963B:Destruction of a Tree
You are given a tree (a graph with n vertices and n - 1 edges in which it's possible to reach any vertex from any other vertex using only its edges).
A vertex can be destroyed if this vertex has even degree. If you destroy a vertex, all edges connected to it are also deleted.
Destroy all vertices in the given tree or determine that it is impossible.
The first line contains integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 2·105) — number of vertices in a tree.
The second line contains n integers p1, p2, ..., pn (0 ≤ pi ≤ n). If pi ≠ 0 there is an edge between vertices i and pi. It is guaranteed that the given graph is a tree.
If it's possible to destroy all vertices, print "YES" (without quotes), otherwise print "NO" (without quotes).
If it's possible to destroy all vertices, in the next n lines print the indices of the vertices in order you destroy them. If there are multiple correct answers, print any.
5
0 1 2 1 2
YES
1
2
3
5
4
4
0 1 2 3
NO
In the first example at first you have to remove the vertex with index 1 (after that, the edges (1, 2) and (1, 4) are removed), then the vertex with index 2 (and edges (2, 3) and (2, 5) are removed). After that there are no edges in the tree, so you can remove remaining vertices in any order.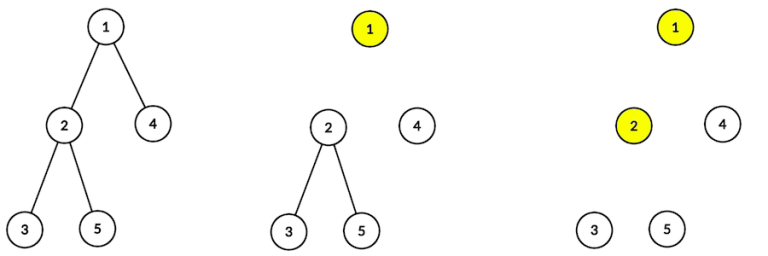
规定一个顺序,使分为父子结点,则每次删除只能往子节点查找
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <iomanip>
#include <cmath>
#include <cassert>
#include <ctime>
#include <map>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
#pragma comment(linker, "/stck:1024000000,1024000000")
#define lowbit(x) (x&(-x))
#define max(x,y) (x>=y?x:y)
#define min(x,y) (x<=y?x:y)
#define MAX 100000000000000000
#define MOD 1000000007
#define pi acos(-1.0)
#define ei exp(1)
#define PI 3.1415926535897932384626433832
#define ios() ios::sync_with_stdio(true)
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
#define mem(a) (memset(a,0,sizeof(a)))
#define ll long long
vector<int>v[],ans;
stack<int>q;
int cnt[],vis[];
int n,x,pos,par[];
void bfs(int now)
{
ans.push_back(now);
vis[now]=;
for(int i=;i<v[now].size();i++)
{
cnt[v[now][i]]--;
if(v[now][i]==par[now] || vis[v[now][i]]) continue;//当前节点已经被找过,或者是now节点的父节点
if(!(cnt[v[now][i]]&)) bfs(v[now][i]);
}
}
void dfs(int fa,int now)
{
par[now]=fa;
q.push(now);
for(int i=;i<v[now].size();i++)
{
if(v[now][i]==fa) continue;
dfs(now,v[now][i]);
}
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&x);
if(x)
{
v[i].push_back(x);
v[x].push_back(i);
cnt[i]++;
cnt[x]++;
}
else pos=i;
}
dfs(,pos);//n-1条边,则必有一个为0,不妨把这点作为根节点遍历。
memset(vis,,sizeof(vis));
while(!q.empty())
{
int fr=q.top();
q.pop();
if(!(cnt[fr]&)) bfs(fr);//从后向前遍历,若存在,必只有一个结点符合初始为偶数
}
if(ans.size()==n)
{
printf("YES\n");
for(int i=;i<ans.size();i++)
printf("%d\n",ans[i]);
}
else printf("NO\n");
return ;
}
963B:Destruction of a Tree的更多相关文章
- CodeForces - 963B Destruction of a Tree (dfs+思维题)
B. Destruction of a Tree time limit per test 1 second memory limit per test 256 megabytes input stan ...
- codeforces 963B Destruction of a Tree
B. Destruction of a Tree time limit per test 1 second memory limit per test 256 megabytes input stan ...
- Codeforces963B - Destruction of a Tree
Portal Description 给出一个\(n(n\leq2\times10^5)\)个点的树,每次可以删除一个度数为偶数的点及其相连的边,求一种能够删掉整棵树的方案. Solution 简单起 ...
- leetcode算法: Find Bottom Left Tree Value
leetcode算法: Find Bottom Left Tree ValueGiven a binary tree, find the leftmost value in the last row ...
- LeetCode第[98]题(Java):Validate Binary Search Tree(验证二叉搜索树)
题目:验证二叉搜索树 难度:Medium 题目内容: Given a binary tree, determine if it is a valid binary search tree (BST). ...
- 二叉树系列 - 二叉搜索树 - [LeetCode] 中序遍历中利用 pre节点避免额外空间。题:Recover Binary Search Tree,Validate Binary Search Tree
二叉搜索树是常用的概念,它的定义如下: The left subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys less than the node's ke ...
- Tinkoff Internship Warmup Round 2018 and Codeforces Round #475 (Div. 1) 963B 964D B Destruction of a Tree
题 OvO http://codeforces.com/contest/963/problem/B CF 963B 964D 解 对于题目要求,显然一开始的树,要求度数为偶数的节点个数为奇数个,通过奇 ...
- Codeforces 963B Destruction of a Tree 思维+dfs
题目大意: 给出一棵树,每次只能摧毁有偶数个度的节点,摧毁该节点后所有该节点连着的边都摧毁,判断一棵树能否被摧毁,若能,按顺序输出摧毁的点,如果有多种顺序,输出一种即可 基本思路: 1)我一开始自然而 ...
- [LeetCode]题解(python):110 Balanced Binary Tree
题目来源 https://leetcode.com/problems/balanced-binary-tree/ Given a binary tree, determine if it is hei ...
随机推荐
- Windows和Linux的编译理解
Windows一般编译出来的x86的软件,就是只能在x86的系统上才能运行,同理,在x64系统上也是一样的道理. Linux利用gcc编译器编译,可以在Linux上面运行,但是想要在嵌入式系统上运行的 ...
- 【codeforces 816C】Karen and Game
[题目链接]:http://codeforces.com/contest/816/problem/C [题意] 给你一个n*m的矩阵; 一开始所有数字都是0; 每次操作,你能把某一行,或某一列的数字全 ...
- Redis学习总结(3)——Redis整合Spring结合使用缓存实例
摘要:本文介绍了如何在Spring中配置redis,并通过Spring中AOP的思想,将缓存的方法切入到有需要进入缓存的类或方法前面. 一.Redis介绍 什么是Redis? redis是一个key- ...
- OCP-1Z0-051-题目解析-第50题
50. SLS is a private synonym for the SH.SALES table. The user SH issues the following command: DRO ...
- Intellij使用"easyexplore"
刚开始接触Intellij,里面有很多东西还不太会用,平时在eclipse里面用的很方便的easyexplore能帮助快速打开文件目录,Intellij中本身就有这样的功能,只是默认没有开启,需要我们 ...
- IHttpHandler的学习(0)
本片文章转自网络 问题1:什么是HttpHandler?(Handler:处理者:那就是对Http请求的处理拉) 问题2:什么是HttpModule? 问题3:什么时候应该使用HttpHandler什 ...
- Scala之面向对象
1. Scala基础练习 不使用str.toLong,str.toInt/Integer.valueOf()/Long.valueOf/Integer.parseInt()等,将字符串"12 ...
- 3065: 带插入区间K小值_树套树_替罪羊树_权值线段树
经过周六一天,周一3个小时的晚自习,周二2个小时的疯狂debug,终于凭借自己切掉了这道树套树题. Code: #include <cstdio> #include <algorit ...
- CSS命令
border-bottom-right-radius: 10px;/* 文本框的角的弯曲度*/ border-bottom-left-radius: 10px; border-top-left-rad ...
- c3p0-config.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE xml> <c3p0-confi ...
