Boost IPC Persistence Of Interprocess Mechanisms 例子
下面这一段摘抄自 Boost 1_55_0 的文档,显然标注了 每一个的生命期。
One of the biggest issues with interprocess communication mechanisms is the lifetime of the interprocess communication mechanism. It's important to know when an interprocess communication mechanism disappears from the system. In Boost.Interprocess, we can have 3 types of persistence:
- Process-persistence: The mechanism lasts until all the processes that have opened the mechanism close it, exit or crash.
- Kernel-persistence: The mechanism exists until the kernel of the operating system reboots or the mechanism is explicitly deleted.
- Filesystem-persistence: The mechanism exists until the mechanism is explicitly deleted.
Some native POSIX and Windows IPC mechanisms have different persistence so it's difficult to achieve portability between Windows and POSIX native mechanisms. Boost.Interprocess classes have the following persistence:
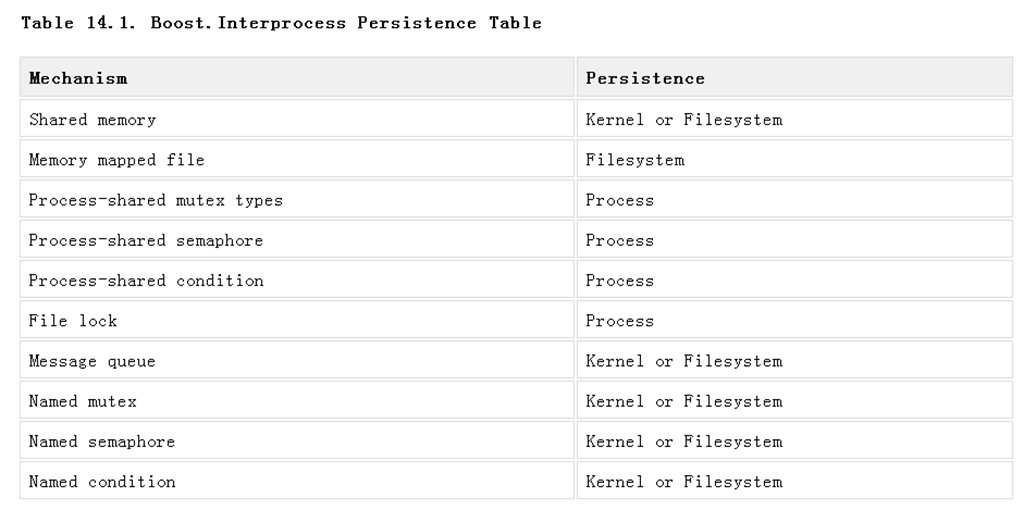
As you can see, Boost.Interprocess defines some mechanisms with "Kernel or Filesystem" persistence. This is because POSIX allows this possibility to native interprocess communication implementations. One could, for example, implement shared memory using memory mapped files and obtain filesystem persistence (for example, there is no proper known way to emulate kernel persistence with a user library for Windows shared memory using native shared memory, or process persistence for POSIX shared memory, so the only portable way is to define "Kernel or Filesystem" persistence).
最好的是下面这一个简单的example。
#include <boost/interprocess/shared_memory_object.hpp>
#include <boost/interprocess/mapped_region.hpp>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <string>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
using namespace boost::interprocess;
if(argc == 1){ //Parent process
//Remove shared memory on construction and destruction
struct shm_remove
{
shm_remove() { shared_memory_object::remove("MySharedMemory"); }
~shm_remove(){ shared_memory_object::remove("MySharedMemory"); }
} remover;
//Create a shared memory object.
shared_memory_object shm (create_only, "MySharedMemory", read_write);
//Set size
shm.truncate(1000);
//Map the whole shared memory in this process
mapped_region region(shm, read_write);
//Write all the memory to 1
std::memset(region.get_address(), 1, region.get_size());
//Launch child process
std::string s(argv[0]); s += " child ";
if(0 != std::system(s.c_str()))
return 1;
}
else{
//Open already created shared memory object.
shared_memory_object shm (open_only, "MySharedMemory", read_only);
//Map the whole shared memory in this process
mapped_region region(shm, read_only);
//Check that memory was initialized to 1
char *mem = static_cast<char*>(region.get_address());
for(std::size_t i = 0; i < region.get_size(); ++i)
if(*mem++ != 1)
return 1; //Error checking memory
}
return 0;
}
.csharpcode, .csharpcode pre
{
font-size: small;
color: black;
font-family: consolas, "Courier New", courier, monospace;
background-color: #ffffff;
/*white-space: pre;*/
}
.csharpcode pre { margin: 0em; }
.csharpcode .rem { color: #008000; }
.csharpcode .kwrd { color: #0000ff; }
.csharpcode .str { color: #006080; }
.csharpcode .op { color: #0000c0; }
.csharpcode .preproc { color: #cc6633; }
.csharpcode .asp { background-color: #ffff00; }
.csharpcode .html { color: #800000; }
.csharpcode .attr { color: #ff0000; }
.csharpcode .alt
{
background-color: #f4f4f4;
width: 100%;
margin: 0em;
}
.csharpcode .lnum { color: #606060; }
在主进程中创建另一个进程,这个进程来验证之前的共享内存是否被初始化为1。 因为我们的shared memory的生命期是 Kernel 或者是filesystem,所以进程2 是可以验证的。 值得注意一点的是这里的remover,他是一个栈对象,所以每次都销毁,显式调用了 remove,如果去掉这个remover,那么只需要执行一次,以后每次输入这个显式内存都是存在的。因为他的生命期是 kernel 或者filesystem。 所以这里的remover 至关重要!
Boost IPC Persistence Of Interprocess Mechanisms 例子的更多相关文章
- IPC介绍——10个ipcs例子
IPC介绍——10个ipcs例子 semaphorearrays2010performancesystemaccess ipcs是一个uinx/linux的命令.用于报告系统的消息队列.信号量.共享内 ...
- boost库asio详解8——几个TCP的简单例子
摘于boost官网的几个例子, 做了点小修改, 笔记之. 同步客户端 void test_asio_synclient() { typedef boost::asio::io_service IoSe ...
- BOOST 线程完全攻略 - 基础篇
http://blog.csdn.net/iamnieo/article/details/2908621 2008-09-10 12:48 9202人阅读 评论(3) 收藏 举报 thread多线程l ...
- [C++Boost]程序参数项解析库Program_options使用指南
介绍 程序参数项(program options)是一系列name=value对,program_options 允许程序开发者获得通过命令行(command line)和配置文件(config fi ...
- boost::thread类
前言 标准C++线程即将到来.预言它将衍生自Boost线程库,现在让我们探索一下Boost线程库. 几年前,用多线程执行程序还是一件非比寻常的事.然而今天互联网应用服务程序普遍使用多线程来提高与多客户 ...
- Android查缺补漏(IPC篇)-- 进程间通讯基础知识热身
本文作者:CodingBlock 文章链接:http://www.cnblogs.com/codingblock/p/8479282.html 在Android中进程间通信是比较难的一部分,同时又非常 ...
- System V IPC 之共享内存
IPC 是进程间通信(Interprocess Communication)的缩写,通常指允许用户态进程执行系列操作的一组机制: 通过信号量与其他进程进行同步 向其他进程发送消息或者从其他进程接收消息 ...
- 详解 boost 库智能指针(scoped_ptr<T> 、shared_ptr<T> 、weak_ptr<T> 源码分析)
一.boost 智能指针 智能指针是利用RAII(Resource Acquisition Is Initialization:资源获取即初始化)来管理资源.关于RAII的讨论可以参考前面的文章.在使 ...
- Boost总结汇总
从开始接触Boost已经有好几年了,而对它的掌握却难言熟悉,有对它部分的源代码的剖析也是蜻蜓点水.有时间一点点梳理一下吧. 1. 概述 [Boost]C++ Boost库简介[Boost]C++ Bo ...
随机推荐
- AsyncTask的用法
在开发Android应用时必须遵守单线程模型的原则: Android UI操作并不是线程安全的并且这些操作必须在UI线程中执行.在单线程模型中始终要记住两条法则: 1. 不要阻塞UI线程 2. 确保只 ...
- 建索引让SQL飞起来
今天帮助看了一个哥们的数据库,帮他抓了一下等待事件,刚好有一个sql在等待事件中,顺便看看 监控等待事件 select a.SID, a.EVENT, b.OSUSER, b.username, b. ...
- Java基础知识强化之网络编程笔记20:Android网络通信之 Android常用OAuth登录和分享
1. 申请百度开发者账号及百度OAuth简介. (1)申请开发者账号: http://developer.baidu.com/ (2)创建项目: http://developer.baidu.com ...
- Android 100多个Styles快速开发布局XML,一行搞定View属性,一键统一配置UI...
Android开发中大量使用XML代码作为界面的布局,使用styles能大幅精简XML代码. 比如下面这个界面从AlertDialog至PlacePickerWindow有19个样式相同的跳转Item ...
- 使用GDB调试Android NDK native(C/C++)程序
使用GDB调试Android NDK native(C/C++)程序 先说明下,这里所谓的ndk native程序跟Android上层java应用没有什么关系,也不需要涉及jni来封装native接口 ...
- 常用CSS技巧资料收集
1.重置浏览器的字体大小 重置浏览器的默认值 ,然后重设浏览器的字体大小你可以使用雅虎的用户界面重置的CSS方案 ,如果你不想下载9MB的文件,代码如下: body,div,dl,dt,dd,ul, ...
- MySQL高可用解决方案(MySQL HA Solution)
http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_7e89c3f501012vtr.html 什么是高可用性?很多公司的服务都是24小时*365天不间断的.比如Call Center.这就 ...
- ASP缓存类收集
木鸟写的 '********************************************** ' vbs Cache类 ' ' 属性valid,是否可用,取值前判断 ' 属性name,ca ...
- 通过GitHub部署网站到Azure WebSite
一.将代码上传到GitHub存储库中 第一步:创建Github新账户 第二步:新建仓库 第三步:安装Github shell程序,地址:http://windows.github.com/ 第四步:打 ...
- Apache Rewrite url重定向功能的简单配置
http://www.jb51.net/article/24435.htm 1.Apache Rewrite的主要功能 就是实现URL的跳转和隐藏真实地址,基于Perl语言的正则表达式规范.平时帮助我 ...
