hdu 2586 How far away?(LCA模板题+离线tarjan算法)
How far away ?
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 25408 Accepted Submission(s): 10111
For each test case,in the first line there are two numbers n(2<=n<=40000) and m (1<=m<=200),the number of houses and the number of queries. The following n-1 lines each consisting three numbers i,j,k, separated bu a single space, meaning that there is a road connecting house i and house j,with length k(0<k<=40000).The houses are labeled from 1 to n.
Next m lines each has distinct integers i and j, you areato answer the distance between house i and house j.
3 2
1 2 10
3 1 15
1 2
2 3
2 2
1 2 100
1 2
2 1
25
100
100
LCA_Tarjan
TarjanTarjan 算法求 LCA 的时间复杂度为 O(n+q)O(n+q) ,是一种离线算法,要用到并查集。(注:这里的复杂度其实应该不是 O(n+q)O(n+q) ,还需要考虑并查集操作的复杂度 ,但是由于在多数情况下,路径压缩并查集的单次操作复杂度可以看做 O(1)O(1),所以写成了 O(n+q)O(n+q) 。)
TarjanTarjan 算法基于 dfs ,在 dfs 的过程中,对于每个节点位置的询问做出相应的回答。
dfs 的过程中,当一棵子树被搜索完成之后,就把他和他的父亲合并成同一集合;在搜索当前子树节点的询问时,如果该询问的另一个节点已经被访问过,那么该编号的询问是被标记了的,于是直接输出当前状态下,另一个节点所在的并查集的祖先;如果另一个节点还没有被访问过,那么就做下标记,继续 dfs 。
当然,暂时还没那么容易弄懂,所以建议结合下面的例子和标算来看看。
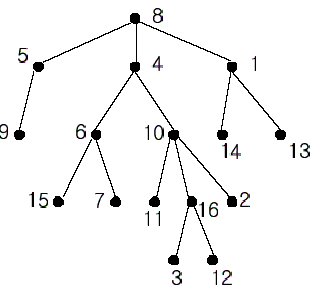
(下面的集合合并都用并查集实现)
比如:8−1−14−138−1−14−13 ,此时已经完成了对子树 11 的子树 1414 的 dfsdfs 与合并( 1414 子树的集合与 11 所代表的集合合并),如果存在询问 (13,14)(13,14) ,则其 LCA 即 getfather(14)getfather(14) ,即 11 ;如果还存在由节点 1313 与 已经完成搜索的子树中的 节点的询问,那么处理完。然后合并子树 1313 的集合与其父亲 11 当前的集合,回溯到子树 11 ,并深搜完所有 11 的其他未被搜索过的儿子,并完成子树 11 中所有节点的合并,再往上回溯,对节点 11 进行类似的操作即可。
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <cmath>
#include <queue>
#include <deque>
#include <stack>
#include <map>
#include <set>
typedef long long LL;
const int MAX_N=;
const int MAX_M=;
const int INF=; struct tedge
{
int to,w,next;
};
tedge edge[MAX_N*+];
int head1[MAX_N+],cnt1; void addedge(int a,int b,int c)
{
edge[cnt1]=(tedge){b,c,head1[a]};head1[a]=cnt1++;
edge[cnt1]=(tedge){a,c,head1[b]};head1[b]=cnt1++;
} struct tquery
{
int to,next;
int index;
};
tquery query[MAX_M*+];
int head2[MAX_N+],cnt2; void addquery(int a,int b,int i)
{
query[cnt2]=(tquery){b,head2[a],i};head2[a]=cnt2++;
query[cnt2]=(tquery){a,head2[b],i};head2[b]=cnt2++;
} int fa[MAX_N]; int getf(int x)
{
if(fa[x]==x)
return x;
else
return fa[x]=getf(fa[x]);
} int vis[MAX_N+];
int depth[MAX_N+];
int ans[MAX_M+]; void LCA(int x,int pa,int dis)
{
for(int i=head1[x];i!=-;i=edge[i].next)
{
int l=edge[i].to;
if(l!=pa)
{
LCA(l,x,dis+edge[i].w);
}
}
depth[x]=dis;
for(int i=head2[x];i!=-;i=query[i].next)
{
int l=query[i].to;
if(vis[l])
{
int ancst=getf(l);
ans[query[i].index]=depth[l]+depth[x]-depth[ancst]*;
//printf("%d %d %d\n",l,x,ancst);
}
}
fa[x]=pa;vis[x]=;
} void init()
{
memset(head1,-,sizeof(head1));cnt1=;
memset(head2,-,sizeof(head2));cnt2=;
memset(vis,,sizeof(vis));
} int main()
{
int T;
scanf("%d",&T);
while(T--)
{
init();
int n,m;
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
for(int i=,a,b,c;i<=n-;i++)
{
scanf("%d%d%d",&a,&b,&c);
addedge(a,b,c);
}
for(int i=,a,b;i<=m;i++)
{
scanf("%d%d",&a,&b);
addquery(a,b,i);
}
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
fa[i]=i;
LCA(,-,);
for(int i=;i<=m;i++)
printf("%d\n",ans[i]);
}
return ;
}
hdu 2586 How far away?(LCA模板题+离线tarjan算法)的更多相关文章
- hdu 3549 Flow Problem 最大流问题 (模板题)
Flow Problem Time Limit: 5000/5000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65535/32768 K (Java/Others)Tota ...
- 近期公共祖先(LCA)——离线Tarjan算法+并查集优化
一. 离线Tarjan算法 LCA问题(lowest common ancestors):在一个有根树T中.两个节点和 e&sig=3136f1d5fcf75709d9ac882bd8cfe0 ...
- HDU - 2586 How far away ?(LCA模板题)
HDU - 2586 How far away ? Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 32768KB 64bit IO Format: %I64d & ...
- HDU 2586——How far away ?——————【LCA模板题】
How far away ? Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)To ...
- HDU 2602 - Bone Collector - [01背包模板题]
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=2602 Many years ago , in Teddy’s hometown there was a ...
- HDU 2544 最短路 【Dijkstra模板题】
传送门:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=2544 思路:最短路的模板题 Dijkstra 算法是一种类似于贪心的算法,步骤如下: 1.当到一个点时, ...
- 【网络流#2】hdu 1533 - 最小费用最大流模板题
最小费用最大流,即MCMF(Minimum Cost Maximum Flow)问题 嗯~第一次写费用流题... 这道就是费用流的模板题,找不到更裸的题了 建图:每个m(Man)作为源点,每个H(Ho ...
- hdu 1711 Number Sequence(KMP模板题)
我的第一道KMP. 把两个数列分别当成KMP算法中的模式串和目标串,这道题就变成了一个KMP算法模板题. #include<stdio.h> #include<string.h> ...
- HDU 1874 畅通工程续(模板题——Floyd算法)
题目: 某省自从实行了很多年的畅通工程计划后,终于修建了很多路.不过路多了也不好,每次要从一个城镇到另一个城镇时,都有许多种道路方案可以选择,而某些方案要比另一些方案行走的距离要短很多.这让行人很困扰 ...
随机推荐
- [转发]CSR8670的DFU功能
本文源自:https://blog.csdn.net/wzz4420381/article/details/52371409 作者:RyomaWang 申明:为了保持原作者内容,这里不进行任何修改,后 ...
- JS三座大山再学习(二、作用域和闭包)
原文地址 作用域 JS中有两种作用域:全局作用域|局部作用域 栗子1 console.log(name); //undefined var name = '波妞'; var like = '宗介' c ...
- Java内存模型与volatile关键字
Java内存模型与volatile关键字 一).并发程序开发 并行程序的开发要涉及多线程.多任务间的协作和数据共享问题. 常用的并发控制:内部锁.重入锁.读写锁.信号量. 二).线程的特点 线程的特点 ...
- firefox浏览器中使用vux的x-input报错TypeError: _this3.$refs.input.scrollIntoViewIfNeeded is not a function
最近做公众号项目,想着统一风格,所以决定使用vux. 在调试时发现,只要鼠标点击x-input输入框,就会报错 TypeError: _this3.$refs.input.scrollIntoView ...
- Linux基础命令复习01
一.Linux中的基本查看.查找命令: 1.ls 查看目录信息: -l #查看属性,以长格式显示 -d #查看本身属性 -A #显示包括以.开头的隐藏文档 -h #提供易读的单位 -R #表示递 ...
- 两步搞定Activity的向右滑动返回的功能
向右滑动返回,对于屏幕过大的手机来说,在单手操作时,是一个不错的用户体验,用户不必再费力的或者用另一个手去点击屏幕左上角的返回按钮或者,手机右下角的返回按钮,轻轻向右滑动屏幕即可返回上一页,这个功能如 ...
- CentOS7中安装MariaDB
什么是mariaDB? 在线安装(慢的要命) RPM离线安装(CentOS7.X) 在线安装 打开官方网站 https://mariadb.org/ 点击Download,跳转到下一页面 继续点击Do ...
- 2019-9-9:渗透测试,基础学习,pydictor使用,sql盲注,docker使用,笔记
pydictor,强大的密码生成工具,可以合并密码字典,词频统计,去重,枚举数字字典生成字典python3 pydictor.py -base d --len 4 4 生成纯数字4位密码python3 ...
- es3设置属性不能修改
/*es3*/ { var Person =function () { var data ={ name:'zs', sex:'男', age:18 } this.get=function (key) ...
- Spring(Bean)3
bean的继承<!-- bean 的继承 作为模板来使用. 可以通过abstract="true"来指定把该bean配置为·抽象的. 通过abstract="tru ...
