Python逆向(四)—— Python内置模块dis.py源码详解
一、前言
上一节我们对Python编译及反汇编做了讲解,大家知道dis模块可以将编译好的pyc文件中提取出来的PyCodeObject反汇编为可以阅读字节码形式。本节我们对dis模块中的源码进行详细的解读。
二、dis模块原理解析
官方文档说明:https://docs.python.org/2/library/dis.html
The dis module supports the analysis of CPython bytecode by disassembling it. The CPython bytecode which this module takes as an input is defined in the file Include/opcode.h and used by the compiler and the interpreter.
dis模块通过反汇编来支持对python字节码形式的分析。dis模块可以将编译好的二进制数据或者python源码当作模块的输入源。
dis模块可以将python源码文件、内存中的类或者方法、或者经过反序列化的PyCodeObject翻译为相应的字节码供分析。
2.1、dis反汇编源码文件:
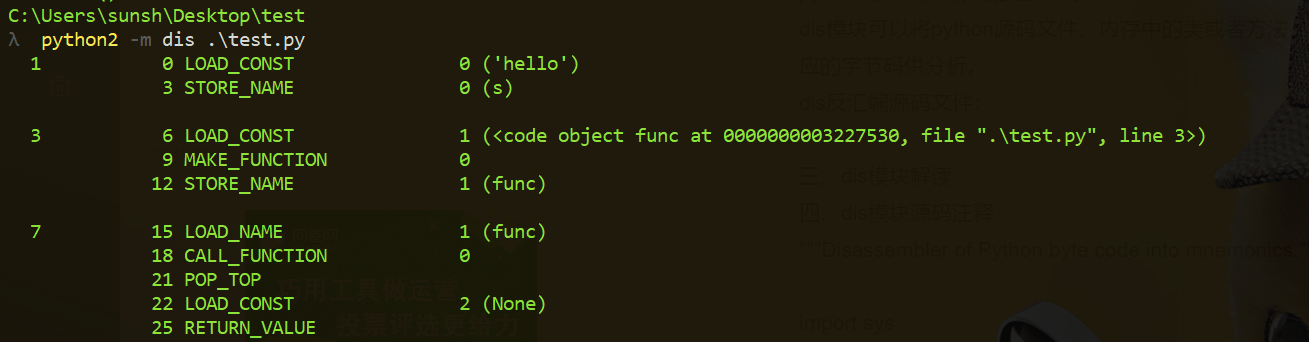
将源码文件作为dis模块的输入,dis模块将直接输入该源码文件编译后对应的字节码文本。
2.2、dis反汇编内存中的类或者函数:
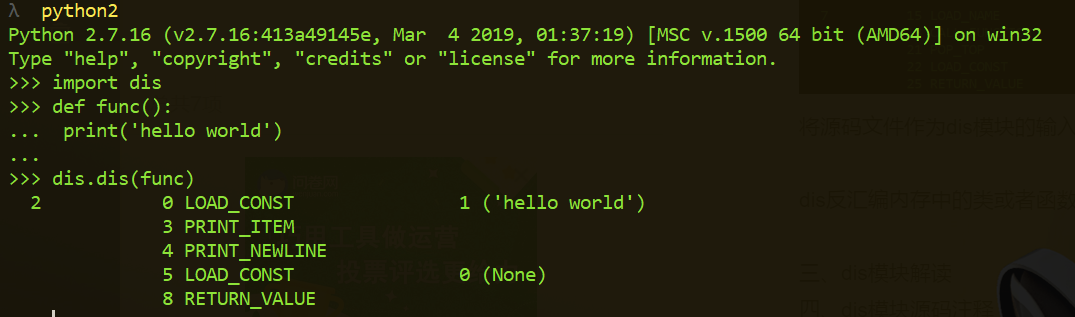
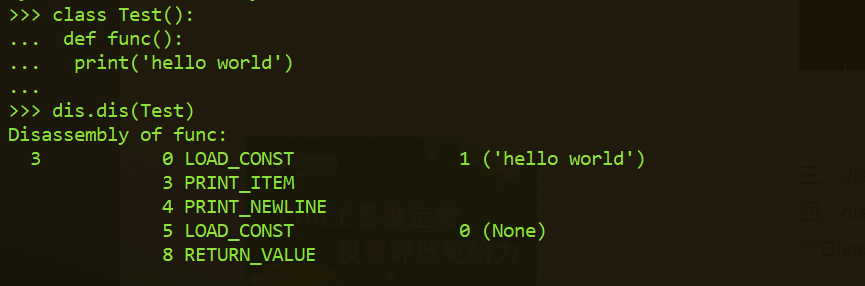
将内存中的类、函数,甚至时普通的变量作为参数传递给dis模块中的dis函数,也可以返回该类对应的编译后的字节码形式。
2.3、dis反汇编PyCodeObject对象:

这一类情况是我们在做python逆向或者pyc文件分析时常用到的形式。
2.4、dis无参数:

如果dis.dis无参数传入,该方法默认会返回当前python shell上次报错时堆栈中储存的内存信息的字节码形式。
三、dis模块解读
dis模块包含许多类和方法,具体用法如下表:
| 方法或者属性 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| dis.dis([bytesource]) | Disassemble the bytesource object. bytesource can denote either a module, a class, a method, a function, or a code object. For a module, it disassembles all functions. For a class, it disassembles all methods. For a single code sequence, it prints one line per bytecode instruction. If no object is provided, it disassembles the last traceback. |
| dis.distb([tb]) | Disassembles the top-of-stack function of a traceback, using the last traceback if none was passed. The instruction causing the exception is indicated. |
| dis.disassemble(code[, lasti]) | Disassembles a code object, indicating the last instruction if lasti was provided. |
| dis.disco(code[, lasti]) | A synonym for disassemble(). It is more convenient to type, and kept for compatibility with earlier Python releases. |
| dis.findlinestarts(code) | This generator function uses the co_firstlineno and co_lnotab attributes of the code object code to find the offsets which are starts of lines in the source code. They are generated as (offset, lineno) pairs. |
| dis.findlabels(code) | Detect all offsets in the code object code which are jump targets, and return a list of these offsets. |
| dis.opname | Sequence of operation names, indexable using the bytecode. |
| dis.opmap | Dictionary mapping operation names to bytecodes. |
| dis.cmp_op | Sequence of all compare operation names. |
| dis.hasconst | Sequence of bytecodes that access a constant. |
| dis.hasfree | Sequence of bytecodes that access a free variable. |
| dis.hasname | Sequence of bytecodes that access an attribute by name. |
| dis.hasjrel | Sequence of bytecodes that have a relative jump target. |
| dis.hasjabs | Sequence of bytecodes that have an absolute jump target. |
| dis.haslocal | Sequence of bytecodes that access a local variable. |
| dis.hascompare | Sequence of bytecodes of Boolean operations. |
上表摘自官方文档整理,对各个方法及属性进行了详细的说明。下文将对dis模块运行流程进行说明。
3.1
dis模块主函数为dis,所有对dis模块的调用默认都会将参数传送给dis.dis(不排除进阶玩家直接调用dis.disb等其他模块来完成特定功能)
3.2
dis.dis先进行参数检查,根据无参数、字典、PyCodeObject实例化对象,代码段等不同类型参数调用不同的方法。如果提交的参数是字典,dis模块会通过迭代,将字典中的每个键值作为参数传递给dis.dis
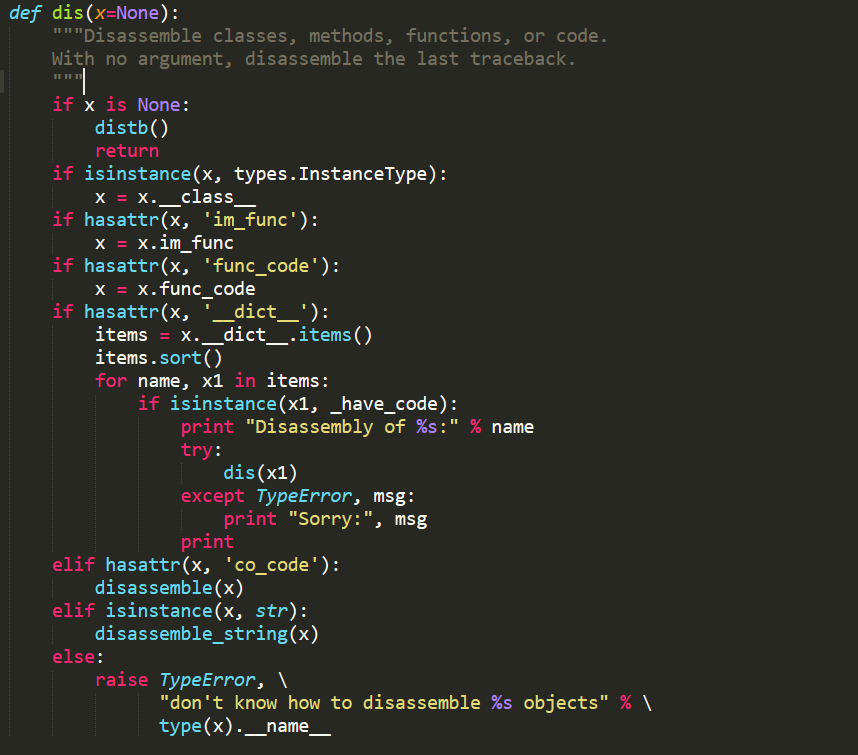
3.3
经过dis方法的处理,最终参数会被交给disassemble或者disassemble_string方法处理,disassemble方法负责对提交的对象进行反汇编,disassemble_string方法负责对代码段进行反汇编,因为disassemble_string方法代码类似于disassemble,不对disassemble_string进行解读。
3.4
disassemble方法用来将PyCodeObject实例化对象翻译为可读字节码。首先调用findlabels和findlinestarts。findlabels将所有字节码跳转指向目的字节码地址存入堆栈。findlinestarts用来标记字节码对应的源码位置,官方注释说明findlinestarts会生成(offset, lineno)元组,其中offset为字节码偏移地址,lineno为源码偏移地址。
3.5
disassemble方法对字节码代码部分逐行翻译,并且添加必要变量及标志注释。
四、dis模块源码注释版本
"""Disassembler of Python byte code into mnemonics."""
import sys
import types
from opcode import *
from opcode import __all__ as _opcodes_all
__all__ = ["dis", "disassemble", "distb", "disco",
"findlinestarts", "findlabels"] + _opcodes_all
del _opcodes_all
_have_code = (types.MethodType, types.FunctionType, types.CodeType,
types.ClassType, type)
'''根据x所属type,判断对输入参数x执行何种反编译,其中co_code选项是
对pyc文件中提取的marshal数据进行反编译过程中常用的'''
def dis(x=None):
"""Disassemble classes, methods, functions, or code.
With no argument, disassemble the last traceback.
"""
if x is None:
distb()
return
if isinstance(x, types.InstanceType):
x = x.__class__
if hasattr(x, 'im_func'):
x = x.im_func
if hasattr(x, 'func_code'):
x = x.func_code
if hasattr(x, '__dict__'):
items = x.__dict__.items()
items.sort()
for name, x1 in items:
if isinstance(x1, _have_code):
print "Disassembly of %s:" % name
try:
dis(x1)
except TypeError, msg:
print "Sorry:", msg
print
elif hasattr(x, 'co_code'):
disassemble(x)
elif isinstance(x, str):
disassemble_string(x)
else:
raise TypeError, \
"don't know how to disassemble %s objects" % \
type(x).__name__
'''无参数x传入时,对上次报错的堆栈信息进行反编译'''
def distb(tb=None):
"""Disassemble a traceback (default: last traceback)."""
if tb is None:
try:
tb = sys.last_traceback
except AttributeError:
raise RuntimeError, "no last traceback to disassemble"
while tb.tb_next: tb = tb.tb_next
disassemble(tb.tb_frame.f_code, tb.tb_lasti)
'''反编译的主函数'''
def disassemble(co, lasti=-1):
"""Disassemble a code object."""
code = co.co_code
labels = findlabels(code)
linestarts = dict(findlinestarts(co))
n = len(code)
i = 0
'''***'''
extended_arg = 0
free = None
while i < n:
c = code[i]
op = ord(c)
'''字节码对应源码偏移量标注'''
if i in linestarts:
if i > 0:
print
print "%3d" % linestarts[i],
else:
print ' ',
if i == lasti: print '-->',
else: print ' ',
'''标注跳转标记'''
if i in labels: print '>>',
else: print ' ',
'''标注字节码偏移和opcode名字'''
print repr(i).rjust(4),
print opname[op].ljust(20),
i = i+1
if op >= HAVE_ARGUMENT:
'''根据不同的变量类型进行变量标注'''
oparg = ord(code[i]) + ord(code[i+1])*256 + extended_arg
extended_arg = 0
i = i+2
if op == EXTENDED_ARG:
extended_arg = oparg*65536L
print repr(oparg).rjust(5),
if op in hasconst:
print '(' + repr(co.co_consts[oparg]) + ')',
elif op in hasname:
print '(' + co.co_names[oparg] + ')',
elif op in hasjrel:
print '(to ' + repr(i + oparg) + ')',
elif op in haslocal:
print '(' + co.co_varnames[oparg] + ')',
elif op in hascompare:
print '(' + cmp_op[oparg] + ')',
elif op in hasfree:
if free is None:
free = co.co_cellvars + co.co_freevars
print '(' + free[oparg] + ')',
print
'''字符串反编译的主函数'''
def disassemble_string(code, lasti=-1, varnames=None, names=None,
constants=None):
labels = findlabels(code)
n = len(code)
i = 0
while i < n:
c = code[i]
op = ord(c)
if i == lasti: print '-->',
else: print ' ',
if i in labels: print '>>',
else: print ' ',
print repr(i).rjust(4),
print opname[op].ljust(15),
i = i+1
if op >= HAVE_ARGUMENT:
oparg = ord(code[i]) + ord(code[i+1])*256
i = i+2
print repr(oparg).rjust(5),
if op in hasconst:
if constants:
print '(' + repr(constants[oparg]) + ')',
else:
print '(%d)'%oparg,
elif op in hasname:
if names is not None:
print '(' + names[oparg] + ')',
else:
print '(%d)'%oparg,
elif op in hasjrel:
print '(to ' + repr(i + oparg) + ')',
elif op in haslocal:
if varnames:
print '(' + varnames[oparg] + ')',
else:
print '(%d)' % oparg,
elif op in hascompare:
print '(' + cmp_op[oparg] + ')',
print
disco = disassemble # XXX For backwards compatibility
'''遍历寻找co_code中为跳转操作的opcode,并将跳转的目的地址(字节码的偏
移地址)存入labels中'''
def findlabels(code):
"""Detect all offsets in a byte code which are jump targets.
Return the list of offsets.
"""
labels = []
n = len(code)
i = 0
while i < n:
c = code[i]
op = ord(c)
i = i+1
if op >= HAVE_ARGUMENT:
'''计算argv表示的偏移地址'''
oparg = ord(code[i]) + ord(code[i+1])*256
i = i+2
label = -1
'''根据跳转类型将跳转后的地址加入数组labels中'''
if op in hasjrel:
label = i+oparg
elif op in hasjabs:
label = oparg
if label >= 0:
if label not in labels:
labels.append(label)
return labels
def findlinestarts(code):
"""Find the offsets in a byte code which are start of lines in the source.
Generate pairs (offset, lineno) as described in Python/compile.c.
"""
'''汇编偏移'''
byte_increments = [ord(c) for c in code.co_lnotab[0::2]]
'''源码偏移'''
line_increments = [ord(c) for c in code.co_lnotab[1::2]]
'''上一行源码的绝对地址'''
lastlineno = None
'''当前汇编对应源码的行'''
lineno = code.co_firstlineno
addr = 0
for byte_incr, line_incr in zip(byte_increments, line_increments):
if byte_incr:
if lineno != lastlineno:
yield (addr, lineno)
lastlineno = lineno
addr += byte_incr
lineno += line_incr
'''byte偏移量一定每次递增不为零,但是源码可能出现lambda类似
语句,因此不同区块的字节码可能对应于源码的同一行'''
if lineno != lastlineno:
yield (addr, lineno)
def _test():
"""Simple test program to disassemble a file."""
if sys.argv[1:]:
if sys.argv[2:]:
sys.stderr.write("usage: python dis.py [-|file]\n")
sys.exit(2)
fn = sys.argv[1]
if not fn or fn == "-":
fn = None
else:
fn = None
if fn is None:
f = sys.stdin
else:
f = open(fn)
source = f.read()
if fn is not None:
f.close()
else:
fn = "<stdin>"
code = compile(source, fn, "exec")
dis(code)
if __name__ == "__main__":
_test()Python逆向(四)—— Python内置模块dis.py源码详解的更多相关文章
- Mybatis源码详解系列(四)--你不知道的Mybatis用法和细节
简介 这是 Mybatis 系列博客的第四篇,我本来打算详细讲解 mybatis 的配置.映射器.动态 sql 等,但Mybatis官方中文文档对这部分内容的介绍已经足够详细了,有需要的可以直接参考. ...
- [转]【视觉 SLAM-2】 视觉SLAM- ORB 源码详解 2
转载地址:https://blog.csdn.net/kyjl888/article/details/72942209 1 ORB-SLAM2源码详解 by 吴博 2 https://github.c ...
- saltstack源码详解一
目录 初识源码流程 入口 1.grains.items 2.pillar.items 2/3: 是否可以用python脚本实现 总结pillar源码分析: @(python之路)[saltstack源 ...
- spring事务详解(三)源码详解
系列目录 spring事务详解(一)初探事务 spring事务详解(二)简单样例 spring事务详解(三)源码详解 spring事务详解(四)测试验证 spring事务详解(五)总结提高 一.引子 ...
- [转]Linux内核源码详解--iostat
Linux内核源码详解——命令篇之iostat 转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/york-hust/p/4846497.html 本文主要分析了Linux的iostat命令的源码, ...
- Shiro 登录认证源码详解
Shiro 登录认证源码详解 Apache Shiro 是一个强大且灵活的 Java 开源安全框架,拥有登录认证.授权管理.企业级会话管理和加密等功能,相比 Spring Security 来说要更加 ...
- Activiti架构分析及源码详解
目录 Activiti架构分析及源码详解 引言 一.Activiti设计解析-架构&领域模型 1.1 架构 1.2 领域模型 二.Activiti设计解析-PVM执行树 2.1 核心理念 2. ...
- 源码详解系列(六) ------ 全面讲解druid的使用和源码
简介 druid是用于创建和管理连接,利用"池"的方式复用连接减少资源开销,和其他数据源一样,也具有连接数控制.连接可靠性测试.连接泄露控制.缓存语句等功能,另外,druid还扩展 ...
- 源码详解系列(七) ------ 全面讲解logback的使用和源码
什么是logback logback 用于日志记录,可以将日志输出到控制台.文件.数据库和邮件等,相比其它所有的日志系统,logback 更快并且更小,包含了许多独特并且有用的特性. logback ...
随机推荐
- Microsoft Compiled HTML Help / Uncompiled .chm File XML External Entity
[+] Credits: John Page (aka hyp3rlinx) [+] Website: hyp3rlinx.altervista.org[+] Source: http://hyp3 ...
- 如何在backoffice里创建Hybris image container以及分配给product
登录backoffice,在media container视图点击新建按钮: Catalog选择Product Catalog: 在Properties界面,可以选择media实例放入该contain ...
- 在SAP Hybris commerce Storefront里购物下单
操作过程和大家平时在网上购物没有太大差别. 选中一款心仪的产品,点击Add to cart加到购物车里: 点击Check out结帐: 生成一个购物车ID: 维护发货地址: 维护发货方式: 点击Pla ...
- 设置Layer模态框的 z-index
$.get(url, {}, function(data){ layui.use(['layer'],function () { var layer = layui.layer,$=layui.$; ...
- uc/xi
一个较为通用的定义为:嵌入式系统是对对象进行自动控制而使其具有智能化并可嵌入对象体系统中的专用计算机系统. 实时性:目前,嵌入式系统广泛应用于生产过程控制.数据采集.传输通信等场合,这些应用的共同特点 ...
- MaxScale ERROR 2006 (HY000): MySQL server has gone away
Error: MaxScale cannot be run as root.Failed to write child process message!解决办法:# maxscale -f /etc/ ...
- Linux下使用shell脚本自动备份和移动数据到大容量存储
自动备份数据库,并将备份前一天的数据移动拷贝到存储上. 需求来源是因为linux系统层的磁盘存储容量过小,数据库自动备份之后日积月累数据越来越多,而且还不想删除旧数据.那解决方法就是在linux系统主 ...
- Android笔记(七十二) Style和Theme
我们尝尝需要使用setText.setColor.setTextSize等属性来设置控件的样式,但是每个控件都需要设置这些属性,工作量无疑是巨大的,并且后期维护起来也不方便. Style Androi ...
- Kali下进行局域网断网攻击
今天我就来演示一下在kali下的局域网断网攻击,即ARP地址欺骗,下图所要用到的arp地址欺骗状态图: 则: 第一步:假设主机A访问某网站,那么要告知某网站我的IP和MAC地址,但这是以广播的方式告知 ...
- 大量javascript代码的项目如何改善可维护性
项目中有点javascript文件,javascript代码行数达到7000多行,维护很费力,主要体现在以下几个方面: 1,方法没有注释,没有注释方法的作用,从上到下罗列,很难知道这个方法应该啥时候调 ...
