netty核心组件之channel、handler、ChannelHandlerContext、pipeline
channel介绍:
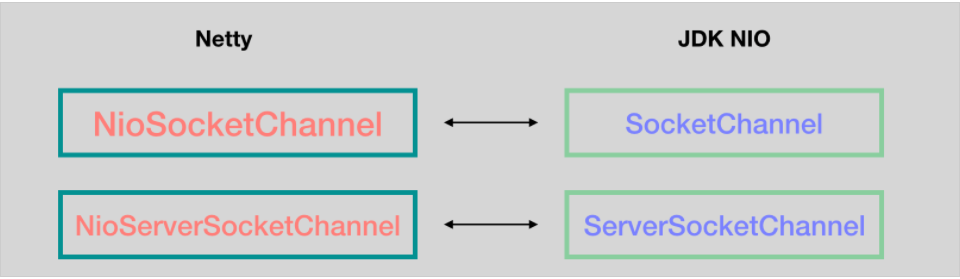
netty中channel分为NioServerScoketChannel和NioSocketChannel,分别对应java nio中的ServerScoketChannel和SocketChannel
channel、pipeline、context、handler关系
ScoketChannel都会注册到EventLoop上的selector中,每个channel内部都会有一个pipeline,pipeline管道 里面由多个handler连接成一个双向链表结构,而handler又由ChannelHandlerContext包裹着,context相当于一个handler上下文,做到了承上启下的作用,
从context可以得到handler,自然也能得到channel和pipeline,context内部有两个指针分别指向前 后context,handler在pipeline向前或向后进行传递,当然顺序只能由一个方向传递
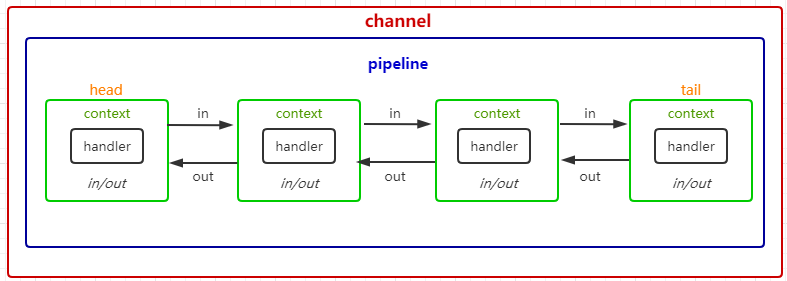
head和tail表示头尾,每一次有io事件进入,netty称为入站 它始终从head入站像后进行传递,反之io事件出去称为出站,也是从head出去,图中入站出站看似形成了一个完整的双向链表,但实际可能还没到tail就结束了,
context分为inbound和outbound,入站和出站会判断当前context是否符合 也是判断context中handler是inboundhandler还是outboundhandler,入站只执行入站的context,出站也是如此,在初始化pipeline会默认创建head、tail,
它们分别表示头 尾 位置固定不许修改,head和tail同时为inbound、outbound
先来看看handler是如何先加入pipeline中的,handler添加顺序无论怎么添加,头都是head 尾都是tail pipeline初始化就固定了
bossGroup.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
public void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline p = ch.pipeline();
// 像pipeline添加一个handler
p.addLast(new EchoServerHandler());
}
});
// 将context添加到pipeline的"最后"
private void addLast0(AbstractChannelHandlerContext newCtx) {
AbstractChannelHandlerContext prev = tail.prev;
newCtx.prev = prev;
newCtx.next = tail;
prev.next = newCtx;
// 重新指向 依然保持着 tail》context》tail
tail.prev = newCtx;
}
在创建ServerBootGroup时会给workerGroup分配一个handler,后面每一个NioSocketChannel都会添加一个该handler, ChannelInitializer可以理解为帮助我们创建channel,它是一个inboundhandler,在第一次注册时会调用initChannel来执行我们自定义的实现
public final void channelRegistered(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {// 这里会调用我们实现的initChannel方法,并把ctx中的channel传过去
if (initChannel(ctx)) {
// 初始化成功,这里就是我们入站的入口了,它是从pipeline发起的
ctx.pipeline().fireChannelRegistered();
} else {
// 如果已经初始化过了,说明已经进入pipeline了,直接向后传递
ctx.fireChannelRegistered();
}
}
下面分别列举ChannelInboundHandler和ChannelOutboundHandler的方法让大家知道哪些是入站执行的,哪些是出站执行的
public interface ChannelInboundHandler extends ChannelHandler {
// 注册
void channelRegistered(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception;
// 取消注册
void channelUnregistered(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception;
// 处于活动状态
void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception;
// 处于非活动状态
void channelInactive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception;
// 读取数据
void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception;
// 读取数据完毕
void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception;
// 用户自定义事件触发,如发生心跳检测时,会调用该方法把当前心跳事件传播进来
void userEventTriggered(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object evt) throws Exception;
// channel可写状态改变
void channelWritabilityChanged(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception;
// 发生异常
void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception;
}
public interface ChannelOutboundHandler extends ChannelHandler {
// 绑定
void bind(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, SocketAddress localAddress, ChannelPromise promise) throws Exception;
// 连接
void connect(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, SocketAddress remoteAddress, SocketAddress localAddress, ChannelPromise promise) throws Exception;
// 断开连接
void disconnect(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ChannelPromise promise) throws Exception;
// 关闭
void close(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ChannelPromise promise) throws Exception;
// 注销
void deregister(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ChannelPromise promise) throws Exception;
// 暂时不知道这一步干啥的,按理说read操作是入站操作
void read(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception;
// 写
void write(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg, ChannelPromise promise) throws Exception;
// 刷新刚执行的操作
void flush(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception;
}
还有一个特殊的handler ChannelDuplexHandler,它同时继承ChannelInboundHandler和ChannelOutboundHandler,但不推荐用它,容易混淆,建议我们自己写的时候把入站和出站的handler分开
public class ChannelDuplexHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter implements ChannelOutboundHandler
ChannelHandlerContext传播行为
前面我们讲入站是像后进行事件传递,出站是向前进行事件传递,那么事件入口是如何进来的、怎么出去的,怎么保证执行的顺序
如读事件,发生read事件时,会交给NioUnsafe方法,Unsafe随后会有介绍 它是netty中用来操作jdk中的nio,因为事件操作还是都交给jdk中的nio来,读取数据时会调用pipeline.fireChannelRead(readBuf.get(i)),这样就进入pipeline了 来开始事件传播
private final class NioMessageUnsafe extends AbstractNioUnsafe {
@Override
public void read() {
~~~~~~~~~~~~~
int size = readBuf.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i ++) {
readPending = false;
// >>>>>>>>>进入入站读操作
pipeline.fireChannelRead(readBuf.get(i));
}
readBuf.clear();
allocHandle.readComplete();
// 完成操作
pipeline.fireChannelReadComplete();
~~~~~~~~
}
}
pipeline开启事件传播
// 调用pipeline该方法开始事件传播
public final ChannelPipeline fireChannelRead(Object msg) {
AbstractChannelHandlerContext.invokeChannelRead(head, msg);
return this;
} // >>>AbstractChannelHandlerContext.invokeChannelRead(head, msg) 由pipeline调用 然后进入context事件传递
static void invokeChannelRead(final AbstractChannelHandlerContext next, Object msg) {
final Object m = next.pipeline.touch(ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(msg, "msg"), next);
EventExecutor executor = next.executor();
// 判断是否在当前线程,如果在当前线程直接调用,否则当成任务交给executor执行
if (executor.inEventLoop()) {
next.invokeChannelRead(m);
} else {
executor.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
next.invokeChannelRead(m);
}
});
}
} private void invokeChannelRead(Object msg) {
// 判断handler是否已经被调用
if (invokeHandler()) {
try {
/**
* 调用handler的读操作,用户通过实现该方法完成自定义读事件逻辑,如果读取完后需要向后传递,需要在channelRead自定义方法中继续调用context.fireChannelRead(msg)
*
**/
((ChannelInboundHandler) handler()).channelRead(this, msg);
} catch (Throwable t) {
notifyHandlerException(t);
}
} else {
// 已经被调用 调过当前handler向后传递
fireChannelRead(msg);
}
} public ChannelHandlerContext fireChannelRead(final Object msg) {
// 找出下一个入站handler继续向后传递
invokeChannelRead(findContextInbound(), msg);
return this;
} private AbstractChannelHandlerContext findContextInbound() {
AbstractChannelHandlerContext ctx = this;
// 不停地获取下一个handler直到是inboundhandler返回
do {
ctx = ctx.next;
} while (!ctx.inbound);
return ctx;
}
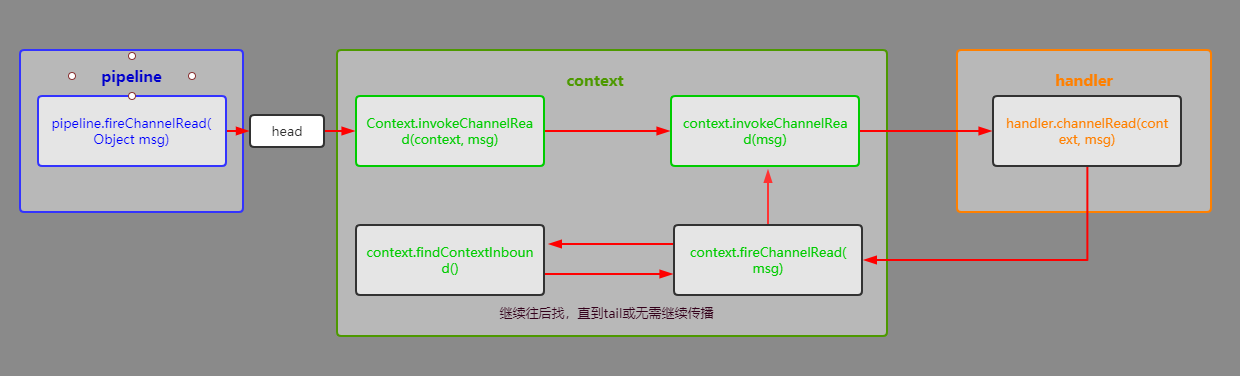
这就是读数据入站的大致传播流程,从head入站直至tail或中途停止事件传播, 出站流程类似 我就不贴了
在讲解服务端和客户端启动流程前我们还需要再熟悉几个重要类
ChannelFuture、Promise、Unsafe
我们先来channelfuture和promise的继承结构
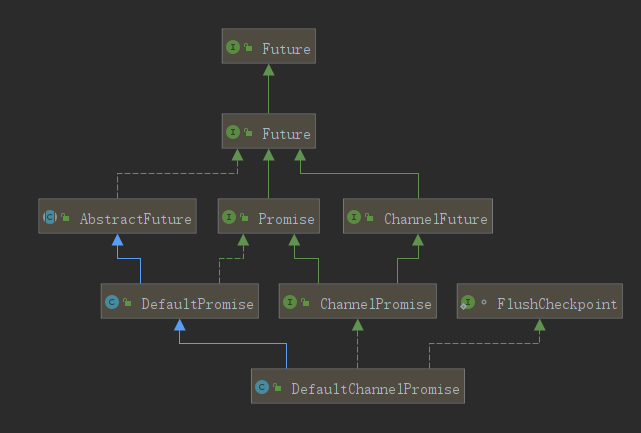
- ChannelFuture:nio既然是异步执行的,那么必定有异步执行结果,跟线程池一样,netty也对应有一个future
- Promise:Promise也继承于future,听起来是不是和channelfuture功能重复了是不是,它两主要区别是,channelfuture可以得到对应的channel,promise可以主动设置异步执行状态,实际使用的ChannelPromise的实现类DefaultChannelPromise,channelPromise又同时继承channelfuture和实现promise,我个人不太理解为啥有channelfuture还多设计一个promise,直接在channelfuture加一个设置异步状态的接口不就好了,我猜想可能是promise可以当做一个脱离channel普通的异步实现,优秀的框架内部“果然都是可高度自定义重写的”
- Unsafe:unsafe读过jdk源码的人应该很熟悉了,它是一个可直接进行原子化操作的工具,netty中的unsafe是用来操作jdk中的nio操作,我们前面说过netty就是一个在jdk原生nio上进行封装优化,所以内部网络通信肯定还是依靠jdk的nio实现的
public interface Future<V> extends java.util.concurrent.Future<V> {
// 是否成功
boolean isSuccess();
// 是否取消
boolean isCancellable();
// 执行时候发生的异常
Throwable cause();
// 添加监听器
Future<V> addListener(GenericFutureListener<? extends Future<? super V>> listener);
// 批量添加监听器
Future<V> addListeners(GenericFutureListener<? extends Future<? super V>>... listeners);
// 移除监听器
Future<V> removeListener(GenericFutureListener<? extends Future<? super V>> listener);
// 移除多个监听器
Future<V> removeListeners(GenericFutureListener<? extends Future<? super V>>... listeners);
// 同步阻塞,内部先执行await() 如果执行任务有发生异常会重新抛出
Future<V> sync() throws InterruptedException;
// 与sync区别是,如果等待过程中发生中断,会将当前线程也一起中断,不响应中断
Future<V> syncUninterruptibly();
// 同步阻塞,它与sync区别是,任务执行失败不会抛出异常
Future<V> await() throws InterruptedException;
// 同理
Future<V> awaitUninterruptibly();
boolean await(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException;
boolean await(long timeoutMillis) throws InterruptedException;
boolean awaitUninterruptibly(long timeout, TimeUnit unit);
boolean awaitUninterruptibly(long timeoutMillis);
// 获得执行结果,但不阻塞
V getNow();
// 取消任务,并调用通知唤醒阻塞,然后调用监听器,mayInterruptIfRunning值好像没啥作用
boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning);
}
public interface Promise<V> extends Future<V> {
// 设置任务结果为成功 如果任务已经完成则抛出异常
Promise<V> setSuccess(V result);
// 设置任务结果为成功,返回设置结果 不抛出异常
boolean trySuccess(V result);
// 设置任务结果为失败 如果任务已经完成则抛出异常
Promise<V> setFailure(Throwable cause);
// 设置任务结果为失败,返回设置结果 不抛出异常
boolean tryFailure(Throwable cause);
}
public interface ChannelFuture extends Future<Void> {
// 返回当前channel
Channel channel();
}
我们这节先大致介绍channel、handler、ChannelHandlerContext、pipeline 作用和方法,具体如何创建并使用,它们之前是怎么相互配合工作,我们下节通过对服务端和客户端启动过程进行分析过就会清晰许多
netty核心组件之channel、handler、ChannelHandlerContext、pipeline的更多相关文章
- Netty 核心组件 Pipeline 源码分析(二)一个请求的 pipeline 之旅
目录大纲: 前言 针对 Netty 例子源码做了哪些修改? 看 pipeline 是如何将数据送到自定义 handler 的 看 pipeline 是如何将数据从自定义 handler 送出的 总结 ...
- 【转】Netty那点事(三)Channel中的Pipeline
[原文]https://github.com/code4craft/netty-learning/blob/master/posts/ch3-pipeline.md Channel是理解和使用Nett ...
- Netty 核心组件 Pipeline 源码分析(一)之剖析 pipeline 三巨头
目录大纲: 前言 ChannelPipeline | ChannelHandler | ChannelHandlerContext 三巨头介绍 三巨头编织过程(创建过程) ChannelPipelin ...
- netty系列之:Event、Handler和Pipeline
目录 简介 ChannelPipeline ChannelHandler ChannelHandlerContext ChannelHandler中的状态变量 异步Handler 总结 简介 上一节我 ...
- 5. 彤哥说netty系列之Java NIO核心组件之Channel
你好,我是彤哥,本篇是netty系列的第五篇. 简介 上一章我们一起学习了如何使用Java原生NIO实现群聊系统,这章我们一起来看看Java NIO的核心组件之一--Channel. 思维转变 首先, ...
- Netty核心组件介绍及手写简易版Tomcat
Netty是什么: 异步事件驱动框架,用于快速开发高i性能服务端和客户端 封装了JDK底层BIO和NIO模型,提供高度可用的API 自带编码解码器解决拆包粘包问题,用户只用关心业务逻辑 精心设计的Re ...
- netty中的Channel、ChannelPipeline
一.Channel与ChannelPipeline关系 每一个新创建的 Channel 都将会被分配一个新的 ChannelPipeline.这项关联是永久性 的:Channel 既不能附加另外一个 ...
- Netty服务端Channel的创建与初始化
Netty创建服务端Channel时,从服务端 ServerBootstrap 类的 bind 方法进入,下图是创建服务端Channel的函数调用链.在后续代码中通过反射的方式创建服务端Channel ...
- 一文聊透 Netty IO 事件的编排利器 pipeline | 详解所有 IO 事件的触发时机以及传播路径
欢迎关注公众号:bin的技术小屋,本文图片加载不出来的话可查看公众号原文 本系列Netty源码解析文章基于 4.1.56.Final版本 1. 前文回顾 在前边的系列文章中,笔者为大家详细剖析了 Re ...
随机推荐
- Hello!OA!Hello!工作流!寻找OA和工作流的旅途记录
最近新到了一家公司,这家公司做的人力资源管理,需要一个OA系统,所以就让我做一个选型,经过我2周时间的筛选,试用,沟通,测试,最终确定了几款,这个艰辛的路程,在这里记录一下~ 寻找OA的路程----- ...
- 冲刺Day5
每天举行站立式会议照片: 前后端交互: 昨天已完成的工作: 1.确认搜索栏界面 2.订单模块的大部分代码 3.用户模块的大部分代码 4.测试登录注册功能 燃尽图: 今天计划完成的工作: 成员 任务 高 ...
- Spring RestTemplate具备负载均衡功能
在创建RestTemplate的Bean时使用@LoadBalanced注解, 就可以自动配置为使用ribbon.如下面的示例所示: @Configuration public class MyCo ...
- Struts2 S2-061(CVE-2020-17530)漏洞复现
0x00 漏洞简介 Apache Struts2框架是一个用于开发Java EE网络应用程序的Web框架.Apache Struts于2020年12月08日披露 S2-061 Struts 远程代码执 ...
- STL—— 容器(vector)数据插入insert()方法 的返回值
vector 容器下的 insert() 方法拥有返回值,由于insert() 方法拥有4种重载函数,他的返回值不尽相同. 第一种,插入单个元素后的返回值: 1 #include <iostre ...
- Java中四舍五入
1.Math中四舍五入的方法 Math.ceil(double a)向上舍入,将数值向上舍入为最为接近的整数,返回值是double类型 Math.floor(double a)向下舍入,将数值向下舍入 ...
- router.push query 路由 跳转 传参使用
this.$router.push({path:'/shop',query:{ goods_name:goods_name, goods_price:goods_price, uid:goods_pr ...
- # spring boot + mybatis 读取数据库
spring boot + mybatis 读取数据库 创建数据库 use testdb; drop table if exists t_city; create table t_city( id i ...
- mysql单机多实例配置
Windows上配置多个mysql实例,主要改下配置文件即可,mysql目录如下: my2中主要改两个配置内容 datadir = D:/Program Files/Mysql/mysql-5.7.2 ...
- springMVC项目中配置log4j.properties路径
log4j.properties不打到war包中,单独写到一个存放配置文件的文件夹中,在容器中将该文件夹放入classpath,在web.xml中可以如下配置: <context-param&g ...
