openebula vm无法获取IP问题解决
http://archives.opennebula.org/documentation:archives:rel2.2:cong
Contextualizing Virtual Machines 2.2
There are two contextualization mechanisms available in OpenNebula: the automatic IP assignment, and a more generic way to give any file and configuration parameters. You can use any of them individually, or both.
Using Virtual Network Leases within a Virtual Machine
With OpenNebula you can derive the IP address assigned to the VM from the MAC address using the MAC_PREFFIX:IP rule. In order to achieve this we provide context scripts for Debian, Ubuntu, CentOS and openSUSE based systems. This scripts can be easily adapted for other distributions, check dev.opennebula.org.
To configure the Virtual Machine follow these steps:
- Copy the script
$ONE_SRC_CODE_PATH/share/scripts/vmcontext.shinto the/etc/init.ddirectory in the VM root file system.
- Execute the script at boot time before starting any network service, usually runlevel 2 should work.
$ ln /etc/init.d/vmcontext.sh /etc/rc2.d/S01vmcontext.sh
Having done so, whenever the VN boots it will execute this script, which in turn would scan the available network interfaces, extract their MAC addresses, make the MAC to IP conversion and construct a /etc/network/interfaces that will ensure the correct IP assignment to the corresponding interface.
Generic Contextualization
The method we provide to give configuration parameters to a newly started virtual machine is using an ISO image (OVF recommendation). This method is network agnostic so it can be used also to configure network interfaces. In the VM description file you can specify the contents of the iso file (files and directories), tell the device the ISO image will be accessible and specify the configuration parameters that will be written to a file for later use inside the virtual machine.
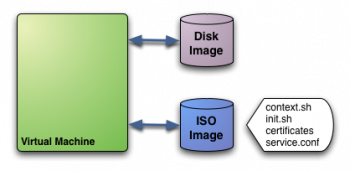
In this example we see a Virtual Machine with two associated disks. The Disk Image holds the filesystem where the Operating System will run from. The ISO image has the contextualization for that VM:
context.sh: file that contains configuration variables, filled by OpenNebula with the parameters specified in the VM description fileinit.sh: script called by VM at start that will configure specific services for this VM instancecertificates: directory that contains certificates for some serviceservice.conf: service configuration
context.sh is included by default. You have to specify the values that will be written inside context.sh and the files that will be included in the image.Defining Context
In VM description file you can tell OpenNebula to create a contextualization image and to fill it with values using CONTEXTparameter. For example:
CONTEXT = [
hostname = "MAINHOST",
ip_private = "$NIC[IP]",
dns = "$NETWORK[DNS, NAME=\"Public\"]",
ip_gen = "10.0.0.$VMID",
files = "/service/init.sh /service/certificates /service/service.conf"
]
Variables inside CONTEXT section will be added to context.sh file inside the contextualization image. These variables can be specified in three different ways:
- Hardcoded variables:
hostname = "MAINHOST"
- Using template variables
$<template_variable>: any single value variable of the VM template, like for example:\\ip_gen = "10.0.0.$VMID"
$<template_variable>[<attribute>]: Any single value contained in a multiple value variable in the VM template, like for example:ip_private = $NIC[IP]
$<template_variable>[<attribute>, <attribute2>=<value2>]: Any single value contained in a multiple value variable in the VM template, setting one atribute to discern between multiple variables called the same way, like for example:ip_public = "$NIC[IP, NETWORK=\"Public\"]"
- Using Virtual Network template variables
$NETWORK[<vnet_attribute>, NAME=<vnet_name>]: Any single value variable in the Virtual Network (vnet_name) template, like for example:dns = "$NETWORK[DNS, NAME=\"Public\"]"
The file generated will be something like this:
# Context variables generated by OpenNebula
hostname="MAINHOST"
ip_private="192.168.0.5"
dns="192.168.4.9"
ip_gen="10.0.0.85"
files="/service/init.sh /service/certificates /service/service.conf"
target="sdb"
Some of the variables have special meanings, but none of them are mandatory:
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| files | Files and directories that will be included in the contextualization image |
| target | device where the contextualization image will be available to the VM instance. Please note that the proper device mapping may depend on the guest OS, e.g. ubuntu VMs should use hd* as the target device |
Using Context
The VM should be prepared to use the contextualization image. First of all it needs to mount the contextualization image somewhere at boot time. Also a script that executes after boot will be useful to make use of the information provided.
The file context.sh is compatible with bash syntax so you can easilly source it inside a shellscript to get the variables that it contains.
EXAMPLE
Here we propose a way to use this contextualization data. Each unix has their own filesystem layout and way of handling init scripts, this examples assumes a debian-based virtual machine.
We are going to use contextualization data to set the hostname, the IP address and a user with known ssh keys.
First thing, lets outline the CONTEXT section of the VM template:
CONTEXT = [
hostname = "$NAME",
ip_public = "$NIC[IP, NETWORK=\"Public\"]",
username = virtualuser
files = "/vms_configuration/id_rsa.pub /vms_configuration/init.sh"
]
The OpenNebula front-end will thus require a /vms_configuration folder with:
id_rsa.pub: Public ssh key to be added to the trusted ssh keys of the new userinit.sh: script that will perform the configuration. Explained below.
Now we will need to configure the VM to make use of this data. We are going to place in /etc/rc.local as:
#!/bin/sh -e
mount -t iso9660 /dev/sdc /mnt
if [ -f /mnt/context.sh ]; then
. /mnt/init.sh
fi
umount /mnt
exit 0
We use an indirection (rc.local calls init.sh) so changing the script means editing a file locally rather that changing it inside the VMs.
The init.sh script will be the one actually doing the work:
#!/bin/bash
if [ -f /mnt/context.sh ]; then
. /mnt/context.sh
fi
hostname $HOSTNAME
ifconfig eth0 $IP_PUBLIC
useradd -m $USERNAME
mkdir -p ~$USERNAME/.ssh
cat /mnt/id_rsa.pub >> ~$USERNAME/.ssh/authorized_keys
chown -R $USERNAME /home/$USERNAME
openebula vm无法获取IP问题解决的更多相关文章
- Oracle VM Virtual 下CentOS不能自动获取IP地址
在CentOS配置网卡开机自动获取IP地址: vi /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0 将 ONBOOT="no" 改为 ONBOO ...
- VM无法正常使用桥接模式获取IP上网
问题: 有时候会遇到VM使用桥接模式时无法正常获取IP的情况 原因: 初步怀疑是因为你的电脑是双网卡 解决方法: 这时候,就需要修改VM的虚拟网络编辑器的配置 解决步骤: 编辑->虚拟网络编辑器 ...
- VMware桥接模式无法自动化获取IP的解决方法
虚拟机桥接无法自动获取IP的解决方法 在虚拟机VM里面装了centos系统,网卡选用桥接方式. 刚开始的时候还能自动获取到IP地址,突然有一天IP消失了,再怎么重启都无法获取IP地址.因为之前是可以获 ...
- Linux VM 设置静态ip地址上网
因为是路由器共享上网,VM每次都是通过DHCP方式自动获取ip地址,连接Linux VM时ip地址经常变,很麻烦.现在把VM设置静态ip的方法总结一下,以免以后忘了. 1. VM上网方式设置为桥接. ...
- [解决]Kali Linux DHCP自动获取IP失败 坑爹的VMWare桥接
root@kali:~# service networking restart [....] Running /etc/init.d/networking restart is deprecated ...
- 【linux】centos6.9设置etc0网卡开机自动获取ip
在vm新安装的centos系统中,一般选择NAT来设置和主机共享局域网,通过ifconfig etc0 192.168.xx.xx 这种作法机器重启之后就会失效,所以可以使用更改文件的方式完成设置ce ...
- 四、获取IP地址工具包
由于getHostAddress()方法在Linux下读取hosts文件获取的是127.0.0.1 InetAddress.getLocalHost().getHostAddress() 所以这里采用 ...
- windows下获取IP地址的两种方法
windows下获取IP地址的两种方法: 一种可以获取IPv4和IPv6,但是需要WSAStartup: 一种只能取到IPv4,但是不需要WSAStartup: 如下: 方法一:(可以获取IPv4和I ...
- Azure PowerShell (9) 使用PowerShell导出订阅下所有的Azure VM的Public IP和Private IP
<Windows Azure Platform 系列文章目录> 笔者在之前的工作中,有客户提出想一次性查看Azure订阅下的所有Azure VM的Public IP和Private IP. ...
随机推荐
- 【MFC】MFC改变对话框中静态文本的字体大小
MFC改变对话框中静态文本的字体大小 2010/08/09 11:30 VC的对话框字体设置对所有控件都有效,你不能单独地改变某个静态文本的字体.对于你的问题,需要首先用CreateFont来建立一个 ...
- asp.net 操作共享目录文件
背景: 服务器A为程序服务器,服务器B为文件服务器.服务器A的程序需要修改删除服务器B的文件. 实现方式:采用虚拟目录映射 操作步骤: 1.在服务器A与服务器B建立相同账号和密码的windows用户 ...
- BZOJ4260,LOJ10051 Nikitosh 和异或
题意 给定一个含 \(N\) 个元素的数组 \(A\),下标从 \(1\) 开始.请找出下面式子的最大值:\((A[l_1]\bigoplus A[l_1+1]\bigoplus -\bigoplus ...
- 洛谷 1600 (NOIp2016) 天天爱跑步——树上差分
题目:https://www.luogu.org/problemnew/show/P1600 看TJ:https://blog.csdn.net/clove_unique/article/detail ...
- (装)Android高性能编程基本规范
最近总结了一些,Android应用开发中,需要注意的一些事项,与大家分享 1.尽量少的声明全局变量 2.声明全局静态变量,一定要加final声明 3.声明非静态的全局变量,最好不要初始 ...
- Java-Maven-Runoob:Maven 构建配置文件
ylbtech-Java-Maven-Runoob:Maven 构建配置文件 1.返回顶部 1. Maven 构建配置文件 构建配置文件是一系列的配置项的值,可以用来设置或者覆盖 Maven 构建默认 ...
- 1131 Subway Map
题意:给出起点和终点,计算求出最短路径(最短路径即所经过的站点最少的),若最短路径不唯一,则选择其中换乘次数最少的一条线路. 思路:本题虽然也是求最短路径,但是此路径是不带权值的,路径长度即所经过的边 ...
- php中,如何将编译后的代码,反编译回去。
编译后 <?php /*********************/ /* */ /* Version : 5.1.0 */ /* Author : RM */ /* Comment : 0712 ...
- 固定容器内任意个div填充算法
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content ...
- 3.solr学习速成之索引添加 查询 删除
solrserver.java public class solrServer { private solrServer(){}; final static String SOLR_URL = &qu ...
