STL源码标注_空间适配器
/* stl_alloc.h */
SGI STL空间适配器的主要由alloc.h和stl_alloc.h实现
SGI STL空间适配器的核心:
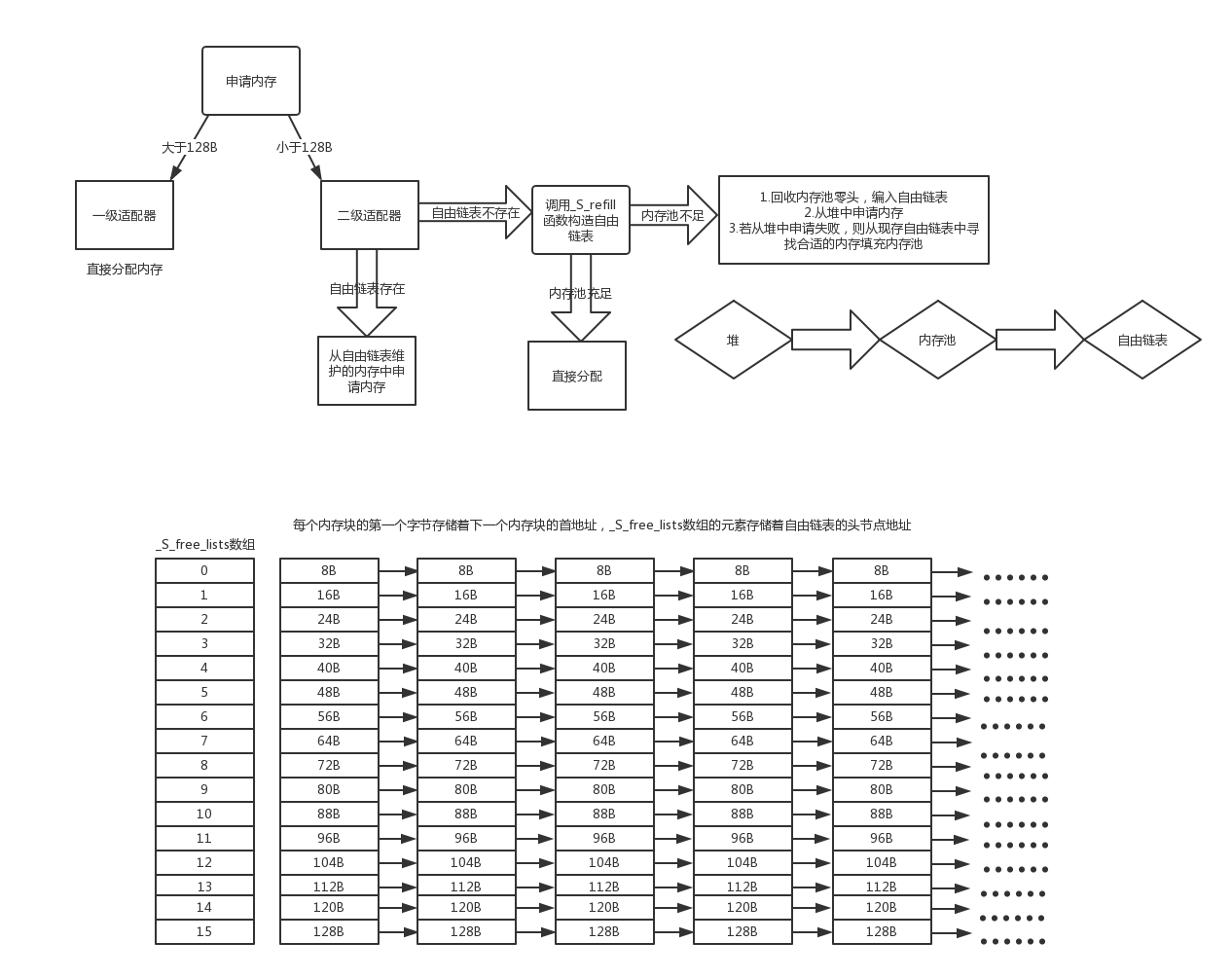
第一级适配器__malloc_alloc_template:直接调用malloc()和free()函数
第二级适配器__default_alloc_template:当配置区块超过128B时调用一级适配器;否则采用内存池管理空间的分配
第二级配置器工作流程:当配置区块超过128B时调用一级适配器;否则,从自由链表维护的内存块中申请内存,若没有对应申请大小的自由链表,则从内存池中申请内存构造自由链表,内存池中内存不足时,从堆中申请内存填充内存池(自由链表:负责维护不同大小的内存块,由于第二级配置器会将任何内存需求量上调为8的倍数,且能够分配的最大内存为128B,则自由链表的个数为128/8=16个;每个链表分别维护区块内存大小为8,16,24,32,40,48,56,64,72,80,88,96,104,112,120,128B)
例子:
1、请求168字节内存:由于其大于128字节,则交由一级内存适配器
2、请求16字节内存:由于其小于128字节,二级配置器接管请求,对应第2个自由链表,数组下标为1,自由链表为空,则调用_S_refill函数申请内存并构造自由链表;此时s_refill(16)接收到请求后,调用_S_chunk_alloc(16,20)函数完成从内存池的内存分配,_S_chunk_alloc(16,20)被调用后,若内存池是空的,接着从堆中申请足够大的内存块给内存池,内存池填充完毕后,分配16*20个字节的内存给自由链表,该自由链表维护单位为16B的内存
3、请求64字节内存由于其小于128字节,二级配置器接管请求,对应第8个自由链表,数组下标为7,自由链表为空,则调用_S_refill函数申请内存并构造自由链表;此时s_refill(64)接收到请求后,调用_S_chunk_alloc(64,20)函数完成从内存池的内存分配,_S_chunk_alloc(64,20)被调用后,若内存池是空的,接着从堆中申请足够大的内存块给内存池,内存池填充完毕后,分配64*20个字节的内存给自由链表,该自由链表维护单位为64B的内存
4、再次请求16字节内存:由于其小于128字节,二级配置器接管请求,对应第2个自由链表,数组下标为1,自由链表不为空,从自由链表维护的内存中申请内存,同时调整自由链表头调整位置
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//++定义一级内存适配器
template <int __inst>
class __malloc_alloc_template {
private:
static void* _S_oom_malloc(size_t); //allocate函数分配内存失败时执行的函数
static void* _S_oom_realloc(void*, size_t); //reallocate函数分配内存失败时执行的函数
#ifndef __STL_STATIC_TEMPLATE_MEMBER_BUG
static void (* __malloc_alloc_oom_handler)(); //定义分配出错时执行的函数指针
#endif
public:
static void* allocate(size_t __n) //内存分配函数
{
void* __result = malloc(__n);
== __result) __result = _S_oom_malloc(__n);
return __result;
}
static void deallocate(void* __p) //内存释放函数
{
free(__p);
}
static void* reallocate(void* __p, size_t __new_sz) //内存重新分配函数
{
void* __result = realloc(__p, __new_sz);
== __result) __result = _S_oom_realloc(__p, __new_sz);
return __result;
}
static void (* __set_malloc_handler(void (*__f)()))()//指定自己的异常处理,__set_malloc_handler为一个函数,参数为void (*__f)(),返回值为static void(*)()
{
void (* __old)() = __malloc_alloc_oom_handler;
__malloc_alloc_oom_handler = __f;
return(__old);
}
};
#ifndef __STL_STATIC_TEMPLATE_MEMBER_BUG
template <int __inst>
;
#endif
//++定义_S_oom_malloc(size_t)
template <int __inst>
void* __malloc_alloc_template<__inst>::_S_oom_malloc(size_t __n)
{
void (* __my_malloc_handler)();
void* __result;
for (;;) //不断执行循环,每次都尝试申请内存,直至分配成功,内存分配失败时若存在内存分配失败函数则执行,否则抛出异常
{
__my_malloc_handler = __malloc_alloc_oom_handler;
== __my_malloc_handler) { __THROW_BAD_ALLOC; }
(*__my_malloc_handler)();
__result = malloc(__n);
if (__result) return(__result);
}
}
//++定义_S_oom_realloc(size_t)
template <int __inst>
void* __malloc_alloc_template<__inst>::_S_oom_realloc(void* __p, size_t __n)
{
void (* __my_malloc_handler)();
void* __result;
for (;;) //不断执行循环,每次都尝试申请内存,直至分配成功,内存分配失败时若存在内存分配失败函数则执行,否则抛出异常
{
__my_malloc_handler = __malloc_alloc_oom_handler;
== __my_malloc_handler) { __THROW_BAD_ALLOC; }
(*__my_malloc_handler)();
__result = realloc(__p, __n);
if (__result) return(__result);
}
}
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
#ifdef __USE_MALLOC
typedef malloc_alloc alloc;
typedef malloc_alloc single_client_alloc;
#else
#if defined(__SUNPRO_CC) || defined(__GNUC__)
};
};
};
#endif
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//++定义二级内存适配器
template <bool threads, int inst>
class __default_alloc_template {
private:
#if !(defined(__SUNPRO_CC) || defined(__GNUC__))
}; //对齐字节数
}; //最大分配字节数
}; //_MAX_BYTES/_ALIGN
#endif
) & ~((size_t)_ALIGN - )); } //计算向上对齐后的字节数
__PRIVATE:
union _Obj //自由链表节点
{
union _Obj* _M_free_list_link;
];
};
private:
#if defined(__SUNPRO_CC) || defined(__GNUC__) || defined(__HP_aCC) //定义自由链表数组
static _Obj* __STL_VOLATILE _S_free_list[];
#else
static _Obj* __STL_VOLATILE _S_free_list[_NFREELISTS];
#endif
)/(size_t)_ALIGN - );} //计算对应自由链表在数组中的位置
static void* _S_refill(size_t __n); //填充空间,把大小为__n的内存空间加到自由链表中
static char* _S_chunk_alloc(size_t __size, int& __nobjs); //从内存池中分配空间给自由链表,该空间可容纳__nobjs个大小为__size的区块
static char* _S_start_free; //内存池起始位置
static char* _S_end_free; //内存池结束位置
static size_t _S_heap_size; //当前内存池大小
#ifdef __STL_THREADS
static _STL_mutex_lock _S_node_allocator_lock;
#endif
class _Lock;
friend class _Lock;
class _Lock
{
public:
_Lock() { __NODE_ALLOCATOR_LOCK; }
~_Lock() { __NODE_ALLOCATOR_UNLOCK; }
};
public:
static void* allocate(size_t __n)
{
;
if (__n > (size_t)_MAX_BYTES) //申请内存大于128B时,采用一级内存适配器
{
__ret = malloc_alloc::allocate(__n);
}
else //申请内存小于128B时,从自由链表中申请内存
{
_Obj* __STL_VOLATILE* __my_free_list = _S_free_list + _S_freelist_index(__n); //单位为__n大小的自由链表头节点
#ifndef _NOTHREADS
_Lock __lock_instance;
#endif
_Obj* __RESTRICT __result = *__my_free_list; //从自由链表中截取内存赋值给__result
)
__ret = _S_refill(_S_round_up(__n)); //若数组中不存在单位为__n大小的自由链表,则调用_S_refill函数生成单位为__n大小的自由链表
else
{
*__my_free_list = __result -> _M_free_list_link; //若数组中存在单位为__n大小的自由链表,则自由链表头节点后移一个单位
__ret = __result;
}
}
return __ret;
};
static void deallocate(void* __p, size_t __n)
{
if (__n > (size_t) _MAX_BYTES)
malloc_alloc::deallocate(__p, __n); //释放内存大于128B时,采用一级内存适配器
else //释放内存小于128B时,从自由链表中申请内存
{
_Obj* __STL_VOLATILE* __my_free_list = _S_free_list + _S_freelist_index(__n); //单位为__n大小的自由链表头节点
_Obj* __q = (_Obj*)__p;
#ifndef _NOTHREADS
_Lock __lock_instance;
#endif
__q -> _M_free_list_link = *__my_free_list;
*__my_free_list = __q; //将内存归还至单位为__n的自由链表中,并将自由链表头节点指向新归还的地址
}
}
};
static void* reallocate(void* __p, size_t __old_sz, size_t __new_sz);
typedef __default_alloc_template<__NODE_ALLOCATOR_THREADS, > alloc;
typedef __default_alloc_template<> single_client_alloc;
template <bool __threads, int __inst>
inline bool operator==(const __default_alloc_template<__threads, __inst>&,const __default_alloc_template<__threads, __inst>&)
{
return true;
}
# ifdef __STL_FUNCTION_TMPL_PARTIAL_ORDER
template <bool __threads, int __inst>
inline bool operator!=(const __default_alloc_template<__threads, __inst>&,const __default_alloc_template<__threads, __inst>&)
{
return false;
}
# endif
//++定义_S_chunk_alloc函数
template <bool __threads, int __inst>
char* __default_alloc_template<__threads, __inst>::_S_chunk_alloc(size_t __size, int& __nobjs)
{
char* __result; //预返回的内存块儿首地址
size_t __total_bytes = __size * __nobjs; //预分配的内存块总大小,通常情况下nojbs的大小为20,nobjs的大小由s_refill函数传进
size_t __bytes_left = _S_end_free - _S_start_free; //memory pool剩余内存块大小
if (__bytes_left >= __total_bytes) //内存池剩余空间满足20个需求,直接分配
{
__result = _S_start_free;
_S_start_free += __total_bytes;
return (__result);
}
else if (__bytes_left >= __size) //内存池剩余空间不满足20个需求,但满足一个或多个,取出最多个能满足条件区块的个数
{
__nobjs = (int)(__bytes_left/__size);
__total_bytes = __size * __nobjs;
__result = _S_start_free;
_S_start_free += __total_bytes;
return(__result);
}
else //内存池剩余空间不足一个区块大小,则向堆中重新申请内存至内存池
{
size_t __bytes_to_get = * __total_bytes + _S_round_up(_S_heap_size >> ); //扩大需要量, 新需求量是原需求量的二倍与现有内存池大小的十六分之一的和
) //判断内存池中是否有残余空间,如果有则将其编入自由链表
{
_Obj* __STL_VOLATILE* __my_free_list = _S_free_list + _S_freelist_index(__bytes_left);
((_Obj*)_S_start_free) -> _M_free_list_link = *__my_free_list;
*__my_free_list = (_Obj*)_S_start_free;
}
_S_start_free = (char*)malloc(__bytes_to_get); //从堆中申请内存
== _S_start_free) //若从堆中申请内存失败,则循环的从所有自由链表中寻找未用且足够大的内存块,释放这些内存块并将其编入内存池
{
size_t __i;
_Obj* __STL_VOLATILE* __my_free_list;
_Obj* __p;
for (__i = __size;__i <= (size_t)_MAX_BYTES;__i += (size_t)_ALIGN) //每次增加8个字节,查找每一个单位大于__size的自由链表
{
__my_free_list = _S_free_list + _S_freelist_index(__i);
__p = *__my_free_list;
!= __p) {
*__my_free_list = __p -> _M_free_list_link;
_S_start_free = (char*)__p;
_S_end_free = _S_start_free + __i;
return(_S_chunk_alloc(__size, __nobjs)); //递归调用_S_chunk_alloc函数填充内存池
}
}
_S_end_free = ; //从自由链表中找不到合适的内存,则调用一级内存适配器再次申请内存
_S_start_free = (char*)malloc_alloc::allocate(__bytes_to_get);
}
_S_heap_size += __bytes_to_get;
_S_end_free = _S_start_free + __bytes_to_get;
return(_S_chunk_alloc(__size, __nobjs)); //递归调用_S_chunk_alloc函数填充内存池
}
}
//++定义_S_refill函数
template <bool __threads, int __inst>
void* __default_alloc_template<__threads, __inst>::_S_refill(size_t __n)
{
; //默认自由链表管理的块数
char* __chunk = _S_chunk_alloc(__n, __nobjs); //内存池头指针
_Obj* __STL_VOLATILE* __my_free_list; //当前空闲内存块地址
_Obj* __result; //返回的地址
_Obj* __current_obj; //当前内存块头
_Obj* __next_obj; //下一个内存块头
int __i; //循环变量
== __nobjs) return(__chunk); //如果只有一个块则返回,自由链表没有接区块管理
__my_free_list = _S_free_list + _S_freelist_index(__n);
__result = (_Obj*)__chunk; //将第一个内存块返回,其余内存块编入自由链表
*__my_free_list = __next_obj = (_Obj*)(__chunk + __n);
; ; __i++) //for循环,生成单位大小为__n的自由链表
{
__current_obj = __next_obj;
__next_obj = (_Obj*)((char*)__next_obj + __n);
== __i) {
__current_obj -> _M_free_list_link = ;
break;
} else {
__current_obj -> _M_free_list_link = __next_obj;
}
}
return(__result);
}
//++定义reallocate函数
template <bool threads, int inst>
void*__default_alloc_template<threads, inst>::reallocate(void* __p,size_t __old_sz,size_t __new_sz)
{
void* __result;
size_t __copy_sz;
if (__old_sz > (size_t) _MAX_BYTES && __new_sz > (size_t) _MAX_BYTES)
{
return(realloc(__p, __new_sz));
}
if (_S_round_up(__old_sz) == _S_round_up(__new_sz)) return(__p);
__result = allocate(__new_sz);
__copy_sz = __new_sz > __old_sz? __old_sz : __new_sz;
memcpy(__result, __p, __copy_sz);
deallocate(__p, __old_sz);
return(__result);
}
#ifdef __STL_THREADS
template <bool __threads, int __inst>
_STL_mutex_lock
__default_alloc_template<__threads, __inst>::_S_node_allocator_lock
__STL_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
#endif
//++二级内存适配器类变量初始化操作
template <bool __threads, int __inst>
;
template <bool __threads, int __inst>
;
template <bool __threads, int __inst>
size_t __default_alloc_template<__threads, __inst>::_S_heap_size = ;
template <bool __threads, int __inst>
typename __default_alloc_template<__threads, __inst>::_Obj* __STL_VOLATILE __default_alloc_template<__threads, __inst> ::_S_free_list[
#if defined(__SUNPRO_CC) || defined(__GNUC__) || defined(__HP_aCC)
_NFREELISTS
#else
__default_alloc_template<__threads, __inst>::_NFREELISTS
#endif
] = {, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , };
#endif /* __USE_MALLOC */
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//++标准内存适配器标准接口
#ifdef __STL_USE_STD_ALLOCATORS
template <class _Tp>
class allocator
{
typedef alloc _Alloc; //二级内存适配器
public:
typedef size_t size_type;
typedef ptrdiff_t difference_type;
typedef _Tp* pointer;
typedef const _Tp* const_pointer;
typedef _Tp& reference;
typedef const _Tp& const_reference;
typedef _Tp value_type;
template <class _Tp1>
structs rebind
{
typedef allocator<_Tp1> other;
};
allocator() __STL_NOTHROW {} //默认构造函数,__STL_NOTHROW在stl_config.h中定义,要么为空,要么为throw()异常
allocator(const allocator&) __STL_NOTHROW {} //复制构造函数
template <class _Tp1> allocator(const allocator<_Tp1>&) __STL_NOTHROW {} //泛化的复制构造函数
~allocator() __STL_NOTHROW {} //析构函数
pointer address(reference __x) const { return &__x; } //返回对象的地址
const_pointer address(const_reference __x) const { return &__x; } //返回const对象的地址
_Tp* allocate(size_type __n, )
{
? static_cast<_Tp*>(_Alloc::allocate(__n * ; //如果申请的空间块数不为0,那么调用二级内存适配器的allocate函数来分配内存
}
void deallocate(pointer __p, size_type __n) //释放内存
{
_Alloc::deallocate(__p, __n * sizeof(_Tp));
}
size_type max_size() const __STL_NOTHROW
{
) / sizeof(_Tp); //size_t为unsigned类型,将-1强制转换为unsigned类型会得到unsiged类型的最大数,结果就是计算可分配_Tp类型的最大个数
}
/* 调用new与delete完成内存分配与释放*/
void construct(pointer __p, const _Tp& __val) { new(__p) _Tp(__val); }
void destroy(pointer __p) { __p->~_Tp(); }
};
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
STL源码标注_空间适配器的更多相关文章
- STL源码剖析之空间配置器
本文大致对STL中的空间配置器进行一个简单的讲解,由于只是一篇博客类型的文章,无法将源码表现到面面俱到,所以真正感兴趣的码农们可以从源码中或者<STL源码剖析>仔细了解一下. 1,为什么S ...
- STL源码分析之空间配置器
前言 SGI STL将new的申请空间和调用构造函数的两个功能分开实现, 如果对new不太清楚的, 可以先去看看这一篇new实现再来看配置器也不迟. 本节是STL分析的第一篇, 主要分析STL各个部分 ...
- 重温《STL源码剖析》笔记 第三章
源码之前,了无秘密. --侯杰 第三章:迭代器概念与traits编程技法 迭代器是一种smart pointer auto_Ptr 是一个用来包装原生指针(native pointer)的对象,声明狼 ...
- STL源码分析《3》----辅助空间不足时,如何进行归并排序
两个连在一起的序列 [first, middle) 和 [middle, last) 都已经排序, 归并排序最核心的算法就是 将 [first, middle) 和 [middle, last) 在 ...
- STL源码分析读书笔记--第二章--空间配置器(allocator)
声明:侯捷先生的STL源码剖析第二章个人感觉讲得蛮乱的,而且跟第三章有关,建议看完第三章再看第二章,网上有人上传了一篇读书笔记,觉得这个读书笔记的内容和编排还不错,我的这篇总结基本就延续了该读书笔记的 ...
- STL源码剖析 — 空间配置器(allocator)
前言 以STL的实现角度而言,第一个需要介绍的就是空间配置器,因为整个STL的操作对象都存放在容器之中. 你完全可以实现一个直接向硬件存取空间的allocator. 下面介绍的是SGI STL提供的配 ...
- STL源码剖析——空间配置器Allocator#1 构造与析构
以STL的运用角度而言,空间配置器是最不需要介绍的东西,因为它扮演的是幕后的角色,隐藏在一切容器的背后默默工作.但以STL的实现角度而言,最应该首先介绍的就是空间配置器,因为这是这是容器展开一切运作的 ...
- 《STL源码剖析》——第一、二、三章
第一章:概论: 换句话说,STL所实现的,是依据泛型思维架设起来的一个概念结构.这个以抽象概念(abstract concepts)为主体而非以实际类(classes)为主体的结构,形成了一个严谨的 ...
- STL源码剖析 迭代器(iterator)概念与编程技法(三)
1 STL迭代器原理 1.1 迭代器(iterator)是一中检查容器内元素并遍历元素的数据类型,STL设计的精髓在于,把容器(Containers)和算法(Algorithms)分开,而迭代器(i ...
随机推荐
- 使用dom4j技术对xml文档进行增删改练习(一)
整个流程如下面代码所以,并对一些重要代码意义做出详细解释: import java.io.File; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import org.dom4j ...
- 关于会话、进程、请求的几个常用SQL
1.检查自己的SID SELECT sid FROM v$session WHERE sid = (SELECT sid FROM v$mystat WHERE rownum = 1); 2. 几个I ...
- 分布式进阶(十三)Docker Container间实现数据共享
sudo docker run -it -v /usr/lib:/usr/lib/dbdata --name dbcontainer-192.168.1.184 ubuntu:14.04 sudo d ...
- ViewPager 实现 Galler 效果, 中间大图显示,两边小图展示
正常情况下, ViewPager 一页只能显示一项数据, 但是我们常常看到网上,特别是电视机顶盒的首页经常出现中间大图显示两端也都露出一点来,这种效果怎么实现呢?先上一张效果图: 大家第一眼肯定想到了 ...
- FreeMarker 生成Java、mybatis文件
FreeMarker 生成Java.mybatis文件 将mysql数据库表通过FreeMarker生成对应的Java文件和对应的mybatis文件. FreeMarker是一款模板引擎: 即一种基于 ...
- javascript语法之for-in语句
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/ ...
- Mahout 算法
Mahout 包括协同过滤,基于User和Item的推荐:kmeans.Fuzzy-kmeans .Mean shift .Dirichlet process .LDA聚类:奇异值分解:并行频繁项集挖 ...
- Linux下使用GDAL进行开发(automake使用)
首先写三个源代码文件,分别是GDALTest.cpp.Fun.cpp和Fun.h,将这三个存放在一个叫GDALTest的文件夹中,然后打开终端,切换到该目录,如下图所示(注:这个图是最后截图的,所以文 ...
- 【Unity插件】LitJson杂谈
距离上一次更新博客已有一段时间了,一实习就懒了,嘿嘿.这次谈一下在实习里新碰到的一个Unity插件--LitJson(也可以去官网下载最新版). 开场白 LitJson是一个开源项目,比较小巧轻便,安 ...
- 【linux学习笔记】在ubuntu下使用QT Cmake支持C++11
今天在ubuntu下使用QT来进行C++编程,选择了Cmake,当用到initializer_list的时候提示不支持C++11,现提供一下解决方案: 错误提示: error: This file r ...
