深入理解sudo
[root@cairui ~]# cat /etc/sudoers
## Sudoers allows particular users to run various commands as
## the root user, without needing the root password. #sudoers允许特定的用户去执行各种命令以rot的身份,不需要root密码。
##
## Examples are provided at the bottom of the file for collections
## of related commands, which can then be delegated out to particular
## users or groups.
##
## This file must be edited with the 'visudo' command. ## Host Aliases
## Groups of machines. You may prefer to use hostnames (perhaps using
## wildcards for entire domains) or IP addresses instead.
# Host_Alias FILESERVERS = fs1, fs2
# Host_Alias MAILSERVERS = smtp, smtp2 ## User Aliases
## These aren't often necessary, as you can use regular groups
## (ie, from files, LDAP, NIS, etc) in this file - just use %groupname
## rather than USERALIAS
# User_Alias ADMINS = jsmith, mikem ## Command Aliases
## These are groups of related commands... ## Networking
# Cmnd_Alias NETWORKING = /sbin/route, /sbin/ifconfig, /bin/ping, /sbin/dhclient, /usr/bin/net, /sbin/iptables, /usr/bin/rfcomm, /usr/bin/wvdial, /sbin/iwconfig, /sbin/mii-tool ## Installation and management of software
# Cmnd_Alias SOFTWARE = /bin/rpm, /usr/bin/up2date, /usr/bin/yum ## Services
# Cmnd_Alias SERVICES = /sbin/service, /sbin/chkconfig ## Updating the locate database
# Cmnd_Alias LOCATE = /usr/bin/updatedb ## Storage
# Cmnd_Alias STORAGE = /sbin/fdisk, /sbin/sfdisk, /sbin/parted, /sbin/partprobe, /bin/mount, /bin/umount ## Delegating permissions
# Cmnd_Alias DELEGATING = /usr/sbin/visudo, /bin/chown, /bin/chmod, /bin/chgrp ## Processes
# Cmnd_Alias PROCESSES = /bin/nice, /bin/kill, /usr/bin/kill, /usr/bin/killall ## Drivers
# Cmnd_Alias DRIVERS = /sbin/modprobe # Defaults specification #
# Refuse to run if unable to disable echo on the tty.
#
Defaults !visiblepw #
# Preserving HOME has security implications since many programs
# use it when searching for configuration files. Note that HOME
# is already set when the the env_reset option is enabled, so
# this option is only effective for configurations where either
# env_reset is disabled or HOME is present in the env_keep list.
#
Defaults always_set_home Defaults env_reset
Defaults env_keep = "COLORS DISPLAY HOSTNAME HISTSIZE INPUTRC KDEDIR LS_COLORS"
Defaults env_keep += "MAIL PS1 PS2 QTDIR USERNAME LANG LC_ADDRESS LC_CTYPE"
Defaults env_keep += "LC_COLLATE LC_IDENTIFICATION LC_MEASUREMENT LC_MESSAGES"
Defaults env_keep += "LC_MONETARY LC_NAME LC_NUMERIC LC_PAPER LC_TELEPHONE"
Defaults env_keep += "LC_TIME LC_ALL LANGUAGE LINGUAS _XKB_CHARSET XAUTHORITY" #
# Adding HOME to env_keep may enable a user to run unrestricted
# commands via sudo.
#
# Defaults env_keep += "HOME" Defaults secure_path = /sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin ## Next comes the main part: which users can run what software on
## which machines (the sudoers file can be shared between multiple
## systems).
## Syntax:
##
## user MACHINE=COMMANDS
##
## The COMMANDS section may have other options added to it.
##
## Allow root to run any commands anywhere
root ALL=(ALL) ALL ## Allows members of the 'sys' group to run networking, software,
## service management apps and more.
# %sys ALL = NETWORKING, SOFTWARE, SERVICES, STORAGE, DELEGATING, PROCESSES, LOCATE, DRIVERS ## Allows people in group wheel to run all commands
# %wheel ALL=(ALL) ALL ## Same thing without a password
# %wheel ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD: ALL ## Allows members of the users group to mount and unmount the
## cdrom as root
# %users ALL=/sbin/mount /mnt/cdrom, /sbin/umount /mnt/cdrom ## Allows members of the users group to shutdown this system
# %users localhost=/sbin/shutdown -h now ## Read drop-in files from /etc/sudoers.d (the # here does not mean a comment)
#includedir /etc/sudoers.d
注意:修改完(visudo)之后,需要visudo -c检查一下是否有错误。
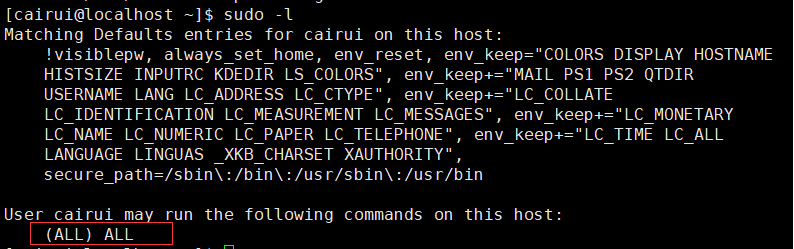
sudo -l查看用户拥有的权限。

1、sudoers配置文件别名介绍
(1)Host Aliases(主机别名)
生产环境中一般不会设置主机别名,一般主机别名不太常用
root ALL=(ALL) ALL #第一个ALL就是主机别名的应用位置 (2)User Aliases(用户别名)
如果表示用户组那么前面加%
root ALL=(ALL) ALL #root就是用户别名的应用位置
User_Aliases ADMINS = jsmith,mikem (3)Runas_Alias别名
此别名是指定“用户身份”,即sudo允许切换到的用户
root ALL=(ALL) ALL #第二个ALL就是用户别名的应用位置
Runas_Alias OP = root (4)Cmnd_Alias(命令别名)
就是定义一个别名,它可以包含一堆命令的内容(一组相关命令的集合)
root ALL=(ALL) ALL Cmnd_Alias DRIVERS = /sbin/modpro 2、sudo日志审计
(1)生产环境中日志方案
a、syslog全部操作日志审计,这种方法信息量大,不便查看
b、sudo日志配置syslog服务进行日志审查
c、堡垒机日志审查
d、bash安装监视器,记录用户使用操作
(2)配合sudo日志审计
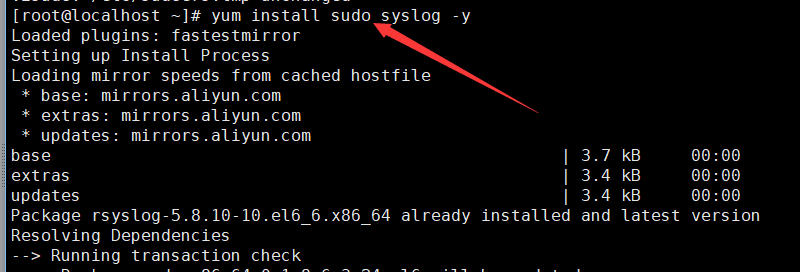
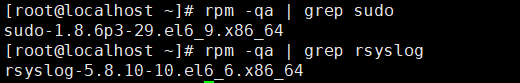
安装sudo与syslog服务
配置服务
创建日志保存目录
[root@localhost ~]# mkdir -p /var/log/
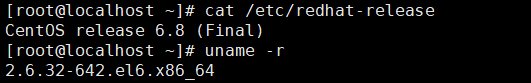
查看服务器版本,6.x为/etc/rsyslog.conf,5.x版本为syslog.conf

上述为rsyslog的配置文件

上述为sudoers的配置文件
测试结果:
[root@localhost ~]# su - cairui
[cairui@localhost ~]$ sudo visudo
[sudo] password for cairui:
visudo: /etc/sudoers.tmp unchanged
[cairui@localhost ~]$ cd /tmp/
[cairui@localhost tmp]$ touch .txt
[cairui@localhost tmp]$ sudo ll
sudo: ll: command not found
[cairui@localhost tmp]$ sudo ls -ll
total
-rw-rw-r-- cairui cairui Feb : .txt
-rw-------. root root Feb : yum.log
[cairui@localhost tmp]$ sudo cat /var/log/sudo.log
Feb :: : cairui : TTY=pts/ ; PWD=/home/cairui ; USER=root ;
COMMAND=/usr/sbin/visudo
Feb :: : cairui : TTY=pts/ ; PWD=/tmp ; USER=root ; COMMAND=/bin/ls
-ll
Feb :: : cairui : TTY=pts/ ; PWD=/tmp ; USER=root ; COMMAND=/bin/cat
/var/log/sudo.log
深入理解sudo的更多相关文章
- 深入理解 sudo 与 su 之间的区别【转】
深入理解 sudo 与 su 之间的区别 两个命令的最大区别是: sudo 命令需要输入当前用户的密码,su 命令需要输入 root 用户的密码.另外一个区别是其默认行为.sudo 命令只允许使用提升 ...
- 深入理解 sudo 与 su 之间的区别
深入理解 sudo 与 su 之间的区别 作者: Himanshu Arora 译者: LCTT zhb127 在早前的一篇文章中,我们深入讨论了 sudo 命令的相关内容.同时,在该文章的末尾有提到 ...
- Linux中su和sudo的用法整理
一.为什么会有su和sudo命令? 主要是因为在实际工作当中需要在Linux不同用户之间进行切换.root用户权限最高很多时候需要root用户才能执行一些关键命令.所以需要临时切换为root用户.工作 ...
- npm常用命令小结
目录(更新于2016.09.23): 1.认识和使用NPM 2.npm包安装模式 3.npm包管理(package的安装.卸载.升级.查看.搜索.发布,其他等) npm install [-g] 本地 ...
- extjs的使用笔记
2006年jack slocum斯洛克姆 基于yui写的扩展前端框架(就是由一些前端可视化组件如表单,树, 表格,等组成的frameset或者叫做 ui engine),叫yui-ext, 后来成熟后 ...
- 深入理解 JavaScript,以及 Linux 下的开发调试工具
前言 JavaScript 是我接触到的第二门编程语言,第一门是 C 语言.然后才是 C++.Java 还有其它一些什么.所以我对 JavaScript 是非常有感情的,毕竟使用它有十多年了.早就想写 ...
- linux su和sudo命令的区别
一. 使用 su 命令临时切换用户身份 1.su 的适用条件和威力 su命令就是切换用户的工具,怎么理解呢?比如我们以普通用户beinan登录的,但要添加用户任务,执行useradd ,beinan用 ...
- 理解Docker(4):Docker 容器使用 cgroups 限制资源使用
本系列文章将介绍Docker的有关知识: (1)Docker 安装及基本用法 (2)Docker 镜像 (3)Docker 容器的隔离性 - 使用 Linux namespace 隔离容器的运行环境 ...
- Linux sudo 命令的应用
.note-content { font-family: "Helvetica Neue", Arial, "Hiragino Sans GB", STHeit ...
随机推荐
- Spring 与 MyBatis 的整合
本文讨论 Spring 与 MyBatis 的整合. 在 beans.xml 中我们定义了两个 bean: SqlSessionFactoryBean.SqlSessionTemplate. 1.Sq ...
- 机器学习:多项式回归(scikit-learn中的多项式回归和 Pipeline)
一.scikit-learn 中的多项式回归 1)实例过程 模拟数据 import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt x = np.random. ...
- Python:格式化操作符(%)
原文作者:田小计划 原文出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/wilber2013/ (若转载,请标明原文出处) 在编写程序的过程中,经常需要进行格式化输出,每次用每次查.干脆就在这里整 ...
- Codeforce 101B. Buses(线段树or树状数组+离散化)
Buses ...
- canvas绘制中的API
canvas绘制Z 先贴代码吧: /** * Created by Administrator on 2016/1/26. */ var i; function draw (id){ var canv ...
- Cassandra 学习二
Cassandra的架构 Cassandra的设计目的是处理跨多个节点的大数据工作负载,而没有任何单点故障.Cassandra在其节点之间具有对等分布式系统,并且数据分布在集群中的所有节点之间. 1 ...
- Nor Flash的CFI与JEDEC接口
Flash 存储器接口还有两个标准:CFI和JEDEC.CFI为公共Flash接口[Common Flash Interface],用来帮助程序从Flash芯片中获取操作方式信息(发送命令,从nor ...
- 使用like查询text类型字段
使用like查询text类型字段 public bool Exists(GetReadType GRT, ClientMessageGetRead TypeID, string MessageID, ...
- 1106SQLserver基础--变量、运算符的使用,if...else,while语句
数据库---变量(对数据库中的数据没有任何影响) 作用:临时存储数据的作用,起一个衔接的作用,为了方便理解存储过程. 例:Declare @hello varchar(20) Set @hello=’ ...
- struts1.2里的ActionMessages的使用
转自:https://blog.csdn.net/oswin_jiang/article/details/4582187