第1章 Linux命令行简介
1.1 Linux命令行概述
1.2 在Linux命令行下查看命令帮助
1.3 Linux关机、重启、注销命令
1.4 老男孩的运维思想
1.1 Linux命令行概述
1.1.1 Linux命令行的作用与意义
Linux是一个主要通过命令来进行管理的操作系统。
1.1.2 Linux命令行介绍
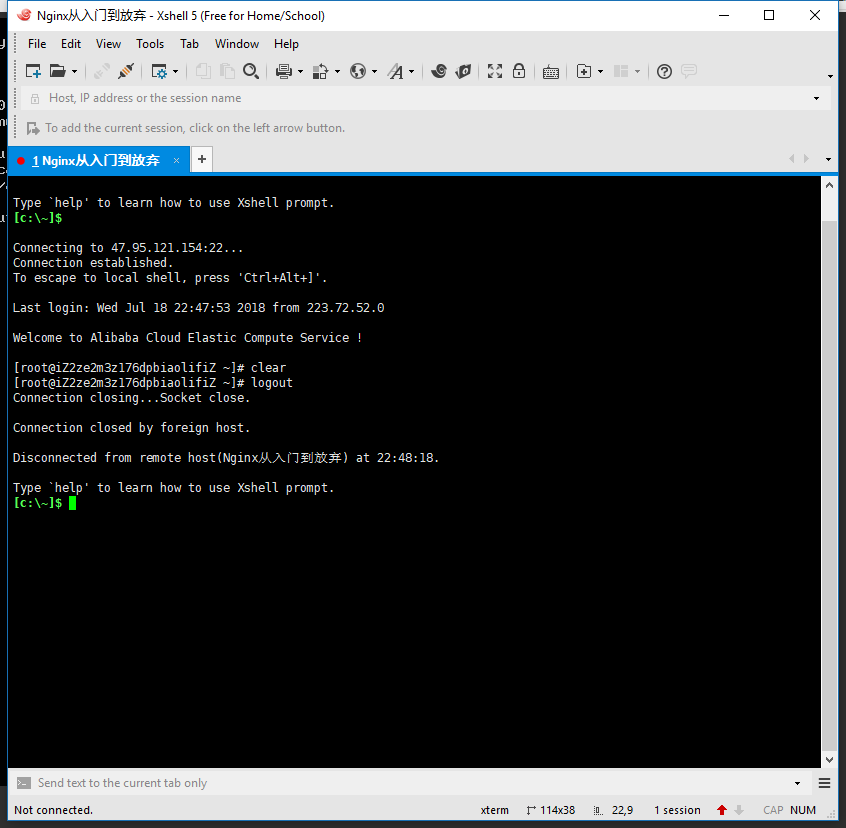
1)通过SSH工具远程连接阿里云ECS服务器,如Xshell;

2)使用阿里云Web控制台-远程连接ECS服务器
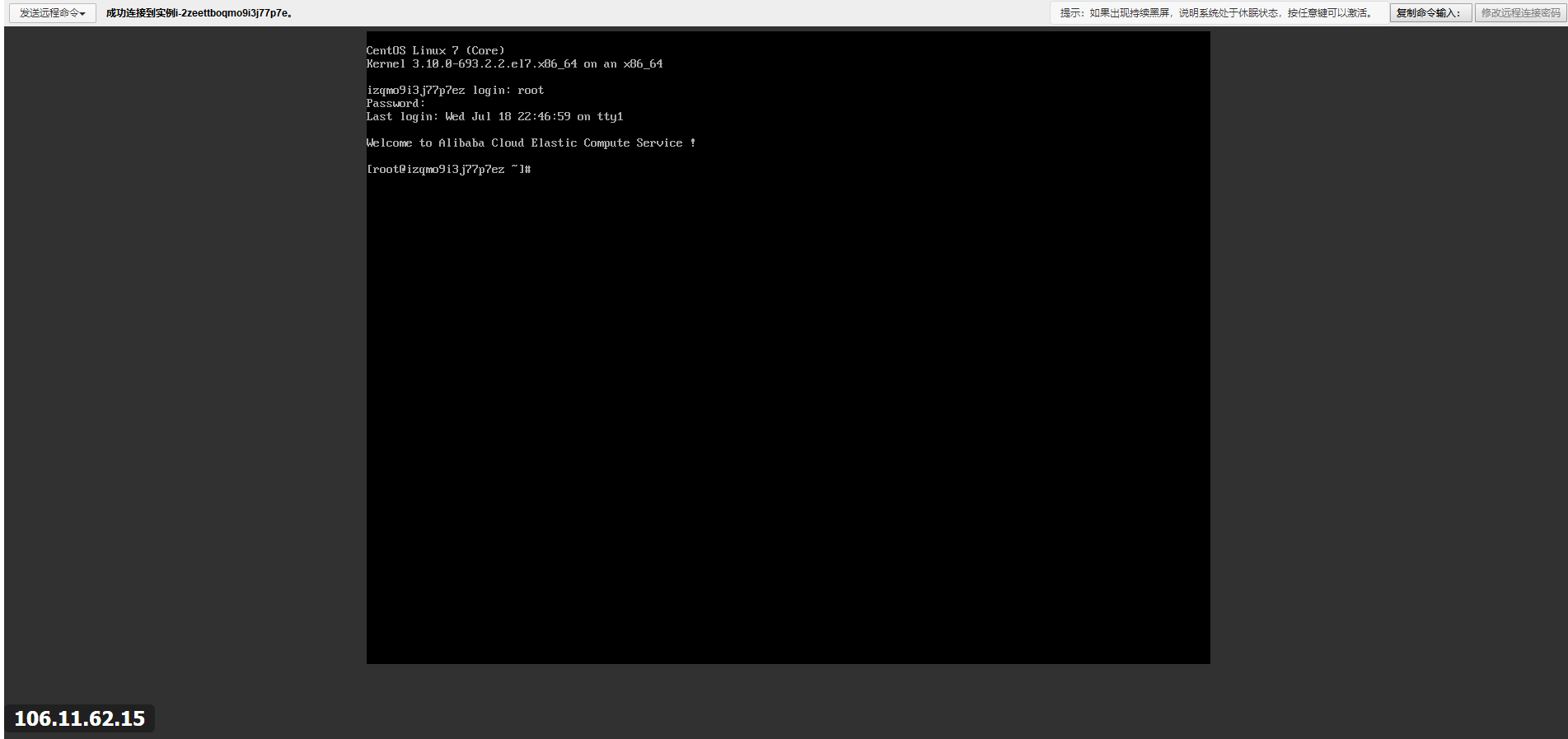
3)CentOS Linux命令行退出命令操作的界面
1.1.3 Linux命令行常用快捷键
常见的Linux远程连接工具:SecureCRT、Xshell客户端软件;
1)最有用的快捷键;
- tab 命令自动补全快捷键;
2)移动光标快捷键;
- Ctrl +a
- Ctrl + e
- Ctrl + f
- Ctrl + b
3)剪切、粘贴、清除快捷键;
- Ctrl + Insert
- Shift + Insert
- Ctrl + k
- Ctrl + u
- Ctrl + w
- Ctrl + y
- Ctrl + e
- Ctrl + h
4)重复执行命令快捷键
- Ctrl + d
- Ctrl + r
- Ctrl + g
5)控制快捷键
- Ctrl + l
- Ctrl + s
- Ctrl + q
- Ctrl + z
6)!开头的快捷键
- !!
- !pw
- !pw:p
- !num(指数字)
- !$
7)Esc相关
- Esc + .
- Esc + b
- Esc + f
1.2 在Linux命令行下查看命令帮助
1.2.1 使用man获取命令帮助信息
1)man命令的基本用法
man命令是LInux系统中最核心的命令之一,可通过其查看其它Linux命令的使用、用法信息。还可查看软件服务配置文件、系统调用、库函数等帮助信息;
2) 语法格式
man 参数选项 命令/文件
3)选项说明
- User Commands 用户命令相关
- System calls 系统函数调用
- C Library Function C的库函数相关
- Device and Special Files 设备和特殊文件相关
- File Formats and Conventions 文件格式和规划
- Games et.AI 游戏及其他
- Miscellanea 宏、包及其他杂项
- System Administration tools and Deamons 系统管理员命令和进程
4)实战举例
man man
man cp
man ls

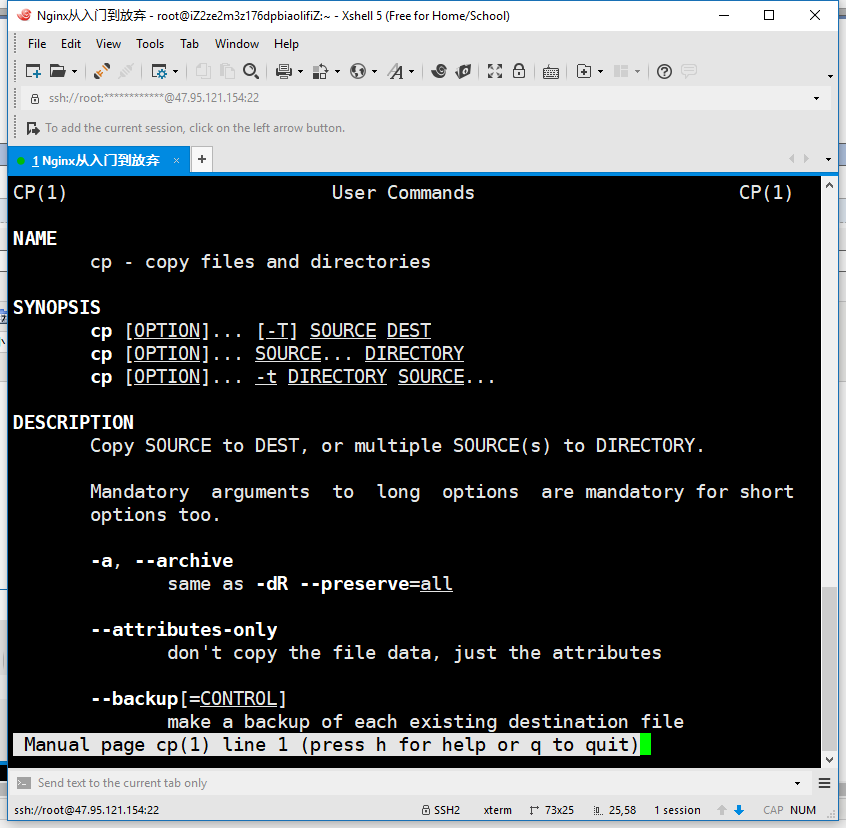

5) man帮助页的快捷键
- Page Down
- Page Up
- Home
- End
- /cuixiaozhao
- ?cuixiaozhao
- n,N
- q
1.2.2 使用--help参数获取命令帮助信息

[root@iZ2ze2m3z176dpbiaolifiZ ~]# cat --help
Usage: cat [OPTION]... [FILE]...
Concatenate FILE(s), or standard input, to standard output. -A, --show-all equivalent to -vET
-b, --number-nonblank number nonempty output lines, overrides -n
-e equivalent to -vE
-E, --show-ends display $ at end of each line
-n, --number number all output lines
-s, --squeeze-blank suppress repeated empty output lines
-t equivalent to -vT
-T, --show-tabs display TAB characters as ^I
-u (ignored)
-v, --show-nonprinting use ^ and M- notation, except for LFD and TAB
--help display this help and exit
--version output version information and exit With no FILE, or when FILE is -, read standard input. Examples:
cat f - g Output f's contents, then standard input, then g's contents.
cat Copy standard input to standard output. GNU coreutils online help: <http://www.gnu.org/software/coreutils/>
For complete documentation, run: info coreutils 'cat invocation'
[root@iZ2ze2m3z176dpbiaolifiZ ~]# more --help
more: unknown option -help
Usage: more [options] file... Options:
-d display help instead of ring bell
-f count logical, rather than screen lines
-l suppress pause after form feed
-p do not scroll, clean screen and display text
-c do not scroll, display text and clean line ends
-u suppress underlining
-s squeeze multiple blank lines into one
-NUM specify the number of lines per screenful
+NUM display file beginning from line number NUM
+/STRING display file beginning from search string match
-V output version information and exit
[root@iZ2ze2m3z176dpbiaolifiZ ~]#

小结:
- 命令 --help 获取的是常用帮助信息;
- man 命令 获取的更多更复杂的帮助信息;
1.2.3 使用help命令获取bash内置命令帮助

BASH_BUILTINS(1) General Commands Manual BASH_BUILTINS(1) NAME
bash, :, ., [, alias, bg, bind, break, builtin, caller, cd, command, compgen, complete, compopt, continue, declare, dirs, disown, echo, enable, eval, exec, exit, export, false, fc, fg, getopts, hash, help, history, jobs, kill, let, local, logout, mapfile,
popd, printf, pushd, pwd, read, readonly, return, set, shift, shopt, source, suspend, test, times, trap, true, type, typeset, ulimit, umask, unalias, unset, wait - bash built-in commands, see bash(1) BASH BUILTIN COMMANDS
Unless otherwise noted, each builtin command documented in this section as accepting options preceded by - accepts -- to signify the end of the options. The :, true, false, and test builtins do not accept options and do not treat -- specially. The exit,
logout, break, continue, let, and shift builtins accept and process arguments beginning with - without requiring --. Other builtins that accept arguments but are not specified as accepting options interpret arguments beginning with - as invalid options
and require -- to prevent this interpretation.
: [arguments]
No effect; the command does nothing beyond expanding arguments and performing any specified redirections. A zero exit code is returned.

举例如下:

[root@iZ2ze2m3z176dpbiaolifiZ ~]# help cd
cd: cd [-L|[-P [-e]]] [dir]
Change the shell working directory.Change the current directory to DIR. The default DIR </span><span style="color: #0000ff;">is</span><span style="color: #000000;"> the value of the
HOME shell variable. The variable CDPATH defines the search path </span><span style="color: #0000ff;">for</span><span style="color: #000000;"> the directory containing
DIR. Alternative directory names </span><span style="color: #0000ff;">in</span><span style="color: #000000;"> CDPATH are separated by a colon (:).
A null directory name </span><span style="color: #0000ff;">is</span><span style="color: #000000;"> the same as the current directory. If DIR begins
with a slash (</span>/), then CDPATH <span style="color: #0000ff;">is</span> <span style="color: #0000ff;">not</span><span style="color: #000000;"> used. If the directory </span><span style="color: #0000ff;">is</span> <span style="color: #0000ff;">not</span> found, <span style="color: #0000ff;">and</span> the shell option `cdable_vars<span style="color: #800000;">'</span><span style="color: #800000;"> is set,</span>
the word <span style="color: #0000ff;">is</span><span style="color: #000000;"> assumed to be a variable name. If that variable has a value,
its value </span><span style="color: #0000ff;">is</span> used <span style="color: #0000ff;">for</span><span style="color: #000000;"> DIR. Options:
</span>-<span style="color: #000000;">L force symbolic links to be followed
</span>-<span style="color: #000000;">P use the physical directory structure without following symbolic
links
</span>-e <span style="color: #0000ff;">if</span> the -P option <span style="color: #0000ff;">is</span> supplied, <span style="color: #0000ff;">and</span><span style="color: #000000;"> the current working directory
cannot be determined successfully, exit with a non</span>-<span style="color: #000000;">zero status The default </span><span style="color: #0000ff;">is</span> to follow symbolic links, as <span style="color: #0000ff;">if</span> `-L<span style="color: #800000;">'</span><span style="color: #800000;"> were specified.</span>
Exit Status:
Returns 0 if the directory is changed, and if $PWD is set successfully when
-P is used; non-zero otherwise.
[root@iZ2ze2m3z176dpbiaolifiZ ~]# help history
history: history [-c] [-d offset] [n] or history -anrw [filename] or history -ps arg [arg...]
Display or manipulate the history list.Display the history list with line numbers, prefixing each modified
entry with a `</span>*<span style="color: #800000;">'</span><span style="color: #800000;">. An argument of N lists only the last N entries.</span>
Options:
-c clear the history list by deleting all of the entries
-d offset delete the history entry at offset OFFSET.</span>-a append history lines <span style="color: #0000ff;">from</span><span style="color: #000000;"> this session to the history file
</span>-n read all history lines <span style="color: #0000ff;">not</span> already read <span style="color: #0000ff;">from</span><span style="color: #000000;"> the history file
</span>-r read the history file <span style="color: #0000ff;">and</span><span style="color: #000000;"> append the contents to the history
list
</span>-<span style="color: #000000;">w write the current history to the history file
</span><span style="color: #0000ff;">and</span><span style="color: #000000;"> append them to the history list </span>-p perform history expansion on each ARG <span style="color: #0000ff;">and</span><span style="color: #000000;"> display the result
without storing it </span><span style="color: #0000ff;">in</span><span style="color: #000000;"> the history list
</span>-<span style="color: #000000;">s append the ARGs to the history list as a single entry If FILENAME </span><span style="color: #0000ff;">is</span> given, it <span style="color: #0000ff;">is</span><span style="color: #000000;"> used as the history file. Otherwise,
</span><span style="color: #0000ff;">if</span> $HISTFILE has a value, that <span style="color: #0000ff;">is</span> used, <span style="color: #0000ff;">else</span> ~/<span style="color: #000000;">.bash_history. If the $HISTTIMEFORMAT variable </span><span style="color: #0000ff;">is</span> set <span style="color: #0000ff;">and</span> <span style="color: #0000ff;">not</span> null, its value <span style="color: #0000ff;">is</span><span style="color: #000000;"> used
as a format string </span><span style="color: #0000ff;">for</span> strftime(3) to <span style="color: #0000ff;">print</span><span style="color: #000000;"> the time stamp associated
with each displayed history entry. No time stamps are printed otherwise. Exit Status:
Returns success unless an invalid option </span><span style="color: #0000ff;">is</span> given <span style="color: #0000ff;">or</span><span style="color: #000000;"> an error occurs.
[root@iZ2ze2m3z176dpbiaolifiZ ~]#

1.2.4 使用info获取帮助信息
- info ls
- info cd
- info man
1.2.5 通过互联网寻求帮助信息
搜索引擎的使用优先顺序(建议)
www.google.com ->www.bing.com ->www.baidu.com
1.3 Linux关机、重启、注销命令
1.3.1 重启或关机命令:shutdown
shutdown总体来讲,是一个用来安全关闭或重启Linux系统的命令。
与shutdown功能类似的有init halt poweroff reboot

SHUTDOWN(8) shutdown SHUTDOWN(8) NAME
shutdown - Halt, power-off or reboot the machine SYNOPSIS
shutdown [OPTIONS...] [TIME] [WALL...] DESCRIPTION
shutdown may be used to halt, power-off or reboot the machine.The first argument may be a time string (which </span><span style="color: #0000ff;">is</span> usually <span style="color: #800000;">"</span><span style="color: #800000;">now</span><span style="color: #800000;">"</span>). Optionally, this may be followed by a wall message to be sent to all logged-<span style="color: #0000ff;">in</span><span style="color: #000000;"> users before going down. The time string may either be </span><span style="color: #0000ff;">in</span> the format <span style="color: #800000;">"</span><span style="color: #800000;">hh:mm</span><span style="color: #800000;">"</span> <span style="color: #0000ff;">for</span> hour/minutes specifying the time to execute the shutdown at, specified <span style="color: #0000ff;">in</span> 24h clock format. Alternatively it may be <span style="color: #0000ff;">in</span> the syntax <span style="color: #800000;">"</span><span style="color: #800000;">+m</span><span style="color: #800000;">"</span> referring to the specified number of minutes m <span style="color: #0000ff;">from</span> now. <span style="color: #800000;">"</span><span style="color: #800000;">now</span><span style="color: #800000;">"</span>
<span style="color: #0000ff;">is</span> an alias <span style="color: #0000ff;">for</span> <span style="color: #800000;">"</span><span style="color: #800000;">+0</span><span style="color: #800000;">"</span>, i.e. <span style="color: #0000ff;">for</span> triggering an immediate shutdown. If no time argument <span style="color: #0000ff;">is</span> specified, <span style="color: #800000;">"</span><span style="color: #800000;">+1</span><span style="color: #800000;">"</span> <span style="color: #0000ff;">is</span><span style="color: #000000;"> implied. Note that to specify a wall message you must specify a time argument, too. If the time argument </span><span style="color: #0000ff;">is</span> used, 5 minutes before the system goes down the /run/nologin file <span style="color: #0000ff;">is</span> created to ensure that further logins shall <span style="color: #0000ff;">not</span><span style="color: #000000;"> be allowed.
OPTIONS
The following options are understood:</span>--<span style="color: #000000;">help
Print a short help text </span><span style="color: #0000ff;">and</span><span style="color: #000000;"> exit. </span>-H, --<span style="color: #000000;">halt
Halt the machine. </span>-P, --<span style="color: #000000;">poweroff
Power</span>-<span style="color: #000000;">off the machine (the default). </span>-r, --<span style="color: #000000;">reboot
Reboot the machine. </span>-<span style="color: #000000;">h
Equivalent to </span>--poweroff, unless --halt <span style="color: #0000ff;">is</span><span style="color: #000000;"> specified. </span>-<span style="color: #000000;">k
Do </span><span style="color: #0000ff;">not</span> halt, power-<span style="color: #000000;">off, reboot, just write wall message. </span>--no-<span style="color: #000000;">wall
Do </span><span style="color: #0000ff;">not</span> send wall message before halt, power-<span style="color: #000000;">off, reboot. </span>-<span style="color: #000000;">c
Cancel a pending shutdown. This may be used cancel the effect of an invocation of shutdown with a time argument that </span><span style="color: #0000ff;">is</span> <span style="color: #0000ff;">not</span> <span style="color: #800000;">"</span><span style="color: #800000;">+0</span><span style="color: #800000;">"</span> <span style="color: #0000ff;">or</span> <span style="color: #800000;">"</span><span style="color: #800000;">now</span><span style="color: #800000;">"</span><span style="color: #000000;">.
EXIT STATUS
On success, 0 is returned, a non-zero failure code otherwise.SEE ALSO
systemd(1), systemctl(1), halt(8), wall(1)Manual page shutdown(8) line 1 (press h for help or q to quit)

shutdown实战举例
- shutdown -h +1 #一分钟后关闭Linux操作系统
- shutdown -c #取消shutdown操作
- shutdown -r 11:11 #11:11重启Linux系统
- shutdown -h now#now即现在,立刻关闭操作系统
1.3.2 关机与重启命令:halt/poweroff/reboot
从Redhat或CentOS6开始,这三者对应的man帮助信息都是同一个,而halt和poweroff命令是reboot命令的链接文件;
- reboot 选项
- halt 选项
- poweroff 选项
通常情况下,该3命令都不带任何参数

[root@iZ2ze2m3z176dpbiaolifiZ ~]# ls /sbin/poweroff
/sbin/poweroff
[root@iZ2ze2m3z176dpbiaolifiZ ~]# ls /sbin/halt
/sbin/halt
[root@iZ2ze2m3z176dpbiaolifiZ ~]# ls /sbin/reboot
/sbin/reboot
[root@iZ2ze2m3z176dpbiaolifiZ ~]# ls -l /sbin/poweroff
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 16 Oct 15 2017 /sbin/poweroff -> ../bin/systemctl
[root@iZ2ze2m3z176dpbiaolifiZ ~]# ls -l /sbin/halt
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 16 Oct 15 2017 /sbin/halt -> ../bin/systemctl
[root@iZ2ze2m3z176dpbiaolifiZ ~]# ls -l /sbin/reboot
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 16 Oct 15 2017 /sbin/reboot -> ../bin/systemctl
[root@iZ2ze2m3z176dpbiaolifiZ ~]#

1.3.3 关机、重启和注销的命令列表
1)关机命令
- shutdown -h now
- shutdown -h +1
- halt
- init 0
- poweroff
2)重启命令
- reboot
- shutdown -r now
- shutdown -r +1
- init 6
3)注销命令
- logout
- exit
- Ctrl + d(本质就是logout)
1.4 老男孩的运维思想
基础不牢,地动山摇!很多高大上的技术都是由细小的基础知识累积而成的!
Linux命令正是组成Linux系统最核心的、重要的基础之一。牢牢掌握基础命令,方能在日后使用Linux时随心所欲。
第1章 Linux命令行简介的更多相关文章
- 核心系统命令实战 第一章Linux命令行简介
第一章Linux命令行简介 1.1 Linux命令行概述 1.1.1 Linux 命令行的开启和退出 开启:登陆账号密码进入系统 退出:exit/logout 快捷键:Ctrl+d 1.1.2 Li ...
- 第一章 Linux命令行简介
1 Linux系统命令操作语法的格式 命令_[参数选项]_[文件或路径] 其中 _ 至少一个空格 如:rm -f /etc/hosts 其中/etc/hosts完整路径不带空格 ...
- SLAM+语音机器人DIY系列:(一)Linux基础——3.Linux命令行基础操作
摘要 由于机器人SLAM.自动导航.语音交互这一系列算法都在机器人操作系统ROS中有很好的支持,所以后续的章节中都会使用ROS来组织构建代码:而ROS又是安装在Linux发行版ubuntu系统之上的, ...
- 40个超有趣的Linux命令行彩蛋和游戏
40个有趣的Linux命令行彩蛋和游戏,让你假装成日理万机的黑客高手.附一键安装脚本,在树莓派和ubuntu云主机上亲测成功,有些还可以在Windows的DOS命令行中运行. 本文配套B站视频:40个 ...
- Linux命令行–初识Linux shell
shell及脚本简介 GNU/Linux shell 是个交互工具,它为用户提供了启动程序.管理文件系统上的文件以及管理运行在Linux系统上的进程的途径 . shell的核心是命令行提示符 它是s ...
- 20个linux命令行工具监视性能(下)
昨天晚上第一次翻译了<20 Command Line Tools to Monitor Linux Performance>中的前十个命令,翻译得不是很好,今天晚上继续把后面的十个也翻译给 ...
- 在 Linux 命令行中使用和执行 PHP 代码
PHP是一个开源服务器端脚本语言,最初这三个字母代表的是“Personal Home Page”,而现在则代表的是“PHP:Hypertext Preprocessor”,它是个递归首字母缩写.它是一 ...
- 《Linux命令行大全》系列(三、Linux 系统)
在<Linux命令行大全>一书中,第3章名称是 Linux 系统. 概念太大,不过该节内容却是 Linux 系统最为核心的基础——查看 Linux 系统. ls 命令 显示目录自身信息或目 ...
- [Android] 基于 Linux 命令行构建 Android 应用(七):自动化构建
本章将演示如何基于 Linux 命令行构建 Android 应用,在开始本章之前,希望你已经阅读之前几章内容. 本文环境为 RHEL Sandiego 32-bits,要基于 Linux CLI 构建 ...
随机推荐
- Git忽略提交 .gitignore配置。自动生成IDE的.gitignore。解决gitignore不生效
语法 以”#”号开头表示注释: 以斜杠“/”开头表示目录: 以星号“*”通配多个字符: 以问号“?”通配单个字符 以方括号“[]”包含单个字符的匹配列表: 以叹号“!”表示不忽略(跟踪)匹配到的文件或 ...
- BZOJ2286:[SDOI2011]消耗战(树形DP,虚树)
Description 在一场战争中,战场由n个岛屿和n-1个桥梁组成,保证每两个岛屿间有且仅有一条路径可达.现在,我军已经侦查到敌军的总部在编号为1的岛屿,而且他们已经没有足够多的能源维系战斗,我军 ...
- HBase学习之路 (十)HBase表的设计原则
建表高级属性 下面几个 shell 命令在 hbase 操作中可以起到很大的作用,且主要体现在建表的过程中,看 下面几个 create 属性 1. BLOOMFILTER 默认是 NONE 是否使用布 ...
- jenkins + sonar 安装配置
最近把snoar 添加上了 [root@snoar data]# wget https://sonarsource.bintray.com/Distribution/sonarqube/sonar ...
- Selenium启动最新的火狐浏览器异常排查
报错如下: WebDriverException: Message: 'Can\'t load the profile 打开谷歌浏览器和IE浏览器均正常 网上查阅资料,疑似与selenium版本相关联 ...
- Jmeter之八大可执行元件及执行顺序
初步接触Jmeter,对比LoadRunner进行熟悉,╮(╯▽╰)╭.毕竟我对LoadRunner还是比Jmeter熟悉. 1.配置元件 用来提供对静态数据配置的支持.例CSV Data Set c ...
- 【图像处理】Schmid滤波器
Schmid也是一种类Gabor图像滤波器,在这篇文章[1]中有详细推导和介绍. 一种更简洁的表达公式是: 当中,r为核半径,Z为归一化參数,τ和σ是比較重要的參数,在ReID提取TextFeatur ...
- Linux基础命令之文件过滤及内容编辑处理(一)
. cat 功能是连接多个文件并且打印到屏幕输出,或重定向到指定的文件 五大功能: 1.查看文件内容 cat file.txt 2.合并文件内容 cat file1 file2>newfile3 ...
- echart 对双折线的使用
在使用echart的时候,我们会使用到双折线的情况.双折线不仅可以显示和隐藏,还可以根据实际的情况设置刻度的大小,比如Y坐标上的刻度大小.参考网址见:https://www.echartsjs.com ...
- Hadoop源码学习笔记之NameNode启动场景流程一:源码环境搭建和项目模块及NameNode结构简单介绍
最近在跟着一个大佬学习Hadoop底层源码及架构等知识点,觉得有必要记录下来这个学习过程.想到了这个废弃已久的blog账号,决定重新开始更新. 主要分以下几步来进行源码学习: 一.搭建源码阅读环境二. ...
