内核中dump_stack的实现原理(2) —— symbol
环境
正文
static __printf(, )
void __check_printsym_format(const char *fmt, ...)
{
} static inline void print_symbol(const char *fmt, unsigned long addr)
{
__check_printsym_format(fmt, "");
__print_symbol(fmt, (unsigned long)
__builtin_extract_return_addr((void *)addr));
}

/* Look up a kernel symbol and print it to the kernel messages. */
void __print_symbol(const char *fmt, unsigned long address)
{
char buffer[KSYM_SYMBOL_LEN]; sprint_symbol(buffer, address); printk(fmt, buffer);
}
/**
* sprint_symbol - Look up a kernel symbol and return it in a text buffer
* @buffer: buffer to be stored
* @address: address to lookup
*
* This function looks up a kernel symbol with @address and stores its name,
* offset, size and module name to @buffer if possible. If no symbol was found,
* just saves its @address as is.
*
* This function returns the number of bytes stored in @buffer.
*/
int sprint_symbol(char *buffer, unsigned long address)
{
return __sprint_symbol(buffer, address, , );
}
/* Look up a kernel symbol and return it in a text buffer. */
static int __sprint_symbol(char *buffer, unsigned long address,
int symbol_offset, int add_offset)
{
char *modname;
const char *name;
unsigned long offset, size;
int len; address += symbol_offset;
name = kallsyms_lookup(address, &size, &offset, &modname, buffer);
if (!name)
return sprintf(buffer, "0x%lx", address - symbol_offset); if (name != buffer)
strcpy(buffer, name);
len = strlen(buffer);
offset -= symbol_offset; if (add_offset)
len += sprintf(buffer + len, "+%#lx/%#lx", offset, size); if (modname)
len += sprintf(buffer + len, " [%s]", modname); return len;
}
上面的第11行的kallsyms_lookup就是根据address获取size,offset,modname
/*
* Lookup an address
* - modname is set to NULL if it's in the kernel.
* - We guarantee that the returned name is valid until we reschedule even if.
* It resides in a module.
* - We also guarantee that modname will be valid until rescheduled.
*/
const char *kallsyms_lookup(unsigned long addr,
unsigned long *symbolsize,
unsigned long *offset,
char **modname, char *namebuf)
{
const char *ret; namebuf[KSYM_NAME_LEN - ] = ;
namebuf[] = ; if (is_ksym_addr(addr)) {
unsigned long pos; pos = get_symbol_pos(addr, symbolsize, offset);
/* Grab name */
kallsyms_expand_symbol(get_symbol_offset(pos),
namebuf, KSYM_NAME_LEN);
if (modname)
*modname = NULL; ret = namebuf;
goto found;
} /* See if it's in a module or a BPF JITed image. */
ret = module_address_lookup(addr, symbolsize, offset,
modname, namebuf);
if (!ret)
ret = bpf_address_lookup(addr, symbolsize,
offset, modname, namebuf); found:
cleanup_symbol_name(namebuf);
return ret;
}
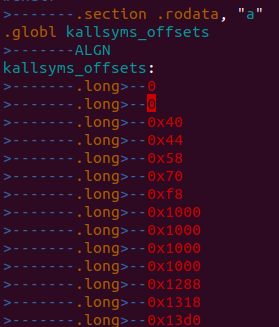
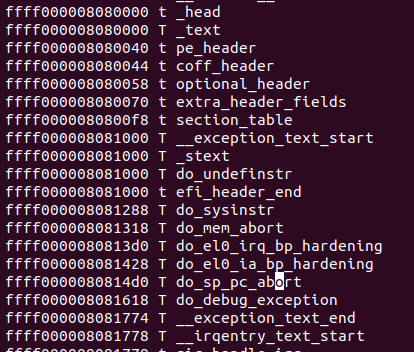
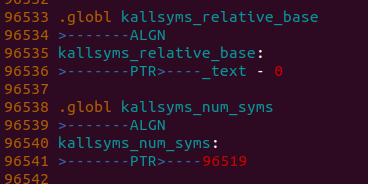

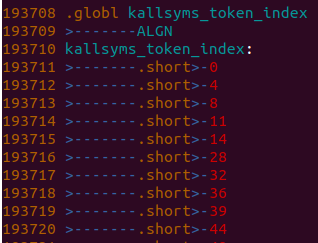
static unsigned long get_symbol_pos(unsigned long addr,
unsigned long *symbolsize,
unsigned long *offset)
{
unsigned long symbol_start = , symbol_end = ;
unsigned long i, low, high, mid; /* This kernel should never had been booted. */
if (!IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_KALLSYMS_BASE_RELATIVE))
BUG_ON(!kallsyms_addresses);
else
BUG_ON(!kallsyms_offsets); /* Do a binary search on the sorted kallsyms_addresses array. */
low = ;
high = kallsyms_num_syms; while (high - low > ) {
mid = low + (high - low) / ;
if (kallsyms_sym_address(mid) <= addr)
low = mid;
else
high = mid;
} /*
* Search for the first aliased symbol. Aliased
* symbols are symbols with the same address.
*/
while (low && kallsyms_sym_address(low-) == kallsyms_sym_address(low))
--low; symbol_start = kallsyms_sym_address(low); /* Search for next non-aliased symbol. */
for (i = low + ; i < kallsyms_num_syms; i++) {
if (kallsyms_sym_address(i) > symbol_start) {
symbol_end = kallsyms_sym_address(i);
break;
}
} /* If we found no next symbol, we use the end of the section. */
if (!symbol_end) {
if (is_kernel_inittext(addr))
symbol_end = (unsigned long)_einittext;
else if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_KALLSYMS_ALL))
symbol_end = (unsigned long)_end;
else
symbol_end = (unsigned long)_etext;
} if (symbolsize)
*symbolsize = symbol_end - symbol_start;
if (offset)
*offset = addr - symbol_start; return low;
}
/*
* Find the offset on the compressed stream given and index in the
* kallsyms array.
*/
static unsigned int get_symbol_offset(unsigned long pos)
{
const u8 *name;
int i; /*
* Use the closest marker we have. We have markers every 256 positions,
* so that should be close enough.
*/
name = &kallsyms_names[kallsyms_markers[pos >> ]]; /*
* Sequentially scan all the symbols up to the point we're searching
* for. Every symbol is stored in a [<len>][<len> bytes of data] format,
* so we just need to add the len to the current pointer for every
* symbol we wish to skip.
*/
for (i = ; i < (pos & 0xFF); i++)
name = name + (*name) + ; return name - kallsyms_names;
}
/*
* Expand a compressed symbol data into the resulting uncompressed string,
* if uncompressed string is too long (>= maxlen), it will be truncated,
* given the offset to where the symbol is in the compressed stream.
*/
static unsigned int kallsyms_expand_symbol(unsigned int off,
char *result, size_t maxlen)
{
int len, skipped_first = ;
const u8 *tptr, *data; /* Get the compressed symbol length from the first symbol byte. */
data = &kallsyms_names[off];
len = *data;
data++; /*
* Update the offset to return the offset for the next symbol on
* the compressed stream.
*/
off += len + ; /*
* For every byte on the compressed symbol data, copy the table
* entry for that byte.
*/
while (len) {
tptr = &kallsyms_token_table[kallsyms_token_index[*data]];
data++;
len--; while (*tptr) {
if (skipped_first) {
if (maxlen <= )
goto tail;
*result = *tptr;
result++;
maxlen--;
} else
skipped_first = ;
tptr++;
}
} tail:
if (maxlen)
*result = '\0'; /* Return to offset to the next symbol. */
return off;
}
内核中dump_stack的实现原理(2) —— symbol的更多相关文章
- 内核中dump_stack的实现原理(3) —— 内核函数printk的实现
参考内核文档: Documentation/printk-formats.txt 在内核中使用dump_stack的时候可以看到如下用法: static inline void print_i ...
- 内核中dump_stack的实现原理(1) —— 栈回溯
环境 Aarch64 Qemu aarch64-linux-gnu-gcc linux-4.14 概述 栈回溯的目的是将函数的调用栈打印出来,对于分析函数调用和debug系统异常会很有帮助 ...
- 内核中dump_stack()的实现,并在用户态模拟dump_stack()【转】
转自:https://blog.csdn.net/jasonchen_gbd/article/details/44066815?utm_source=blogxgwz8 版权声明:本文为博主原创文章, ...
- linux内核中打印栈回溯信息 - dump_stack()函数分析【转】
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/jasonchen_gbd/article/details/45585133 版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,转载请附上原博链接. 目录(?)[-] ...
- Openvswitch原理与代码分析(5): 内核中的流表flow table操作
当一个数据包到达网卡的时候,首先要经过内核Openvswitch.ko,流表Flow Table在内核中有一份,通过key查找内核中的flow table,即可以得到action,然后执行acti ...
- Linux 2.6内核中新的锁机制--RCU
转自:http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/linux/l-rcu/ 一. 引言 众所周知,为了保护共享数据,需要一些同步机制,如自旋锁(spinlock),读写锁 ...
- Linux VFS中write系统调用实现原理【转】
转自:http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-28362602-id-3425881.html 目录 用户空间的write函数在内核里面的服务例程为sys_write Vfs_wr ...
- [php-src]理解Php内核中的函数与INI
内容均以php-5.6.14为例. 一. 函数结构 内核中定义一个php函数使用 PHP_FUNCTION 宏 包装,扩展也不例外,该宏在 ./main/php.h:343 有着一系列类似以 PHP ...
- linux内核中异步通信机制--信号处理机制【转】
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/lu_embedded/article/details/51131663 什么是异步通信?很简单,一旦设备准备好,就主动通知应用程序,这种情况下应用程序 ...
随机推荐
- LOJ2778 [BOI2018]基因工程 随机化
题面 不想写了...留坑吧... 基本思想可参照随机化解决判同问题的总结 代码: #include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; #define ...
- BootStrap Table 合并单元格
为了更直观展示表格的一大堆乱七八糟的数据,合并单元格就派上用场: 效果: 贴上JSON数据(后台查询数据一定要对合并字段排序): [ { "city": "广州市&quo ...
- STRING Cytoscape 网络互作图
网络图(Network)看似复杂,其实构成非常简单,网络图是一种图解模型,形状如同网络,故称网络图,由节点(node)和连线(edge)两个因素组成的.其中 node 又分为 source node( ...
- Javascript Asynchronous Investigation
介绍 同步任务:在主线程上排队执行的任务,只有前一个任务执行完毕,才能执行后一个任务: 异步任务:不进入主线程,而进入任务队列中的任务,只有任务队列通知主线程,某个异步任务可以执行了,这个任务才会进入 ...
- Qt应用程序主窗口之二:拖放操作与打印文档
一.拖放操作 对于一个实用的应用程序,不仅希望能从文件菜单中打开一个文件,更希望可以通过拖动直接将桌面上的文件拖入程序界面上来打开,就像可以将.pro文件拖入Creator中来打开整个项目一样.Qt中 ...
- vim常用命令整理
#创建文件 vim test.txt vi test.txt touch test.txt #在vim中要想退出,先按[esc],再输入如下命令 [:wq]保存并退出 [:q]退出,未修改 [:q!] ...
- docker 学习操作记录 5-1
记录5-1 [BEGIN] // :: Connecting to ... Connection established. To escape to local shell, press Ctrl+A ...
- docker 学习操作记录 1
记录1 Xshell (Build ) Copyright (c) NetSarang Computer, Inc. All rights reserved. Type `help' to learn ...
- 59 网络编程(一)——端口与InetSocketAddress
端口与几个CMD命令 公认端口:0-1023 比如80端口分配给www,21端口分配给FTP等 注册端口:2014-49151 分配给用户进程或引用程序 动态/私有端口:49151-65535 需要 ...
- kubeadm安装依赖镜像
使用kubeadm安装的时候如果不能翻墙下载镜像是个很大的问题,这里自己把需要的镜像下载push下留作不时之需 docker pull davygeek/kube-proxy:v1.14.2 dock ...
