【转】How-to: Enable User Authentication and Authorization in Apache HBase
With the default Apache HBase configuration, everyone is allowed to read from and write to all tables available in the system. For many enterprise setups, this kind of policy is unacceptable.
Administrators can set up firewalls that decide which machines are allowed to communicate with HBase. However, machines that can pass the firewall are still allowed to read from and write to all tables. This kind of mechanism is effective but insufficient because HBase still cannot differentiate between multiple users that use the same client machines, and there is still no granularity with regard to HBase table, column family, or column qualifier access.
In this post, we will discuss how Kerberos is used with Hadoop and HBase to provide User Authentication, and how HBase implements User Authorization to grant users permissions for particular actions on a specified set of data.
Secure HBase: Authentication & Authorization
A secure HBase aims to protect against sniffers, unauthenticated/unauthorized users and network-based attacks. It does not protect against authorized users who accidentally delete all the data.
HBase can be configured to provide User Authentication, which ensures that only authorized users can communicate with HBase. The authorization system is implemented at the RPC level, and is based on the Simple Authentication and Security Layer (SASL), which supports (among other authentication mechanisms) Kerberos. SASL allows authentication, encryption negotiation and/or message integrity verification on a per connection basis ( “hbase.rpc.protection” configuration property).
The next step after enabling User Authentication is to give an admin the ability to define a series of User Authorization rules that allow or deny particular actions. The Authorization system, also known as the Access Controller Coprocessor or Access Control List (ACL), is available from HBase 0.92 (CDH4) onward and gives the ability to define authorization policy (Read/Write/Create/Admin), with table/family/qualifier granularity, for a specified user.
Kerberos
Kerberos is a networked authentication protocol. It is designed to provide strong authentication for client/server applications by using secret-key cryptography. The Kerberos protocol uses strong cryptography (AES, 3DES, …) so that a client can prove its identity to a server (and vice versa) across an insecure network connection. After a client and server have used Kerberos to prove their identities, they can also encrypt all of their communications to assure privacy and data integrity as they go about their business.
Ticket exchange protocol
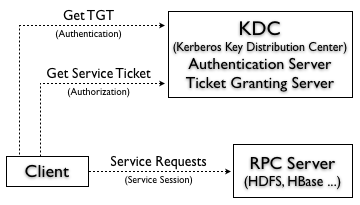
At a high level, to access a service using Kerberos, each client must follow three steps:
- Kerberos Authentication: The client authenticates itself to the Kerberos Authentication Server and receive a Ticket Granting Ticket (TGT).
- Kerberos Authorization: The client request a service ticket from the Ticket Granting Server, which issues a ticket and a session key if the client TGT sent with the request is valid.
- Service Request: The client uses the service ticket to authenticate itself to the server that is providing the service the client is using (e.g. HDFS, HBase, …)
HBase, HDFS, ZooKeeper SASL
Since HBase depends on HDFS and ZooKeeper, secure HBase relies on a secure HDFS and a secure ZooKeeper. This means that the HBase servers need to create a secure service session, as described above, to communicate with HDFS and ZooKeeper.
All the files written by HBase are stored in HDFS. As in Unix filesystems, the access control provided by HDFS is based on users, groups and permissions. All the files created by HBase have “hbase” as user, but this access control is based on the username provided by the system, and everyone that can access the machine is potentially able to “sudo” as the user “hbase”. Secure HDFS adds the authentication steps that guarantee that the “hbase” user is trusted.
ZooKeeper has an Access Control List (ACL) on each znode that allows read/write access to the users based on user information in a similar manner to HDFS.
HBase ACL
Now that our users are authenticated via Kerberos, we are sure that the username that we received is one of our trusted users. Sometimes this is not enough granularity – we want to control that a specified user is able to read or write a table. To do that, HBase provides an Authorization mechanism that allows restricted access for specified users.
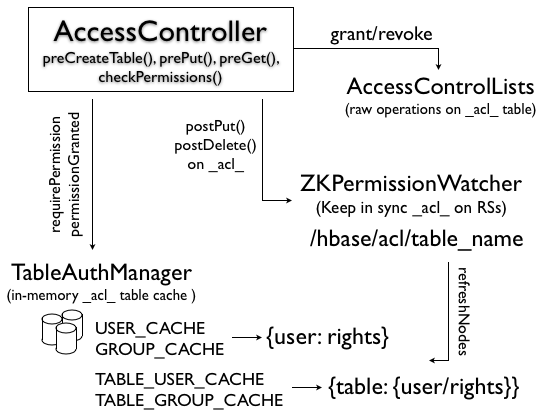
To enable this feature, you must enable the Access Controller coprocessor, by adding it to hbase-site.xml under the master and region server coprocessor classes. (See how to setup the HBase security configuration here.)
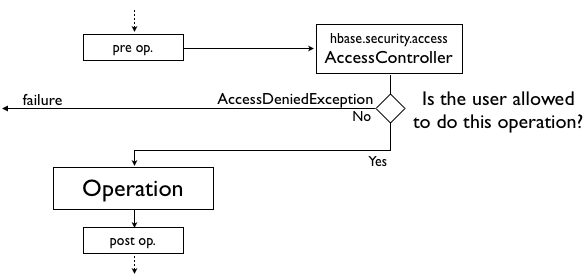
A coprocessor is code that runs inside each HBase Region Server and/or Master. It is able to intercept most operations (put, get, delete, …), and run arbitrary code before and/or after the operation is executed.
Using this ability to execute some code before each operation, the Access Controller coprocessor can check the user rights and decide if the user can or cannot execute the operation.
Rights management and _acl_ table
The HBase shell has a couple of commands that allows an admin to manage the user rights:
grant [table] [family] [qualifier]revoke [table] [family] [qualifier]
As you see, an admin has the ability to restrict user access based on the table schema:
- Give User-W only read rights to Table-X/Family-Y (
grant 'User-W', 'R', 'Table-X', 'Family-Y') - Give User-W the full read/write rights to Qualifier-Z (
grant 'User-W', 'RW', 'Table-X', 'Family-Y', 'Qualifier-Z')
An admin also has the ability to grant global rights, which operate at the cluster level, such as creating tables, balancing regions, shutting down the cluster and so on:
- Give User-W the ability to create tables (
grant 'User-W', 'C') - Give User-W the ability to manage the cluster (
grant 'User-W', 'A')
All the permissions are stored in a table created by the Access Controller coprocessor, called _acl_. The primary key of this table is the table name that you specify in the grant command. The _acl_ table has just one column family and each qualifier describes the granularity of rights for a particular table/user. The value contains the actual rights granted.
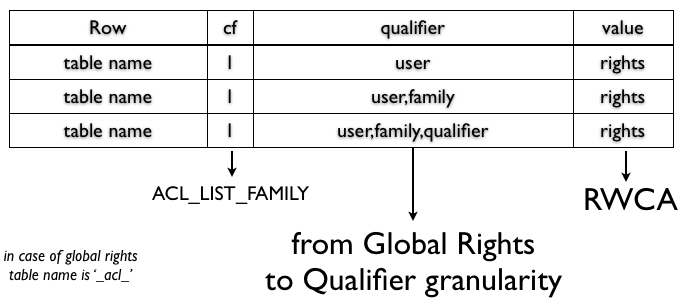
As you can see, the HBase shell commands are tightly related to how the data is stored. The grant command adds or updates one row, and the revoke command removes one row from the _acl_ table.
Access Controller under the hood
As mentioned previously, the Access Controller coprocessor uses the ability to intercept each user request, and check if the user has the rights to execute the operations.
For each operation, the Access Controller needs to query the _acl_ table to see if the user has the rights to execute the operation.
However, this operation can have a negative impact on performance. The solution to fix this problem is using the _acl_ table for persistence and ZooKeeper to speed up the rights lookup. Each region server loads the _acl_ table in memory and get notified of changes by the ZkPermissionWatcher. In this way, every region server has the updated value every time and each permission check is performed by using an in-memory map.
Roadmap
While Kerberos is a stable, well-tested and proven authentication system, the HBase ACL feature is still very basic and its semantics are still evolving. HBASE-6096 is the umbrella JIRA as reference for all the improvements to ship in a v2 of the ACL feature.
Another open topic on authorization and access control is implementing a per-KeyValue security system (HBASE-6222) that will give the ability to have different values on the same cell associated with a security tag. That would allow to showing a particular piece of information based on the user’s permissions.
Conclusion
HBase Security adds two extra features that allow you to protect your data against sniffers or other network attacks (by using Kerberos to authenticate users and encrypt communications between services), and allow you to define User Authorization policies, restrict operations, and limit data visibility for particular users.
原文地址:http://blog.cloudera.com/blog/2012/09/understanding-user-authentication-and-authorization-in-apache-hbase/
【转】How-to: Enable User Authentication and Authorization in Apache HBase的更多相关文章
- How-to: Enable User Authentication and Authorization in Apache HBase
With the default Apache HBase configuration, everyone is allowed to read from and write to all table ...
- Claims-Based Authentication and Authorization
Introduction You can download the Visual Studio solutions for this article at this location. With al ...
- Authentication和Authorization的区别
搞不太清楚Authentication和Authorization的区别,在网上搜了一下,lucky16的一篇文章讲的通俗,看了就懂,记录下来: 你要登机,你需要出示你的身份证和机票,身份证是为了证明 ...
- Authentication and Authorization in ASP.NET Web API
You've created a web API, but now you want to control access to it. In this series of articles, we ...
- authentication vs authorization 验证与授权的区别
认证和授权的区别 Authentication vs. Authorization简单来说,认证(Authentication )是用来回答以下问题: 用户是谁 当前用户是否真的是他所代表的角色 通常 ...
- ASP.NET Core Authentication and Authorization
最近把一个Asp .net core 2.0的项目迁移到Asp .net core 3.1,项目启动的时候直接报错: InvalidOperationException: Endpoint CoreA ...
- WebApi2官网学习记录--- Authentication与Authorization
Authentication(认证) WebAPI中的认证既可以使用HttpModel也可以使用HTTP message handler,具体使用哪个可以参考一下依据: 一个HttpModel可以 ...
- authentication 和 authorization
单词 词性 解释 authentication n. 认证 authentic adj. 真实的 authorization n. 授权 authorise vt. 授权 authentication ...
- 认证和授权(Authentication和Authorization)
什么是OAuth 如今很多网站的功能都强调彼此间的交互,因此我们需要一种简单,标准的解决方案来安全的完成应用的授权,于是,OAuth应运而生,看看官网对其的定义: An open protocol t ...
随机推荐
- 织梦DEDECMS 5.7文章列表第一页dedefield.content
功能介绍:有很多DEDEcms使用者,在二级文章列表中加入了{dede:field.content/},但在二级栏目中的每一页列表中都存在内容:使用该功能可以只在第一页显示. 注意:只针对最新dede ...
- python 写入JSON中文乱码解决方法
在将一个字典添加入json中时多加入一个参数就可以了 json.dumps(dict(item), ensure_ascii=False) 例子 with open('zh-cn.json','w', ...
- openstack mitaka开启三层网络vxlan
在这之前,先把之前基于flat模式创建的虚机,全部删除 控制节点: 配置 修改/etc/neutron/neutron.conf的[DEFAULT]区域 将 core_plugin = ml2 ser ...
- Gh0st与云安全
黑产攻击途径升级,云服务成重灾区 在我们的印象里,黑产以及相关的肉鸡DDOS攻击总是离我们很远.可实际情况并非如此,特别是在云服务大行其道的今天. 日前,腾讯反病毒实验室就观察到了国内云服务中Gh0s ...
- PAT Basic 1004 成绩排名 (20 分)
读入 n(>)名学生的姓名.学号.成绩,分别输出成绩最高和成绩最低学生的姓名和学号. 输入格式: 每个测试输入包含 1 个测试用例,格式为 第 1 行:正整数 n 第 2 行:第 1 个学生的姓 ...
- Tableau Sheet中的操作
如果想要给数据排名,例如给饼图中的数据排名 1 创建一个Rank 描述为INDEX()的测度 2.将RANK用Label形式显示并且编辑计算方法选择特定的属性. 属性本身也有可以快速计算的一些方式. ...
- [uboot] (第三章)uboot流程——uboot-spl代码流程 后续2018版本分析
board_init_f在/u-boot-2018.07-fmxx/arch/arm/mach-fmxx/spl.c中定义 board_init_f之后,和转载的部分有出入: u-boot-2018. ...
- Java & Mysql 餐饮管理系统 过程心得记录
------------------------------------------Have a Good Day~---------------------------------- 准备国赛和AC ...
- 【leetcode】1237. Find Positive Integer Solution for a Given Equation
题目如下: Given a function f(x, y) and a value z, return all positive integer pairs x and y where f(x,y ...
- Idea 设置maven配置文件settings.xml的位置
1.[File] > [Other Settings] > [Default Settings] 2.设置 settings.xml 配置 本博文来源于:https://blog.csd ...
