PCL超体聚类
超体聚类是一种图像的分割方法。
超体(supervoxel)是一种集合,集合的元素是“体”。与体素滤波器中的体类似,其本质是一个个的小方块。与大部分的分割手段不同,超体聚 类的目的并不是分割出某种特定物体,超体是对点云实施过分割(over segmentation),将场景点云化成很多小块,并研究每个小块之间的关系。这种将更小单元合并的分割思路已经出现了有些年份了,在图像分割中,像 素聚类形成超像素,以超像素关系来理解图像已经广为研究。本质上这种方法是对局部的一种总结,纹理,材质,颜色类似的部分会被自动的分割成一块,有利于后 续识别工作。比如对人的识别,如果能将头发,面部,四肢,躯干分开,则能更好的对各种姿态,性别的人进行识别。
点云和图像不一样,其不存在像素邻接关系。所以,超体聚类之前,必须以八叉树对点云进行划分,获得不同点团之间的邻接关系。与图像相似点云的邻接关系也有很多,如面邻接,线邻接,点邻接。
超体聚类实际上是一种特殊的区域生长算法,和无限制的生长不同,超体聚类首先需要规律的布置区域生长“晶核”。晶核在空间中实际上是均匀分布的,并指定晶核距离(Rseed)。再指定粒子距离(Rvoxel)。再指定最小晶粒(MOV),过小的晶粒需要融入最近的大晶粒。
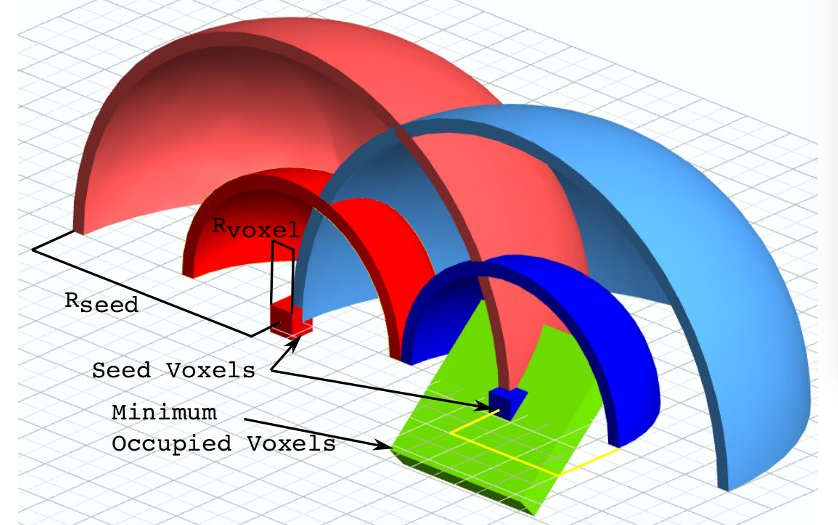
这些基本参数在接下来的参数中会有设置
#include <pcl/console/parse.h>
#include <pcl/point_cloud.h>
#include <pcl/point_types.h>
#include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h>
#include <pcl/visualization/pcl_visualizer.h>
#include <pcl/segmentation/supervoxel_clustering.h> //VTK include needed for drawing graph lines
#include <vtkPolyLine.h> // 数据类型
typedef pcl::PointXYZRGBA PointT;
typedef pcl::PointCloud<PointT> PointCloudT;
typedef pcl::PointNormal PointNT;
typedef pcl::PointCloud<PointNT> PointNCloudT;
typedef pcl::PointXYZL PointLT;
typedef pcl::PointCloud<PointLT> PointLCloudT; //可视化
void addSupervoxelConnectionsToViewer (PointT &supervoxel_center,
PointCloudT &adjacent_supervoxel_centers,
std::string supervoxel_name,
boost::shared_ptr<pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer> & viewer); int
main (int argc, char ** argv)
{
//解析命令行
if (argc < )
{
pcl::console::print_error ("Syntax is: %s <pcd-file> \n "
"--NT Dsables the single cloud transform \n"
"-v <voxel resolution>\n-s <seed resolution>\n"
"-c <color weight> \n-z <spatial weight> \n"
"-n <normal_weight>\n", argv[]);
return ();
} //打开点云
PointCloudT::Ptr cloud = boost::shared_ptr <PointCloudT> (new PointCloudT ());
pcl::console::print_highlight ("Loading point cloud...\n");
if (pcl::io::loadPCDFile<PointT> (argv[], *cloud))
{
pcl::console::print_error ("Error loading cloud file!\n");
return ();
} bool disable_transform = pcl::console::find_switch (argc, argv, "--NT"); float voxel_resolution = 0.008f; //分辨率
bool voxel_res_specified = pcl::console::find_switch (argc, argv, "-v");
if (voxel_res_specified)
pcl::console::parse (argc, argv, "-v", voxel_resolution); float seed_resolution = 0.1f;
bool seed_res_specified = pcl::console::find_switch (argc, argv, "-s");
if (seed_res_specified)
pcl::console::parse (argc, argv, "-s", seed_resolution); float color_importance = 0.2f;
if (pcl::console::find_switch (argc, argv, "-c"))
pcl::console::parse (argc, argv, "-c", color_importance); float spatial_importance = 0.4f;
if (pcl::console::find_switch (argc, argv, "-z"))
pcl::console::parse (argc, argv, "-z", spatial_importance); float normal_importance = 1.0f;
if (pcl::console::find_switch (argc, argv, "-n"))
pcl::console::parse (argc, argv, "-n", normal_importance); //如何使用SupervoxelClustering函数
pcl::SupervoxelClustering<PointT> super (voxel_resolution, seed_resolution);
if (disable_transform)//如果设置的是参数--NT 就用默认的参数
super.setUseSingleCameraTransform (false);
super.setInputCloud (cloud);
super.setColorImportance (color_importance); //0.2f
super.setSpatialImportance (spatial_importance); //0.4f
super.setNormalImportance (normal_importance); //1.0f std::map <uint32_t, pcl::Supervoxel<PointT>::Ptr > supervoxel_clusters; pcl::console::print_highlight ("Extracting supervoxels!\n");
super.extract (supervoxel_clusters);
pcl::console::print_info ("Found %d supervoxels\n", supervoxel_clusters.size ()); boost::shared_ptr<pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer> viewer (new pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer ("3D Viewer"));
viewer->setBackgroundColor (, , ); PointCloudT::Ptr voxel_centroid_cloud = super.getVoxelCentroidCloud ();//获得体素中心的点云
viewer->addPointCloud (voxel_centroid_cloud, "voxel centroids");
viewer->setPointCloudRenderingProperties (pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_POINT_SIZE,2.0, "voxel centroids"); //渲染点云
viewer->setPointCloudRenderingProperties (pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_OPACITY,0.95, "voxel centroids"); PointLCloudT::Ptr labeled_voxel_cloud = super.getLabeledVoxelCloud ();
viewer->addPointCloud (labeled_voxel_cloud, "labeled voxels");
viewer->setPointCloudRenderingProperties (pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_OPACITY,0.8, "labeled voxels"); PointNCloudT::Ptr sv_normal_cloud = super.makeSupervoxelNormalCloud (supervoxel_clusters); //We have this disabled so graph is easy to see, uncomment to see supervoxel normals
//viewer->addPointCloudNormals<PointNormal> (sv_normal_cloud,1,0.05f, "supervoxel_normals"); pcl::console::print_highlight ("Getting supervoxel adjacency\n"); std::multimap<uint32_t, uint32_t> supervoxel_adjacency;
super.getSupervoxelAdjacency (supervoxel_adjacency);
//To make a graph of the supervoxel adjacency, we need to iterate through the supervoxel adjacency multimap
//为了使整个超体形成衣服图,我们需要遍历超体的每个临近的个体
std::multimap<uint32_t,uint32_t>::iterator label_itr = supervoxel_adjacency.begin ();
for ( ; label_itr != supervoxel_adjacency.end (); )
{
//First get the label
uint32_t supervoxel_label = label_itr->first;
//Now get the supervoxel corresponding to the label
pcl::Supervoxel<PointT>::Ptr supervoxel = supervoxel_clusters.at (supervoxel_label); //Now we need to iterate through the adjacent supervoxels and make a point cloud of them
PointCloudT adjacent_supervoxel_centers;
std::multimap<uint32_t,uint32_t>::iterator adjacent_itr = supervoxel_adjacency.equal_range (supervoxel_label).first;
for ( ; adjacent_itr!=supervoxel_adjacency.equal_range (supervoxel_label).second; ++adjacent_itr)
{
pcl::Supervoxel<PointT>::Ptr neighbor_supervoxel = supervoxel_clusters.at (adjacent_itr->second);
adjacent_supervoxel_centers.push_back (neighbor_supervoxel->centroid_);
}
//Now we make a name for this polygon
std::stringstream ss;
ss << "supervoxel_" << supervoxel_label;
//This function is shown below, but is beyond the scope of this tutorial - basically it just generates a "star" polygon mesh from the points given
//从给定的点云中生成一个星型的多边形,
addSupervoxelConnectionsToViewer (supervoxel->centroid_, adjacent_supervoxel_centers, ss.str (), viewer);
//Move iterator forward to next label
label_itr = supervoxel_adjacency.upper_bound (supervoxel_label);
} while (!viewer->wasStopped ())
{
viewer->spinOnce ();
}
return ();
} //VTK可视化构成的聚类图
void
addSupervoxelConnectionsToViewer (PointT &supervoxel_center,
PointCloudT &adjacent_supervoxel_centers,
std::string supervoxel_name,
boost::shared_ptr<pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer> & viewer)
{
vtkSmartPointer<vtkPoints> points = vtkSmartPointer<vtkPoints>::New ();
vtkSmartPointer<vtkCellArray> cells = vtkSmartPointer<vtkCellArray>::New ();
vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyLine> polyLine = vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyLine>::New (); //Iterate through all adjacent points, and add a center point to adjacent point pair
PointCloudT::iterator adjacent_itr = adjacent_supervoxel_centers.begin ();
for ( ; adjacent_itr != adjacent_supervoxel_centers.end (); ++adjacent_itr)
{
points->InsertNextPoint (supervoxel_center.data);
points->InsertNextPoint (adjacent_itr->data);
}
// Create a polydata to store everything in
vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyData> polyData = vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyData>::New ();
// Add the points to the dataset
polyData->SetPoints (points);
polyLine->GetPointIds ()->SetNumberOfIds(points->GetNumberOfPoints ());
for(unsigned int i = ; i < points->GetNumberOfPoints (); i++)
polyLine->GetPointIds ()->SetId (i,i);
cells->InsertNextCell (polyLine);
// Add the lines to the dataset
polyData->SetLines (cells);
viewer->addModelFromPolyData (polyData,supervoxel_name);
}
可执行文件生成后的图像显示如下
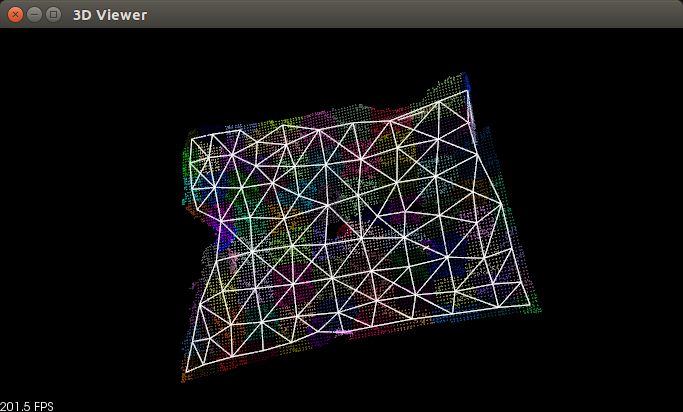
当然也可以自己设定参数生成自己想要的效果。同时在不同的场景中,使用的参数是十分重要的,
只是先了解超体的概念,如果想应用到实际的应用中,还需要很多其他的知识 ,所以这里只是基本的学习
有兴趣这关注我的微信公众号

PCL超体聚类的更多相关文章
- PCL—低层次视觉—点云分割(超体聚类)
1.超体聚类——一种来自图像的分割方法 超体(supervoxel)是一种集合,集合的元素是“体”.与体素滤波器中的体类似,其本质是一个个的小方块.与之前提到的所有分割手段不同,超体聚类的目的并不是分 ...
- PCL—点云分割(超体聚类) 低层次点云处理
博客转载自:http://www.cnblogs.com/ironstark/p/5013968.html 1.超体聚类——一种来自图像的分割方法 超体(supervoxel)是一种集合,集合的元素是 ...
- PCL—低层次视觉—点云分割(基于凹凸性)
1.图像分割的两条思路 场景分割时机器视觉中的重要任务,尤其对家庭机器人而言,优秀的场景分割算法是实现复杂功能的基础.但是大家搞了几十年也还没搞定——不是我说的,是接下来要介绍的这篇论文说的.图像分割 ...
- PCL—点云分割(基于凹凸性) 低层次点云处理
博客转载自:http://www.cnblogs.com/ironstark/p/5027269.html 1.图像分割的两条思路 场景分割时机器视觉中的重要任务,尤其对家庭机器人而言,优秀的场景分割 ...
- 基于传统方法点云分割以及PCL中分割模块
之前在微信公众号中更新了以下几个章节 1,如何学习PCL以及一些基础的知识 2,PCL中IO口以及common模块的介绍 3,PCL中常用的两种数据结构KDtree以及Octree树的介绍 ...
- [PCL]3 欧式距离分类EuclideanClusterExtraction
EuclideanClusterExtraction这个名字起的很奇怪,欧式距离聚类这个该如何理解?欧式距离只是一种距离测度的方法呀!有了一个Cluster在里面,我以为是某一种聚类算法,层次聚类?k ...
- PCL—低层次视觉—点云滤波(基于点云频率)
1.点云的频率 今天在阅读分割有关的文献时,惊喜的发现,点云和图像一样,有可能也存在频率的概念.但这个概念并未在文献中出现也未被使用,谨在本博文中滥用一下“高频”一词.点云表达的是三维空间中的一种信息 ...
- PCL—低层次视觉—点云分割(邻近信息)
分割给人最直观的影响大概就是邻居和我不一样.比如某条界线这边是中华文明,界线那边是西方文,最简单的分割方式就是在边界上找些居民问:"小伙子,你到底能不能上油管啊?”.然后把能上油管的居民坐标 ...
- PCL点云分割(3)
(1)Euclidean分割 欧几里德分割法是最简单的.检查两点之间的距离.如果小于阈值,则两者被认为属于同一簇.它的工作原理就像一个洪水填充算法:在点云中的一个点被“标记”则表示为选择在一个的集群中 ...
随机推荐
- rational rose 2003完整汉化版 win7版
下载链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1InpgNS_1-Rigw4fE3OX1Eg 软件介绍 Rational Rose 2003破解版是一款基于UML的可视化建模工具.可用于软 ...
- linux环境下matlab连接mysql
因为matlab是基于java的,但是原生的matlab是没有jdbc的,这是一个java的mysql connection. 只有matlab有这个包,才能正确的连接mysql. 1.在http:/ ...
- Matlab中classperf对象各属性解释[原创]
1.ClassLabels:类型标识.第一个label作为pos,第二次label作为neg. 2.GroundTruth:各次实验的观察值,也就是真实值. 3.ValidationCounter: ...
- Atitit it行业图像处理行业软件行业感到到迷茫的三大原因和解决方案
Atitit it行业图像处理行业软件行业感到到迷茫的三大原因和解决方案 1. 迷茫的原因最大原因是未知1 1.1. 我在哪里??自己的定位,1 1.2. 正确方向是什么??1 1.3. 虽然找到方向 ...
- Java 格式化数字
; ){ DecimalFormat df = "); String xs = df.format(x); System.out.println(xs); x++; } 将 1 格式化为 0 ...
- 记一次docker问题定位(perf,iostat等性能分析)
背景 最近参与的项目是基于 OpenStack 提供容器管理能力,丰富公司 IaaS 平台的能力.日常主要工作就是在开源的 novadocker 项目(开源社区已停止开发)基础上进行增强,与公司的其他 ...
- 菜鸟调错(五)——jetty运行时无法保存文件
背景交代: 上一篇博客写的是用jetty和Maven做开发.测试.在使用的过程中遇到一个小问题,就是在jetty启动以后,修改了jsp.xml等文件无法保存. 错误信息: 解决方案: 到Maven库( ...
- CAS无锁实现原理以及ABA问题
CAS(比较与交换,Compare and swap) 是一种有名的无锁算法.无锁编程,即不使用锁的情况下实现多线程之间的变量同步,也就是在没有线程被阻塞的情况下实现变量的同步,所以也叫非阻塞同步(N ...
- 【转】MySQL中information_schema是什么
大家在安装或使用MYSQL时,会发现除了自己安装的数据库以外,还有一个information_schema数据库. information_schema数据库是做什么用的呢,使用WordPress博客 ...
- opencv项目报错_pFirstBlock==pHead解决办法
备注: 我上次遇到这个问题的原因是项目设置为MTd导致的 OpenCV是MTd的,我要是改成MDd就编译报错,所以不能采用把项目改为MDd的办法,只能把OpenCV重新编译为MDd的,下载CMAKE, ...
