剑指offer第七章&第八章
剑指offer第七章&第八章
class Solution {
public:
int StrToInt(string str)
{
if(str.empty())
return ;
int symbol = ;//正负号初始化为1表示正数
if(str[] == '-')
{//处理负号
symbol = -;//表示是负数
str[] = ''; //这里是‘0’ 不是0
}
else if(str[] == '+')
{//处理正号
symbol = ;//表示是正数
str[] = '';
}
int sum = ;
for(int i=;i<str.size();++i)
{
if(str[i] < '' || str[i] > '')
{
sum = ;
break;
}
sum = sum * + str[i] - '';
}
return symbol * sum;//正负号乘以sum,即表示字符串所表示的整数
}
};
2..数组中重复的数字
class Solution {
public:
// Parameters:
// numbers: an array of integers
// length: the length of array numbers
// duplication: (Output) the duplicated number in the array number
// Return value: true if the input is valid, and there are some duplications in the array number
// otherwise false
bool duplicate(int numbers[], int length, int* duplication)
{
if(numbers==NULL||length<=)
return false;
for(int i=;i<length;++i)
{
if(numbers[i]<||numbers[i]>length-)
return false;
}
for(int i=;i<length;++i)
{
while(numbers[i]!=i)
{
if(numbers[i]==numbers[numbers[i]])
{
*duplication=numbers[i];
return true;
}
int temp=numbers[i];
numbers[i]=numbers[temp];
numbers[temp]=temp;
}
}
return false;
}
};
3.构建乘积数组
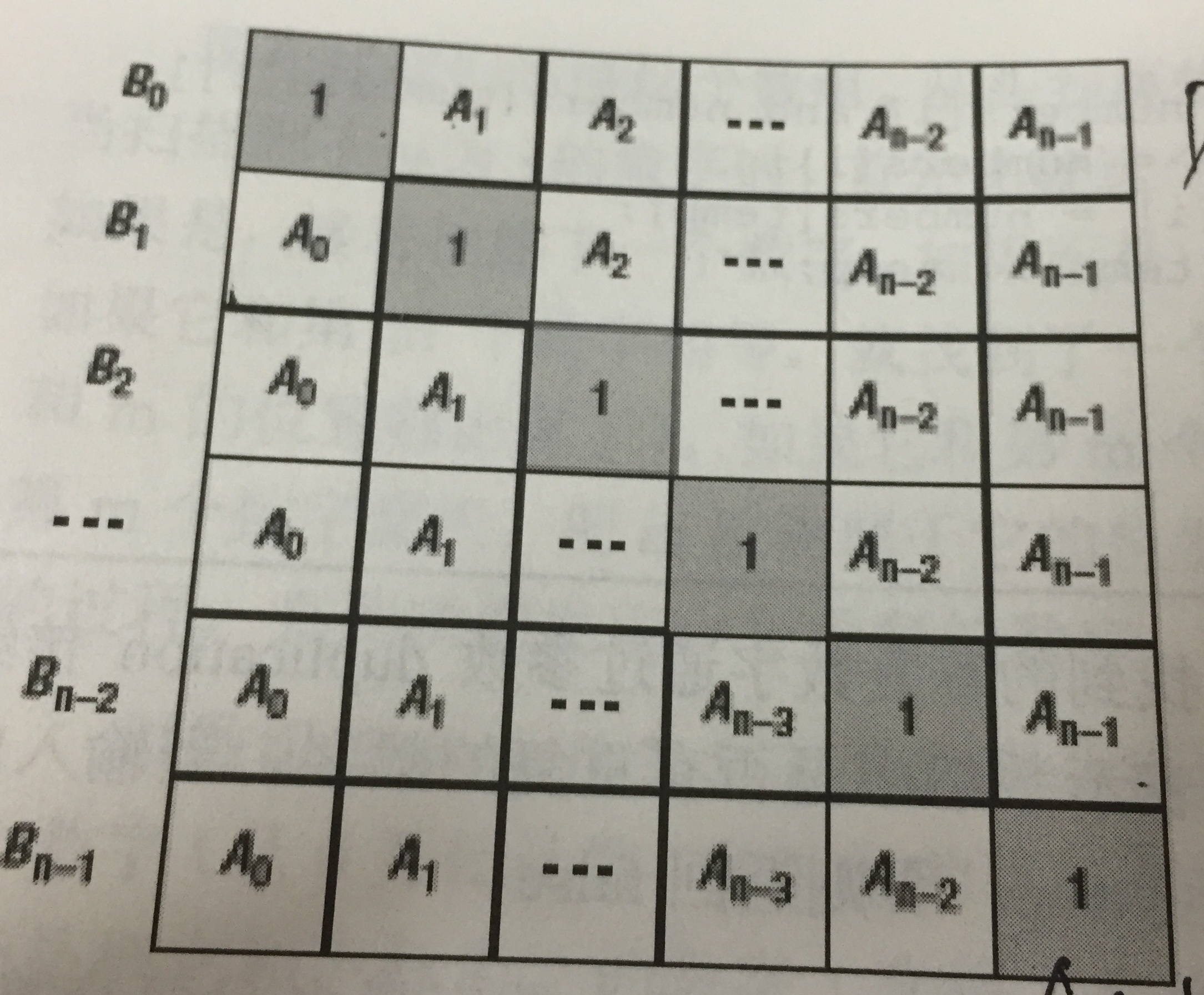
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> multiply(const vector<int>& A)
{
int n=A.size();
vector<int> B(n);
B[]=;
for(int i=;i<n;++i)
{
B[i]=B[i-]*A[i-];
}
double temp=;
for(int i=n-;i>=;--i)
{
temp*=A[i+];
B[i]*=temp;
}
return B;
}
};
4.表示数值的字符串
class Solution {
public:
bool isNumeric(char* string)
{
if(string==NULL)
return false;
if(*string=='+'||*string=='-')//首先判断第一个字符是不是正负号
++string;
if(*string=='\0')//边界判断
return false;
bool numeric=true;
scanDigits(&string);//扫描数位
if(*string!='\0')
{
if(*string=='.')//小数
{
++string;
scanDigits(&string);
if(*string=='e'||*string=='E')//科学记数法
numeric=isExp(&string);
}
//整数
else if(*string=='e'||*string=='E')
numeric=isExp(&string);
else
numeric=false;
}
return numeric&&*string=='\0';
}
void scanDigits(char** string)//扫描字符串中0到9的数位
{
while(**string !='\0'&&**string>=''&&**string<='')
++(*string);
}
bool isExp(char** string)//用来匹配用科学记数法表示数值的结尾部分,结尾部分的第一个字符是‘e’或者‘E’,接下来可能有一个正负号
{
if(**string!='e'&&**string!='E')
return false;
++(*string);
if(**string=='+'||**string=='-')
++(*string);
if(**string=='\0')
return false;
scanDigits(string);
return (**string=='\0') ? true:false;
}
};
5.字符流中第一个不重复的字符
class Solution
{
public:
string s;
char hash[]={};
//Insert one char from stringstream
void Insert(char ch)
{
s+=ch;
hash[ch]++;
}
//return the first appearence once char in current stringstream
char FirstAppearingOnce()
{
int size=s.size();
for(int i=;i<size;++i)
{
if(hash[s[i]]==)
return s[i];
}
return '#';
}
};
6.链表中环的入口结点
/*
struct ListNode {
int val;
struct ListNode *next;
ListNode(int x) :
val(x), next(NULL) {
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
//在链表中存在环的前提下找到一快一慢两个指针相遇的结点,一定在环内
ListNode* MeetingNode(ListNode* pHead)
{
if(pHead==NULL)
return NULL;
ListNode* pSlow=pHead->next;
if(pSlow==NULL)
return NULL;
ListNode* pFast=pSlow->next;
while(pFast!=NULL&&pSlow!=NULL)
{
if(pFast==pSlow)
return pFast;
pSlow=pSlow->next;
pFast=pFast->next;
if(pFast!=NULL)
pFast=pFast->next;
}
return NULL;
}
//找到环中任意一个结点之后,就能得出环中结点的数目,并找到环的入口结点
ListNode* EntryNodeOfLoop(ListNode* pHead)
{
ListNode* meetingNode=MeetingNode(pHead);
if(meetingNode==NULL)//没有环
return NULL;
//计算环中结点数
int nodesInLoop=;
ListNode* pNode1=meetingNode;
//从相遇的结点开始,一边继续向前移动一边计数,当再次回到这个结点,就统计出了环中节点数
while(pNode1->next!=meetingNode)
{
pNode1=pNode1->next;
++nodesInLoop;
}
//接下来找链表环的入口结点
//分三步:
//第一步:指针p1和p2初始化时都指向链表头结点
//第二步:由于环中有nodesInLoop个结点,指针p1先在链表上向前移动nodesInLoop步
//第三步:指针p1和p2以相同速度移动,直到相遇,相遇结点就是环的入口结点
pNode1=pHead;
for(int i=;i<nodesInLoop;++i)
pNode1=pNode1->next;
ListNode* pNode2=pHead;
while(pNode1!=pNode2)
{
pNode1=pNode1->next;
pNode2=pNode2->next;
}
return pNode1;
}
};
7.删除链表中重复的结点
/*
struct ListNode {
int val;
struct ListNode *next;
ListNode(int x) :
val(x), next(NULL) {
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* deleteDuplication(ListNode* pHead)
{
if(pHead==nullptr)
return pHead;
ListNode dummy(INT_MIN);//头结点
dummy.next=pHead;
ListNode *prev=&dummy,*cur=pHead;
while(cur!=nullptr){
bool duplicates=false;
while(cur->next!=nullptr&&cur->val==cur->next->val)
{
duplicates=true;
ListNode *tmp=cur;
cur=cur->next;
delete tmp;
}
if(duplicates)
{
//删除重复的最后一个元素
ListNode *tmp=cur;
cur=cur->next;
delete tmp;
continue;
}
prev->next=cur;
prev=prev->next;
cur=cur->next;
}
prev->next=cur;
return dummy.next;
}
};
8.二叉树的下一个结点
/*
struct TreeLinkNode {
int val;
struct TreeLinkNode *left;
struct TreeLinkNode *right;
struct TreeLinkNode *next;
TreeLinkNode(int x) :val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL), next(NULL) { }
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeLinkNode* GetNext(TreeLinkNode* pNode)
{
if(pNode==NULL)
return NULL;
TreeLinkNode* pNext=NULL;
if(pNode->right!=NULL)
{
TreeLinkNode* pRight=pNode->right;
while(pRight->left!=NULL)
pRight=pRight->left;
pNext=pRight;
}
else if(pNode->next!=NULL)
{
TreeLinkNode* pCurrent=pNode;
TreeLinkNode* pParent=pNode->next;
while(pParent!=NULL&&pCurrent==pParent->right)
{
pCurrent=pParent;
pParent=pParent->next;
}
pNext=pParent;
}
return pNext;
}
};
9.对称二叉树
/*
struct TreeNode {
int val;
struct TreeNode *left;
struct TreeNode *right;
TreeNode(int x) :
val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {
}
};
*/ class Solution {
public:
bool help(TreeNode *root1,TreeNode *root2)
{
if(root1==)
return root2==;
if(root2==)
return false;
return(root1->val==root2->val)&&help(root1->left,root2->right)&&help(root1->right,root2->left);
}
bool isSymmetrical(TreeNode *root)
{
if(root==){
return true;
}
return help(root->left,root->right);
}
};
10.按之字顺序打印二叉树
/*
struct TreeNode {
int val;
struct TreeNode *left;
struct TreeNode *right;
TreeNode(int x) :
val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int> > Print(TreeNode* pRoot)
{
vector<vector<int>> vv;
if(pRoot == NULL)
return vv;
deque<TreeNode *> q;
q.push_back(pRoot);
bool flag = true;//true表示从左向右存储层次遍历,否则是从右向左
int levelCnt = ;//上一层的节点数目
int curLevelCnt = ;//下一层节点数目
vector<int> v;
while(!q.empty())
{
TreeNode *cur;
if(flag)
{
cur = q.front();
q.pop_front();
}
else
{
cur = q.back();
q.pop_back();
}
if(flag)
{
if(cur->left)
{
q.push_back(cur->left);
++curLevelCnt;
}
if(cur->right)
{
q.push_back(cur->right);
++curLevelCnt;
}
}
else
{
if(cur->right)
{
q.push_front(cur->right);
++curLevelCnt;
}
if(cur->left)
{
q.push_front(cur->left);
++curLevelCnt;
}
}
v.push_back(cur->val);
--levelCnt;
if(levelCnt == )
{//这一层完毕
vv.push_back(v);
v.clear();
levelCnt = curLevelCnt;
curLevelCnt = ;
flag = !flag;
}
}
return vv;
}
};
11.把二叉树打印成多行
/*
struct TreeNode {
int val;
struct TreeNode *left;
struct TreeNode *right;
TreeNode(int x) :
val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int> > Print(TreeNode* pRoot)
{
vector<vector<int> > result;
queue<TreeNode*> current,next;
if(pRoot==NULL)
return result;
else
current.push(pRoot);
while(!current.empty()){
vector<int> level;//元素在一层
while(!current.empty()){
TreeNode* node=current.front();
current.pop();
level.push_back(node->val);
if(node->left!=NULL)
next.push(node->left);
if(node->right!=NULL)
next.push(node->right);
}
result.push_back(level);
swap(next,current);
}
return result;
}
};
12.二叉搜索树的第k个结点
/*
struct TreeNode {
int val;
struct TreeNode *left;
struct TreeNode *right;
TreeNode(int x) :
val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
//按照中序遍历的顺序遍历一颗二叉搜索树,遍历序列的数值是递增排序的
TreeNode* KthNode(TreeNode* pRoot, int k)
{
if(pRoot==NULL||k==)
return NULL;
return KthNodeCore(pRoot,k);
}
TreeNode* KthNodeCore(TreeNode* pRoot, int& k)
{
TreeNode* target=NULL;
if(pRoot->left!=NULL)
target=KthNodeCore(pRoot->left,k);
if(target==NULL)
{
if(k==)
target=pRoot;
k--;
}
if(target==NULL&&pRoot->right!=NULL)
target=KthNodeCore(pRoot->right,k);
return target;
}
};
剑指offer第七章&第八章的更多相关文章
- 剑指offer第六章
剑指offer第六章 1.数字在排序数组中出现的次数 统计一个数字在排序数组中出现的次数.例如输入排序数组{1,2,3,3,3,3,4,5}和数字3,由于3在数组中出现了4次,所以输出4 分析:思路1 ...
- 剑指offer第五章
剑指offer第五章 1.数组中出现次数超过一半的数 数组中有一个数字出现的次数超过数组长度的一半,请找出这个数字. 例如输入一个长度为9的数组{1,2,3,2,2,2,5,4,2}.由于数字2在数组 ...
- 剑指offer第四章
剑指offer第四章 1.二叉树的镜像 二叉树的镜像:输入一个二叉树,输出它的镜像 分析:求树的镜像过程其实就是在遍历树的同时,交换非叶结点的左右子结点. 求镜像的过程:先前序遍历这棵树的每个结点,如 ...
- 剑指offer第三章
剑指offer第三章 1.数值的整数次方 给定一个double类型的浮点数base和int类型的整数exponent.求base的exponent次方. class Solution { public ...
- 《剑指Offer》第二章(一)题3-8
为春招实习做准备,记录一下<剑指Offer>里面的面试题 第二章 面试题3:数组之中的重复数字. 这个题吧,虽然不难,但是不知道为什么就是看了很久,可能很久没有做算法题了.最后面一句话说的 ...
- 《剑指Offer》第二章(一)题 9 -12
第二章 面试题9:用两个栈实现队列 题目:如面试题,给你两个栈, 实现队列的先进先出,即在队列头删除一个元素以及在队列的尾部添加一个元素 思路:这个题的分析感觉很巧妙,从一个具体的例子入手,找出其中的 ...
- 剑指offer—第三章高质量代码(o(1)时间删除链表节点)
题目:给定单向链表的头指针和一个节点指针,定义一个函数在O(1)时间删除该节点,链表节点与函数的定义如下:struct ListNode{int m_nValue;ListNode* m_pValue ...
- 剑指offer—第三章高质量的代码(按顺序打印从1到n位十进制数)
题目:输入一个数字n,按照顺序打印出1到最大n位十进制数,比如输入3,则打印出1,2,3直到最大的3位数999为止. 本题陷阱:没有考虑到大数的问题. 本题解题思路:将要打印的数字,看成字符串,不足位 ...
- 剑指offer—第三章高质量代码(数值的整数次方)
高质量的代码:容错处理能力,规范性,完整性.尽量展示代码的可扩展型和可维护性. 容错处理能力:特别的输入和处理,异常,资源回收. 规范性:清晰的书写,清晰的布局,合理的命名. 完整性:功能测试,边界测 ...
随机推荐
- CentOS7下Firewall常用命令
安装它,只需 yum install firewalld 如果需要图形界面的话,则再安装 yum install firewall-config 一.介绍 防火墙守护 firewalld 服务引入了一 ...
- ctci4.1
; ) ; ) return false; else return true; }
- SQLServer 2005 和自增长主键identity说再见——NEWSEQUENTIALID()
``code 在SQLServer2005环境下,表的主键应该怎样设计. 目前主要用到的主键方案共三种 自动增长主键 手动增长主键 UNIQUEIDENTIFIER主键 1.先说自动增长主键,它的优点 ...
- 修改linux系统用户最大线程数限制
linux系统对线程数量有个最大限制,当达到系统限制的最大线程数时使用账号密码ssh到系统时是无法登陆的,会报Write failed: Broken pipe,或者是shell request fa ...
- Educational Codeforces Round 40 I. Yet Another String Matching Problem
http://codeforces.com/contest/954/problem/I 给你两个串s,p,求上一个串的长度为|p|的所有子串和p的差距是多少,两个串的差距就是每次把一个字符变成另一个字 ...
- 已经安装了node和npm,输入node -v 未找到命令
昨天虚拟机上安装了nvm.node.npm,今天打开输入node -v,就显示未找到命令 输入nvm --version 发现还是有nvm版本的,不然都要以为刚配好的虚拟机又要重新安装... 再输入 ...
- 关闭多个screen
由于开了很多个screen同时工作,关闭是一个一个比较麻烦,写个命令在这以便日后想不起来时可以用到. 1.先看看有多少个screen screen -ls |awk '/Socket/'|awk ...
- 016——数组(十六)usort uasort uksort
<?php /*数组 usort uasort uksort */ //usort()通过自定义函数对数组进行排序,原数组索引不保留 /*$arr = array(5, 3, 7, 6, 4, ...
- [Eclipse]Eclipse快捷键
查看一个方法被谁调用:选中方法名字,Search-->Reference-->Workspace
- Java进阶4表达式中的陷阱
Java进阶4表达式中的陷阱 20131103 表达式是Java中最基本的组成单元,各种表达式是Java程序员最司空见惯的内容,Java中的表达式并不是十分的复杂,但是也有一些陷阱.例如当程序中使用算 ...
