MySQL 5.7: Enhanced Multi-threaded slaves
http://geek.rohitkalhans.com/2013/09/enhancedMTS-deepdive.html 科学上网
Introduction
The infamous out of order commit problem
On Master we apply T1 and T2 in that order.
State0: x= 1, y= 1 T2: { y:= Read(x);
|
On the slave however these two transactions commit out of order (Say T2 and then T1).
State0: x= 1, y= 1 T1: { x:= Read(y);
|
As we see above the final state state 2 is different in the two cases. Needless to say that we need to control the transactions that can execute in parallel.
Controlled parallelization
The process of committing: On the slave we need to make sure that the transactions that we schedule for parallel execution will be the one which do not have conflicting read and write set. This is the only and the necessary requirement for the slave workers to work without conflicts. This also implies that if the transactions being executed in parallel do not have intersecting read and write sets, we don't care if they are committed out of order. Since MySQL uses lock based scheduling, all the transactions that have entered the prepared stage but not as yet committed will have disjoint read and write sets and hence can be executed in parallel.
Logical clock and commit parent
The pseudo code is as follows.
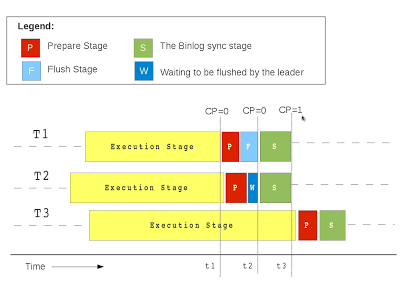
Another thing to note here is that the "group" of transactions that are being executed in parallel are not bounded by binlog commit group. There is a possibility that a transaction have entered the binlog prepare stage but could not make it to the current binlog group. Our approach takes care of such cases and makes sure that we relax the boundary of the group being executed in parallel on the slave.
Conclusion
This feature provides the great enhancement to the existing MySQL replication. To know more about the configuration options of this enhancement refer to this post.
This feature is available inMySQL 5.7.2 release. You can try it out and let us know the feedback.
About the author

Rohit Kalhans is a Software Development Engineer based out of Banglore India. His area of focus revolves around Row-based replication and Multi-threaded parallel slave. His interests include system programming, highly-available and scalable systems. In his free time, he plays guitar and piano and loves to write short stories and poems. More Information can be found on his homepage.
MySQL 5.7: Enhanced Multi-threaded slaves的更多相关文章
- MySQL复制配置(多主一从)
复制多主一从 replicaion 原理 复制有三个步骤:(分为三个线程 slave:io线程 sql线程 master:io线程) 1.master将改变记录到二进制日志(binary log)中( ...
- MySql集群FAQ----mysql主从配置与集群区别、集群中需要多少台计算机呢?为什么? 等
抽取一部分显示在这里,如下, What's the difference in using Clustervs using replication? 在复制系统中,一个MySQL主服务器会更新一个或多 ...
- MySQL数据很大的时候
众所周知,mysql在数据量很大的时候查询的效率是很低的,因为假如你需要 OFFSET 100000 LIMIT 5 这样的数据,数据库就需要跳过前100000条数据,才能返回给你你需要的5条数据.由 ...
- mysql 2006
1.在my.ini文件中添加或者修改以下两个变量:wait_timeout=2880000interactive_timeout = 2880000 关于两个变量的具体说明可以google或者看官方手 ...
- MySQL高可用架构:mysql+keepalived实现
系统环境及架构 #主机名 系统版本 mysql版本 ip地址 mysqlMaster <a href="https://www.linuxprobe.com/" title= ...
- MySQL之备份
MySQL备份和备份 备份/还原 冷备:需要停止当前正在运行mysqld,然后直接拷贝或打包数据文件. 半热备:mysqldump+binlog --适合数据量比较小的应用 在线热备:AB复制 --实 ...
- linux MySql 的主从复制部署
MySql 复制 mysql 复制:将某一台主机上的 Mysql 数据复制到其它主机(slaves)上,并重新执行一遍从而实现 当前主机上的 mysql 数据与(master)主机上数据保持一致的过程 ...
- java面试一日一题:讲对mysql的MVCC的理解
问题:请讲下对mysql中MVCC的理解 分析:这个问题要回答的是对MVCC的理解,以及MVCC解决了什么问题这几个方面入手. 回答要点: 主要从以下几点去考虑, 1.什么是MVCC? 2.MVCC用 ...
- BlackArch-Tools
BlackArch-Tools 简介 安装在ArchLinux之上添加存储库从blackarch存储库安装工具替代安装方法BlackArch Linux Complete Tools List 简介 ...
随机推荐
- ORACLE临时表总结[转]
临时表概念 临时表就是用来暂时保存临时数据(亦或叫中间数据)的一个数据库对象,它和普通表有些类似,然而又有很大区别.它只能存储在临时表空间,而非用户的表空间.ORACLE临时表是会话或事务级别的,只对 ...
- 【和我一起学Python吧】Python3.0与2.X版本的区别
做为一个前端开发的码农,却正在阅读最新版的<A byte of Python>.发现Python3.0在某些地方还是有些改变的.准备慢慢的体会,与老版本的<A byte of Pyt ...
- mybatis系列-10-一对一查询
10.1 需求 查询订单信息,关联查询创建订单的用户信息 10.2 resultType 10.2.1 sql语句 确定查询的主表:订单表 确定查询的关联表:用户表 关联查询 ...
- linux网络编程笔记——UDP
目前这部分代码会出现阻塞问题,暂时尚未解决 #include "udp.h" #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> ...
- Java邮件服务学习之四:邮箱服务客户端Spring Mail
一.Spring Mail API Spring邮件抽象层的主要包为org.springframework.mail,Spring提供的邮件发送不仅支持简单邮件的发送.添加附件. 1.邮件发送的核心接 ...
- FrameWork 建模时查询项的usage
§ Identifier:代表被用于分组或汇总与其相关的Fact数据的列.也代表一个索引列.还代表日期或时间列.§ Fact:代表一个包含数值数据可被分组或汇总的列,例如,产品成本.§ Attribu ...
- ecstore 后台登陆跳转到 api失败,中心请求网店API失败
解决过程没有具体参与,官方解决后回复的邮件,可以参考一下: 后台登陆错误图: 商派解决方法邮件: 特别注意:这个错误提示有时候也跟ecstore的nginx服务器伪静态有关,具体参考: htt ...
- 【转】强大的vim配置文件,让编程更随意
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/ma6174/archive/2011/12/10/2283393.html 花了很长时间整理的,感觉用起来很方便,共享一下. 我的vim配置主 ...
- Laravel Controllers
Basic Controllers Instead of defining all of your route-level logic in a single routes.php file, you ...
- scp命令获取远程文件
一.scp是什么? scp是secure copy的简写,用于在Linux下进行远程拷贝文件的命令,和它类似的命令有cp,不过cp只是在本机进行拷贝不能跨服务器,而且scp传输是加密的,可能会稍微影响 ...
