ConcurrentHashMap原理详解
参考链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/chengxiao/p/6842045.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/ITtangtang/p/3948786.html
一、背景:
众所周知,哈希表是中非常高效,复杂度为O(1)的数据结构,在Java开发中,我们最常见到最频繁使用的就是HashMap和HashTable,但是在线程竞争激烈的并发场景中使用都不够合理。
HashMap :先说HashMap,HashMap是线程不安全的,在并发环境下,可能会形成环状链表(扩容时可能造成),导致get操作时,cpu空转,所以,在并发环境中使用HashMap是非常危险的。
HashTable : HashTable和HashMap的实现原理几乎一样,差别无非是1.HashTable不允许key和value为null;2.HashTable是线程安全的。但是HashTable线程安全的策略实现代价却太大了,简单粗暴,get/put所有相关操作都是synchronized的,这相当于给整个哈希表加了一把大锁,多线程访问时候,只要有一个线程访问或操作该对象,那其他线程只能阻塞,相当于将所有的操作串行化,在竞争激烈的并发场景中性能就会非常差。
锁分段技术
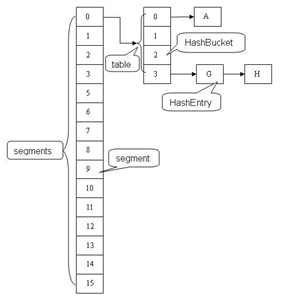
二、应用场景
三、源码解读
/**
* The segments, each of which is a specialized hash table
*/
final Segment<K,V>[] segments;
不变(Immutable)和易变(Volatile)
static final class HashEntry<K,V> {
final K key;
final int hash;
volatile V value;
final HashEntry<K,V> next;
}
其它
定位操作:
初始化方法有三个参数,如果用户不指定则会使用默认值,initialCapacity为16,loadFactor为0.75(负载因子,扩容时需要参考),concurrentLevel为16。
Segment数组的大小ssize是由concurrentLevel来决定的,但是却不一定等于concurrentLevel,ssize一定是大于或等于concurrentLevel的最小的2的次幂。比如:默认情况下concurrentLevel是16,则ssize为16;若concurrentLevel为14,ssize为16;若concurrentLevel为17,则ssize为32。为什么Segment的数组大小一定是2的次幂?其实主要是便于通过按位与的散列算法来定位Segment的index
segmentShift和segmentMask这两个全局变量的主要作用是用来定位Segment,int j =(hash >>> segmentShift) & segmentMask。
segmentMask:段掩码,假如segments数组长度为16,则段掩码为16-1=15;segments长度为32,段掩码为32-1=31。这样得到的所有bit位都为1,可以更好地保证散列的均匀性
segmentShift:2的sshift次方等于ssize,segmentShift=32-sshift。若segments长度为16,segmentShift=32-4=28;若segments长度为32,segmentShift=32-5=27。而计算得出的hash值最大为32位,无符号右移segmentShift,则意味着只保留高几位(其余位是没用的),然后与段掩码segmentMask位运算来定位Segment。
final Segment<K,V> segmentFor(int hash) {
return segments[(hash >>> segmentShift) & segmentMask];
}
final Segment<K,V> segmentFor(int hash) {
return segments[(hash >>> segmentShift) & segmentMask];
}
数据结构
static final class Segment<K,V> extends ReentrantLock implements Serializable {
/**
* The number of elements in this segment's region.
*/
transient volatileint count;
/**
* Number of updates that alter the size of the table. This is
* used during bulk-read methods to make sure they see a
* consistent snapshot: If modCounts change during a traversal
* of segments computing size or checking containsValue, then
* we might have an inconsistent view of state so (usually)
* must retry.
*/
transient int modCount;
/**
* The table is rehashed when its size exceeds this threshold.
* (The value of this field is always <tt>(int)(capacity *
* loadFactor)</tt>.)
*/
transient int threshold;
/**
* The per-segment table.
*/
transient volatile HashEntry<K,V>[] table;
/**
* The load factor for the hash table. Even though this value
* is same for all segments, it is replicated to avoid needing
* links to outer object.
* @serial
*/
final float loadFactor;
}
删除操作remove(key)
public V remove(Object key) {
hash = hash(key.hashCode());
return segmentFor(hash).remove(key, hash, null);
}
V remove(Object key, int hash, Object value) {
lock();
try {
int c = count - 1;
HashEntry<K,V>[] tab = table;
int index = hash & (tab.length - 1);
HashEntry<K,V> first = tab[index];
HashEntry<K,V> e = first;
while (e != null && (e.hash != hash || !key.equals(e.key)))
e = e.next;
V oldValue = null;
if (e != null) {
V v = e.value;
if (value == null || value.equals(v)) {
oldValue = v;
// All entries following removed node can stay
// in list, but all preceding ones need to be
// cloned.
++modCount;
HashEntry<K,V> newFirst = e.next;
*for (HashEntry<K,V> p = first; p != e; p = p.next)
*newFirst = new HashEntry<K,V>(p.key, p.hash,
newFirst, p.value);
tab[index] = newFirst;
count = c; // write-volatile
}
}
return oldValue;
} finally {
unlock();
}
}


get操作
V get(Object key, int hash) {
if (count != 0) { // read-volatile 当前桶的数据个数是否为0
HashEntry<K,V> e = getFirst(hash); 得到头节点
while (e != null) {
if (e.hash == hash && key.equals(e.key)) {
V v = e.value;
if (v != null)
return v;
return readValueUnderLock(e); // recheck
}
e = e.next;
}
}
returnnull;
}
V readValueUnderLock(HashEntry<K,V> e) {
lock();
try {
return e.value;
} finally {
unlock();
}
}
put操作
V put(K key, int hash, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
lock();
try {
int c = count;
if (c++ > threshold) // ensure capacity
rehash();
HashEntry<K,V>[] tab = table;
int index = hash & (tab.length - 1);
HashEntry<K,V> first = tab[index];
HashEntry<K,V> e = first;
while (e != null && (e.hash != hash || !key.equals(e.key)))
e = e.next;
V oldValue;
if (e != null) {
oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
e.value = value;
}
else {
oldValue = null;
++modCount;
tab[index] = new HashEntry<K,V>(key, hash, first, value);
count = c; // write-volatile
}
return oldValue;
} finally {
unlock();
}
}
- 是否需要扩容。在插入元素前会先判断Segment里的HashEntry数组是否超过容量(threshold),如果超过阀值,数组进行扩容。值得一提的是,Segment的扩容判断比HashMap更恰当,因为HashMap是在插入元素后判断元素是否已经到达容量的,如果到达了就进行扩容,但是很有可能扩容之后没有新元素插入,这时HashMap就进行了一次无效的扩容。
- 如何扩容。扩容的时候首先会创建一个两倍于原容量的数组,然后将原数组里的元素进行再hash后插入到新的数组里。为了高效ConcurrentHashMap不会对整个容器进行扩容,而只对某个segment进行扩容。
boolean containsKey(Object key, int hash) {
if (count != 0) { // read-volatile
HashEntry<K,V> e = getFirst(hash);
while (e != null) {
if (e.hash == hash && key.equals(e.key))
returntrue;
e = e.next;
}
}
returnfalse;
}
size()操作
ConcurrentHashMap原理详解的更多相关文章
- Spring框架系列(6) - Spring IOC实现原理详解之IOC体系结构设计
在对IoC有了初步的认知后,我们开始对IOC的实现原理进行深入理解.本文将帮助你站在设计者的角度去看IOC最顶层的结构设计.@pdai Spring框架系列(6) - Spring IOC实现原理详解 ...
- Spring框架系列(7) - Spring IOC实现原理详解之IOC初始化流程
上文,我们看了IOC设计要点和设计结构:紧接着这篇,我们可以看下源码的实现了:Spring如何实现将资源配置(以xml配置为例)通过加载,解析,生成BeanDefination并注册到IoC容器中的. ...
- Spring框架系列(8) - Spring IOC实现原理详解之Bean实例化(生命周期,循环依赖等)
上文,我们看了IOC设计要点和设计结构:以及Spring如何实现将资源配置(以xml配置为例)通过加载,解析,生成BeanDefination并注册到IoC容器中的:容器中存放的是Bean的定义即Be ...
- Spring框架系列(9) - Spring AOP实现原理详解之AOP切面的实现
前文,我们分析了Spring IOC的初始化过程和Bean的生命周期等,而Spring AOP也是基于IOC的Bean加载来实现的.本文主要介绍Spring AOP原理解析的切面实现过程(将切面类的所 ...
- Spring框架系列(10) - Spring AOP实现原理详解之AOP代理的创建
上文我们介绍了Spring AOP原理解析的切面实现过程(将切面类的所有切面方法根据使用的注解生成对应Advice,并将Advice连同切入点匹配器和切面类等信息一并封装到Advisor).本文在此基 ...
- Spring框架系列(11) - Spring AOP实现原理详解之Cglib代理实现
我们在前文中已经介绍了SpringAOP的切面实现和创建动态代理的过程,那么动态代理是如何工作的呢?本文主要介绍Cglib动态代理的案例和SpringAOP实现的原理.@pdai Spring框架系列 ...
- Spring框架系列(12) - Spring AOP实现原理详解之JDK代理实现
上文我们学习了SpringAOP Cglib动态代理的实现,本文主要是SpringAOP JDK动态代理的案例和实现部分.@pdai Spring框架系列(12) - Spring AOP实现原理详解 ...
- I2C 基础原理详解
今天来学习下I2C通信~ I2C(Inter-Intergrated Circuit)指的是 IC(Intergrated Circuit)之间的(Inter) 通信方式.如上图所以有很多的周边设备都 ...
- Zigbee组网原理详解
Zigbee组网原理详解 来源:互联网 作者:佚名2015年08月13日 15:57 [导读] 组建一个完整的zigbee网状网络包括两个步骤:网络初始化.节点加入网络.其中节点加入网络又包括两个 ...
随机推荐
- Java-API:java.util.regex.Pattern
ylbtech-Java-API:java.util.regex.Pattern 1.返回顶部 2.返回顶部 3.返回顶部 4.返回顶部 5.返回顶部 1. https://docs. ...
- 3D柜体导出CAD优化参考方案
前言: 近期在做系统柜和衣柜导出CAD的工作,现阶段的工作是根据不同的厂商定制不同的CAD导出,其中房间平面图.顶脚线截面图.柜体立面图.侧视图.平面图.门板图等模块功能都基本固定,不同的是不同厂商的 ...
- 开源JS代码前面加!,+的意义
我们都知道,函数的声明方式有这两种 function fnA(){alert('msg');}//声明式定义函数 var fnB = function(){alert('msg');}//函数赋值表达 ...
- Java8 日期和时间实用技巧
新的日期API ZoneId: 时区ID,用来确定Instant和LocalDateTime互相转换的规则 Instant: 用来表示时间线上的一个点 LocalDate: 表示没有时区的日期, Lo ...
- 01-20Asp.net--Linq语法
Linq语法--语言集成查询 同Sqlserver语句,但顺序颠倒了. 使用方法: 新建Linq类.dbml结尾的文件 在web窗体源代码中设计表,使用Repeater中转存放: <asp:Re ...
- 11-16网页基础--HTML
网页制作部分主要讲解三大部分: 1.HTML 超文本标记语言( 全称:Hyper Text Markup Language) 专门编辑静态网页 2.CSS 网页美化:是HTML控制的 ...
- 类型:.net;问题:asp.net window验证;结果:细说ASP.NET Windows身份认证
细说ASP.NET Windows身份认证 阅读目录 开始 认识ASP.NET Windows身份认证 访问 Active Directory 在ASP.NET中访问Active Directory ...
- leetcode559
class Solution { public: int maxDepth(Node* root) { ; if (root != NULL) { queue<Node> Q; Q.pus ...
- 利用rowid删除数据库中无主键的相同记录
数据库中表没有添加主键,误插入了两条数据,现在需要删除其中一条记录. 利用rowid号,因为表中的每一行数据都有一个rowid,这个rowid 号是不同的,用select可以查询出来. select ...
- Codeforces #495 Div2 problem E. Sonya and Ice Cream(1004E)
网上的大多是用树的直径做的,但是一些比较巧妙的做法,来自https://www.cnblogs.com/qldabiaoge/p/9315722.html. 首先用set数组维护每一个节点所连接的边的 ...
