树(Heap)
对于大量的输入数据,链表的线性访问时间太慢,不宜使用——《数据结构与算法分析——C 语言描述》 p 65
对于大量的输入数据,适合用树结构,大部分操作都是 O( log N )。
二叉树
1. 实现
节点定义
template<typename T>
struct Node
{
Node(T v) : val(v), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}; T val;
struct Node *left;
struct Node *right;
};
构建树并添加节点
按照如图的树构建
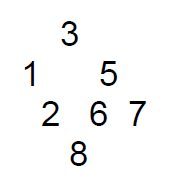
Node<int> *root = new Node<int>(); //根节点 root->left = new Node<int>(); //根节点的左子树
root->left->right = new Node<int>(); root->right = new Node<int>(); //根节点的又子树
root->right->left = new Node<int>();
root->right->left->left = new Node<int>();
root->right->right = new Node<int>();
遍历
递归方式
template<typename T>
void traversalRecursion(const struct Node<T>* const p)
{
if (p != nullptr)
{
cout << p->val; traversalRecursion(p->left);
traversalRecursion(p->right);
}
else
cout << "#";
}
非递归方式——用栈消除递归
template<typename T>
void traversalStack(struct Node<T> *const root)
{
stack<struct Node<T>*> s; s.push(root); while (s.size())
{
struct Node<T> *const p = s.top(); s.pop(); if (p == nullptr)
{
cout << "#";
continue;
} cout << p->val; s.push(p->right);
s.push(p->left);
}
}
表达式树
后缀表达式: a b + c d e + * *
从“后缀表达式”开始构造一颗表达式树,仅类定义
template<typename T>
class ExpressionTree
{
public:
struct Node<T>* initFormPostfix(const string &postfix)
{
istringstream iss(postfix);
T c; while (iss >> c)
{
struct Node<T> *const p = new struct Node<T>(c); switch (characterType(c))
{
case :
sk.push(p);
break; case :
p->right = sk.top(); sk.pop();
p->left = sk.top(); sk.pop(); sk.push(p);
break;
}
} return sk.top();
} private:
int characterType(const T &c) const
{
if (c == "+" || c == "-" || c == "*" || c == "/")
return ; return ;
} stack<struct Node<T>*> sk;
};
完整代码
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <sstream>
#include <stack>
#include <memory> using namespace std; template<typename T>
struct Node
{
Node(T v) : val(v), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {};
T val;
struct Node *left;
struct Node *right;
}; template<typename T>
class ExpressionTree
{
public:
struct Node<T>* initFormPostfix(const string &postfix)
{
istringstream iss(postfix);
T c; while (iss >> c)
{
struct Node<T> *const p = new struct Node<T>(c); switch (characterType(c))
{
case :
sk.push(p);
break; case :
p->right = sk.top(); sk.pop();
p->left = sk.top(); sk.pop(); sk.push(p);
break;
}
} return sk.top();
} private:
int characterType(const T &c) const
{
if (c == "+" || c == "-" || c == "*" || c == "/")
return ; return ;
} stack<struct Node<T>*> sk;
}; template<typename T>
void traversalRecursion(const struct Node<T>* const p)
{
if (p != nullptr)
{
cout << p->val; traversalRecursion(p->left);
traversalRecursion(p->right);
}
else
cout << "#";
} int main()
{
string postfix = "a b + c d e + * *"; ExpressionTree<string> et; const struct Node<string> *root = et.initFormPostfix(postfix); traversalRecursion(root); return ;
}
二叉查找树
构建
构建如图所示的二叉查找树
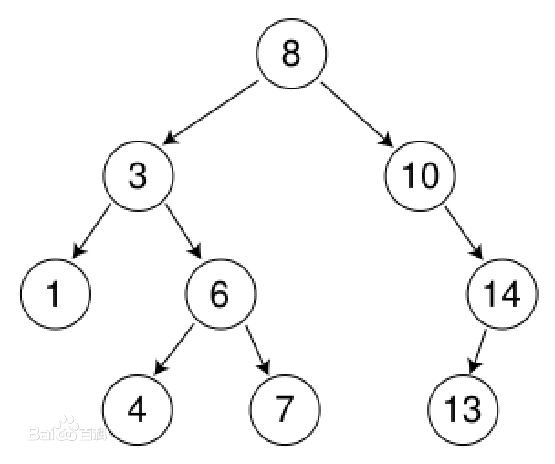
构建 + 遍历 代码如下
#include <iostream>
#include <initializer_list>
#include <stack> using namespace std; template<typename T>
struct Node
{
Node(T v) : val(v), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
T val;
struct Node* left;
struct Node* right;
}; template<typename T>
class BinarySearchTree
{
public:
BinarySearchTree()
{
root = new struct Node<T>();
} BinarySearchTree(const initializer_list<T> il) : BinarySearchTree()
{
initializer_list<T>::iterator it = il.begin(); root->val = *it++; while (it != il.end())
insert(*it++);
} void insert(const T &val)
{
struct Node<T> **p = &root; while (*p != nullptr)
{
if (val == (*p)->val)
return; if (val < (*p)->val)
{
p = &((*p)->left);
continue;
} if (val > (*p)->val)
{
p = &((*p)->right);
continue;
}
} *p = new struct Node<T>(val);
} void traversalStack()
{
stack<struct Node<T>*> s; s.push(root); while (s.size())
{
struct Node<T> *const p = s.top(); s.pop(); if (p == nullptr)
{
cout << "#";
continue;
} cout << p->val; s.push(p->right);
s.push(p->left);
}
} private:
struct Node<T> *root;
}; int main(void)
{
BinarySearchTree<int> bst({ , , , , , , , , }); bst.traversalStack(); return ;
}
查找 代码如下
struct Node<T>* find(const T &val) const
{
struct Node<T> *p = root; while (p != nullptr)
{
if (p->val == val)
return p; if (val < p->val)
p = p->left; if (val > p->val)
p = p->right;
} return nullptr;
}
树的遍历
后序遍历
利用后序遍历求树的深度
unsigned getBinaryTreeHeigt(const struct Node *const p)
{
if (p == nullptr)
return -;
else
return + max(getBinaryTreeHeigt(p->left), getBinaryTreeHeigt(p->right));
}
层序遍历
代码一,非递归实现
void levelOrderTraversal(struct Node *root)
{
queue<struct Node*> q; q.push(root); while (q.size())
{
struct Node *p = q.front(); q.pop(); if (p == nullptr)
continue; q.push(p->left);
q.push(p->right); cout << p->val << " ";
}
}
代码二,递归实现
void levelVisit(queue<struct Node*> &que) {
if (que.empty()) return;
struct Node *p = que.front(); que.pop();
if (p == nullptr) return;
cout << p->val << " ";
que.push(p->left);
que.push(p->right);
levelVisit(que);
}
利用队列可以完成二叉树的层序遍历(广度优先遍历);利用栈可以完成二叉树的深度优先遍历。
树(Heap)的更多相关文章
- BZOJ.3489.A simple rmq problem(主席树 Heap)
题目链接 当时没用markdown写,可能看起来比较难受...可以复制到别的地方看比如DevC++. \(Description\) 给定一个长为n的序列,多次询问[l,r]中最大的只出现一次的数.强 ...
- 清北学堂 2020 国庆J2考前综合强化 Day2
目录 1. 题目 T1 一 题目描述 Sol T2 二 题目描述 Sol T3 三 题目描述 Sol T4 四 题目描述 Sol 2. 算法 -- 数据结构 1. 题目 T1 一 题目描述 问题描述 ...
- 左偏树(Leftist Heap/Tree)简介及代码
左偏树是一种常用的优先队列(堆)结构.与二叉堆相比,左偏树可以高效的实现两个堆的合并操作. 左偏树实现方便,编程复杂度低,而且有着不俗的效率表现. 它的一个常见应用就是与并查集结合使用.利用并查集确定 ...
- Codeforces Round #300 F - A Heap of Heaps (树状数组 OR 差分)
F. A Heap of Heaps time limit per test 3 seconds memory limit per test 512 megabytes input standard ...
- zoj-3963 Heap Partition(贪心+二分+树状数组)
题目链接: Heap Partition Time Limit: 2 Seconds Memory Limit: 65536 KB Special Judge A sequence ...
- 笛卡尔树 POJ ——1785 Binary Search Heap Construction
相应POJ 题目:点击打开链接 Binary Search Heap Construction Time Limit: 2000MS Memory Limit: 30000K Total Subm ...
- POJ-1785-Binary Search Heap Construction(笛卡尔树)
Description Read the statement of problem G for the definitions concerning trees. In the following w ...
- L - A Heap of Heaps CodeForces - 538F 主席树
L - A Heap of Heaps CodeForces - 538F 这个是一个还比较裸的静态主席树. 这个题目的意思是把这个数组变成k叉树,然后问构成的树的子树小于等于它的父节点的对数有多少. ...
- POJ 1785 Binary Search Heap Construction(裸笛卡尔树的构造)
笛卡尔树: 每个节点有2个关键字key.value.从key的角度看,这是一颗二叉搜索树,每个节点的左子树的key都比它小,右子树都比它大:从value的角度看,这是一个堆. 题意:以字符串为关键字k ...
随机推荐
- python读取文件行号和内容的便捷方法
处理数据时候,需要得到数据所在和行号,使用enumerate时便捷的方法: file = open('file.txt','r') for (num,value) in enumerate(file) ...
- Codeforces Round #433 (Div. 2, based on Olympiad of Metropolises)
A. Fraction 题目链接:http://codeforces.com/contest/854/problem/A 题目意思:给出一个数n,求两个数a+b=n,且a/b不可约分,如果存在多组满足 ...
- 使用Intel IPT技术保护您的帐号安全
使用Intel IPT技术保护您的帐号安全
- 21.5.3 Updatable and Insertable Views
http://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.7/en/view-updatability.html Some views are updatable and reference ...
- Core Data with Mantle
Mantle makes it easy to write a simple model layer for your Cocoa or Cocoa Touch application. Mantl ...
- NYOJ 275 队花的烦恼一
队花的烦恼一 时间限制:3000 ms | 内存限制:65535 KB 难度:1 描写叙述 ACM队的队花C小+常常抱怨:"C语言中的格式输出中有十六.十.八进制输出,然而却没有二进制输 ...
- css内边距 边框
/*1 元素的各边都有 10 像素的内边距 四个值上.右.下.左 两个上下,左右 三个值:上,左右,下*/ /*p {padding: 10%;}*/ h1 { padding-top: 10px; ...
- 011-spring cloud gateway-使用
一.pom增加 <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId> ...
- ASP.NET一个页面的生命周期
在学习ASP.NET页面生命周期前,需要先了解之前的ASP.NET的基本运行机制,在理解ASP.NET基本运行机制原理后,下面将介绍ASP.NET的生命周期中,页面从创建到处理结束的过程中ASP.NE ...
- vue-watch
<template> <div> <!-- 监听值的改变: --> <button class="th" @click="add ...
