Codeforces 689B. Mike and Shortcuts SPFA/搜索
3 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Recently, Mike was very busy with studying for exams and contests. Now he is going to chill a bit by doing some sight seeing in the city.
City consists of n intersections numbered from 1 to n. Mike starts walking from his house located at the intersection number 1 and goes along some sequence of intersections. Walking from intersection number i to intersection j requires |i - j| units of energy. The total energy spent by Mike to visit a sequence of intersections p1 = 1, p2, ..., pk is equal to  units of energy.
units of energy.
Of course, walking would be boring if there were no shortcuts. A shortcut is a special path that allows Mike walking from one intersection to another requiring only 1 unit of energy. There are exactly n shortcuts in Mike's city, the ith of them allows walking from intersection i to intersection ai (i ≤ ai ≤ ai + 1) (but not in the opposite direction), thus there is exactly one shortcut starting at each intersection. Formally, if Mike chooses a sequence p1 = 1, p2, ..., pk then for each 1 ≤ i < k satisfying pi + 1 = api and api ≠ pi Mike will spend only 1 unit of energy instead of |pi - pi + 1| walking from the intersection pi to intersection pi + 1. For example, if Mike chooses a sequencep1 = 1, p2 = ap1, p3 = ap2, ..., pk = apk - 1, he spends exactly k - 1 units of total energy walking around them.
Before going on his adventure, Mike asks you to find the minimum amount of energy required to reach each of the intersections from his home. Formally, for each 1 ≤ i ≤ n Mike is interested in finding minimum possible total energy of some sequence p1 = 1, p2, ..., pk = i.
The first line contains an integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 200 000) — the number of Mike's city intersection.
The second line contains n integers a1, a2, ..., an (i ≤ ai ≤ n , 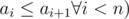 , describing shortcuts of Mike's city, allowing to walk from intersection i to intersection ai using only 1 unit of energy. Please note that the shortcuts don't allow walking in opposite directions (from ai to i).
, describing shortcuts of Mike's city, allowing to walk from intersection i to intersection ai using only 1 unit of energy. Please note that the shortcuts don't allow walking in opposite directions (from ai to i).
In the only line print n integers m1, m2, ..., mn, where mi denotes the least amount of total energy required to walk from intersection 1 to intersection i.
3
2 2 3
0 1 2
5
1 2 3 4 5
0 1 2 3 4
7
4 4 4 4 7 7 7
0 1 2 1 2 3 3
In the first sample case desired sequences are:
1: 1; m1 = 0;
2: 1, 2; m2 = 1;
3: 1, 3; m3 = |3 - 1| = 2.
In the second sample case the sequence for any intersection 1 < i is always 1, i and mi = |1 - i|.
In the third sample case — consider the following intersection sequences:
1: 1; m1 = 0;
2: 1, 2; m2 = |2 - 1| = 1;
3: 1, 4, 3; m3 = 1 + |4 - 3| = 2;
4: 1, 4; m4 = 1;
5: 1, 4, 5; m5 = 1 + |4 - 5| = 2;
6: 1, 4, 6; m6 = 1 + |4 - 6| = 3;
7: 1, 4, 5, 7; m7 = 1 + |4 - 5| + 1 = 3.
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/contest/689/problem/B
题意:任意两点的距离为两点序号差的绝对值,有一些特殊的点,i到ai的距离为1.求1到每个点的最短距离。
思路:SPFA模板题。任意两个编号相邻的点的距离为1构造双向边,再加上n个特殊点构成的边。因为n最大为200000,套用SPFA模板。
代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int MAXN = 6e5+, mod = 1e9 + , inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
struct node
{
int to,d;
} edge[*MAXN];
int head[MAXN],nextt[*MAXN];
int sign[MAXN];
queue<int>Q;
int dist[MAXN];
int n;
void add(int i,int u,int v,int d)
{
edge[i].to=v;
edge[i].d=d;
nextt[i]=head[u];
head[u]=i;
}
void SPFA(int v)
{
int i,u;
for(i=; i<=n; i++)
{
dist[i]=inf;
sign[i]=;
}
dist[v]=;
Q.push(v);
sign[v]=;
while(!Q.empty())
{
u=Q.front();
Q.pop();
sign[u]=;
i=head[u];
while(i!=)
{
if(dist[edge[i].to]>dist[u]+edge[i].d)
{
dist[edge[i].to]=dist[u]+edge[i].d;
if(!sign[edge[i].to])
{
Q.push(edge[i].to);
sign[edge[i].to]=;
}
}
i=nextt[i];
}
}
}
int a[];
int main()
{
int i,j;
scanf("%d",&n);
memset(head,,sizeof(head));
j=;
for(i=; i<=n; i++)
{
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
if(i!=a[i]) add(j++,i,a[i],);
if(i>)
{
add(j++,i-,i,);
add(j++,i,i-,);
}
}
SPFA();
for(i=; i<=n; i++)
cout<<dist[i]<<" ";
cout<<endl;
return ;
}
SPFA
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int MAXN = 6e5+, mod = 1e9 + , inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
vector<int>V[];
int dist[];
void DFS(int u)
{
int i;
for(i=; i<V[u].size(); i++)
{
if(dist[V[u][i]]>dist[u]+)
{
dist[V[u][i]]=dist[u]+;
DFS(V[u][i]);
}
}
}
int main()
{
int i,n,a;
scanf("%d",&n);
for(i=; i<=n; i++)
{
scanf("%d",&a);
V[i].push_back(a);
if(i+<=n) V[i].push_back(i+);
if(i->=) V[i].push_back(i-);
}
for(i=; i<=n; i++) dist[i]=inf;
dist[]=;
DFS();
for(i=;i<=n;i++)
cout<<dist[i]<<" ";
cout<<endl;
return ;
}
DFS
Codeforces 689B. Mike and Shortcuts SPFA/搜索的更多相关文章
- CodeForces 689B Mike and Shortcuts (bfs or 最短路)
Mike and Shortcuts 题目链接: http://acm.hust.edu.cn/vjudge/contest/121333#problem/F Description Recently ...
- CodeForces 689B Mike and Shortcuts (BFS or 最短路)
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/689/B 题目大意: 留坑 明天中秋~
- codeforces 689B Mike and Shortcuts 最短路
题目大意:给出n个点,两点间的常规路为双向路,路长为两点之间的差的绝对值,第二行为捷径,捷径为单向路(第i个点到ai点),距离为1.问1到各个点之间的最短距离. 题目思路:SPFA求最短路 #incl ...
- codeforces 689 Mike and Shortcuts(最短路)
codeforces 689 Mike and Shortcuts(最短路) 原题 任意两点的距离是序号差,那么相邻点之间建边即可,同时加上题目提供的边 跑一遍dijkstra可得1点到每个点的最短路 ...
- codeforces 689B B. Mike and Shortcuts(bfs)
题目链接: B. Mike and Shortcuts time limit per test 3 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input ...
- Codeforces Round #361 (Div. 2)——B. Mike and Shortcuts(BFS+小坑)
B. Mike and Shortcuts time limit per test 3 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standa ...
- Codeforces Round #361 (Div. 2) B. Mike and Shortcuts bfs
B. Mike and Shortcuts 题目连接: http://www.codeforces.com/contest/689/problem/B Description Recently, Mi ...
- hdu4135-Co-prime & Codeforces 547C Mike and Foam (容斥原理)
hdu4135 求[L,R]范围内与N互质的数的个数. 分别求[1,L]和[1,R]和n互质的个数,求差. 利用容斥原理求解. 二进制枚举每一种质数的组合,奇加偶减. #include <bit ...
- codeforces 547E Mike and Friends
codeforces 547E Mike and Friends 题意 题解 代码 #include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; #define ...
随机推荐
- MNIST数据集入门
简单的训练MNIST数据集 (0-9的数字图片) 详细地址(包括下载地址):http://www.tensorfly.cn/tfdoc/tutorials/mnist_beginners.html # ...
- B站上的一个MATLAB与神经网络的视频,捡漏
▶ av15514817.这里集中了一些从视频中学到的散点. ▶ 语句 "edit + 函数名" 可以打开部分内置函数的源代码.非公开的源代码这会打开一个全是注释的文档. ▶ 函数 ...
- Some facts about topological sort
Definition: a topological sort of a DAG G is a sort such that for all edge (i,j) in G, i precedes j. ...
- 黑盒测试用例设计——PICT
一.简单用法 在PICT安装目录下新建一个txt文本.把参数填入txt文本中.[内容包括(注意格式<ParamName> : <Value1>, <Value2> ...
- restfull 风格 参考 https://blog.csdn.net/jaryle/article/details/52141097
https://www.cnblogs.com/xiaoxian1369/p/4332390.html :
- maven项目--Eclipse报错:java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: ContextLoaderListener
转自:https://yq.aliyun.com/ziliao/597445 Eclipse中tomcat部署工程启动后报错: 二月 25, 2016 2:34:00 下午 org.apache.to ...
- location 对象属性
Location 对象属性 hash 返回一个URL的锚部分 host 返回一个URL的主机名和端口 hostname 返回URL的主机名 href 返回完整的URL pathname 返回的URL路 ...
- Activity服务类-7 RepositoryService服务类
Activity服务类-1 RepositoryService服务类一共47个接口1.创建部署//开始创建一个新的部署.DeploymentBuilder createDeployment(); 2. ...
- rssh RSA(非对称密钥)
rssh ,非对称密钥,分为密钥和公钥 ,密钥在对面机器,需要进入的文件中,公钥是放在本地机器上 import paramiko private_key = paramiko.RSAKey.from_ ...
- Gradle 语法
参考文章: Gradle学习系列之二——创建Task的多种方法(http://www.cnblogs.com/CloudTeng/p/3417970.html) Gradle基本知识点与常用配置(ht ...
