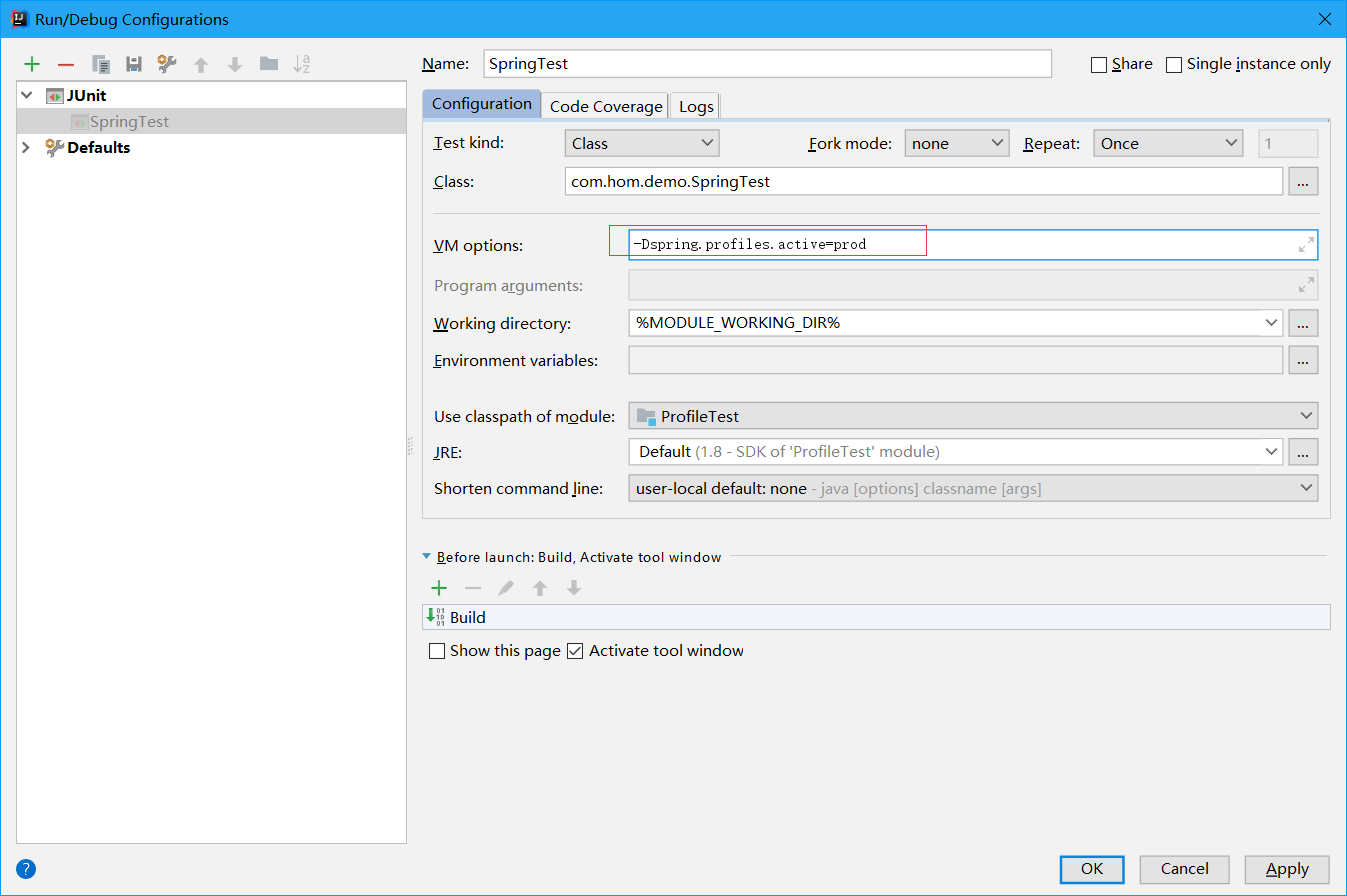
如果使用的是main函数进行真正的开发、测试和上线时,我们需要设置一下运行参数:
-Dspring.profiles.active=prod
3.2.XML中配置profile
application.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd"
profile="dev">
<bean id="chinese" class="com.hom.demo.Chinese"></bean>
</beans>
我们还可以在<beans>中嵌套定义<beans>元素,而不是为没个环境都创建一个profile.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd"
>
<beans profile="dev"> <!--这里可以指定需要的profile名-->
<bean id="chinese" class="com.hom.demo.Chinese"></bean>
</beans>
<beans profile="qa">
<bean id="english" class="com.hom.demo.English"></bean>
</beans>
</beans>
3.3.激活profile
Spring在确定那个profile处于激活状态时,需要依赖两个独立的属性:
spring.Profile.active(激活的Profile)
spring.Profile.default(默认的Profile)
这里有多种方式来设置这两个属性:
- 作为DispathServlet的初始参数
- 作为Web应用的上下文参数
- 作为JNDI条目
- 作为环境变量
- 作为JVM的系统属性
- 在集成测试类上,使用@ActiveProfile注解设置
我所喜欢的一种方式是使用DispatcherServlet的参数将spring.rpofiles.default设置开发环境的Profile,我会在Servlet上下文中配置,如下所示:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_0.xsd" version="3.0" id="WebApp_1525601902125">
<display-name>Archetype Created Web Application</display-name>
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLoacation</param-name>
<param-value>application.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
<!--为上下文设置默认的profile-->
<context-param>
<param-name>spring.rpofiles.default</param-name>
<param-value>dev</param-value>
</context-param>
<listener>
<listener-class> org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<!--为Servlet设置默认的profile-->
<servlet>
<servlet-name>appServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>spring.rpofiles.default</param-name>
<param-value>dev</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>appServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
Spring提供了@ActiveProfile注解设置激活状态
第3章—高级装配—配置profile bean的更多相关文章
- Spring高级装配(一) profile
Spring高级装配要学习的内容包括: Spring profile 条件化的bean声明 自动装配与歧义性 bean的作用域 Spring表达式语言 以上属于高级一点的bean装配技术,如果你没有啥 ...
- spring对bean的高级装配之profile机制
最近在读spring实战一书,个人感觉内容通俗易懂,学到了一些之前并不知道的知识,于是打算在博客里记录一下这些知识点便于后期记忆: 今天要记录的就是spring的条件化创建bean,针对条件化创建be ...
- 第3章—高级装配—条件化的Bean
条件化的Bean 通过活动的profile,我们可以获得不同的Bean.Spring 4提供了一个更通用的基于条件的Bean的创建方式,即使用@Conditional注解. @Conditional根 ...
- Spring实战(四)Spring高级装配中的bean profile
profile的原意为轮廓.剖面等,软件开发中可以译为“配置”. 在3.1版本中,Spring引入了bean profile的功能.要使用profile,首先要将所有不同的bean定义整理到一个或多个 ...
- 第3章—高级装配—bean的作用域
bean的作用域 bean的默认作用域 Spring定义了多种作用域,可以基于这些作用域创建bean,包括: 单例(Singleton):在整个应用中,只创建bean的一个实例. 原型(Prototy ...
- 【Spring】高级装配
前言 前面讲解了bean的核心装配技术,其可应付很多中装配情况,但Spring提供了高级装配技术,以此实现更为高级的bean装配功能. 高级装配 配置profile bean 将所有不同bean定义放 ...
- spring学习总结——高级装配学习一(profile与@Conditional)
前言: 在上一章装配Bean中,我们看到了一些最为核心的bean装配技术.你可能会发现上一章学到的知识有很大的用处.但是,bean装配所涉及的领域并不仅仅局限于上一章 所学习到的内容.Spring提供 ...
- Spring高级装配bean
目录 spring profile 条件化的bean声明 自动装配与歧义性 bean的作用域 Spring表达式语言 一.环境与profile 配置profile bean 在软件开发的时候,有一个 ...
- Spring使用笔记(三) 高级装配
高级装配 一.环境与Profile 一)配置profile bean 环境的改变导致配置改变(需求:通过环境决定使用哪个bean),可以通过Spring的Profile解决. Profile可以在程序 ...
随机推荐
- [转载]关于JAVA中子类和父类的构造方法
原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/chenpi/p/5486096.html#_label0
- Objective-C 学习笔记(五) 指针
Objective-C 指针 每一个变量是一个内存位置和每一个存储单元都有其定义的地址,可以使用符号(&)的运算符,它表示内存中的地址访问. a. 我们定义一个指针变量 b. 分配一个指针变量 ...
- nancyfx的安装笔记
这个安装时很简单的 只要 Install-Package Nancy.Hosting.Aspnet 就行了. 需要注意的是,千万不要用那个模板安装,通过创建nancyfx类型项目的方式安装是有问题的. ...
- MSP430G2553 Launchpad 硬件I2C驱动
一.USCI I2C 驱动介绍 对于MSP430G2553,硬件I2C由外设USCI(Universal Serial Communication Interface)提供.USCI又分为USCI_A ...
- C# GetHashCode、Equals函数和键值对集合的关系
C# GetHashCode.Equals函数和键值对集合的关系 说明 HashCode:Hash码.特性:两个值,相同的的值生成的Hash肯定相同,Hash不同的值肯定不同. 下面一张图中,只有和“ ...
- Rx.net 例子——(1)基础
1.订阅序列 using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using S ...
- uwp ,win10 post json
public static async Task<HttpResponseMessage> PostHttpstringrequest(string requesturl,string j ...
- 1083 矩阵取数问题(DP)
1083 矩阵取数问题 基准时间限制:1 秒 空间限制:131072 KB 分值: 5 难度:1级算法题 收藏 关注 一个N*N矩阵中有不同的正整数,经过这个格子,就能获得相应价值的奖励,从左上走 ...
- C#取得控制台应用程序的根目录方法
如有雷同,不胜荣幸,若转载,请注明 取得控制台应用程序的根目录方法1:Environment.CurrentDirectory 取得或设置当前工作目录的完整限定路径2:AppDomain.Curren ...
- git命令合集及github的克隆推送
安装git 初始化仓库 提交相关 撤销相关 远程推送 分支相关 其他 遇到的错误 github的克隆上传 此文章只是对命令的一个统计,起备忘和复习git只是的作用,不建议从没接触过git的同学通过它来 ...
