CodeForces 492E Vanya and Field (思维题)
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Vanya decided to walk in the field of size n × n cells. The field contains m apple trees, the i-th apple tree is at the cell with coordinates(xi, yi). Vanya moves towards vector (dx, dy). That means that if Vanya is now at the cell (x, y), then in a second he will be at cell 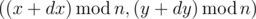 . The following condition is satisfied for the vector:
. The following condition is satisfied for the vector: 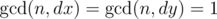 , where
, where 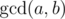 is the largest integer that divides both a and b. Vanya ends his path when he reaches the square he has already visited.
is the largest integer that divides both a and b. Vanya ends his path when he reaches the square he has already visited.
Vanya wonders, from what square of the field he should start his path to see as many apple trees as possible.
The first line contains integers n, m, dx, dy(1 ≤ n ≤ 106, 1 ≤ m ≤ 105, 1 ≤ dx, dy ≤ n) — the size of the field, the number of apple trees and the vector of Vanya's movement. Next m lines contain integers xi, yi (0 ≤ xi, yi ≤ n - 1) — the coordinates of apples. One cell may contain multiple apple trees.
Print two space-separated numbers — the coordinates of the cell from which you should start your path. If there are several answers you are allowed to print any of them.
5 5 2 3
0 0
1 2
1 3
2 4
3 1
1 3
2 3 1 1
0 0
0 1
1 1
0 0
In the first sample Vanya's path will look like: (1, 3) - (3, 1) - (0, 4) - (2, 2) - (4, 0) - (1, 3)
In the second sample: (0, 0) - (1, 1) - (0, 0)
好困╯﹏╰,不填坑了,睡觉去。有需要问思路的留言
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<int,int> pii;
const int INF = 1e9;
const double eps = 1e-;
const int N = ;
int cas = ; struct _node{
int x,y,k;
void set(int _k, int _x, int _y)
{
k = _k;
x = _x;
y = _y;
}
};
_node point[N];
int xk[N],cnt[N];
int n,m,dx,dy; void run()
{
point[].set(,,);
xk[] = ;
for(int i=; i<n; i++)
{
point[i].set(i,(point[i-].x+dx)%n,(point[i-].y+dy)%n);
xk[point[i].x] = i;
}
memset(cnt,,sizeof(cnt));
int x,y,k,y0,yk;
while(m--)
{
scanf("%d%d",&x,&y);
k = xk[x];
yk = point[k].y;
y0 = (y - yk + n) % n;
cnt[y0]++;
}
int mx=cnt[], pos=;
for(int i=;i<n;i++)
if(mx < cnt[i])
mx=cnt[i], pos=i;
printf("0 %d\n",pos);
} int main()
{
#ifdef LOCAL
freopen("case.txt","r",stdin);
#endif
while(scanf("%d%d%d%d",&n,&m,&dx,&dy)!=EOF)
run();
return ;
}
思路:
题目的关键条件是这个 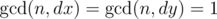
首先想个问题,先是一维的情况下,假设只有一行的格子,长度为x,每次能移动的距离为dx,而且gcd(x,dx)=1,这样手动模拟一下,可以发现规律,从某个点出发直到回到这个点上,步数均为x次,而且每次落下的点都是不重复的,也即这x次的位置覆盖了整条方格上的每一个方格。
那现在二维的情况下,gcd(n,dx) = gcd(n,dy) = 1,也就是从某一行和某一列的交点出发,要重新回到这个交点,就要经过n步而且这n步覆盖了每一行每一列。每个循环必须每个x走一次以及每个y走一次,n个格子属于一组循环里面的,总共有n*n个格子,所以有n组循环。一组循环内的格子是等价的。同一行内的n个格子均来自不同的n组。
现在考虑一组特殊的循环,这组循环从(0,0)开始出发
走了第一步以后就到 (dx%n, dy%n)
第二步到 (2*dx%n, 2*dy%n)
第k步到 (k*dx%n, k*dy%n)
用一个对应关系存储,从(0,0)出发的,经过了k步以后,会到达位置(x[k] , y[k])。
然后考虑普遍的情况了,每组循环都比如经过(0, y0)这个点
从这个点出发的第一步 (dx%n, (y0+dy)%n)
第k步到 (dx%n, (y0+dy)%n), 也即(x[k], (y0+y[k])%n)
那么现在给你某个坐标(x,y),要怎么算出他属于哪一组循环的呢
根据等式x[k]==x,可以求出对应的k的值
那就能求出对应的y[k]了,然后y0+y[k]==y → y0=y-y[k]
这样就知道这个(x,y) 是属于 (0,y0)这一组的了
那么算法大概是这样:
预处理出x[k],y[k],时间复杂度o(n)
遍历每一个apple的坐标(x,y),求出对应的坐标(0,y0),然后cnt[y0]++,复杂度o(m)
找出值最大的cnt[y],答案就是(0,y)了。 总复杂度o(n+m)
代码如上。
CodeForces 492E Vanya and Field (思维题)的更多相关文章
- codeforces 492E. Vanya and Field(exgcd求逆元)
题目链接:codeforces 492e vanya and field 留个扩展gcd求逆元的板子. 设i,j为每颗苹果树的位置,因为gcd(n,dx) = 1,gcd(n,dy) = 1,所以当走 ...
- Codeforces Round #280 (Div. 2) E. Vanya and Field 思维题
E. Vanya and Field time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard ...
- Codeforces 492E Vanya and Field
E. Vanya and Field time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard ...
- Codeforces Round #280 (Div. 2)E Vanya and Field(简单题)
转载请注明出处: http://www.cnblogs.com/fraud/ ——by fraud 本场题目都比较简单,故只写了E题. E. Vanya and Field Vany ...
- C. Nice Garland Codeforces Round #535 (Div. 3) 思维题
C. Nice Garland time limit per test 1 second memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard inpu ...
- Codeforces 515C 题解(贪心+数论)(思维题)
题面 传送门:http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/515/C Drazil is playing a math game with Varda. Let’ ...
- Codeforces 1188B - Count Pairs(思维题)
Codeforces 题面传送门 & 洛谷题面传送门 虽说是一个 D1B,但还是想了我足足 20min,所以还是写篇题解罢( 首先注意到这个式子里涉及两个参数,如果我们选择固定一个并动态维护另 ...
- Codeforces 1365G - Secure Password(思维题)
Codeforces 题面传送门 & 洛谷题面传送门 首先考虑一个询问 \(20\) 次的方案,考虑每一位,一遍询问求出下标的这一位上为 \(0\) 的位置上值的 bitwise or,再一遍 ...
- Codeforces 1129E - Legendary Tree(思维题)
Codeforces 题面传送门 & 洛谷题面传送门 考虑以 \(1\) 为根,记 \(siz_i\) 为 \(i\) 子树的大小,那么可以通过询问 \(S=\{2,3,\cdots,n\}, ...
随机推荐
- SrpingCloud 之SrpingCloud config分布式配置中心实时刷新
默认情况下是不能及时获取变更的配置文件信息 Spring Cloud分布式配置中心可以采用手动或者自动刷新 1.手动需要人工调用接口 监控中心 2.消息总线实时通知 springbus 动态刷新 ...
- Unigui unidbgrid+unidac uniquery联合使用时产生的奇葩问题
如下一个uniquery查询: SELECT a.id,a.userid,a.name,if(a.completed='T',CONCAT('<a class="icons" ...
- DELPHI-Delphi常用类型及定义单元
DELPHI-Delphi常用类型及定义单元 Type Unit Date SysUtils DeleteFile SysUtils or Windows (different versions) D ...
- HTML5 学习记录——2
20150826 1.声明文档类型 <!DOCTYPE> 声明HTML是用什么版本写的. 常用声明; 2.HYML头部元素 <head> <title> 定义 ...
- Android 布局文件
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools=&q ...
- 命令行执行大sql文件
mysql -h localhost -u root -p 123456 < F:/hello world/niuzi.sql
- C++ STL中Map的按Key排序跟按Value排序
C++ STL中Map的按Key排序和按Value排序 map是用来存放<key, value>键值对的数据结构,可以很方便快速的根据key查到相应的value.假如存储学生和其成绩(假定 ...
- C#操作计划任务
昨天有一个任务,就是要下载相关文件,然后保存在相关路径下,这个没什么难度,所以就略过不谈,主要谈谈定时下载,即每天某个固定时间执行下载,这个功能我是用C#代码来操作windows自带的任务计划来实现的 ...
- JSP的一个增删改查例子和总结
总结的几点: 1.在jsp中注意<%! %>声明代码块中的变量只会在项目开始的时候第一次运行jsp的时候执行一遍,有点类似于java类中的static代码块,所以如果是会改变的值不应该声明 ...
- C语言小程序(六)、数组操作
对数组进行操作,查找.插入.删除. #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <time.h> int siz ...
