GBDT,随机森林
author:yangjing
time:2018-10-22
Gradient boosting decision tree
1.main diea
The main idea behind GBDT is to combine many simple models(also known as week kernels),like shallow trees.Each tree can only provide good predictions on part of the data,and so more and more trees are added to iteratively improve performance.
2.parameters setting
the algorithm is a bit more sensitive to parameter settings than random forests,but can provide better accuracy if the parameters are set correctly.
- number of trees
By increasing n_estimators ,also increasing the model complexity,as the model has more chances to correct misticks on the training set. - learning rate
controns how strongly each tree tries to correct the misticks of the previous trees.A higher learning rate means each tree can make stronger correctinos,allowing for more complex models. - max_depth
or alternatively max_leaf_nodes.Usyally max_depth is set very low for gradient-boosted models,often not deeper than five splits.
3.code
from sklearn.ensemble import GradientBoostingClassifier
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.datasets import load_breast_cancer
cancer=load_breast_cancer()
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=train_test_split(cancer.data,cancer.target,random_state=0)
gbrt=GradientBoostingClassifier(random_state=0)
gbrt.fit(X_train,y_train)
gbrt.score(X_test,y_test)
In [261]: X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=train_test_split(cancer.data,cancer.target,random_state=0)
...: gbrt=GradientBoostingClassifier(random_state=0)
...: gbrt.fit(X_train,y_train)
...: gbrt.score(X_test,y_test)
...:
Out[261]: 0.958041958041958
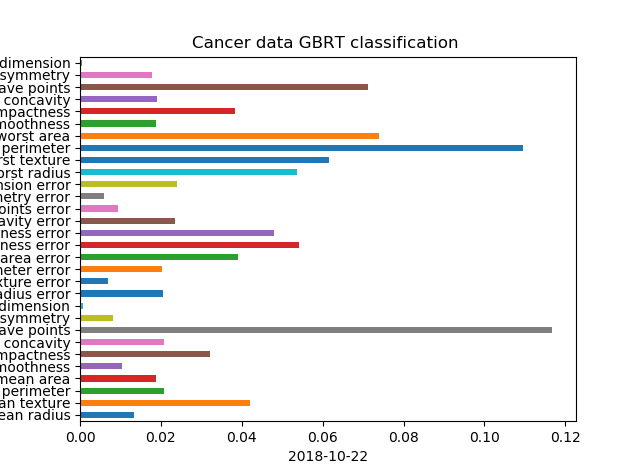
In [262]: gbrt.feature_importances_
Out[262]:
array([0.01337291, 0.04201687, 0.0208666 , 0.01889077, 0.01028091,
0.03215986, 0.02074619, 0.11678956, 0.00820024, 0.00074312,
0.02042134, 0.00680047, 0.02023052, 0.03907398, 0.05406751,
0.04795741, 0.02358101, 0.00934718, 0.00593481, 0.0239241 ,
0.05354265, 0.06160083, 0.10961728, 0.07395201, 0.01867851,
0.03842953, 0.01915824, 0.07128703, 0.01773659, 0.00059199])
In [263]: gbrt.learning_rate
Out[263]: 0.1
In [264]: gbrt.max_depth
Out[264]: 3
In [265]: len(gbrt.estimators_)
Out[266]: 100
In [272]: gbrt.get_params()
Out[272]:
{'criterion': 'friedman_mse',
'init': None,
'learning_rate': 0.1,
'loss': 'deviance',
'max_depth': 3,
'max_features': None,
'max_leaf_nodes': None,
'min_impurity_decrease': 0.0,
'min_impurity_split': None,
'min_samples_leaf': 1,
'min_samples_split': 2,
'min_weight_fraction_leaf': 0.0,
'n_estimators': 100,
'presort': 'auto',
'random_state': 0,
'subsample': 1.0,
'verbose': 0,
'warm_start': False}
Random forest
In [230]: y
Out[230]:
array([1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0,
0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0], dtype=int64)
In [231]: axes.ravel()
Out[231]:
array([<matplotlib.axes._subplots.AxesSubplot object at 0x000001F46F3694A8>,
<matplotlib.axes._subplots.AxesSubplot object at 0x000001F46C099F28>,
<matplotlib.axes._subplots.AxesSubplot object at 0x000001F46E6E3BE0>,
<matplotlib.axes._subplots.AxesSubplot object at 0x000001F46BEB72E8>,
<matplotlib.axes._subplots.AxesSubplot object at 0x000001F46ED67198>,
<matplotlib.axes._subplots.AxesSubplot object at 0x000001F46F292C88>],
dtype=object)
In [232]: from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
In [233]: X_trai,X_test,y_train,y_test=train_test_split(X,y,stratify=y,random_state=42)
In [234]: len(X_trai)
Out[234]: 75
In [235]: fores=RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=5,random_state=2)
In [236]: fores.fit(X_trai,y_train)
Out[236]:
RandomForestClassifier(bootstrap=True, class_weight=None, criterion='gini',
max_depth=None, max_features='auto', max_leaf_nodes=None,
min_impurity_decrease=0.0, min_impurity_split=None,
min_samples_leaf=1, min_samples_split=2,
min_weight_fraction_leaf=0.0, n_estimators=5, n_jobs=1,
oob_score=False, random_state=2, verbose=0, warm_start=False)
In [237]: fores.score(X_test,y_test)
Out[237]: 0.92
In [238]: fores.estimators_
Out[238]:
[DecisionTreeClassifier(class_weight=None, criterion='gini', max_depth=None,
max_features='auto', max_leaf_nodes=None,
min_impurity_decrease=0.0, min_impurity_split=None,
min_samples_leaf=1, min_samples_split=2,
min_weight_fraction_leaf=0.0, presort=False,
random_state=1872583848, splitter='best'),
DecisionTreeClassifier(class_weight=None, criterion='gini', max_depth=None,
max_features='auto', max_leaf_nodes=None,
min_impurity_decrease=0.0, min_impurity_split=None,
min_samples_leaf=1, min_samples_split=2,
min_weight_fraction_leaf=0.0, presort=False,
random_state=794921487, splitter='best'),
DecisionTreeClassifier(class_weight=None, criterion='gini', max_depth=None,
max_features='auto', max_leaf_nodes=None,
min_impurity_decrease=0.0, min_impurity_split=None,
min_samples_leaf=1, min_samples_split=2,
min_weight_fraction_leaf=0.0, presort=False,
random_state=111352301, splitter='best'),
DecisionTreeClassifier(class_weight=None, criterion='gini', max_depth=None,
max_features='auto', max_leaf_nodes=None,
min_impurity_decrease=0.0, min_impurity_split=None,
min_samples_leaf=1, min_samples_split=2,
min_weight_fraction_leaf=0.0, presort=False,
random_state=1853453896, splitter='best'),
DecisionTreeClassifier(class_weight=None, criterion='gini', max_depth=None,
max_features='auto', max_leaf_nodes=None,
min_impurity_decrease=0.0, min_impurity_split=None,
min_samples_leaf=1, min_samples_split=2,
min_weight_fraction_leaf=0.0, presort=False,
random_state=213298710, splitter='best')]
GBDT,随机森林的更多相关文章
- ObjectT5:在线随机森林-Multi-Forest-A chameleon in track in
原文::Multi-Forest:A chameleon in tracking,CVPR2014 下的蛋...原文 使用随机森林的优势,在于可以使用GPU把每棵树分到一个流处理器里运行,容易并行化 ...
- 机器学习中的算法(1)-决策树模型组合之随机森林与GBDT
版权声明: 本文由LeftNotEasy发布于http://leftnoteasy.cnblogs.com, 本文可以被全部的转载或者部分使用,但请注明出处,如果有问题,请联系wheeleast@gm ...
- 机器学习中的算法——决策树模型组合之随机森林与GBDT
前言: 决策树这种算法有着很多良好的特性,比如说训练时间复杂度较低,预测的过程比较快速,模型容易展示(容易将得到的决策树做成图片展示出来)等.但是同时,单决策树又有一些不好的地方,比如说容易over- ...
- 决策树模型组合之(在线)随机森林与GBDT
前言: 决策树这种算法有着很多良好的特性,比如说训练时间复杂度较低,预测的过程比较快速,模型容易展示(容易将得到的决策树做成图片展示出来)等.但是同时, 单决策树又有一些不好的地方,比如说容易over ...
- 机器学习中的算法-决策树模型组合之随机森林与GBDT
机器学习中的算法(1)-决策树模型组合之随机森林与GBDT 版权声明: 本文由LeftNotEasy发布于http://leftnoteasy.cnblogs.com, 本文可以被全部的转载或者部分使 ...
- 随机森林与GBDT
前言: 决策树这种算法有着很多良好的特性,比如说训练时间复杂度较低,预测的过程比较快速,模型容易展示(容易将得到的决策树做成图片展示出来)等.但是同时,单决策树又有一些不好的地方,比如说容易over- ...
- 决策树模型组合之随机森林与GBDT
版权声明: 本文由LeftNotEasy发布于http://leftnoteasy.cnblogs.com, 本文可以被全部的转载或者部分使用,但请注明出处,如果有问题,请联系wheeleast@gm ...
- 随机森林和GBDT
1. 随机森林 Random Forest(随机森林)是Bagging的扩展变体,它在以决策树 为基学习器构建Bagging集成的基础上,进一步在决策树的训练过程中引入了随机特征选择,因此可以概括RF ...
- 随机森林RF、XGBoost、GBDT和LightGBM的原理和区别
目录 1.基本知识点介绍 2.各个算法原理 2.1 随机森林 -- RandomForest 2.2 XGBoost算法 2.3 GBDT算法(Gradient Boosting Decision T ...
随机推荐
- (2)Python 变量和运算符
一.python变量特点 python是弱类型语言,无需声明变量可以直接使用并且变量的数据类型可以动态改变 二.变量命名规则 1.不能使用python关键字 2.不能数字开头 3.不能包含空格 4.不 ...
- tomcat安装规范
创建用户 useradd -u 501 tomcat passwd tomcat tomcat安装 tar zxf apache-tomcat-8.5.5.tar.gz -C /usr/local/ ...
- RPD Volume 168 Issue 4 March 2016 评论6
Natural variation of ambient dose rate in the air of Izu-Oshima Island after the Fukushima Daiichi N ...
- 3Sum Smaller -- LeetCode
Given an array of n integers nums and a target, find the number of index triplets i, j, k with 0 < ...
- 【暴力】洛谷 P2038 NOIP2014提高组 day2 T1 无线网络发射器选址
暴力枚举. #include<cstdio> #include<algorithm> using namespace std; ][],d,n,x,y,z,num,ans=-; ...
- SpringMVC实现操作的第二种方式
一: 运行效果: 点击提交之后显示效果 二: (1).web.xml <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> ...
- Python自带的hmac模块
Python自带的hmac模块实现了标准的Hmac算法 我们首先需要准备待计算的原始消息message,随机key,哈希算法,这里采用MD5,使用hmac的代码如下: import hmac mess ...
- jvm-监控指令-jinfo
格式: jinfo [option] pid 作用: 实时查看和调整虚拟机各项参数. 使用步骤: 1.查看: jinfo vmid. 2.查看指定的参数: jinfo -flag 参数名 v ...
- [Java基础] java多线程关于消费者和生产者
多线程: 生产与消费 1.生产者Producer生产produce产品,并将产品放到库存inventory里:同时消费者Consumer从库存inventory里消费consume产品. 2.库存in ...
- iOS: Xcode7安装KSImageNamed插件,自动读取图片名称
官方文档: ## How do I use it? Build the KSImageNamed target in the Xcode project and the plug-in wil ...
