CentOS 7.x and RHEL 7.x Install qemu-kvm
ref: https://www.linuxtechi.com/install-kvm-hypervisor-on-centos-7-and-rhel-7/
https://www.thegeekstuff.com/2014/10/linux-kvm-create-guest-vm/
KVM is an open source hardware virtualization software through which we can create and run multiple Linux based and windows based virtual machines simultaneously. KVM is known as Kernel based Virtual Machine because when we install KVM package then KVM module is loaded into the current kernel and turns our Linux machine into a hypervisor.
In this post first we will demonstrate how we can install KVM hypervisor on CentOS 7.x and RHEL 7.x and then we will try to install virtual machines.
Before proceeding KVM installation, let’s check whether your system’s CPU supports Hardware Virtualization.
Run the beneath command from the console.
[root@linuxtechi ~]# grep -E '(vmx|svm)' /proc/cpuinfo
We should get the word either vmx or svm in the output, otherwise CPU doesn’t support virtualization.
Step:1 Install KVM and its associate packages
Run the following yum command to install KVM and its associated packages.
[root@linuxtechi ~]# yum install qemu-kvm qemu-img virt-manager libvirt libvirt-python libvirt-client virt-install virt-viewer bridge-utils
Start and enable the libvirtd service
[root@linuxtechi ~]# systemctl start libvirtd
[root@linuxtechi ~]# systemctl enable libvirtd
Run the beneath command to check whether KVM module is loaded or not
[root@linuxtechi ~]# lsmod | grep kvm
kvm_intel 162153 0
kvm 525409 1 kvm_intel
[root@linuxtechi ~]#
In Case you have Minimal CentOS 7 and RHEL 7 installation , then virt-manger will not start for that you need to install x-window package.
[root@linuxtechi ~]# yum install "@X Window System" xorg-x11-xauth xorg-x11-fonts-* xorg-x11-utils -y
Reboot the Server and then try to start virt manager.
Step:2 Start the Virt Manager
Virt Manager is a graphical tool through which we can install and manage virtual machines. To start the virt manager type the ‘virt-manager‘ command from the terminal.
[root@linuxtechi ~]# virt-manager
Step:3 Configure Bridge Interface
Before Start creating VMs , let’s first create the bridge interface. Bridge interface is required if you want to access virtual machines from outside of your hypervisor network.
[root@linuxtechi ~]# cd /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/
[root@linuxtechi network-scripts]# cp ifcfg-eno49 ifcfg-br0
[root@linuxtechi network-scripts]#
Edit the Interface file and set followings:
[root@linuxtechi network-scripts]# vi ifcfg-eno49
TYPE=Ethernet
BOOTPROTO=static
DEVICE=eno49
ONBOOT=yes
BRIDGE=br0
Edit the Bridge file (ifcfg-br0) and set the followings:
[root@linuxtechi network-scripts]# vi ifcfg-br0
TYPE=Bridge
BOOTPROTO=static
DEVICE=br0
ONBOOT=yes
IPADDR=192.168.10.21
NETMASK=255.255.255.0
GATEWAY=192.168.10.1
DNS1=192.168.10.11
Replace the IP address and DNS server details as per your setup.
Restart the network Service to enable the bridge interface.
[root@linuxtechi ~]# systemctl restart network
[root@linuxtechi ~]#
Check the Bridge interface using below command :
[root@linuxtechi ~]# ip addr show br0
Step:4 Start Creating Virtual Machines.
Now Create Virtual Machine either from the command line using ‘virt-install‘ command or from GUI (virt-manager )
Let’s Create a virtual machine of “Windows Server 2012 R2” using virt-manager.
Start the “virt-manager”
Go to the File Option, click on “New Virtual Machine”
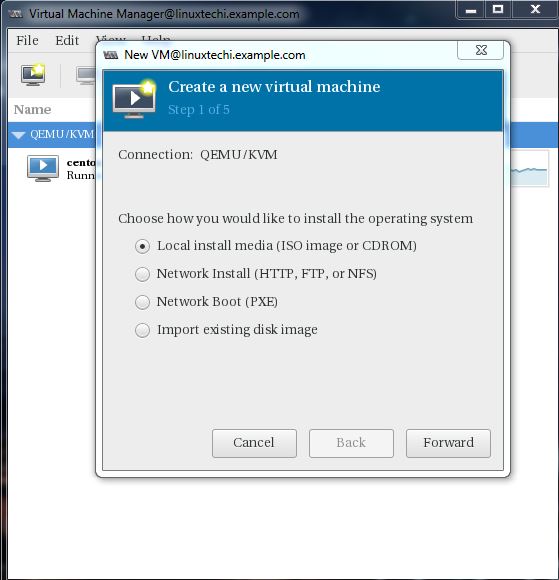
We will be using ISO file as installation media. In the next step Specify the path of ISO file.
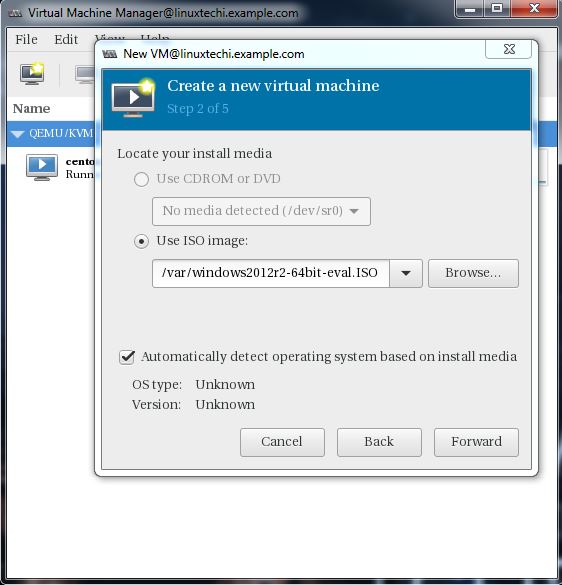
Click on Forward.
Specify the Compute Resources : RAM and CPU as per your setup.
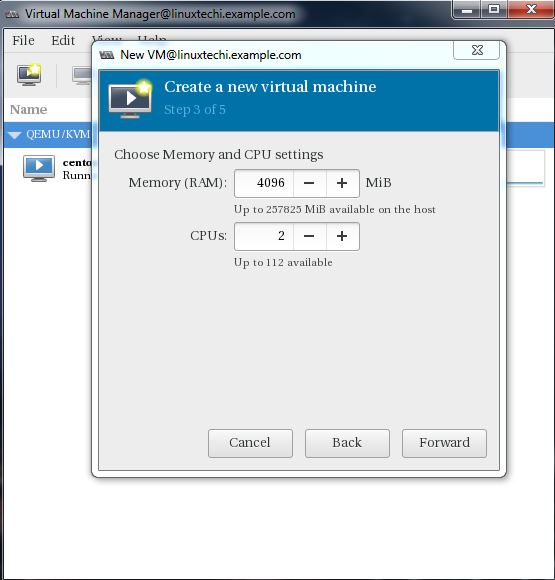
Click on Forward to proceed further.
Specify the storage Size of Virtual Machine, In my case I am using 25G.
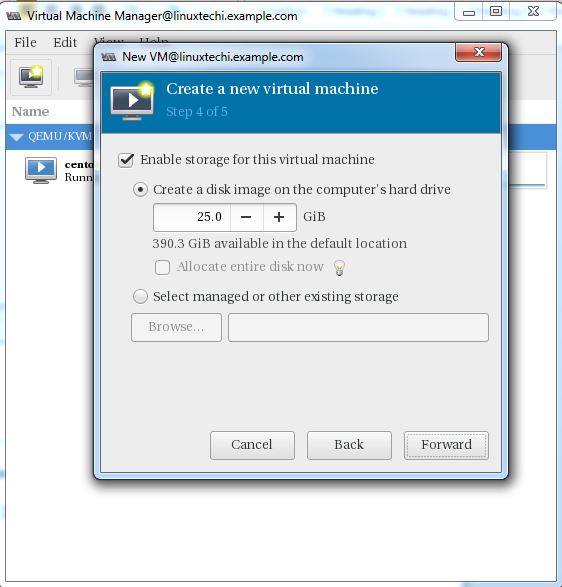
In the Next step Specify the Name of Virtual Machine and select network as ‘ Bridge bro’
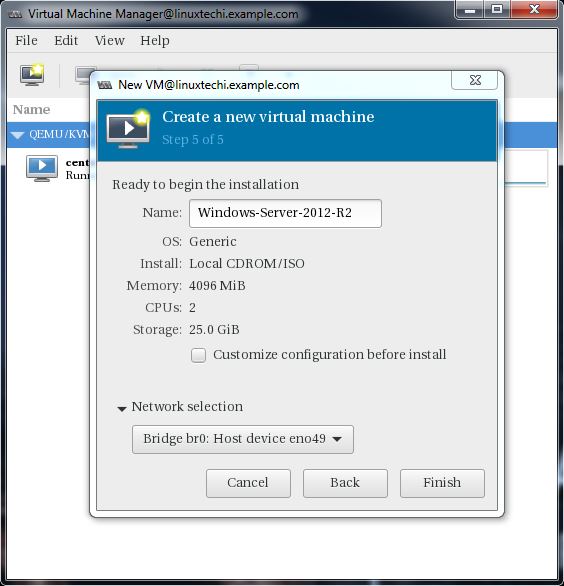
Click on Finish to start the installation.
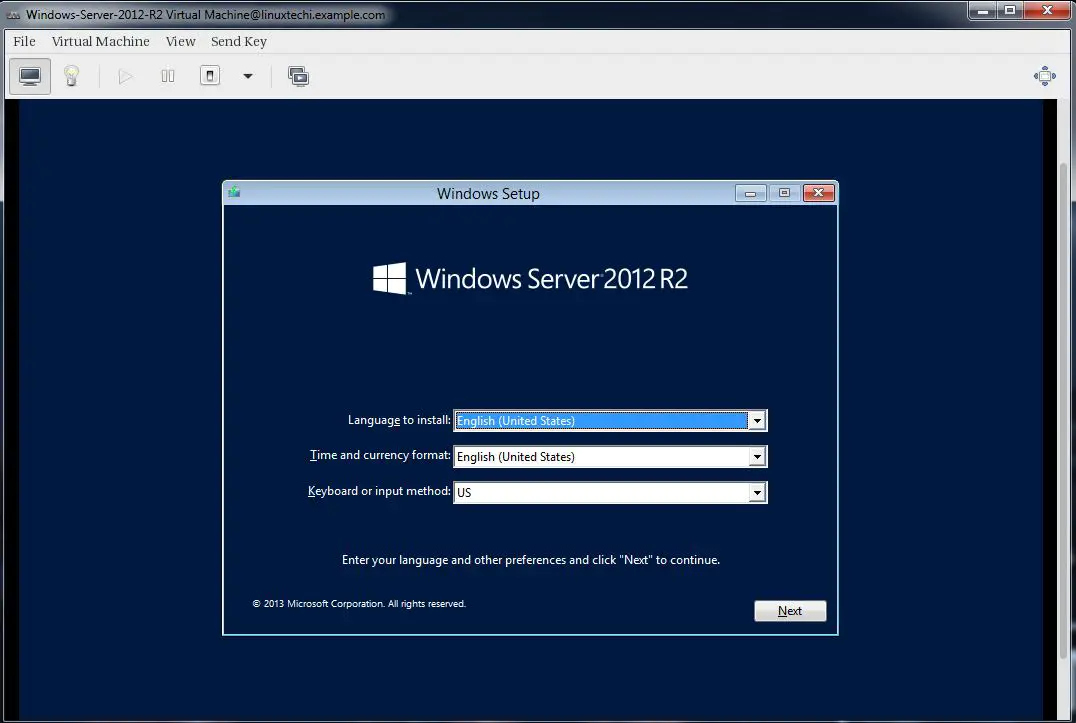
Follow the screen instructions and complete the installation.
Creating a virtual Machine from Command Line:
Virtual Machines can be created from the console as well using ‘virt-install’ command. In the following example i going to virtual machine of Ubuntu 16.04 LTS.
[root@linuxtechi ~]# virt-install --name=Ubuntu-16-04 --file=/var/lib/libvirt/images/ubuntu16-04.dsk --file-size=20 --nonsparse --graphics spice --vcpus=2 --ram=2048 --cdrom=ubuntu-16.04-server-amd64.iso --network bridge=br0 --os-type=linux --os-variant=generic
Starting install...
Allocating 'ubuntu16-04.dsk' | 20 GB 00:00:00
Creating domain...
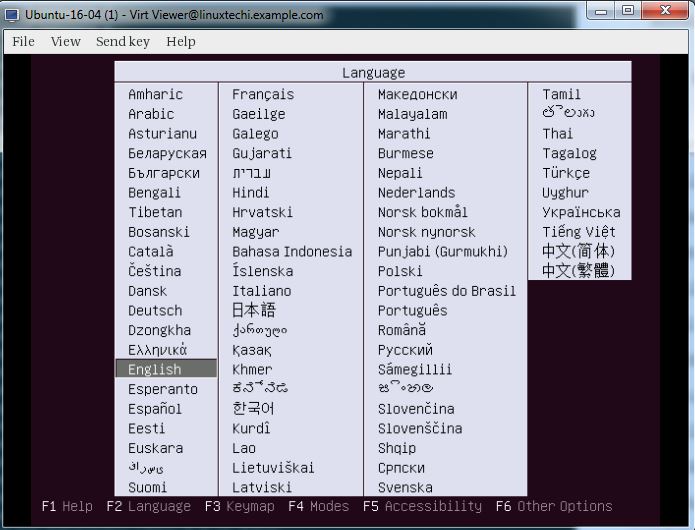
Follow the instruction now and complete the installation.
In the above ‘virt-install’ command we have used following options :
- –name = <Name of the Virtual Machine>
- –file = <Location where our virtual machine disk file will be stored >
- –file-size = < Size of the Virtual Machine, in my case it is 20GB >
- –nonsparse = < Allocate the whole storage while creating>
- –graphics = < Specify the graphical tool for interactive installation, in above example I am using spice >
- –vcpu = < Number of virtual CPU for the Machine >
- –ram = < RAM size for the virtual Machine >
- –cdrom = < Virtual CD ROM which specify the installation media like ISO file >
- –network = < it is used to specify which network we will use for the virtual machine, in this example I am bridge interface>
- –os-type = < Operating system type like linux and window>
- –os-variant= <KVM maintains the OS variants like ‘fedora18′, ‘rhel6’ and ‘winxp’ , this option is optional and if you not sure about OS variant you can mentioned it as generic>
Once the Installation is completed we can access the Virtual Machine console from ‘virt-manager‘ as shown below.
That’s it, basic installation and configuration of KVM hypervisor is completed.
CentOS 7.x and RHEL 7.x Install qemu-kvm的更多相关文章
- 如何在 CentOS 7 / RHEL 7 终端服务器上安装 KVM
如何在 CnetOS 7 或 RHEL 7(Red Hat 企业版 Linux)服务器上安装和配置 KVM(基于内核的虚拟机)?如何在 CentOS 7 上设置 KVM 并使用云镜像 / cloud- ...
- CentOS中实现与Ubuntu下apt-get install build-essential功能类似的命令
CentOS中实现与Ubuntu下apt-get install build-essential功能类似的命令 在Ubuntu中安装完系统后,可以直接使用apt-get install build-e ...
- [RPM,YUM]RHEL Centos mount local source / RHEL CentOS挂载本地源
RHEL: 使用YUM安装Oracle必要软件包,将操作系统ISO文件“rhel-server-6.5-x86_64.iso”分别上传至两个节点主机“/root”目录,以root用户登录,执行以下命令 ...
- CentOS 6.5/6.6 安装(install)mysql 5.7 最完整版教程
Step1: 检测系统是否自带安装mysql # yum list installed | grep mysql Step2: 删除系统自带的mysql及其依赖命令: # yum -y remove ...
- vm安装centos后unknown host问题和yum install安装不成功问题
网上差了很多说要在vi /etc/sysconfig/network新增GATEWAY=192.168.0.1 还有vi /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-et ...
- [qemu][cloud][centos][ovs][sdn] centos7安装高版本的qemu 以及 virtio/vhost/vhost-user咋回事
因为要搭建ovs-dpdk,所以需要vhost-user的qemu centos默认的qemu与qemu-kvm都不支持vhost-user,qemu最高版本是2.0.0, qemu-kvm最高版本是 ...
- CentOS 7下宿主机使用virsh console访问KVM的设置
在CentOS 6下要实现宿主机使用virsh console访问KVM可以说是非常麻烦,但这一问题在CentOS 7已经解决了,只需要两条命令在KVM下即可实现. 1.在KVM(客户机)下开机启动并 ...
- How to install 64-bit Google Chrome 28+ on 64-bit RHEL/CentOS 6 or 7
How to install 64-bit Google Chrome 28+ on 64-bit RHEL/CentOS 6 or 7 The problem Google developers s ...
- Install MySQL 5.7 on Fedora 25/24, CentOS/RHEL 7.3/6.8/5.11
MySQL is a relational database management system (RDBMS) that runs as a server providing multi-user ...
随机推荐
- 转:Zepto的使用以及注意事项
为什么选择Zepto.js的原因: zepto.js的语法借鉴并且兼容jQuery,会使用jquery就会使用Zepto.js.Zepto.js是移动端的js库.Zepto.js相当于PC端的jQue ...
- Day6 && Day7图论
并查集 A - How Many Answers Are Wrong 题意:已知区间[1,n],给出m组数据,即[l,r]区间内数据之和为s,求错误数据的数量. 拿到这道题,真的没思路,知道用并查集, ...
- monkey详解
Monkey是Android系统自带的一个命令行工具,用户主要是通过adb命令来启动Monkey,Monkey在运行时,会根据命令行参数的配置,生成伪随机事件流,并在Android设备上执行对应的测试 ...
- JQuery II
jQuery事件的绑定 <body> <button>点击1</button> <button>点击2</button> </body ...
- 04-再探JavaScript
一. DOM介绍 1. 什么是DOM? DOM:文档对象模型.DOM 为文档提供了结构化表示,并定义了如何通过脚本来访问文档结构. 目的其实就是为了能让js操作html元素而制定的一个规范. DOM就 ...
- 【AMAD】coconut -- 简单,优雅,pythonic的函数式编程语言
动机 简介 个人评分 动机 作者的话: 我喜欢函数式编程,我认为函数式编程提供了一个更自然的方式来思考问题,并且代码也更加优雅,易读.不过如果你看过前20个最受欢迎的编程语言,你会发现没有一个式函数式 ...
- flink部署
参考: https://ververica.cn/developers-resources/ #flink参数 https://blog.csdn.net/qq_35440040/article/de ...
- CentOS 7 配置 kcptun 实现网站加速
目的:shadowsocks+kcptun 实现vpn加速(shadowsocks,kcptun在同一台VPS上) 一.shadowsocks安装(参考 https://www.cnblogs.co ...
- python-redis-订阅和发布
发布:redishelper.py import redis class RedisHelper: def __init__(self): self.__conn = redis.Redis(host ...
- 初试spark java WordCount
初始环境:OS X 10.10.5 准备:boot2docker 进入boot2docker后安装 docker-spark 地址: https://github.com/sequenceiq/do ...
