PTA (Advanced Level) 1014 Waiting in Line
Waiting in Line
Suppose a bank has N windows open for service. There is a yellow line in front of the windows which devides the waiting area into two parts. The rules for the customers to wait in line are:
- The space inside the yellow line in front of each window is enough to contain a line with Mcustomers. Hence when all the N lines are full, all the customers after (and including) the (st one will have to wait in a line behind the yellow line.
- Each customer will choose the shortest line to wait in when crossing the yellow line. If there are two or more lines with the same length, the customer will always choose the window with the smallest number.
- Customeri will take Ti minutes to have his/her transaction processed.
- The first N customers are assumed to be served at 8:00am.
Now given the processing time of each customer, you are supposed to tell the exact time at which a customer has his/her business done.
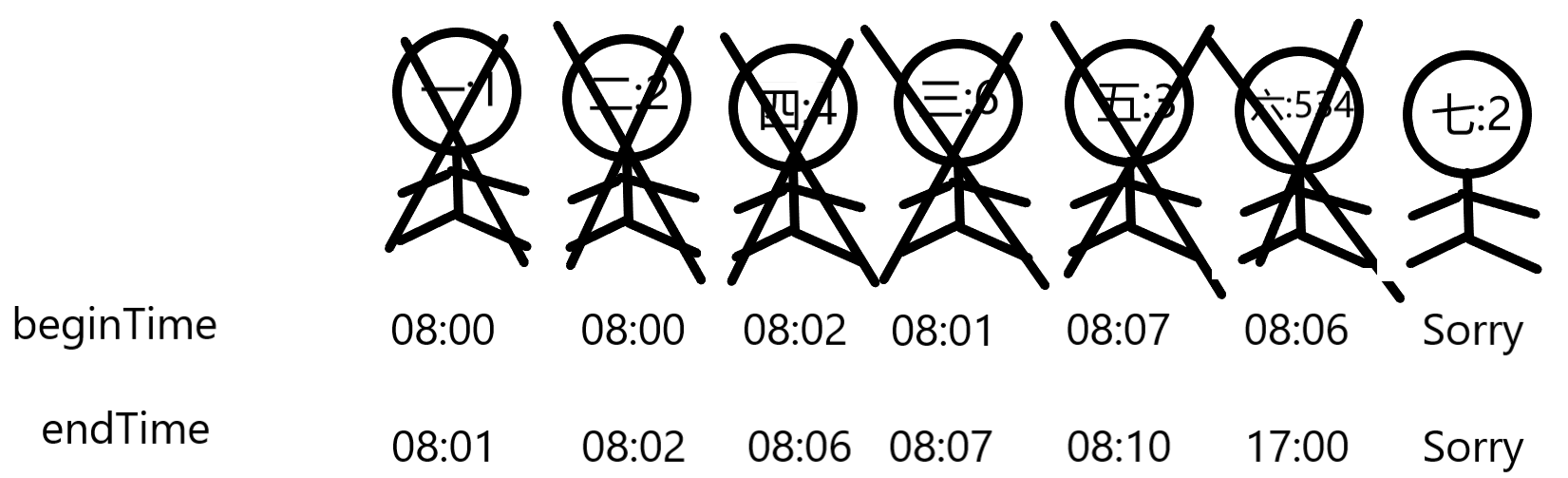
For example, suppose that a bank has 2 windows and each window may have 2 custmers waiting inside the yellow line. There are 5 customers waiting with transactions taking 1, 2, 6, 4 and 3 minutes, respectively. At 08:00 in the morning, customer1 is served at window1 while customer2 is served at window2. Customer3 will wait in front of window1 and customer4 will wait in front of window2. Customer5 will wait behind the yellow line.
At 08:01, customer1 is done and customer5 enters the line in front of window1 since that line seems shorter now. Customer2 will leave at 08:02, customer4 at 08:06, customer3 at 08:07, and finally customer5 at 08:10.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. Each case starts with a line containing 4 positive integers: N (≤, number of windows), M (≤, the maximum capacity of each line inside the yellow line), K (≤, number of customers), and Q (≤, number of customer queries).
The next line contains K positive integers, which are the processing time of the K customers.
The last line contains Q positive integers, which represent the customers who are asking about the time they can have their transactions done. The customers are numbered from 1 to K.
Output Specification:
For each of the Q customers, print in one line the time at which his/her transaction is finished, in the format HH:MM where HH is in [08, 17] and MM is in [00, 59]. Note that since the bank is closed everyday after 17:00, for those customers who cannot be served before 17:00, you must output Sorry instead.
Sample Input:
2 2 7 5
1 2 6 4 3 534 2
3 4 5 6 7
Sample Output:
08:07
08:06
08:10
17:00
Sorry
解题思路:
本题意思是银行有n个窗口,每个窗口前最多可以排m个人,现在有k个人,所有窗口从8点开始服务,到17点停止接受服务,不过如果17点前接受了服务,无论多晚也会服务完该客户。要求按查询输出客户完成服务的时间(愚蠢的顾客们只要选定一个排队的窗口就会一直排到关门,即使其他窗口空了也不换)。
本题每组测试数据首先给出4个整数,分别为窗口数量n、最大排队人数m、客户人数k、查询数量q,之后一行包括k个整数,代表服务每个客户所需要的时间(分钟),下一行包括q个整数,代表查询的客户。
首先分析一下样例
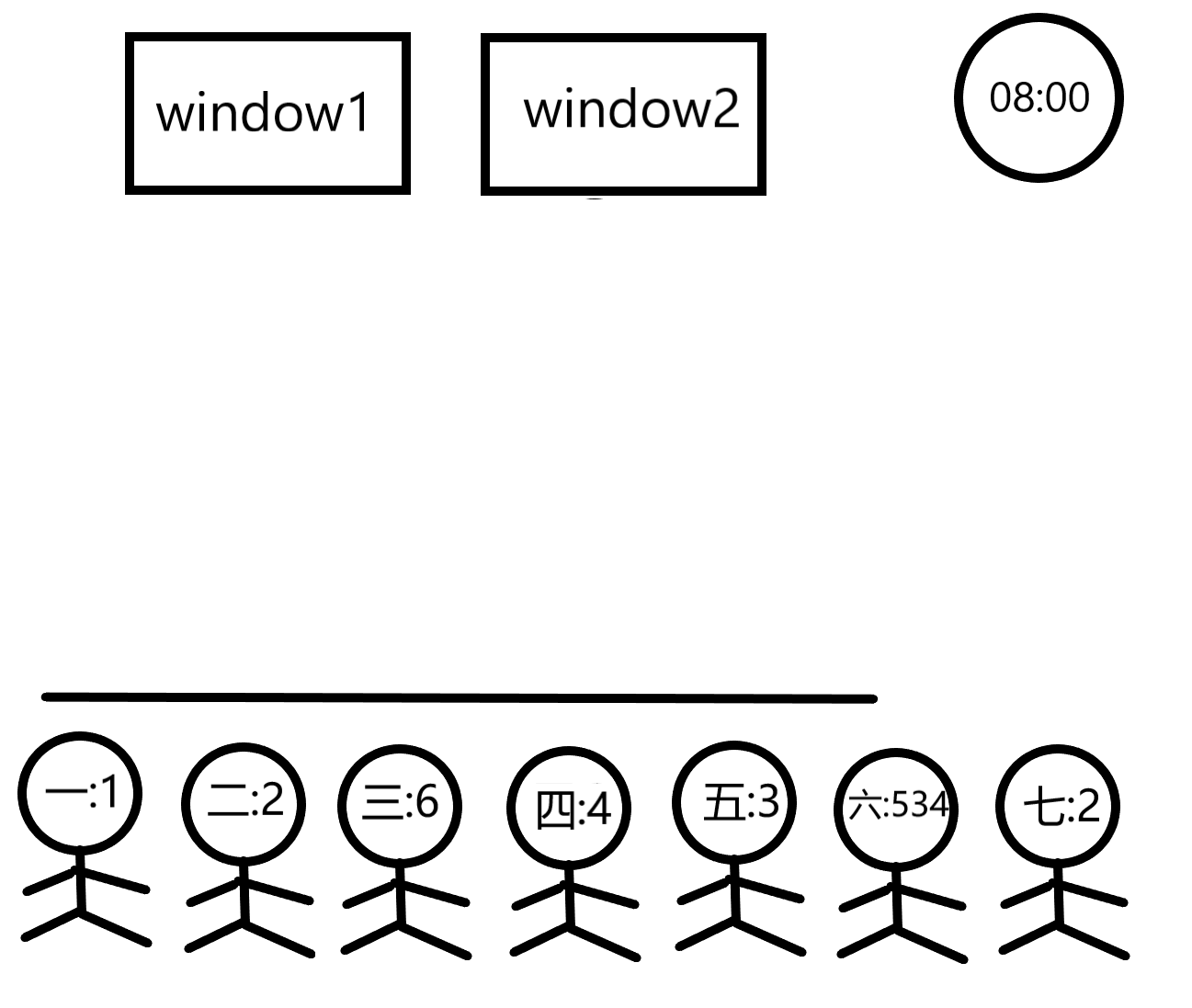

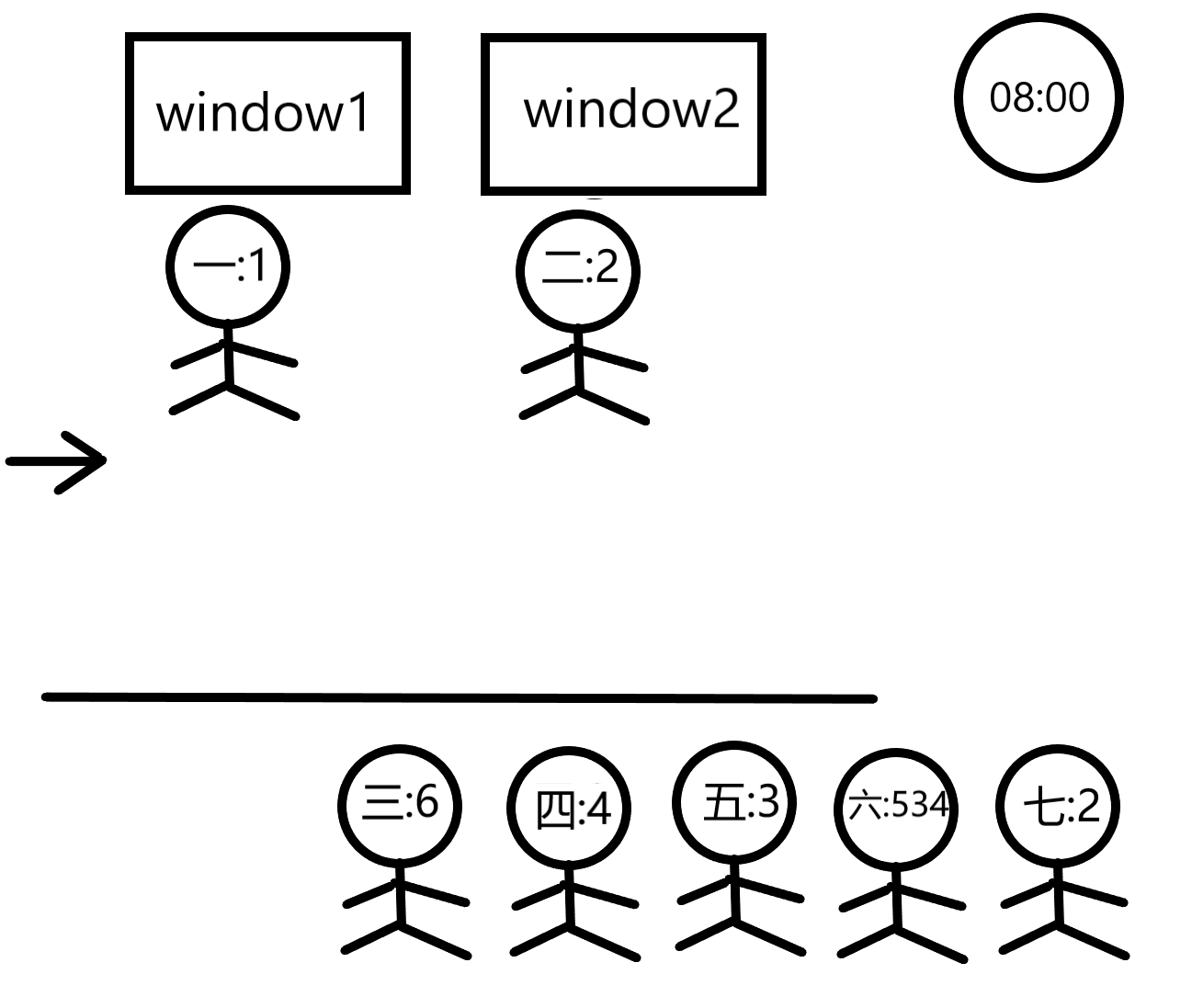

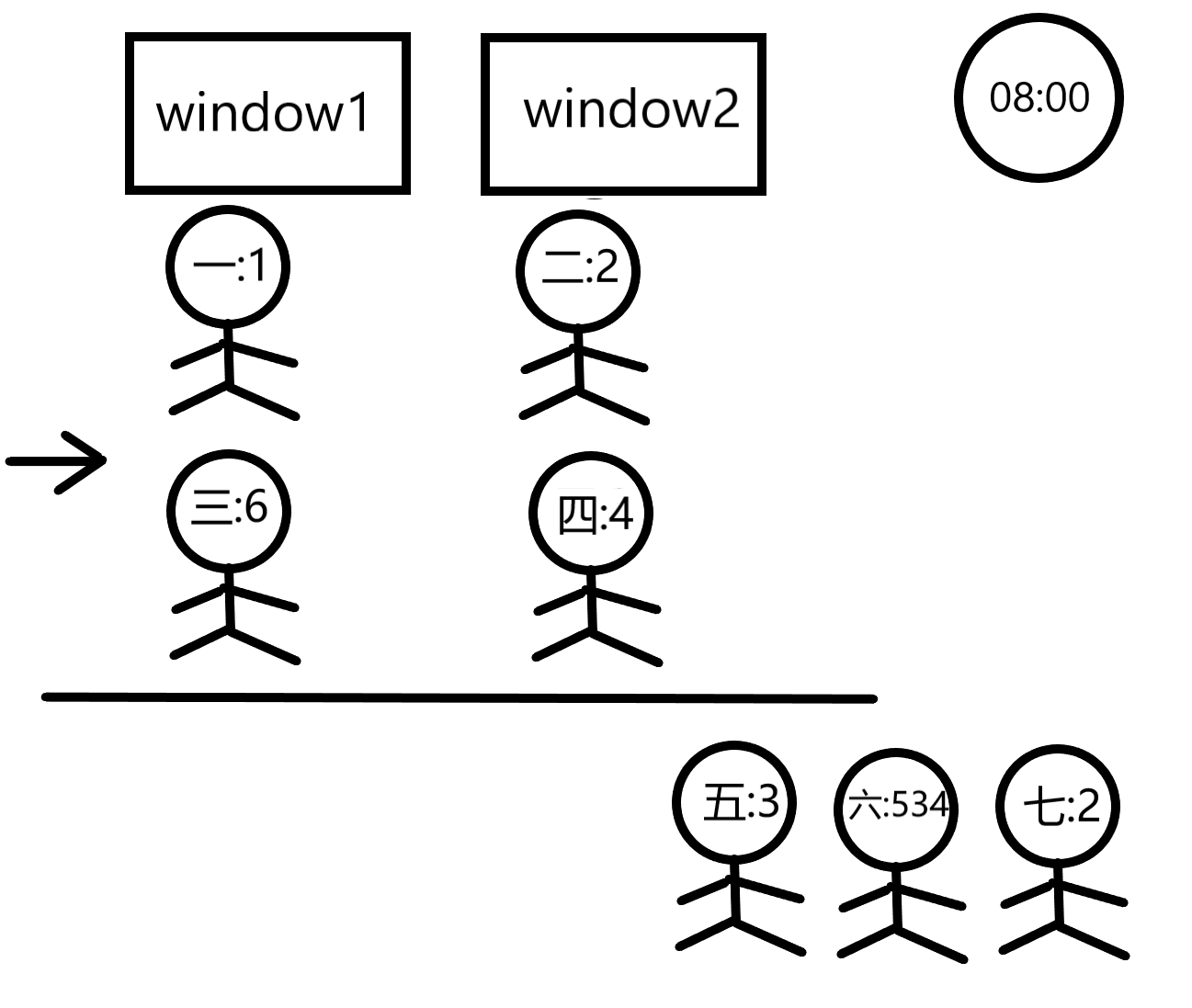
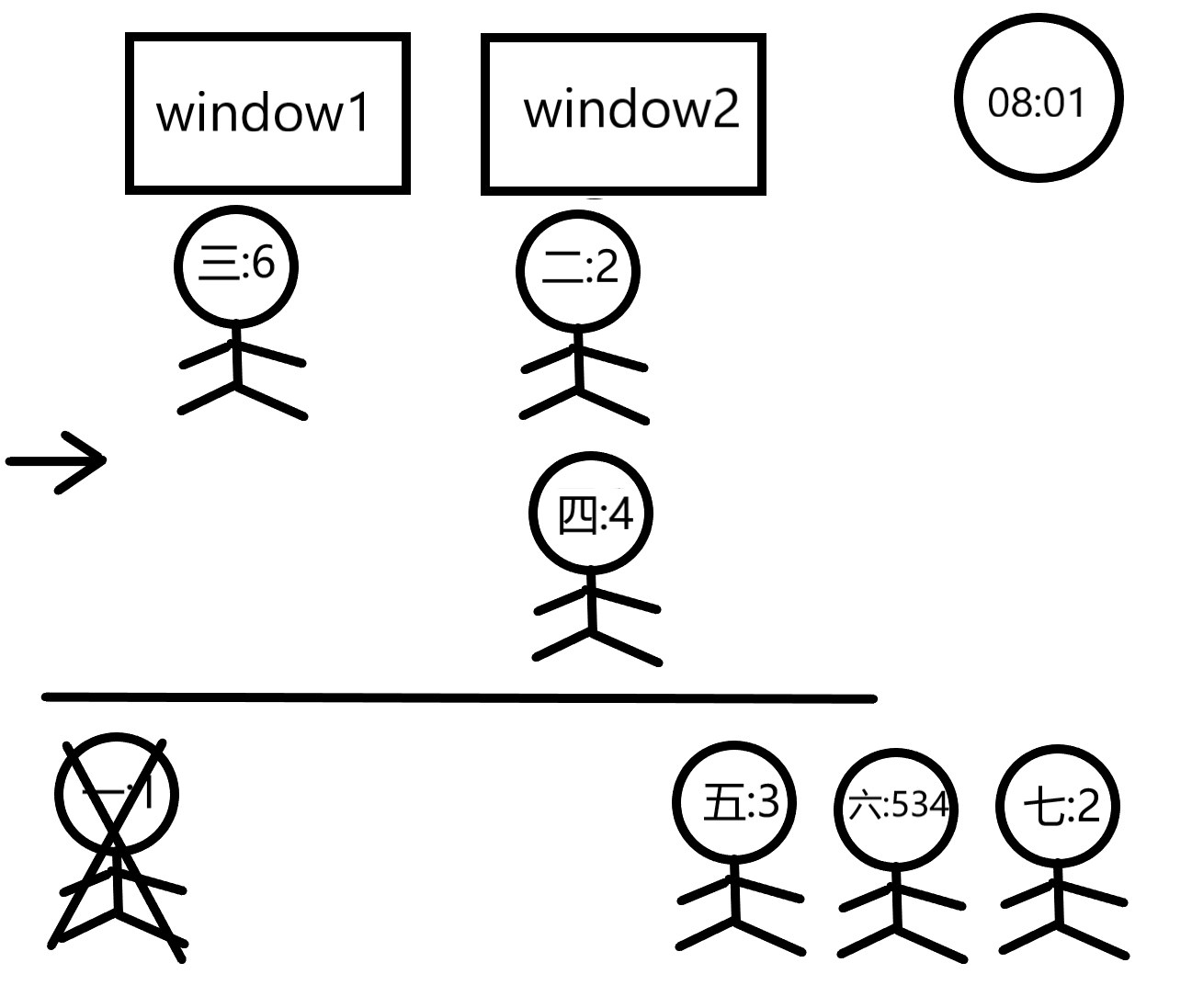
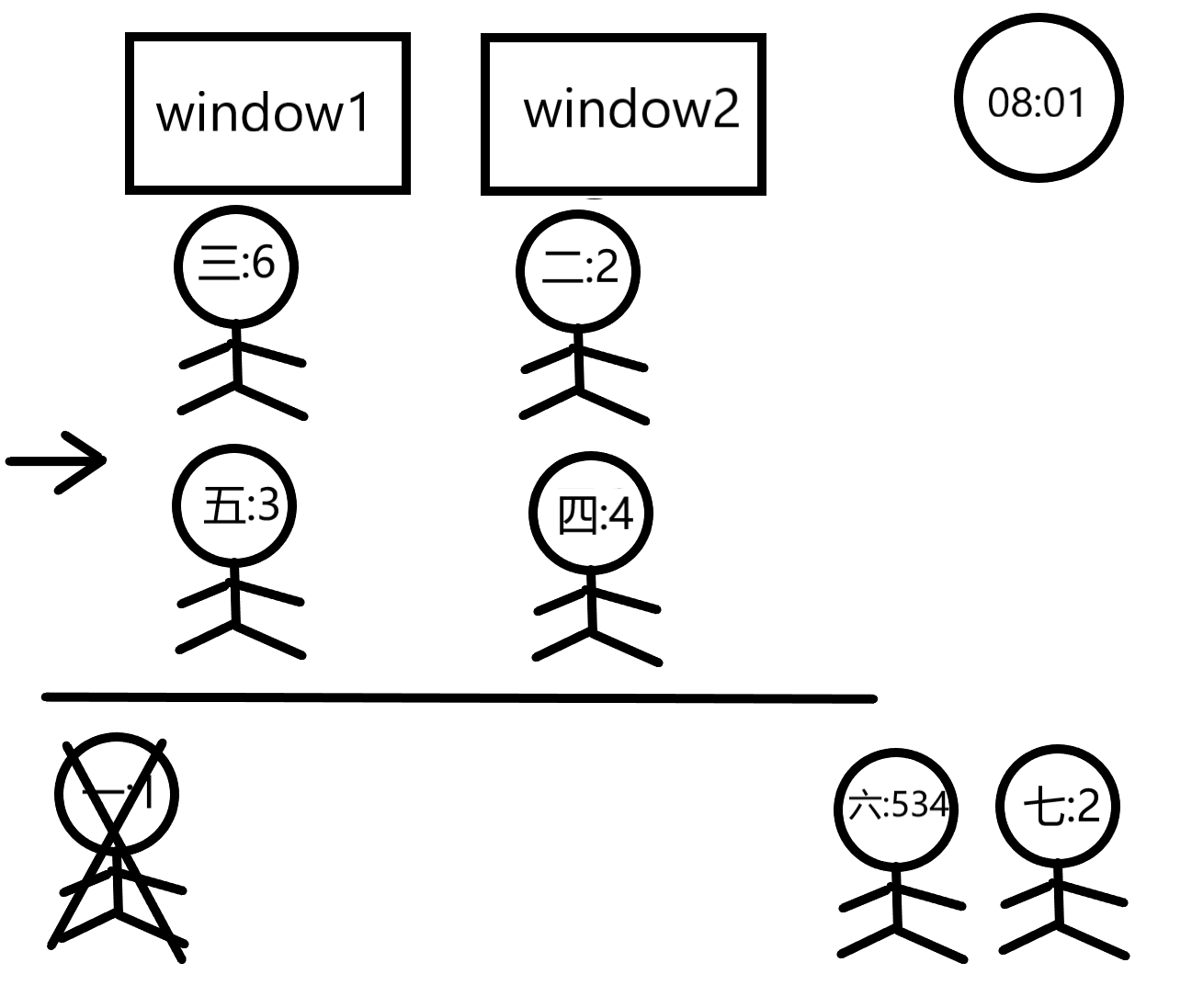
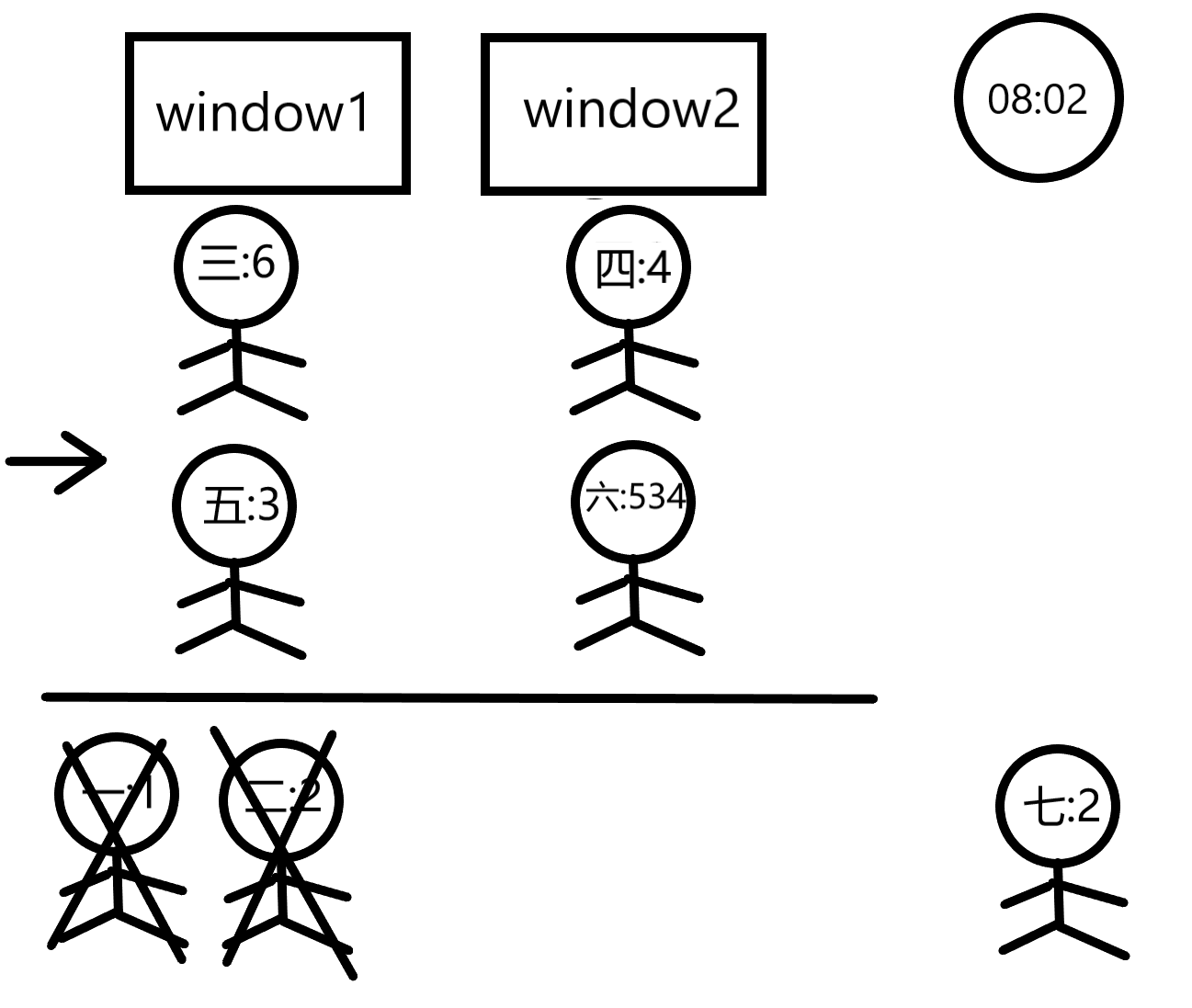
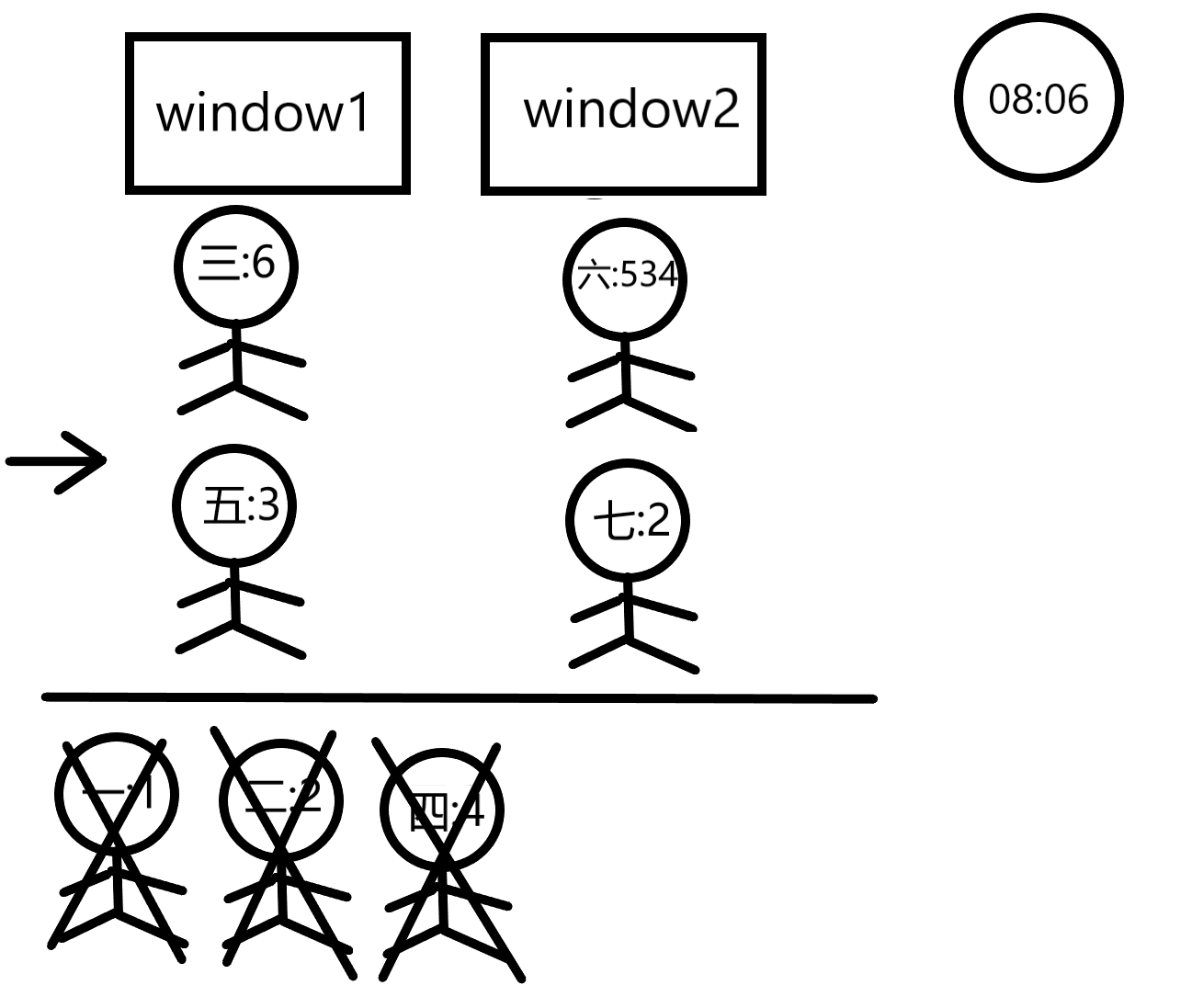


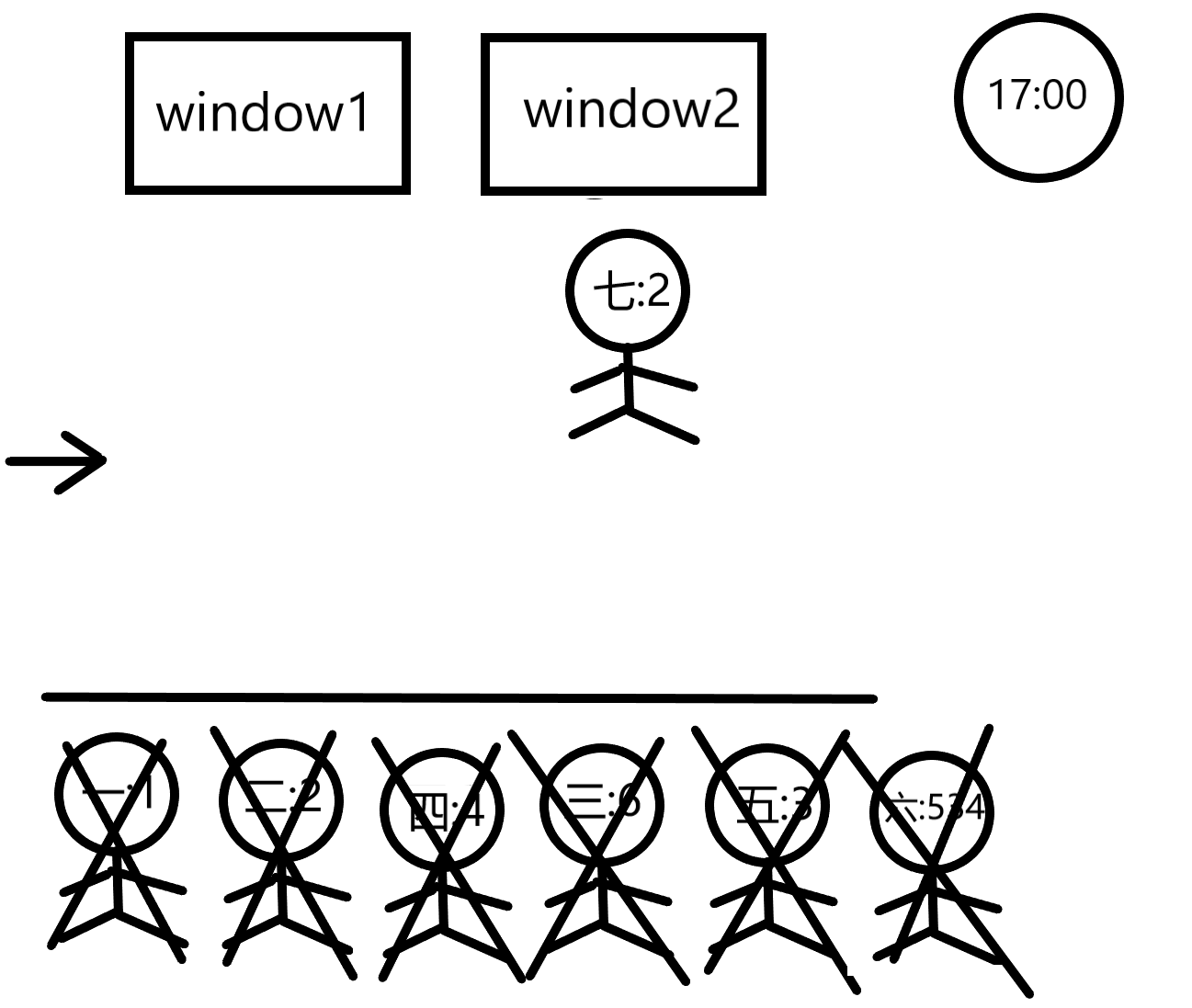

我们可以吧每一个窗口看作一个先进先出的队列,队列的容量为m,一共有n个这样的队列。queue<int> win[maxw] ,win[ i ]便代表第i窗口的队列。由于客户总是会选择最短的队列,所以在所有队列被填满时不会有出队操作。每个队列在开始处理今天第一名客户时记录现在以及消耗的时间为0,在所有队列都被填满后就要执行出队操作了,我们需要找到哪个窗口的客户先处理完,对其所在的窗口进行出队,同时获得当前处理的客户的结束时间与下一名客户的开始时间,之后将下一名客户入队。
在所有客户都入队后需要对所有窗口进行出队操作,这样便可以获得所有客户的开始时间与结束时间。
找到排队最短的窗口
int getMinSize(int &w){ //获得当前排队长度最短的窗口
int minSize = INT_MAX;
for(int i = ; i < n; i++){
if(win[i].size() < minSize){
minSize = win[i].size();
w = i;
}
}
return minSize;
}
找到最先处理完的客户所在的窗口并执行出队
void dispose(){ //找到最先处理完的客户所在的窗口并执行出队
int disWin; //记录最先处理完的客户所在的窗口
int disEdTime = INT_MAX; //记录记录最先处理完的客户的结束时间
for(int i = ; i < n; i++){
if(disEdTime > nowTime[i] + needTime[win[i].front()]){
//服务结束时间为当前窗口消耗时间假设处理该客户需要消耗的时间
disWin = i; //记录窗口与结束时间
disEdTime = nowTime[i] + needTime[win[i].front()];
}
}
edTime[win[disWin].front()] = disEdTime; //记录客户结束时间
win[disWin].pop(); //出队
nowTime[disWin] = disEdTime; //记录该窗口现在已经消耗的时间
if(!win[disWin].empty())
bgTime[win[disWin].front()] = disEdTime;
//下一名客户的开始时间就是上一名客户的结束时间
}
某窗口全部出队
void disposeAll(int w){ //处理某窗口全部出队
while(!win[w].empty()){
edTime[win[w].front()] = nowTime[w] + needTime[win[w].front()];
//获得用户结束时间
nowTime[w] = edTime[win[w].front()];
//记录当前窗口消耗时间
win[w].pop();
if(!win[w].empty())//记录下一个用户的开始时间
bgTime[win[w].front()] = nowTime[w];
}
}
之后读入查询,判断所查询的客户的开始时间是否在17:00前,如果在17:00前输出其结束时间,否则输出Sorry。
AC代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int maxw = ; //最大窗口数
const int maxk = 1e3+; //最大客户数
queue<int> win[maxw]; //窗口队列
int nowTime[maxw]; //记录每个窗口当前服务客户已经消耗的时间
int needTime[maxk]; //记录服务每个客户需要消耗的时间
int bgTime[maxk]; //记录每个客户开始被服务的时间
int edTime[maxk]; //记录每个客户服务结束的时间
int n, m, k, q; //n窗口数,m队列长度,k客户数,q查询数
int getMinSize(int &w){ //获得当前排队长度最短的窗口
int minSize = INT_MAX;
for(int i = ; i < n; i++){
if(win[i].size() < minSize){
minSize = win[i].size();
w = i;
}
}
return minSize;
}
void dispose(){ //找到最先处理完的客户所在的窗口并执行出队
int disWin; //记录最先处理完的客户所在的窗口
int disEdTime = INT_MAX; //记录记录最先处理完的客户的结束时间
for(int i = ; i < n; i++){
if(disEdTime > nowTime[i] + needTime[win[i].front()]){
//服务结束时间为当前窗口消耗时间假设处理该客户需要消耗的时间
disWin = i; //记录窗口与结束时间
disEdTime = nowTime[i] + needTime[win[i].front()];
}
}
edTime[win[disWin].front()] = disEdTime; //记录客户结束时间
win[disWin].pop(); //出队
nowTime[disWin] = disEdTime; //记录该窗口现在已经消耗的时间
if(!win[disWin].empty())
bgTime[win[disWin].front()] = disEdTime;
//下一名客户的开始时间就是上一名客户的结束时间
}
void disposeAll(int w){ //处理某窗口全部出队
while(!win[w].empty()){
edTime[win[w].front()] = nowTime[w] + needTime[win[w].front()];
//获得用户结束时间
nowTime[w] = edTime[win[w].front()];
//记录当前窗口消耗时间
win[w].pop();
if(!win[w].empty())//记录下一个用户的开始时间
bgTime[win[w].front()] = nowTime[w];
}
} int main()
{
while(scanf("%d%d%d%d", &n, &m, &k, &q) != EOF){
//输入n窗口数,m队列长度,k客户数,q查询数
memset(nowTime, , sizeof(nowTime));
memset(needTime, , sizeof(needTime));
memset(edTime, , sizeof(edTime));
memset(bgTime, , sizeof(bgTime));
//将所有时间初始化为0
for(int i = ; i <= k; i++){
scanf("%d", &needTime[i]);
//输入服务每个客户所需要的时间
}
int minSize, minWin;
for(int i = ; i <= k; i++){ //遍历所有客户
minSize = getMinSize(minWin); //找到当前排队最短的窗口
if(minSize >= m){ //如果所有窗口的队都满了
dispose(); //执行最先处理完客户所在的窗口出队
minSize = getMinSize(minWin); //重新获得最短的队
}
win[minWin].push(i); //入队
if(win[minWin].empty()){ //每个窗口的第一个客户信息
nowTime[minSize] = ; //当前窗口消耗时间为0
bgTime[i] = ; //第一名客户的开始时间为0
}
}
for(int i = ; i < n; i++){ //遍历所有窗口全部出队
if(!win[i].empty()){
disposeAll(i);
}
}
while(q--){ //获得查询
int query;
int endtime, begintime;
scanf("%d", &query);
endtime = edTime[query];
begintime = bgTime[query];
//获得查询用户的开始与结束时间
int beginhours = + (begintime / );
int beginminutes = begintime % ;
int endhours = + (endtime / );
int endminutes = endtime % ;
if(beginhours >= ){ //开始时间大于17输出Sorry
printf("Sorry\n");
}else
printf("%02d:%02d\n", endhours, endminutes);
}
}
return ;
}
PTA (Advanced Level) 1014 Waiting in Line的更多相关文章
- PAT (Advanced Level) 1014. Waiting in Line (30)
简单模拟题. #include<iostream> #include<cstring> #include<cmath> #include<algorithm& ...
- PAT甲级1014. Waiting in Line
PAT甲级1014. Waiting in Line 题意: 假设银行有N个窗口可以开放服务.窗前有一条黄线,将等候区分为两部分.客户要排队的规则是: 每个窗口前面的黄线内的空间足以包含与M个客户的一 ...
- PAT 1014 Waiting in Line (模拟)
1014. Waiting in Line (30) 时间限制 400 ms 内存限制 65536 kB 代码长度限制 16000 B 判题程序 Standard 作者 CHEN, Yue Suppo ...
- PAT 甲级 1014 Waiting in Line (30 分)(queue的使用,模拟题,有个大坑)
1014 Waiting in Line (30 分) Suppose a bank has N windows open for service. There is a yellow line ...
- 1014 Waiting in Line (30分)
1014 Waiting in Line (30分) Suppose a bank has N windows open for service. There is a yellow line i ...
- PTA(Advanced Level)1036.Boys vs Girls
This time you are asked to tell the difference between the lowest grade of all the male students and ...
- 【PAT Advanced Level】1014. Waiting in Line (30)
简单模拟题,注意读懂题意就行 #include <iostream> #include <queue> using namespace std; #define CUSTOME ...
- PTA 1014 Waiting in Line (30分) 解题思路及满分代码
题目 Suppose a bank has N windows open for service. There is a yellow line in front of the windows whi ...
- PTA(Basic Level)1014.福尔摩斯的约会 && PTA(Advanced Level)1061.Dating
大侦探福尔摩斯接到一张奇怪的字条:我们约会吧! 3485djDkxh4hhGE 2984akDfkkkkggEdsb s&hgsfdk d&Hyscvnm.大侦探很快就明白了,字条上奇 ...
随机推荐
- 开源WebGIS实施方案(五):基于SLD实现图层符号化及其应用
SLD概述 SLD(OpenGIS® Styled Layer Descriptor):图层样式注记.其当前版本是1.1.0.SLD是一种描述地图图层样式的标准,一般用于WMS中的图层符号化. 说白了 ...
- hibernate 中 fetch=FetchType.LAZY 懒加载失败处理
对这种懒加载问题,最后的做法是利用Spring提供的一个针对Hibernate的一个支持类,其主要意思是在发起一个页面请求时打开Hibernate的Session,一直保持这个Session,使得Hi ...
- Replication--如何使用快照来初始化化请求订阅
这是一篇针对新人的知识普及文章,老人慎入! 在快照发布和事务发布中,SQL Server需要使用快照来将数据库某一时间点的数据传递给订阅,快照使用BCP的机制. 首先我们需要查看和设置快照的生成目录, ...
- 函数IsValid()
功能:检查对象变量是否已经实例化,即实例变量的值是否是个有效的对象句柄. 语法:IsValid(objectname) 参数:objectname:要检查的对象名. 返回值:Boolean.如果指定对 ...
- java学习笔记DOM4J解析(7)
DOM4J即Document Object Model for Java使用java技术以文档方式解析XML数据的模型. DOM4J是开源组织提供的一个免费的.强大的XML解析工具,如果开发者需要在项 ...
- 1305 Pairwise Sum and Divide(数学 ,规律)
HackerRank 1305 Pairwise Sum and Divide 有这样一段程序,fun会对整数数组A进行求值,其中Floor表示向下取整: fun(A) sum = ...
- 详解sizeof与strlen
一,sizeof是C语言的一种单目运算符,与C语言的其他运算符++,--一样,它并不是函数:sizeof()以字节为单位给出了操作数的大小:sizeof的值是无符号int. strlen是一个函数,只 ...
- [AIR] AS3操作文件时报SecurityError: fileWriteResource 错的解决方法
在用File操作(移动,删除等)或者写入文件时,以下写法会报错 var file:File =File.applicationDirectory.resolvePath("1.swf&quo ...
- 移动端<meta>属性配置讲解(整理)
meta标签,是head区的辅助标签 HTML代码如下: <meta charset="utf-8"><meta http-equiv="X-UA-Co ...
- Cookie、session和localStorage的区别
一.Cookie.session和localStorage的区别 cookie的内容主要包括:名字.值.过期时间.路径和域.路径与域一起构成cookie的作用范围.若不设置时间,则表示这个cookie ...
