Python学习之文件操作(二)
CSV文件处理
在Python中处理CSV文件可以使用模块csv。有关csv模块的官方资料看这里。
1 读取csv文件
csv.reader(csvfile, dialect='excel', **fmtparams)
使用reader()函数来读取csv文件,返回一个reader对象。reader对象可以使用迭代获取其中的每一行。
>>> import csv
>>> with open('userlist.csv','rt') as csv_file:
csv_conent = [ row for row in csv.reader(csv_file)] >>> csv_conent
[['Doctor', 'No'], ['Rosa', 'Klebb'], ['Mister', 'Big'], ['Auric', 'Goldfinger'], ['Ernst', 'Blofeld']]
>>>
class csv.DictReader(csvfile, fieldnames=None, restkey=None, restval=None, dialect='excel', *args, **kwds)
可以使用DicReader()按照字典的方式读取csv内容,如下:
>>> import csv
>>> with open('userlist3.csv','rt',newline='') as csvfile:
reader = csv.DictReader(csvfile, fieldnames =[1,2],delimiter=':')
for row in reader:
print(row[1],row[2]) Doctor No
Rosa Klebb
Mister Big
Auric Gold
Ernst Blofeld
>>>
2 写入csv文件
csv.writer(csvfile, dialect='excel', **fmtparams)
使用writer()函数来写csv文件,返回一个writer对象。writer对象可以使用writerow()写一行数据,或者使用。writerows()写多行数据
>>> import csv
>>> namelist = []
>>> namelist = [
['Doctor','No'],
['Rosa','Klebb'],
['Mister','Big'],
['Auric','Gold'],
['Ernst','Blofeld'],
]
>>> with open('userlist2.csv','wt') as c_file:
csvout = csv.writer(c_file, delimiter=':')
csvout.writerows(namelist) >>> with open('userlist3.csv','wt',newline='') as c_file:
csvout = csv.writer(c_file, delimiter=':')
csvout.writerows(namelist)
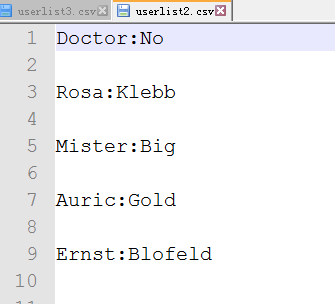
生成的csv文件如下:

class csv.DictWriter(csvfile, fieldnames, restval='', extrasaction='raise', dialect='excel', *args, **kwds)
使用DictWriter把字典类型的数据写入到csv文件中,如下:
>>> import csv
>>> villains = [
{'first': 'Doctor', 'last': 'No'},
{'first': 'Rosa', 'last': 'Klebb'},
{'first': 'Mister', 'last': 'Big'},
{'first': 'Auric', 'last': 'Goldfinger'},
{'first': 'Ernst', 'last': 'Blofeld'},
]
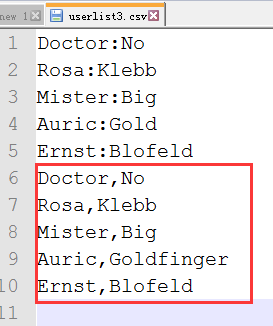
>>> with open('userlist3.csv','at',newline='') as csvfile:
writer = csv.DictWriter(csvfile,['first','last'])
writer.writerows(villains)
XML文件处理
XML是可扩展标记语言,它使用tag来分隔数据。
处理XML文件,可以使用python中的xml模块,它包含下面的几个子模块:
xml.etree.ElementTree: the ElementTree API, a simple and lightweight XML processor
xml.dom: the DOM API definition
xml.dom.minidom: a minimal DOM implementation
xml.dom.pulldom: support for building partial DOM trees
xml.sax: SAX2 base classes and convenience functions
xml.parsers.expat: the Expat parser binding
xml模块更多的相关内容参考官方文档。
使用xml.etree.ElementTree来解析处理XML文件内容,如下:
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<data>
<country name="Liechtenstein">
<rank>1</rank>
<year>2008</year>
<gdppc>141100</gdppc>
<neighbor name="Austria" direction="E"/>
<neighbor name="Switzerland" direction="W"/>
</country>
<country name="Singapore">
<rank>4</rank>
<year>2011</year>
<gdppc>59900</gdppc>
<neighbor name="Malaysia" direction="N"/>
</country>
<country name="Panama">
<rank>68</rank>
<year>2011</year>
<gdppc>13600</gdppc>
<neighbor name="Costa Rica" direction="W"/>
<neighbor name="Colombia" direction="E"/>
</country>
</data>
sample.xml
>>> import xml.etree.ElementTree as et
>>> tree = et.ElementTree(file='sample.xml')
>>> root = tree.getroot()
>>> root.tag
'data'
>>> for child in root:
print('tag:',child.tag, 'attributes:',child.attrib)
for grandchild in child:
print('\ttag:',grandchild.tag,'attributes:',grandchild.attrib) tag: country attributes: {'name': 'Liechtenstein'}
tag: rank attributes: {}
tag: year attributes: {}
tag: gdppc attributes: {}
tag: neighbor attributes: {'name': 'Austria', 'direction': 'E'}
tag: neighbor attributes: {'name': 'Switzerland', 'direction': 'W'}
tag: country attributes: {'name': 'Singapore'}
tag: rank attributes: {}
tag: year attributes: {}
tag: gdppc attributes: {}
tag: neighbor attributes: {'name': 'Malaysia', 'direction': 'N'}
tag: country attributes: {'name': 'Panama'}
tag: rank attributes: {}
tag: year attributes: {}
tag: gdppc attributes: {}
tag: neighbor attributes: {'name': 'Costa Rica', 'direction': 'W'}
tag: neighbor attributes: {'name': 'Colombia', 'direction': 'E'} >>> len(root)
3
>>> len(root[0])
5
>>> len(root[1])
4
>>>
JSON/pickle数据处理
python中使用json模块把复杂结构的数据转换成JSON字符串,或者把JSON字符串转换成数据。
一个典型的复杂结构的数据如下:
>>> menu = \
{
"breakfast": {
"hours": "7-11",
"items": {
"breakfast burritos": "$6.00",
"pancakes": "$4.00"
}
},
"lunch" : {
"hours": "11-3",
"items": {
"hamburger": "$5.00"
}
},
"dinner": {
"hours": "3-10",
"items": {
"spaghetti": "$8.00"
}
}
}
menu
1 转换成JSON字符串
使用dumps()将menu转换成JSON格式的字符串如下:
>>> import json
>>> menu_json = json.dumps(menu)
>>> menu_json
'{"dinner": {"items": {"spaghetti": "$8.00"}, "hours": "3-10"}, "breakfast": {"items": {"pancakes": "$4.00", "breakfast burritos": "$6.00"}, "hours": "7-11"}, "lunch": {"items": {"hamburger": "$5.00"}, "hours": "11-3"}}'
>>>
更多json模块的用法参考官方文档。
2 转换成复杂结构的数据
使用loads()函数把JSON字符串转换成python的结构数据,如下:
>>> menu2 = json.loads(menu_json)
>>> menu2
{'dinner': {'items': {'spaghetti': '$8.00'}, 'hours': '3-10'}, 'breakfast': {'items': {'pancakes': '$4.00', 'breakfast burritos': '$6.00'}, 'hours': '7-11'}, 'lunch': {'items': {'hamburger': '$5.00'}, 'hours': '11-3'}}
>>> type(menu2)
<class 'dict'>
>>> type(menu_json)
<class 'str'>
>>>
pickle的功能类似于json,也可以将python中的结构化的数据序列化(转换为字符串)。其优点是可以序列化更多的python中的数据对象,比如datetime对象。其缺点是只能在python中使用,json的话其他语言也支持。
例子如下:
>>> import json
>>> import pickle
>>> import datetime
>>> now1 = datetime.datetime.utcnow()
>>> jsoned = json.dumps(now1)
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<pyshell#89>", line 1, in <module>
jsoned = json.dumps(now1)
File "C:\Python35-32\lib\json\__init__.py", line 230, in dumps
return _default_encoder.encode(obj)
File "C:\Python35-32\lib\json\encoder.py", line 199, in encode
chunks = self.iterencode(o, _one_shot=True)
File "C:\Python35-32\lib\json\encoder.py", line 257, in iterencode
return _iterencode(o, 0)
File "C:\Python35-32\lib\json\encoder.py", line 180, in default
raise TypeError(repr(o) + " is not JSON serializable")
TypeError: datetime.datetime(2016, 11, 5, 7, 22, 20, 551139) is not JSON serializable
>>> pickled = pickle.dumps(now1)
>>> now1
datetime.datetime(2016, 11, 5, 7, 22, 20, 551139)
>>> now2 = pickle.loads(pickled)
>>> now2
datetime.datetime(2016, 11, 5, 7, 22, 20, 551139)
>>>
YAML文件处理
python使用第三方模块pyyaml来操作数据。官方文档点这里。
一个典型的YAML文件如下:
name:
first: James
last: McIntyre
dates:
birth: 1828-05-25
death: 1906-03-31
details:
bearded: true
themes: [cheese, Canada]
books:
url: http://www.gutenberg.org/files/36068/36068-h/36068-h.htm
poems:
- title: 'Motto'
text: |
Politeness, perseverance and pluck,
To their possessor will bring good luck.
- title: 'Canadian Charms'
text: |
Here industry is not in vain,
For we have bounteous crops of grain,
And you behold on every field
Of grass and roots abundant yield,
But after all the greatest charm
Is the snug home upon the farm,
And stone walls now keep cattle warm.
>>> with open('sample.yml','rt') as y_file:
text = y_file.read()
>>> data = yaml.load(text)
>>> data['poems']
[{'text': 'Politeness, perseverance and pluck,\nTo their possessor will bring good luck.\n', 'title': 'Motto'}, {'text': 'Here industry is not in vain,\nFor we have bounteous crops of grain,\nAnd you behold on every field\nOf grass and roots abundant yield,\nBut after all the greatest charm\nIs the snug home upon the farm,\nAnd stone walls now keep cattle warm.', 'title': 'Canadian Charms'}]
>>> data['details']
{'bearded': True, 'themes': ['cheese', 'Canada']}
>>> data['poems'][0]
{'text': 'Politeness, perseverance and pluck,\nTo their possessor will bring good luck.\n', 'title': 'Motto'}
>>>
配置文件处理
Python中可以使用configparser模块来处理如下格式的配置文件。
[DEFAULT]
ServerAliveInterval = 45
Compression = yes
CompressionLevel = 9
ForwardX11 = yes [bitbucket.org]
User = hg [topsecret.server.com]
Port = 50022
ForwardX11 = no
>>> import configparser
>>> config = configparser.ConfigParser()
>>> config['DEFAULT'] = {'ServerAliveInterval': '',
... 'Compression': 'yes',
... 'CompressionLevel': ''}
>>> config['bitbucket.org'] = {}
>>> config['bitbucket.org']['User'] = 'hg'
>>> config['topsecret.server.com'] = {}
>>> topsecret = config['topsecret.server.com']
>>> topsecret['Port'] = '' # mutates the parser
>>> topsecret['ForwardX11'] = 'no' # same here
>>> config['DEFAULT']['ForwardX11'] = 'yes'
>>> with open('example.ini', 'w') as configfile:
... config.write(configfile)
...
更多configeparser的内容参考官方文档。
Excel表格处理
处理Excel文件的模块有很多,例如openpyxl, xlsxwriter, xlrd等。详细请参考官方文档。
Python学习之文件操作(二)的更多相关文章
- python学习笔记:文件操作和集合(转)
转自:http://www.nnzhp.cn/article/16/ 这篇博客来说一下python对文件的操作. 对文件的操作分三步: 1.打开文件获取文件的句柄,句柄就理解为这个文件 2.通过文件句 ...
- python学习日记(文件操作)
文件操作概述 计算机系统分为:操作系统,计算机硬件,应用程序. 我们用python或其他语言编写的应用程序若想要把数据永久保存下来,必须要保存于硬盘中,这就涉及到应用程序要操作硬件,众所周知,应用程序 ...
- python学习总结---文件操作
# 文件操作 ### 目录管理(os) - 示例 ```python # 执行系统命令 # 清屏 # os.system('cls') # 调出计算器 # os.system('calc') # 查看 ...
- 03 python学习笔记-文件操作(三)
本文内容主要包括以下方面: 1. 文件操作基本认识2. 只读(r, rb)3. 只写(w, wb)4. 追加(a, ab)5. r+读写6. w+写读7. a+写读(追加写读)8. 文件的修改 一.文 ...
- python学习day8 文件操作(深度学习)
文件操作 (day7内容扩展) 1 文件基本操作 obj = open('路径',mode='模式',encoding='编码')obj.write()obj.read()obj.close() 2 ...
- Python学习 :文件操作
文件基本操作流程: 一. 创建文件对象 二. 调用文件方法进行操作 三. 关闭文件(注意:只有在关闭文件后,才会写入数据) fh = open('李白诗句','w',encoding='utf-8') ...
- python 学习分享-文件操作篇
文件操作 f_open=open('*.txt','r')#以只读的方式(r)打开*.txt文件(需要与py文件在同一目录下,如果不同目录,需写全路径) f_open.close()#关闭文件 打开文 ...
- Python学习笔记——文件操作
python中,一切皆对象. 一.文件操作流程 (1)打开文件,得到一个文件句柄(对象),赋给一个对象: (2)通过文件句柄对文件进行操作: (3)关闭文件. 文件对象f通过open()函数来创建 ...
- Python学习之==>文件操作
1.打开文件的模式 r,只读模式(默认)[不可写:文件不存在,会报错] w,只写模式[不可读:不存在则创建:存在则删除内容] a,追加模式[不可读:不存在则创建:存在则追加内容] r+,读写模式[可读 ...
随机推荐
- Python字典列表字段重组形成新的字典
最近遇到这样一个需求,需要将字典列表中的字段进行重组,形成一个新的字典.举个例子吧: l1 = [{"x": 22, "y": 22, "demand ...
- Spring-Security (补充)
一.配置静态资源过滤 直接在xml中配置即可 <!-- 配置静态资源过滤 --> <security:http security="none" pattern=& ...
- Windows内存管理(1)--分配内核内存 和 使用链表
1. 分配内核内存 Windows驱动程序使用的内存资源非常珍贵,分配内存时要尽量节约.和应用程序一样,局部变量是存放在栈空间中的.但栈空间不会像应用程序那么大,所以驱动程序不适合递归调用或 ...
- spring boot jpa没有自动生成表的原因——加上@Entity
别人的项目弄了好久,竟然是忘记加注解,当然配置文件还是要配置jpa的,pom也要依赖jpa. @Entity jpa: hibernate: ddl-auto: update show-sql: tr ...
- hexo next主题深度优化(四),自定义一个share功能,share.js。
文章目录 背景: 开始: 引入资源: 代码 关键的一步 附:方便学习的小demo 一次成功后还出现上面的bug 结束 2018.12.23发现bug(读者可忽略) 个人博客:https://mmmmm ...
- .net与C#
一..net包含什么? 1.包含庞大的代码库,分为多个模块,可以自主选择 2.定义了基本的类型,被称为通用类型系统(CTS,common type system): 3.包含.NET公共语言运行库(C ...
- Android Telephony分析(二) ---- RegistrantList详解
前言 本文主要讲解RegistrantList的原理,以及如何快速分析RegistrantList相关的代码流程.在Telephony模块中,在RIL.Tracker(ServiceStateTrac ...
- 实现solr热词排行榜
现在有业务场景,要求实现词库里面,最新,最热的词并显示,点击热词后可以进入相关信息的文章或者句子 热词的显示频率12小时更新一次. 实现思路: 实现步骤:
- centos yum install 找不到软件包
yum install epel-release 然后再试试yum install 其他安装包
- Oracle SQL外连接
SQL提供了多种类型的连接方式,它们之间的区别在于:从相互交叠的不同数据集合中选择用于连接的行时所采用的方法不同.连接类型 定义内连接 只连接匹配的行左外连接 ...
