A_B_Good Bye 2018_cf
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Alice and Bob are decorating a Christmas Tree.
Alice wants only 33 types of ornaments to be used on the Christmas Tree: yellow, blue and red. They have yy yellow ornaments, bb blue ornaments and rr red ornaments.
In Bob's opinion, a Christmas Tree will be beautiful if:
- the number of blue ornaments used is greater by exactly 11 than the number of yellow ornaments, and
- the number of red ornaments used is greater by exactly 11 than the number of blue ornaments.
That is, if they have 88 yellow ornaments, 1313 blue ornaments and 99 red ornaments, we can choose 44 yellow, 55 blue and 66 red ornaments (5=4+15=4+1 and 6=5+16=5+1).
Alice wants to choose as many ornaments as possible, but she also wants the Christmas Tree to be beautiful according to Bob's opinion.
In the example two paragraphs above, we would choose 77 yellow, 88 blue and 99 red ornaments. If we do it, we will use 7+8+9=247+8+9=24ornaments. That is the maximum number.
Since Alice and Bob are busy with preparing food to the New Year's Eve, they are asking you to find out the maximum number of ornaments that can be used in their beautiful Christmas Tree!
It is guaranteed that it is possible to choose at least 66 (1+2+3=61+2+3=6) ornaments.
The only line contains three integers yy, bb, rr (1≤y≤1001≤y≤100, 2≤b≤1002≤b≤100, 3≤r≤1003≤r≤100) — the number of yellow, blue and red ornaments.
It is guaranteed that it is possible to choose at least 66 (1+2+3=61+2+3=6) ornaments.
Print one number — the maximum number of ornaments that can be used.
8 13 9
24
13 3 6
9
In the first example, the answer is 7+8+9=247+8+9=24.
In the second example, the answer is 2+3+4=92+3+4=9.
我的代码:
#include <iostream> using namespace std; int main()
{
int y,b,r;
while(cin>>y>>b>>r){
for(int i=r;i>=;i--){
if(b>=(i-)&&y>=(i-)){
cout<<i+i-+i-<<endl;
break;
}
}
}
return ;
}
大佬的代码:
/**
* author: tourist
* created: 30.12.2018 17:35:22
**/
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie();
int a, b, c;
cin >> a >> b >> c;
int x = min(b, min(a + , c - ));
cout << * x << '\n';
return ;
}
1.5 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Bob is a pirate looking for the greatest treasure the world has ever seen. The treasure is located at the point TT, which coordinates to be found out.
Bob travelled around the world and collected clues of the treasure location at nn obelisks. These clues were in an ancient language, and he has only decrypted them at home. Since he does not know which clue belongs to which obelisk, finding the treasure might pose a challenge. Can you help him?
As everyone knows, the world is a two-dimensional plane. The ii-th obelisk is at integer coordinates (xi,yi)(xi,yi). The jj-th clue consists of 22integers (aj,bj)(aj,bj) and belongs to the obelisk pjpj, where pp is some (unknown) permutation on nn elements. It means that the treasure is located at T=(xpj+aj,ypj+bj)T=(xpj+aj,ypj+bj). This point TT is the same for all clues.
In other words, each clue belongs to exactly one of the obelisks, and each obelisk has exactly one clue that belongs to it. A clue represents the vector from the obelisk to the treasure. The clues must be distributed among the obelisks in such a way that they all point to the same position of the treasure.
Your task is to find the coordinates of the treasure. If there are multiple solutions, you may print any of them.
Note that you don't need to find the permutation. Permutations are used only in order to explain the problem.
The first line contains an integer nn (1≤n≤10001≤n≤1000) — the number of obelisks, that is also equal to the number of clues.
Each of the next nn lines contains two integers xixi, yiyi (−106≤xi,yi≤106−106≤xi,yi≤106) — the coordinates of the ii-th obelisk. All coordinates are distinct, that is xi≠xjxi≠xj or yi≠yjyi≠yj will be satisfied for every (i,j)(i,j) such that i≠ji≠j.
Each of the next nn lines contains two integers aiai, bibi (−2⋅106≤ai,bi≤2⋅106−2⋅106≤ai,bi≤2⋅106) — the direction of the ii-th clue. All coordinates are distinct, that is ai≠ajai≠aj or bi≠bjbi≠bj will be satisfied for every (i,j)(i,j) such that i≠ji≠j.
It is guaranteed that there exists a permutation pp, such that for all i,ji,j it holds (xpi+ai,ypi+bi)=(xpj+aj,ypj+bj)(xpi+ai,ypi+bi)=(xpj+aj,ypj+bj).
Output a single line containing two integers Tx,TyTx,Ty — the coordinates of the treasure.
If there are multiple answers, you may print any of them.
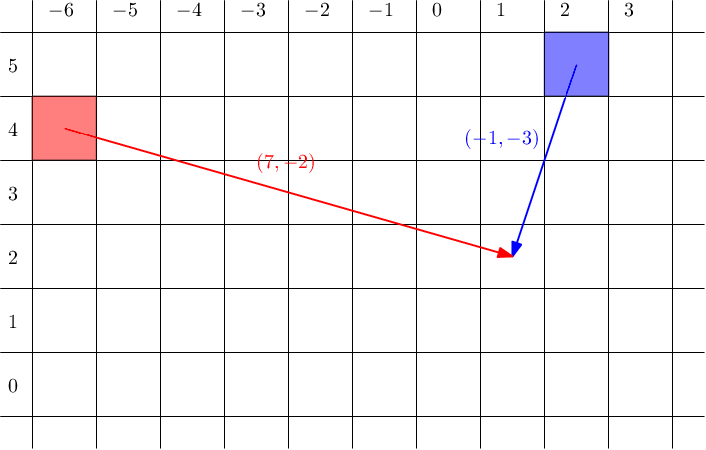
2
2 5
-6 4
7 -2
-1 -3
1 2
4
2 2
8 2
-7 0
-2 6
1 -14
16 -12
11 -18
7 -14
9 -12
As n=2n=2, we can consider all permutations on two elements.
If p=[1,2]p=[1,2], then the obelisk (2,5)(2,5) holds the clue (7,−2)(7,−2), which means that the treasure is hidden at (9,3)(9,3). The second obelisk (−6,4)(−6,4) would give the clue (−1,−3)(−1,−3) and the treasure at (−7,1)(−7,1). However, both obelisks must give the same location, hence this is clearly not the correct permutation.
If the hidden permutation is [2,1][2,1], then the first clue belongs to the second obelisk and the second clue belongs to the first obelisk. Hence (−6,4)+(7,−2)=(2,5)+(−1,−3)=(1,2)(−6,4)+(7,−2)=(2,5)+(−1,−3)=(1,2), so T=(1,2)T=(1,2) is the location of the treasure.
In the second sample, the hidden permutation is [2,3,4,1][2,3,4,1].
我的代码,当然没通过了...在第33组数据超时了.
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <string>
#include <sstream>
#include <cstdio> using namespace std; map<string,int> m1;
int obe[][]; int main()
{
int n,x,y,a,b;
int resx,resy;
cin>>n;
for(int i=;i<n;i++){
cin>>obe[i][]>>obe[i][];
}
int t1,t2;std::stringstream ss;
for(int i=;i<n;i++){
//scanf("%d %d",&t1,&t2);
cin>>t1>>t2;
int newx,newy; for(int j=;j<n;j++){
newx=obe[j][]+t1;
newy=obe[j][]+t2;
string tmp1,tmp2;
ss.clear();
ss<<newx;
ss>>tmp1;
ss.clear();
ss<<newy;
ss>>tmp2;
tmp1=tmp1+",";
tmp1=tmp1+tmp2;
//cout<<tmp1;
m1[tmp1]++;
}
}
map<string,int>::iterator aa=m1.begin();
for(;aa!=m1.end();aa++){
if(aa->second==n){
string tmp=aa->first;
int i;
for(i=;tmp[i]!=',';i++){
cout<<tmp[i];
}
printf(" "); for(i++;i<tmp.size();i++){
//printf("%c",tmp[i]);
cout<<tmp[i];
}
cout<<endl;
break;
}
}
return ;
}
hencuo Code
还是看一下tourist的吧.
题意是n个起点,有n个向量,有个一一对应的关系使每个起点加上一个向量之后是同一个点,让输出那个点的坐标.
所以这些每个起点+向量都是得到相同的坐标,然后把这每个值再加起来就是坐标的n倍啊!
再就是我的基本操作都不会啊,连个int和string 的相互转换都不会...
/**
* author: tourist
* created: 30.12.2018 17:36:58
**/
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie();
int n;
cin >> n;
long long x = , y = ;
for (int i = ; i < * n; i++) {
int xx, yy;
cin >> xx >> yy;
x += xx;
y += yy;
}
cout << (x / n) << " " << (y / n) << '\n';
return ;
}
拖哥的代码中有两句看不懂的:
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
原来c++为了兼容c中的stdin stdout,防止混用cin scanf时出现问题,将输入输入流跟他们绑定到一块,然后就导致c++的cin cout速度慢了,
这两句代码可以解除两者的同步和cin与cout的绑定,加上之后再用cin cout 就与scanf printf的速度没什么差别了.
也有人对此做过测试https://www.byvoid.com/zhs/blog/fast-readfile.
(我的代码方法太挫了,加上这个仍然超时...)
A_B_Good Bye 2018_cf的更多相关文章
- Good Bye 2013 A
A. New Year Candles time limit per test 1 second memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard ...
- codeforces Gym 100500 J. Bye Bye Russia
Problem J. Bye Bye RussiaTime Limit: 20 Sec Memory Limit: 256 MB 题目连接 http://codeforces.com/gym/1005 ...
- Good Bye 2018
Good Bye 2018 2018年最后一场CF,OVER! 弱弱的我只能做出3道A,B,D~~~~ 最后几分钟,感觉找到了C题的规律,结束的那一刻,提交了一发 "Wrong answer ...
- Good Bye 2018 (A~F, H)
目录 Codeforces 1091 A.New Year and the Christmas Ornament B.New Year and the Treasure Geolocation C.N ...
- English Voice of <<Bye Bye Bye>>
Bye Bye Bye - Lovestoned When i see you, looking back at me 当我看到你回首看我时 Watching this eye still 彼此凝视 ...
- Good Bye 2017(送命场)
9815人数场,9500+围观神仙打架...断断续续打Codeforces也快有一年啦,第一次打Good Bye场,满怀前排膜tourist的心愿参加了这场送命场,虽然没看到tourist.不过还是得 ...
- [T-ARA][Bye Bye]
歌词来源:http://music.163.com/#/song?id=22704472 사랑하는 그대 Bye Bye, Bye Bye, Bye Bye, [sa-lang-ha-neun geu ...
- Codeforces Good Bye 2018
咕bye 2018,因为我这场又咕咕咕了 无谓地感慨一句:时间过得真快啊(有毒 A.New Year and the Christmas Ornament 分类讨论后等差数列求和 又在凑字数了 #in ...
- codeforces Good bye 2016 E 线段树维护dp区间合并
codeforces Good bye 2016 E 线段树维护dp区间合并 题目大意:给你一个字符串,范围为‘0’~'9',定义一个ugly的串,即串中的子串不能有2016,但是一定要有2017,问 ...
随机推荐
- 【译】索引进阶(十一):SQL SERVER中的索引碎片【上篇】
原文链接:传送门. 第十章节我们分析了索引的内部结构.有了这些关于索引结构的知识,我们便可以分析索引碎片了:其产生的原因,如何防止,以及何时可以不去关注它们. 一些背景知识 / 复习 以下知识对于理解 ...
- vue面试题总结
1.vue双向绑定的实现原理2.js的继承和原型链3.es6语法箭头函数和普通函数的区别 普通函数的this总是指向它的直接调用者. 在严格模式下,没找到直接调用者,则函数中的this是undefin ...
- python3.5 默认安装路径 | 安装 | 删除
win7 环境下: Python3.5默认安装路径是当前用户的 AppData\.. 下 这么做的一个可能原因是 现在安装过程中默认是install just for me,这个会把python默认 ...
- gatewayworker开发单聊应用解决的问题
绑定唯一id时,遇到的信息发送同步问题 问题:A-B A-C A发送信息给B和C时 A绑定了唯一id 若B.C发送信息给A则A处会同时手到来自于BC的信息 用解绑和生成新的client_id无法避 ...
- Linux下定时备份文件
一. 编写脚本 编写一个脚本文件,使脚本可以执行备份命令. 例如,将文件目录 /home/backups/balalala 备份到/home目录下,并压缩. 1. 创建脚本 命令格式: touch 路 ...
- onscroll 元素滚动事件
阻止事件冒泡 event.stopPropagation(); children():查找合集里面的第一级子元素.(仅儿子辈,这里可以理解为就是父亲-儿子的关) children只查找第一级的子节点 ...
- Linux下系统如何监控服务器硬件、操作系统、应用服务和业务
1.Linux监控概述 Linux服务器要保证系统的高可用性,需要实时了解到服务器的硬件.操作系统.应用服务等的运行状况,各项性能指标是否正常,需要使用各种LINUX命令.做到自动化运维就 ...
- Spring Bean装配
1. Bean注入三种方式: A. 包扫描 + 组件标注注解(@Controller/@Service/@Repository/@Component),适用场景:自己写的类: B. @Bean或xml ...
- SSM框架中写sql在dao文件中以注解的方式
1以注解方式 //两个参数其中一个是对象需写,对象.属性 @Update("update delivery_address set consignee = #{address.consign ...
- GitHub项目功能理解
目录 github账号看板使用方式 code issues Pull Requests Projects Insights Settings date: 2019-4-26 author:yangxi ...
