LeeCode 二叉树问题(一)
二叉树的遍历
二叉树节点定义
public class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode() {}
TreeNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
this.val = val;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
LeeCode 144: 二叉树的前序遍历
题目描述
给你一棵二叉树的根节点
root,返回其节点值的前序遍历。
Java代码实现
递归实现
public List<Integer> preorderRecursive(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
preorderRecursiveImpl(root, res);
return res;
}
public void preorderRecursiveImpl(TreeNode root, List<Integer> res) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
res.add(root.val);
preorderRecursiveImpl(root.left, res);
preorderRecursiveImpl(root.right, res);
return;
}
迭代实现
递归实现本质上是维护了一个隐藏的栈结构,而在迭代时需要手动维护。
public List<Integer> preorderIterative(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) {
return res;
}
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
/**
* 添加顺序: 根 -> 左 -> 右
*/
while (root != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
while (root != null) {
res.add(root.val);
stack.push(root);
root = root.left;
}
root = stack.pop();
root = root.right;
}
return res;
}
Morris 实现
public List<Integer> preorderMorris(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
TreeNode cur = root;
TreeNode prev = null;
while (cur != null) {
// 当前节点没有左子节点,则直接访问当前节点,并将指针指向右子节点
if (cur.left == null) {
res.add(cur.val);
cur = cur.right; // 通过 cur.right 返回父节点
continue;
}
prev = cur.left;
// 寻找当前节点左子节点的最右子结点
while (prev.right != null && prev.right != cur) {
prev = prev.right;
}
if (prev.right == null) {
prev.right = cur;
res.add(cur.val); // 前序访问根节点
cur = cur.left;
}
else {
prev.right = null;
cur = cur.right;
}
}
return res;
}
LeeCode 94: 二叉树的中序遍历
题目描述
给你一棵二叉树的根节点
root,返回其节点值的中序遍历。
Java代码实现
递归实现
public List<Integer> inorderRecursive(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
inorderRecursiveImpl(root, res);
return res;
}
public void inorderRecursiveImpl(TreeNode root, List<Integer> res) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
inorderRecursiveImpl(root.left, res);
res.add(root.val);
inorderRecursiveImpl(root.right, res);
return;
}
迭代实现
public List<Integer> inorderIterative(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) {
return res;
}
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
/**
* 添加顺序: 左 -> 根 -> 右
*/
while (root != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
while (root != null) {
stack.push(root);
root = root.left;
}
root = stack.pop();
res.add(root.val);
root = root.right;
}
return res;
}
Morris 实现
Morris实现的核心想法是找到当前节点的左子节点的最右子结点,即当前节点中序遍历的前一个节点。
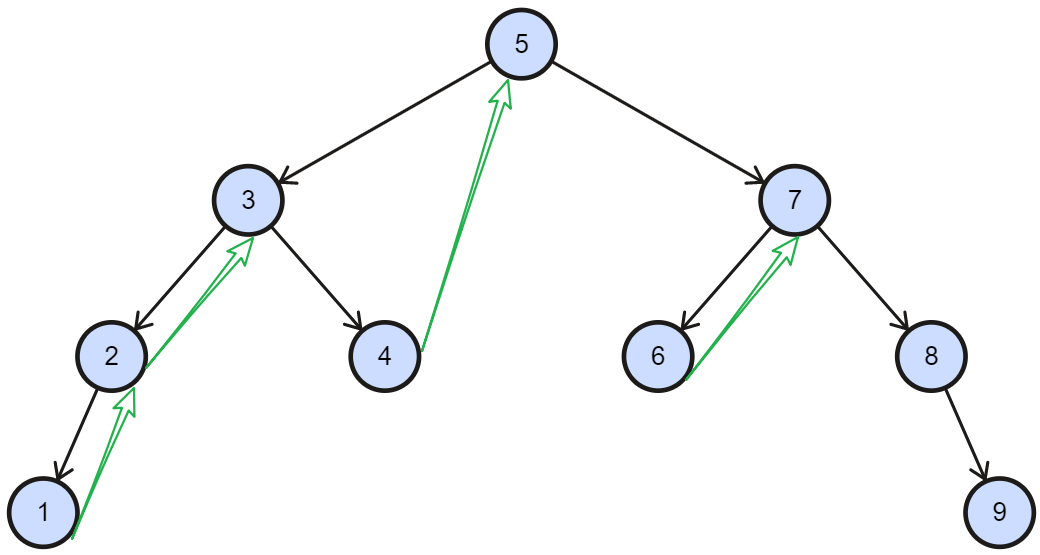
public List<Integer> inorderMorris(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
TreeNode cur = root;
TreeNode prev = null;
while (cur != null) {
// 当前节点没有左子节点,则直接访问该节点,然后将指针指向右子结点
if (cur.left == null) {
res.add(cur.val);
cur = cur.right; // 通过 cur.right 返回父节点
continue;
}
prev = cur.left;
// 寻找当前节点左子节点的最右子结点,即中序遍历中当前节点的前一个节点
while (prev.right != null && prev.right != cur) {
prev = prev.right;
}
if (prev.right == null) {
prev.right = cur;
cur = cur.left;
}
else {
prev.right = null;
res.add(cur.val); // 中序访问根节点
cur = cur.right;
}
}
return res;
}
LeeCode 145: 二叉树的后序遍历
题目描述
给你一棵二叉树的根节点
root,返回其节点值的后序遍历。
Java代码实现
递归实现
public List<Integer> postorderRecursive(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
postorderRecursiveImpl(root, res);
return res;
}
public void postorderRecursiveImpl(TreeNode root, List<Integer> res) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
postorderRecursiveImpl(root.left, res);
postorderRecursiveImpl(root.right, res);
res.add(root.val);
return;
}
迭代实现
public List<Integer> postorderIterative(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) {
return res;
}
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode previous = null;
/**
* 添加顺序: 左 -> 右 -> 根
*/
while (root != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
while (root != null) {
stack.push(root);
root = root.left;
}
root = stack.pop();
// 若右子树为空 或 右子树已经访问过,则添加根节点值
if (root.right == null || root.right == previous) {
res.add(root.val);
previous = root;
root = null;
}
else {
stack.push(root);
root = root.right;
}
}
return res;
}
LeeCode 102: 二叉树的层序遍历
题目描述
给你一棵二叉树的根节点
root,返回其节点值的层序遍历。(即逐层地从左到右访问所有节点)。
建立模型
- 这是一个广度优先搜索的问题,先遍历顶层所有节点,再往下遍历
- 使用一个队列来维护遍历的节点
- 使用变量
size记录当前层节点个数
代码实现
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) {
return res;
}
// 使用基于双向链表实现的队列维护
Deque<TreeNode> deque = new LinkedList<>();
deque.offer(root); // 添加到队尾
while (!deque.isEmpty()) {
int size = deque.size();
List<Integer> temp = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode node = deque.poll(); // 从队首取出
temp.add(node.val);
if (node.left != null) {
deque.offer(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
deque.offer(node.right);
}
}
res.add(new ArrayList<>(temp));
}
return res;
}
LeeCode 二叉树问题(一)的更多相关文章
- leecode刷题(30)-- 二叉树的后序遍历
leecode刷题(30)-- 二叉树的后序遍历 二叉树的后序遍历 给定一个二叉树,返回它的 后序 遍历. 示例: 输入: [1,null,2,3] 1 \ 2 / 3 输出: [3,2,1] 思路 ...
- leecode刷题(29)-- 二叉树的中序遍历
leecode刷题(29)-- 二叉树的中序遍历 二叉树的中序遍历 给定一个二叉树,返回它的中序 遍历. 示例: 输入: [1,null,2,3] 1 \ 2 / 3 输出: [1,3,2] 思路 跟 ...
- leecode刷题(28)-- 二叉树的前序遍历
leecode刷题(28)-- 二叉树的前序遍历 二叉树的前序遍历 给定一个二叉树,返回它的 前序 遍历. 示例: 输入: [1,null,2,3] 1 \ 2 / 3 输出: [1,2,3] 思路 ...
- leecode刷题(24)-- 翻转二叉树
leecode刷题(24)-- 翻转二叉树 翻转二叉树 翻转一棵二叉树. 示例: 输入: 4 / \ 2 7 / \ / \ 1 3 6 9 输出: 4 / \ 7 2 / \ / \ 9 6 3 1 ...
- Leecode刷题之旅-C语言/python-111二叉树的最小深度
/* * @lc app=leetcode.cn id=111 lang=c * * [111] 二叉树的最小深度 * * https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/minim ...
- Leecode刷题之旅-C语言/python-104二叉树最大深度
/* * @lc app=leetcode.cn id=104 lang=c * * [104] 二叉树的最大深度 * * https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/maxim ...
- Leecode刷题之旅-C语言/python-101对称二叉树
/* * @lc app=leetcode.cn id=101 lang=c * * [101] 对称二叉树 * * https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/symmetri ...
- 路径和 二叉树 leecode
题目不难,很快ac,纯粹靠手感.https://oj.leetcode.com/problems/sum-root-to-leaf-numbers/ /** * Definition for bina ...
- leecode第二百三十六题(二叉树的最近公共祖先)
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode ...
- leecode第一百二十四题(二叉树中的最大路径和)
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode ...
随机推荐
- function | fastica
fastica - Fast Independent Component Analysis FastICA for Matlab 7.x and 6.x Version 2.5, October 19 ...
- Nacos 之 Distro 协议
1. 概述 Distro协议是阿里自研的一个最终一致性协议,继承了 Gossip 以及 Eureka 通信(PeerEurekaNodes)的优点并做进一步优化而出来的: 对于原生的Gossip,由于 ...
- nodejs res常用的返回方式
常用的返回方式有四种 res.json([status|body], [body]) 以json的形式返回数据res.render(view [, locals] [, callback]) 返回 ...
- 寄存器与RAM的区别
转自:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_18191333/article/details/106912668 概述 寄存器是"存储设备",主要用于存储和检查微型计算 ...
- redis基础-redis事务
学习总结 原文:https://juejin.im/post/5d29ac845188252cc75e2d5c redis事务: redis是否有事务? redis是有事务的.命令如下: Redis事 ...
- pymysql安装后使用报错处理
1.django启动报错: Error loading MySQLdb module. Did you install mysqlclient? 原因:初次安装配置pymysql时需要在__init_ ...
- A better jump —— 优化游戏中的跳跃
之前一提起角色的跳跃,想当然的想法就是:给角色一个向上的初速,然后由Unity的物理系统接管就好了嘛,这样忽略空气摩擦的影响,根据重力加速度,角色向上跳到最高点的时间和由最高点落下的时间相等,不是很合 ...
- 全新TI AM62xx系列核心板上市,小小身板蕴藏巨大势能!
2011年TI推出AM335x,成为了此后市场上最受欢迎的通用工业级ARM处理器,并广泛应用于工业HMI, 医疗电子,机器人,能源,汽车等领域.随着工业4.0的发展,HMI人机交互.工业工控.医疗等领 ...
- 随便记录一些使用IDEA在ssm阶段的踩过的坑
重命名中括号问题:需要重命名模块+目录 Intellij idea 报错:Error : java 不支持发行版本5_灵颖桥人的博客-CSDN博客_不支持发行版本5 idea中的目标字节码版本总是自动 ...
- 9. 实现包括前端后台的预约洗狗功能 - 使用Power App处理预约信息 - 创建Power Canvas App并实现基础功能
Power Canvas App可以通过画布设计和构建业务应用,无需通过传统编写代码的形式来构建,通过将元素拖动到画布上来设计我们的Power Canvas APP,可以与Miceosoft和第三 ...
